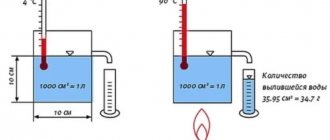
What is an expansion tank
A car engine, like any internal combustion engine, heats up during operation, so it needs to be constantly cooled. Cooling systems are designed for this purpose. According to the principle of operation, they are of two types: liquid and air. The first ones are most widespread, although they are more complex structurally. “Air vents”, despite their simplicity, are much more prone to overheating.
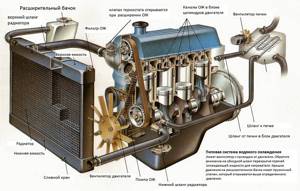
Since all engines today operate with liquid cooling, in the engine compartment of any car there is a small container made of translucent plastic with a lid, designed for pouring antifreeze. This is the expansion tank of the engine cooling system. For different engines, the volume of the expansion tank ranges from 1.5 to 8 liters.
Design of closed expansion tanks
The main part of any closed heating expansion tank is the membrane. This element is made from various materials. It can have different shapes, but usually it is a flat element made of elastic materials.
A membrane is a special shell designed to compensate for pressure when the coolant expands during its heating. Heating of the coolant in the network occurs relatively slowly, which results in a gradual load on the membrane.

Sectional view of expansion tank
When temperatures in the network reach above 90°C, the load on the membrane increases significantly. For this reason, the membrane is made of materials that are resistant to temperature. Typically the membrane is made of synthetic rubber. It divides the tank body into two compartments.

Various expansion tanks
His purpose
What is the expansion unit used for? The fact is that any liquid increases in volume when heated. Thus, the volume of water when heated to 100°C increases by 4.5%, antifreeze and antifreeze - by up to 6%. To prevent the coolant from pouring out of the system when it is heated, an expansion tank is needed, which is a kind of buffer or compensator.
Until the middle of the last century, there were no expansion tanks under the hood, since ordinary water was used as coolant, and the role of a compensator was played by the upper radiator tank, which was not topped up “to capacity.” With the advent of ethylene glycol-based coolants (antifreeze), the coefficient of volumetric expansion of which is greater than that of water, additional expansion tanks appear so as not to enlarge the radiator.
Thus, the expansion tank (EB) is designed to compensate for the volumetric expansion of the coolant as its temperature increases. The RB is located in the engine compartment so that the fluid level is approximately at the middle of the height of the tank.
In this case, the liquid in the radiator and tank is located at the same level according to the principle of communicating vessels. Since the RB is located above the radiator, the expansion tank cap is used as a filler neck, which will be discussed below.
Operating principle and features of the expansion tank
Today's tank design was not developed right away. Now they use new designs, and the old ones are practically not used. In the previous example, after the system warmed up, excess water flowed into the open reservoir, and when the system cooled, the water flowed back into the pipes. In such a system, there was a danger of hot water escaping from the tank, which could cause flooding in the house. (See also: Do-it-yourself boiler installation)
The water coming from the well is under pressure, and at this time the membrane increases, the volume of air decreases, and some pressure is created. The pump turns off when the pressure reaches the required level. Water is consumed, pressure drops accordingly, and the pump turns on to maintain pressure. The disadvantage of an expansion tank is that it is an irrational method of temporarily storing water. The Dutch were the first to propose the use of expansion tanks with a membrane. Today, closed expansion tanks are very aesthetically pleasing and come in a variety of designs.
Figure 3: Expansion tank in action
A membrane expansion tank for water supply also has a drawback, which is that the membrane of this design cannot be replaced. If the heating system is working normally, the liquid expands when the water starts, but otherwise the pressure fluctuations occur smoothly. The membrane of such a tank is made of high-quality material and lasts a very long time.
Figure 4: Diaphragm expansion tank for water supply
Advice! Don't forget to check the air pressure before each heating season. For systems that have large volumes, it is best to use a stationary pressure gauge. (See also: Hydraulic accumulators for water supply)
With the help of a membrane expansion tank, hydrodynamic shock is compensated, which greatly reduces the frequency of pump operation. This design increases service life and saves electricity. When the coolant is heated or cooled, the system remains intact. This compensates for the volume of changes and this is why a membrane expansion tank is installed. Even during a power outage, the reserve tanks have a fire extinguishing function. Membrane tanks can be used not only in domestic systems, but also in industrial ones, since the operating pressure is designed to be up to 16 bar. Hydraulic accumulators can be horizontal and vertical, open and closed. In addition, they differ in water volume and operating pressure.
Design and operation
The expansion tank consists of a polypropylene body, a cover and two pipes for connecting hoses of the liquid system. Using the lower hose, the device is connected to the cooling line, the upper one serves to remove vapors and air bubbles from the system. On modern models, float coolant level sensors are often installed.
For this option, the expansion tank is equipped with another neck on top, intended for installing a sensor. Several control marks are applied on the side surface of the container, from the bottom - min to the top - max. The coolant level should be located in this interval.
How does the device work? First, a little theory. The table shows the operating temperature conditions of modern engines. As we can see, the engines operate in critical temperature conditions.
| Engine temperature, °C | Working | Short term |
| 80 — 100 | 120 — 125 | |
| Boiling point of liquids, °C (at atmospheric pressure) | water | 100 |
| antifreeze | 105 — 110 | |
| antifreeze | 120 |
To raise the bar for permissible temperature, designers increase the pressure in the coolant (more than atmospheric), due to which its boiling point increases. To do this, the system is closed hermetically and excess pressure is maintained in it. For different engines, this value ranges from 0.1 to 0.5 bar (kg/cm²).
At the same time, significant vacuum (more than 0.03 - 0.1 kg/cm²) in the free space of the expander is unacceptable, since air will be sucked into the system, which will lead to the appearance of air pockets that impede coolant circulation and, consequently, to engine overheating . Maintaining the coolant pressure at the required level is the responsibility of a special regulator located in the filler cap.
Types (closed and open)
Depending on the intended purpose and design, the following are distinguished:
• Open-type expansion tanks, which have a direct connection with the atmosphere and are installed mainly in heating systems with natural circulation at the top point, after the coolant acceleration section. Most often, they are made of sheet steel and equipped with hatches for inspection and two or more pipes for inlet or outlet of water, connection with control or discharge devices. Despite all the advantages (cheapness, unlimited volume, simplicity), installing an open tank negatively affects the operation of the system due to evaporation and the need to periodically top up the coolant.
• Closed expansion tanks, which are required to be installed in systems with pumps. This group is represented by both conventional closed containers of large volume (hydraulic accumulators), and devices with flexible balloon and disc-type separating membranes, shifted towards the air chamber when there is excess pressure in the system and returning to the opposite position under normal parameters. Due to a number of advantages, tanks with membranes are gradually replacing other types and are installed in all modern heating and hot water supply systems.
In particular, closed expansion tanks with membranes can be installed at any point in the heating system (preference is given to return sections with laminar movement, but this condition is not critical; there is no need to move the device to the top point after acceleration), operate at excess coolant pressure and respond to changes its pressure with high precision.
Systems with such tanks do not need to be topped up with coolant, which has a positive effect on the stability of their operation and protection from corrosion. Closed membrane tanks do not require additional insulation and are operated at minimal costs.
Tank cover - two in one
So, the RB cover, in addition to its protective function, also performs the task of a pressure regulator. As stated above, the pressure inside the tank should be up to 1.1 - 1.5 kg/cm². How is this achieved?
For this purpose, two valves are mounted in the lid: safety and vacuum. The first is a spring-loaded rubber diaphragm that is pressed from the outside and releases when the pressure exceeds the force of the spring. The second consists of a rubber washer with a small spring installed inside a large one.

At operating coolant temperature, both valves are closed, the pressure in the tank does not exceed the design pressure. Since the expansion tank is hermetically sealed, the pressure increases as the temperature rises, causing the safety valve to open and release some of the air vapor, returning the valve to its previous position.
The absence of a safety mechanism would lead to coolant leaks, damaged connections, and even rupture of the cooling radiators and heater.
After stopping the engine, the liquid in the system cools and decreases in volume, which leads to a vacuum inside the tank. The result may be air leaking through the connections, which will lead to the formation of air bubbles during subsequent startup. And this can lead to overheating and engine failure.
This is where another small valve comes to the rescue - a vacuum valve. Under the influence of vacuum, it opens and equalizes the pressure in the tank with atmospheric pressure.
Types of tanks
- Open type tanks. Installed in attics and roofs of buildings. The water pressure in the system is determined only by the height of the installation.
- Closed tanks - with an elastic partition (membrane), which divides the device’s capacity into two parts: for filling with water and for air.
Types of closed membrane expansion tanks
With stationary membrane:
- as a rule, these are small-capacity containers;
- if the diaphragm fails, it will be impossible to replace it;
- mainly used in heating systems.
With a replaceable diaphragm - balloon type (the balloon is also called a “pear”). Optimal for water supply for the following reasons:
- water enters directly into the bulb membrane and does not come into contact with the metal walls of the tank; accordingly, no corrosion occurs and the quality of the water does not change;
- the pressure necessary for the functioning of the system is easily injected;
- the membrane is easily replaceable;
- devices of this type can have high capacity, which is very important for private households.
This is interesting: Making a homemade water pump with your own hands
Checking the functionality of the lid
Simplified test: are the valves working?
We start the engine and, being careful, unscrew the cap: if you hear the hissing sound of a deflated chamber, the bypass valve is working (however, whether it is correct or not is unknown).
After removing the cover, squeeze any hose of the cooling system with your hand. Continuing to hold it in this way, put the cover in place. If it then regains its shape, the vacuum appears to have been filled. But if, even before starting the engine, the hoses look like they are flattened, the vacuum valve is definitely not working.
More accurately, the safety valve can be checked using a pump and pressure gauge. We connect the pump to the lower supply pipe of the tank, and plug the upper one using improvised means: a bolt or a cylindrical drill that fits tightly into the supply hose.
We create pressure with the pump and control the moment when the safety valve is activated (hissing sound). The pressure value recorded on the device scale shows the actual response pressure.

If the safety valve is too tight, it can be repaired. Why spend extra money when it is enough to shorten the pressure spring by one or two turns, and the spring will become softer. The assembly is easy to disassemble, the main thing is not to lose small parts. And don't overdo it by biting off the coils. Do this little by little and check the results.
How to set the optimal pressure?
The heating system has pressure gauges that control the pressure in the circuit. On the expansion tank itself there is no fitting for installing a measuring device. But there is a nipple or spool for releasing and pumping air or gas. The nipple is the same as on car wheels. Therefore, you can check the pressure level and adjust it using a conventional car pump with a pressure gauge.

Even a simple automobile hand pump with a pressure gauge or an automatic compressor will be suitable for pumping air into the expansion tank.
Before releasing excess pressure or pumping air into the expansion tank of a domestic gas boiler, it is necessary to prepare the system. The car pressure gauge shows the value in MPa; the data obtained must be converted into atmospheres or bars: 1 Bar (1 atm) = 0.1 MPa.
Pressure measurement algorithm:
- Turn off the gas boiler. Wait until water stops circulating through the system.
- In the area with the hydraulic tank, close all shut-off valves and drain the coolant through the drain fitting. For boilers with a built-in tank, the return flow is shut off, as well as the water supply.
- Connect the pump to the tank nipple.
- Pump up the air to 1.5 atm. Wait a little for the remaining water to pour out, then let the air in again.
- Close the valves of the shut-off valves and use a compressor to pump up the pressure to the parameters specified in the passport or to the level - pressure in the system minus 0.2 atm. If the tank is pumped, excess air is released.
- Remove the pump from the nipple, screw on the cap and close the drain fitting. Fill the system with water.
You can check the correct air pressure adjustment when the boiler reaches operating parameters.

If the tank is inflated correctly, then the needle on the pressure gauge of the device during measurement will show a smooth increase in pressure without any jumps or jerks
If the air pressure in the expansion tank is incorrectly adjusted, the entire heating system may malfunction. If the expansion tank is over-inflated, the compensating properties will not work. Because the air will push excess heated water out of the tank, increasing the pressure in the pipes of the heating system.
And with underestimated pressure readings of the compensating tank, water will simply push through the membrane and fill the entire tank. As a result, when the coolant temperature rises, the safety valve will operate.
Sometimes in double-circuit gas boilers, fuses work even if the pressure of the built-in expansion tank is correctly adjusted. This indicates that the tank volume is too small for such a heating system. In this situation, it is recommended to install an additional hydraulic tank.
Adding coolant
The liquid level in the tank is controlled by two extreme marks: min and max. How to properly add coolant to the expansion tank:
A little advice: monitor the external condition of the tank and all elements of the cooling system. Fluid leaks in the engine compartment often indicate a malfunction of the expansion tank, primarily the cap.
As follows from what has been written, it actually depends on such a seemingly secondary unit as the expansion tank of the cooling system how stably the engine of your car will operate.
Installation location
An expansion tank for closed-type heating is installed in a straight section in front of the circulation pump. Before, in the sense that the pump drives water from the expansion tank, and not into it. In this case, the expander works more correctly.
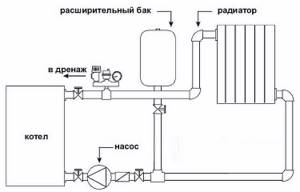
Place for installing a membrane expansion tank
To install a membrane tank, install a tee, from which comes a pipe to which the container is connected. The installation height does not matter. But it is better to install shut-off valves in front of and behind the tank. The membrane fails every few years. Even more often you have to check it and pump it up. To avoid having to stop and drain the system for maintenance, a shut-off valve is installed. It is blocked off and the tank can be removed, checked, and repaired.
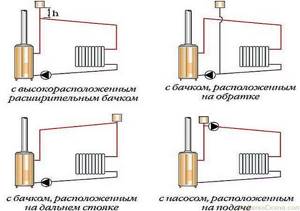
At the highest point
In open-type systems, the installation location of the expansion tank is selected based on other considerations. It is placed at the highest point of the system. In this case, it also works as an air collector. Air bubbles tend to rise, and if there is an expansion tank at the highest point, they rise to the surface, escaping into the atmosphere. So such a tank is deliberately made leaky so that the air from the heating system can escape naturally.
Sanya-SphinX › Blog › Engine cooling system
Purpose and classification of cooling systems
The temperature of the gases in the cylinders of a running engine reaches 1800-2000 degrees. Only part of the heat released in this case is converted into useful work. The remainder is discharged into the environment by the cooling system, lubrication system and external surfaces of the engine. An excessive increase in engine temperature leads to burnout of the lubricant, disruption of normal clearances between its parts, which results in a sharp increase in their wear. There is a danger of sticking and jamming. Engine overheating causes a decrease in the cylinder filling ratio, and in gasoline engines it also causes detonation combustion of the working mixture. A large decrease in the temperature of a running engine is also undesirable. In an overcooled engine, power is reduced due to heat loss; the viscosity of the lubricant increases, which increases friction; part of the combustible mixture condenses, washing away the lubricant from the cylinder walls, thereby increasing wear of parts. As a result of the formation of sulfur and sulfur compounds, the cylinder walls are subject to corrosion. The cooling system is designed to maintain the most favorable thermal conditions. Cooling systems are divided into air and liquid. Airborne ones are extremely rare on cars these days. Liquid cooling systems can be open or closed. Open systems are systems that communicate with the environment through a steam pipe. Closed systems are isolated from the environment, and therefore the coolant pressure in them is higher. As you know, the higher the pressure, the higher the boiling point of the liquid. Therefore, closed systems allow the coolant to be heated to higher temperatures (up to 110-120 degrees).
According to the method of fluid circulation, cooling systems can be: - forced, in which circulation is provided by a pump located on the engine; - thermosyphon, in which the circulation of liquid occurs due to the difference in the density of the liquid heated by the engine parts and cooled in the radiator. While the engine is running, the liquid in the cooling jacket heats up and rises to its upper part, from where it enters the upper radiator tank through a pipe. In the radiator, the liquid gives off heat to the air, its density increases, it falls down and returns to the cooling system through the lower tank. - combined, in which the most heated parts (cylinder heads) are cooled forcibly, and the cylinder blocks are cooled according to the thermosiphon principle.
Cooling system design
The most widespread in automotive internal combustion engines are closed liquid systems with forced circulation of coolant (coolant).
During engine startup, to reduce wear, it is necessary to quickly warm it up to operating temperature and maintain this temperature during further operation. A thermostat is used to speed up engine warm-up and maintain optimal temperature.
.
Basic cooling system malfunctions
External signs of cooling system malfunctions include overheating or undercooling of the engine. Engine overheating is possible as a result of the following reasons: insufficient amount of coolant, weak tension or broken coolant pump belt, failure to engage the clutch or fan motor, thermostat sticking in the closed position, large amounts of scale deposits, severe contamination of the outer surface of the radiator, malfunction of the exhaust (steam) plug valve radiator or expansion tank, coolant pump malfunction. Sticking the thermostat in the closed position stops fluid flowing through the radiator. In this case, the engine overheats, but the radiator remains cold. An insufficient amount of coolant may occur if it leaks or boils over. If the coolant level has dropped as a result of boiling, you should add distilled water; if the liquid has leaked out, add antifreeze. You can open the radiator cap or expansion tank only when the coolant has cooled down sufficiently (10-15 minutes after stopping the engine). Otherwise, the pressurized coolant may splash out and cause burns. Liquid leakage occurs through leaks in the connections of the pipes, cracks in the radiator, expansion tank and cooling jacket, if the coolant pump seal is damaged, the radiator cap is damaged, or the cylinder head gasket is damaged. When operating a car, it is necessary to monitor not only the level, but also the condition of antifreeze. If its color becomes reddish-brown, it means that the system parts are already corroding. Such antifreeze must be replaced immediately. Engine overcooling can occur due to the thermostat sticking in the open position, as well as in the absence of insulating covers in the winter. If the closed cooling system is leaking, then increased pressure is not created in it and the engine does not warm up to operating temperature. And since the engine does not warm up, the ECU constantly enriches the mixture. Thus, a leaky cooling system increases fuel consumption. Systematic operation of the engine on a rich mixture leads to oil dilution, increased carbon formation, and rapid failure of the catalytic converter.
If you have a malfunction on the road, as a result of which the coolant level has dropped below the permissible level, do not worry. You can add any antifreeze or water. This will not make the cooling system work any worse. By the way, not all modern car enthusiasts know that they need to use soft water - it does not form scale. The softest water comes to us from the sky in the form of rain or snow. And groundwater from springs, wells and artesian wells is categorically not recommended for adding to the cooling system - they form a lot of scale. You can soften water by boiling for 20-30 minutes, followed by settling and filtering. The hardness of water in domestic conditions can be easily assessed by the foam formation when washing your hands with soap: in soft water the foam is stable, but in hard water the foam quickly dies out, and a greasy residue remains on your hands. As soon as the emergency situation that forced you to add the “wrong” fluid has passed, the “cocktail” needs to be drained, the cooling system should be flushed and the “correct” antifreeze should be added. We start our choice with the brand - a well-known one will not let you down. Next we find the designation of the antifreeze class. This is where difficulties most often arise. Let's try to clarify the situation. The basis of any antifreeze is an aqueous solution of ethylene glycol, which does not expand when freezing and does not form a solid solid mass. But ethylene glycol is corrosive to metals. To protect cooling system parts from corrosion, three types of additives are used: silicate-based, organic acid salt-based, and mixed (hybrid) antifreeze additives. The first recipe is the most ancient. A striking example is our “Tosol”, which crafty advertising sometimes positions as antifreeze, ideal for domestic cars. Precipitation of silicates leads to clogging of thin radiator tubes. Therefore, we are not even considering this purchase option. In English, such antifreezes are called: Conventional coolants, IAT (Inorganic Acid Technology) or Traditional coolants. Hybrid antifreezes include salts of carboxylic acids and small amounts of silicates or phosphates. And although this recipe is also becoming obsolete, within three years of operation it provides fairly decent protection against corrosion. They are marked: Нybrid coolants, HOAT (Hybrid Organic Acid Technology) or TL 774-C (G-11). More modern ones are carboxylate antifreezes. They contain no inorganic additives. Their service life is at least 5 years. They are indicated by the inscriptions or symbols: Carboxilate coolants, OAT (Organic Acid Technology, TL 774-F (G12+). Several years ago (in 2008), another type of antifreeze appeared, which in the English version is designated Lobrid coolants, SOAT coolants or TL 774- G (G 12++). They are similar in composition to carboxylate ones, but they contain a small amount of silicates. It is believed that such antifreeze can be safely mixed with any other class of coolant. Some manufacturers indicate the composition of the additives on the label, which also allows you to identify the type antifreeze. The absence of amines, borates, nitrites, silicates and phosphates indicates that the antifreeze is carboxylate. Hybrid ones should also not contain anything from this list except silicates, but their amount should not exceed 500 mg/l. A good sign confirming the undoubted The quality of antifreeze is an inscription on the approval of car manufacturers with approval numbers. Such approvals are issued only after lengthy tests of the fluid on cars of the specified brand. The veracity of the inscription on the label can be easily verified by going to the official website of the automaker. But statements like “Meets specifications...” or “Meets the requirements...” are nothing more than promises from the antifreeze manufacturer, but not a guarantee of quality. This is especially true for the markings G11, G12+, G12++. It was introduced by the WV concern only for liquids approved by it. But since such designations have become widespread in our country, some manufacturers indicate them on labels without having the full right to do so. That is, antifreeze may turn out to be good, or maybe not so good - roulette. Well-known brands deserve more trust in such cases, as mentioned above. The inscription “Compatible with all...” only confirms what was said at the beginning of the article. If for some reason the antifreeze is not suitable for your engine, then it can be safely used only for topping up. Antifreeze can be sold as a concentrate or ready for pouring. What to choose depends on the climate of the area where you live and your desire to tinker with the car. For example, if winters are warm, why pour a 40-degree composition? It is better to buy a concentrate and dilute it with distilled water to the desired consistency (proportions for different temperatures are indicated on the label). And the last thing is the color of antifreeze. This property plays absolutely no role. The liquid itself is colorless and the manufacturer can, if desired, paint it in all the colors of the rainbow. And the persistent misconception that G11, G12+ or G12++ can be identified by color alone comes from non-professional implementers.
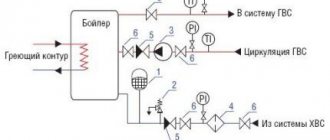
Expansion tank for boiler
Expansion tank for closed heating: device and principle of operation
The heating system, being a complex engineering structure, consists of many elements that have different functional purposes. The expansion tank for heating is one of the most important parts of the heating system circuit.
Why is an expansion tank needed in a heating system?
When the coolant is heated, the pressure in the boiler and the heating system circuit increases significantly due to the temperature increase in the volume of the coolant fluid. Considering that the liquid is a practically incompressible medium and the heating system is sealed, this physical phenomenon can lead to the destruction of the boiler or pipelines. The problem could be solved by installing a simple valve that could release the excess volume of hot coolant into the external environment, if not for one important factor.
When cooling, the liquid contracts and air enters the heating circuit in place of the discharged coolant. Air jams are a headache for any heating system; they make circulation in the network impossible. Therefore, it is necessary to bleed air from heating radiators. Constantly adding new coolant to the system is very expensive; heating cold water is much more expensive than heating the coolant that came into the boiler through the return pipeline.
This problem is solved by installing a so-called expansion tank, which is a reservoir connected to the system by one pipe. Excess pressure in the heating expansion tank is compensated by its volume and allows for stable operation of the circuit. Externally, expansion tanks for the heating system, based on the calculation results and the type of heating circuit, are different in shape and size. Currently, tanks are produced in various shapes, from classic cylindrical tanks to so-called “tablets”.
Types of heating systems
There are two schemes for building heating networks - open and closed. An open (gravity) heating system is used in centralized heating networks and allows water to be directly withdrawn for hot water supply needs, which is impossible in private housing construction. Such a device is located at the top point of the heating system circuit. In addition to leveling pressure drops, the heating expansion tank performs the function of natural separation of air from the system, since it has the ability to communicate with the outside atmosphere.
Thus, structurally, such a device is a compensation tank of the heating system, not under pressure. Sometimes a system with gravitational (natural) circulation of a heat-carrying fluid may be mistakenly called open, which is fundamentally incorrect.
With a more modern closed circuit, an expansion tank of a closed-type heating system with a built-in internal membrane is used.
Sometimes such a device can be called a vacuum expansion tank for heating, which is also true. Such a system provides for forced circulation of the coolant; air is removed from the circuit through special taps (valves) installed on the heating devices and at the top of the system pipelines.
Device and principle of operation
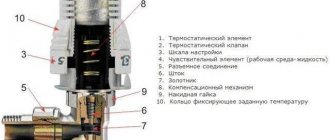
A structurally closed expansion tank in a heating system is a cylindrical tank with a rubber membrane installed inside, which divides the internal volume of the vessel into air and liquid chambers.
Membranes are of the following types:
- balloon type, with the coolant inside the rubber balloon and air or nitrogen under pressure outside;
- in the form of a diaphragm dividing the internal volume of the expansion tank for a closed heating system into two parts - with water and pumped air or gas.
Gas pressure is adjusted individually for each system, which is described in the instructions supplied with devices such as an expansion tank for closed-type heating. Some manufacturers provide the possibility of replacing the membrane in the design of their expansion tanks. This approach slightly increases the initial cost of the device, but subsequently, if the membrane is destroyed or damaged, the cost of replacing it will be lower than the price of a new expansion tank.
From a practical point of view, the shape of the membrane does not in any way affect the operating efficiency of the devices; it should only be noted that a closed-type balloon expansion tank for heating holds a slightly larger volume of heat-carrying liquid.
The principle of their operation is also the same - when the water pressure in the network increases due to expansion when heated, the membrane stretches, compressing the gas on the other side and allows excess coolant to enter the tank. When it cools down and, accordingly, the pressure in the network drops, the process occurs in the reverse order. Thus, regulation of constant pressure in the network occurs automatically.
It is necessary to focus on the fact that if you buy an expansion tank for the heating system at random, without the necessary calculations, then it will be very difficult to achieve stable operation of the heating network. If the tank size is significantly larger than necessary, the pressure required for the system will not be created. If the tank is smaller than the required size, it will not be able to accommodate the excess volume of heat-carrying liquid, which may result in an emergency situation.
Calculation of expansion tanks
To calculate an expansion tank for closed-type heating, you first need to calculate the total volume of the system, consisting of the volumes of the circuit pipelines, heating boiler and heating appliances. The volumes of the boiler and heating radiators are indicated in their passports, and the volume of pipelines is determined by multiplying the internal cross-sectional area of the pipes by their length. If the system contains pipelines of different diameters, then their volumes should be determined separately and then added together.
Further calculations for devices such as an expansion tank for closed-type heating are carried out using the formula V = (Vc x k) / D, where:
Vс – volume of heat-carrying fluid in the heating system, k – coefficient. volumetric thermal expansion, taken for water 4%, for 10% ethylene glycol - 4.4%, for 20% ethylene glycol - 4.8%; D is an indicator of the efficiency of the membrane unit. It is usually indicated by the manufacturer or can be determined by the formula: D = (Рм – Рн) / (Рм +1), where: Рм is the maximum possible pressure in the heating network, usually it is equal to the maximum operating pressure of the safety valve (for private houses it rarely exceeds values 2.5 – 3 atm.) Рн – initial pumping pressure of the air chamber of the expansion tank, taken as 0.5 atm. for every 5 meters of height of the heating system circuit.
In any case, it should be assumed that expansion tanks for heating should provide an increase in the volume of coolant in the network within 10%, that is, with a volume of coolant in the system of 500 liters. The volume including the tank should be 550 liters. Accordingly, an expansion tank of the heating system with a volume of at least 50 liters is required. This method of determining volume is very approximate and can result in unnecessary costs for purchasing a larger expansion tank.
Currently, online calculators for calculating expansion tanks have appeared on the Internet. If such services are used to select equipment, it is necessary to carry out calculations on at least three sites to determine how correct the calculation algorithm of a particular Internet calculator is.
Manufacturers and prices
Currently, the problem of buying an expansion tank for heating lies only in the correct selection of the type and volume of the device, as well as the financial capabilities of the buyer. The market offers a wide selection of instrument models from both domestic and foreign manufacturers. However, it should be noted that if the purchase price for such devices as a closed-type expansion tank for heating is much lower than that of its main competitors, then it is better to refuse such a purchase.
The low cost indicates the unreliability of the manufacturer and the low quality of the materials used in its manufacture. Often these are products from China. As with all other goods, the price for a high-quality expansion tank for heating will not have a significant difference of about two to three times. Conscientious manufacturers use approximately the same materials, and the difference in price of models with similar parameters of about 10-15% is determined only by the location of production and the pricing policy of sellers.
Domestic manufacturers have proven themselves well in this market segment. By installing modern technological lines in their production, they achieved the production of products whose parameters are not inferior to the best global brands at a lower cost.
It should be borne in mind that it is important not only to buy an expansion tank for closed-type heating, it also requires its correct installation.
Having the necessary skills and following the instructions, you can install it yourself. If the technician still has any doubts about his knowledge, then it is best to turn to professionals to guarantee stable operation of the heating network and eliminate possible malfunctions.
- How to fill water into an open and closed heating system?
- Popular floor-standing gas boiler made in Russia
- How to properly bleed air from a heating radiator?
- Expansion tank for closed heating: device and principle of operation
- Gas double-circuit wall-mounted boiler Navien: error codes for malfunctions
Recommended reading
Heating collector: equipment design and installation features Why do you need a heat accumulator for heating? Heating devices: their types and design features How does a heating thermostat work and how does it work?
© 2016–2017 — Leading heating portal. All rights reserved and protected by law
Copying site materials is prohibited. Any copyright infringement will result in legal liability. Contacts
How to choose an expansion tank for a heating system
Each heating system includes a number of elements, without which its normal functioning is impossible. One of these elements is an expansion tank; its purpose and structure will be discussed in this article. We will also look at how to choose an expansion tank for heating a private home.
Why is an expansion tank needed?
It is well known to everyone from the school physics course that any body expands when heated, and liquids and gases increase in volume. Unlike gas, liquid is an incompressible medium, and if it is heated in a closed vessel, such as a boiler tank, this will lead to an increase in pressure inside it, since there is nowhere for it to expand. As a result, the tank walls may rupture.
Imagine a coolant heated in pipelines from a temperature of 20 ºС to 80 ºС. If you do not install an expansion tank in the heating system, then when the liquid medium is heated, the pressure in the network will increase greatly and water may break out at the weakest point. It's good to have a safety valve. The excess water will go through it, since it has nowhere else to go. If there is no valve, the coolant will simply break out at one of the connections.
An expansion tank is needed to accommodate the growing coolant as it heats up. At the same time, during cooling it returns back to the system.
In the case when the safety valve releases water, after cooling it cannot return it back and will allow air to fill the vacated space. This will lead to the formation of an air lock, which will prevent the system from working normally.
Types of expansion tanks
Externally, expansion tanks for heating may differ in shape and size, determined by calculation. Typically this is a tank connected to the heating system via a single pipe. However, different types of containers have design differences, and they are used in different cases. To choose the right tank, you need to understand these differences, so first we present a list of existing types:
- open type;
- closed, equipped with a membrane.
Note. There are also closed expansion vessels without a membrane, but their use is strictly not recommended. We'll explain why below.
Open type containers
These tanks are used for an open heating system (otherwise known as gravity, gravity) and are a metal tank with an open top of any shape. A pipe for connecting a hose or overflow pipe is welded to the upper part of the side wall; the coolant is supplied to the tank from below. The element is installed above the entire system on the supply pipeline, usually in the attic of the house.
Note. In correct technical language, an open system is one from which water is directly taken for the needs of hot water supply. It is not used in private homes, only in centralized networks. A scheme with natural coolant circulation is mistakenly called open.
Any expansion tank for open type heating performs 2 functions:
- serves to compensate for the expansion of the coolant;
- removes air from the system, since its top communicates with the atmosphere.
This is its advantage, but it is not the only one. An open container can also successfully and durablely serve in systems with forced circulation, since the design of the tank is very simple, there is nothing to break. However, it also has many disadvantages:
- a tank installed in the attic requires good insulation;
- During the season, it is necessary to constantly monitor the water level in the tank and replenish it in a timely manner;
- the coolant is constantly saturated with oxygen from the atmosphere, which is why the metal parts of the boiler corrode faster;
- additional consumption of materials and difficulties during installation.
Closed membrane tank
A more modern closed expansion tank is a cylindrical vessel with a rubber membrane built inside. It is used in circuits with forced circulation of coolant and is installed in the combustion room. The coolant is also supplied from below; a service spool for pumping air is installed on top of the device.
The rubber membrane (in common parlance – “pear”), which is equipped with a closed expansion tank of the heating system, comes in 2 types:
- in the form of a diaphragm;
- balloon type.
Note. Some manufacturers' containers have a removable bulb, which makes it possible to change it if cracks appear.
The shape of the membrane does not have a special effect on the operation of the device, although the second type of tank holds a little more water. On the other hand, air (sometimes nitrogen) is pumped from the “pear” under a certain pressure; it must be adjusted individually for each system. All closed expansion tanks operate equally simply: when the coolant heats up, the pressure in the network increases, the membrane stretches and releases water inside the tank. When it cools, everything proceeds in the reverse order.
A sealed expansion tank for a wall-mounted gas boiler is often built inside the heat generator, as it is small in size. In addition, the apparatus does not communicate with the atmosphere and the diffusion of oxygen into the coolant is completely excluded. The weak point of such tanks is the membrane; its service life very rarely reaches 10 years, and it is not always possible to replace it.
There is a third type of compensation device - a vacuum expansion tank for closed-type heating without a “pear”. It is difficult to find them on sale, and there is no point, since this design is the most unfortunate. The role of the membrane in the container is played by the air itself, which leads to its active diffusion into the water, and this is unacceptable. And then, the level in the tank will increase all the time, as a result there will be nowhere to compensate for the expansion.
Recommendations for selection
If a natural circulation circuit is planned or has already been installed in the house, then an open-type expansion tank is just for you. There is no point in playing tricks with a vacuum tank; remember that water in such a system moves only due to the difference in specific gravity and the device may not play its role. You can buy an open vessel, or you can make it yourself; the main thing is to correctly calculate the volume of the expansion tank, which we will discuss below.
With vacuum membrane vessels the situation is a little more complicated. There is one caveat: if you find yourself in a store among many similar products, do not confuse a heating tank with a hydraulic accumulator for water supply. Outwardly, they are very similar, even the color can be the same, so selecting a tank based on this criterion is excluded. The tanks differ according to the inscription on the nameplate; for heating, the operating temperature is indicated up to 120 ºС and pressure up to 3 Bar. On the hydraulic accumulator, respectively, up to 70 ºС and pressure up to 10 Bar.
When making a choice, it is also worth paying attention to the possibility of replacing the “pear” in case of its failure. The size of the device is selected based on the calculation results of a closed tank.
Expansion tank calculation
In the technical literature and on the Internet you can find many methods for calculating an expansion tank for a heating system with natural and forced circulation of coolant. But for the most part, they contain a lot of complex formulas linked to the boiler power and other parameters. You can't go wrong if you use a simpler way to determine the volume of the tank.
The method is based on the statement that the amount of water in the system at maximum heating will increase by no more than 5%. That is, first calculate the volume of water as follows:
- the amount of coolant in the boiler tank - according to the passport;
- volume of water in pipelines - using the formula for the area of a circle, find the cross-sectional area of each pipe and multiply it by the length;
- The capacity of the radiators is also according to the product passport.
Having summed up the results, you select and calculate the expansion tank with a margin, taking not 5, but 10% of the resulting amount. This will be its capacity.
Conclusion
Heating expansion tank
An expansion tank for heating is installed in a closed-type system when the standard capacity in a double-circuit gas boiler is not enough to compensate for the volume of liquid formed when it is heated. Let's explain with a specific example. You heat the room with a double-circuit gas boiler. As you know, water, and batteries are mostly filled with it, expands when heated. To compensate for its excess during heating, a stationary expansion tank is installed in the boiler. When pressure increases due to an increase in the volume of liquid in the pipes, the incoming valve opens and part of the water enters it. When the temperature drops, liquid leaves the expansion tank, filling the radiators. Thus, its quantity in the batteries is a constant value.
The expansion tank in double-circuit gas boilers has a volume of 6-8 liters. As a rule, this is enough for its operation under normal conditions. But if you have a large heated area, there are a lot of radiators, and they are also non-standard; more liquid is required to fill them. It happens that the volume of the tank installed in a gas heater may not be enough.
In this case, excess heated water will fill the expansion tank completely, but the pressure in the batteries will still increase, since there is a lot of liquid. Then there will be an emergency release from the boiler until the pressure in the radiators stabilizes.
Then, when the temperature drops and the liquid cools, it will come out of the tank. But since an emergency release has occurred, the pressure will drop to a level at which the boiler will not be able to automatically start working. If you do not replenish the heating system with water in time, and the outside temperature is low, it may defrost and be destroyed.
To prevent such a negative scenario from happening, an additional expansion tank for heating is installed in the system. In the event that water fills a standard tank installed in the boiler, there will be no emergency discharge; now the liquid will go into an additional container and then return to the radiators. Thus, the volume of liquid in the system will be constant.
Membrane type tanks have different volumes. We wrote how to calculate the expansion tank in the article Pressure drop in the heating system. and we will not repeat ourselves here. In this article we will tell you how to install it on the system.
According to calculations, we will need an additional expansion tank for heating with a volume of 10 liters. But if you install it with a reserve, it won’t be worse. Therefore, we purchased a tank at the store that holds 12 liters of liquid.
Before installing the tank, it must be configured to our conditions. Let's turn it upside down and remove the plastic plug. We will see a nipple for a conventional pump.
Let's connect a car pump to it and bleed off all the air.
Now let’s re-inflate the tank with air to 1.8-2 kPa.
The pressure in the heating system should be 0.2-0.5 kPa lower than in the tank. Now you can start the installation.
EXPANSION TANK FOR HEATING
1. Turn off the double-circuit boiler from the network.
2. Close the water supply taps to the heating device.
3. Let's drain the water from the batteries.
Do not forget to open the Mayevsky taps so that the liquid drains better.
4. Let's prepare the expansion tank for heating for operation. Our system is assembled from polypropylene pipes. Accordingly, to connect it, you will need a device for soldering them and several corners, couplings and fittings. So that later you can remove the container for repair or replacement, we use a special fitting, the so-called “American”.
This is a detachable element consisting of two parts. One part is screwed to the thread on the heating tank, and the second part is screwed to it, to which a polypropylene pipe is soldered. We used these fittings when replacing a heated towel rail. Before screwing the “American” to the heating tank, we will wind flax on the threads and apply a little sealing paste to it,
then use a gas wrench to tighten the first part of the fitting.
5. Having made sure that there is no water in the heating system, we proceed to the installation of polypropylene pipes.
The installation instructions that come with the expansion tank for heating indicate that it should be installed in a place in the system where the pressure is lower. We will install it in the “return”, the pipe through which water flows from the batteries to the gas boiler.
Let's turn on the polypropylene soldering machine and set it to the desired temperature.
Use special scissors to cut the pipe at the intended soldering site.
and, after waiting for the device to warm up, solder the tee.
Already solder the pipe to the tee, then the shut-off valve. so that you can repair the expansion tank for heating without draining the water. After the tap, using corners, we solder the pipes so that the end coupling can be connected to the container.
It is more convenient to carry out soldering work on a self-leveling floor. and only lastly solder the entire structure to the system.
6. Connect the tank by screwing the “American” on it. We will install it on the floor, in a corner, near a wall. so that there is free access to it.
7. While there is no liquid in the pipes, unscrew the coarse water filter and rinse it.
8. At the same time, we will replace the cartridge in the main filter, which is installed immediately after the water supply pumping station.
9. Having installed everything in place, open the liquid supply taps and fill the radiators until the pressure is 1.2-1.3 kPa.
10. Let's bleed the air from the pipes and close the Mayevsky taps.
11. Turn on the boiler and heat the room.
The tank is set to a working pressure of 1.8 kPa. If it increases in the system and exceeds the value of 1.8, the tank valve will open and excess water will flow into it, and, conversely, when the pressure decreases, water will flow into the batteries. Thus, we ensured stable operation of the system by installing an additional expansion tank for heating.
Checking the operation of the tank is very simple. Let's pump it up with air to a pressure of 1.6 atm and provide access to the nipple. Let's turn on the gas boiler. Let's bring the pressure in the heating system to 1.5 Atm. Using the nipple, we will begin to bleed air from the tank. As soon as it drops below 1.5 Atm, water from the system will begin to flow into the tank, and the needle on the boiler pressure gauge will begin to fall. This means that the expansion tank is working and connected correctly.
Purpose of expansion tank
The cooling systems of various cars contain from 5 to 20 or more liters of non-freezing liquid - antifreeze (antifreeze). During operation, the engine, and along with it the antifreeze, heats up from low temperatures in winter to high temperatures in summer.
The temperature difference can reach 100 °C or more. For example, when operating a car in northern regions, where engine warm-up starts at minus 20 °C and ends at an operating temperature of 90 °C, this difference will be 110 °C.
During engine operation, a pressure of about 1 bar arises in the expansion tank
Since any liquid expands in volume when heated, excess is formed in the cooling circuit of the car, which needs to be directed somewhere. Antifreeze is an incompressible medium, so when it expands, it will create high pressure in the system, which can rupture the pipes and radiator honeycombs. Conversely, when cooled, the liquid will decrease in volume and create a vacuum (vacuum), which acts with the same force.
To ensure normal operation of the power unit cooling system and avoid pressure surges, an expansion tank is integrated into it. Its functions are as follows:
Large expansion tanks are used on trucks
Antifreeze, which is a mixture of distilled water with ethylene glycol (sometimes propylene glycol), adds about 5% in volume when heated from zero to 100 °C. In a circuit designed for 10 liters of antifreeze, after complete warming up, as much as 500 ml is formed, which goes into the expansion tank.
Video: why do you need an expansion tank?
Types of expansion tanks by purpose
- For heating. Designed for high temperatures (up to 120 degrees) and pressure range (up to 4-6 atmospheres), typical for heating systems; made from materials not suitable for drinking water. Usually red.
- For water supply. It is made from materials that take into account hygienic requirements for the quality of drinking water (rubber or rubber based on ethylene propylene, steel). The operating pressure should reach 12 atmospheres, the operating temperature - up to 80 degrees. Usually blue for cold water (white for domestic hot water).
Design and principle of operation
Modern expansion tanks for cars are a reservoir made of durable thick-walled plastic with a filler neck and fittings for connection to the elements of the cooling system. The shape of the tank does not matter functionally, so manufacturers customize it to fit the location of the tank.
The shape of the tank depends on the location of its installation and can be different - round, rectangular or flat
The capacity of the container for expanding antifreeze is calculated for each car model and depends on the total volume of liquid in the pipes and units. Moreover, in a cold state, the tank is only half filled with antifreeze, the rest of the space is occupied by air that can compress under pressure. The neck of the tank is closed with a plug with a built-in air valve. The principle of operation of the container is as follows:
The design of the container is quite simple - the tank body is closed with a stopper with a built-in valve
In an emergency situation, when antifreeze or water begins to boil for various reasons, the safety valve releases not only air, but also steam.
The built-in sensor sends a signal about insufficient fluid level to the instrument panel
In some car models, for example, VAZ 2110-2115, the container is equipped with a second neck into which the coolant level sensor is screwed. If, due to a breakdown or leakage of a component, antifreeze begins to leak out and its level in the container drops to a minimum, the sensor will operate and warn the driver with a signal from the corresponding light on the instrument panel.
There are cars (both domestically produced and imported) in which the expansion tank is closed with a simple plug, not equipped with a valve and communicating with the atmosphere. In such systems, the function of releasing pressure and re-injecting air is performed by the main radiator cap, and the reservoir only compensates for the expansion of the liquid.
The radiator cap is equipped with a bypass valve that directs excess antifreeze into the expansion tank
Tanks for heating systems
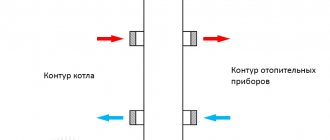
In a situation where the documentation for the tank does not prescribe how to correctly orient it in space, we advise you to always place the tank with the inlet pipe down. This will allow it to work in the heating system for some time if a crack appears in the diaphragm. Then the air at the top will not rush to penetrate the coolant. But when the tank is turned upside down, the lighter gas will quickly flow through the crack and enter the system.

It doesn’t matter where to connect the tank supply – to the supply or return, especially if the heat source is a gas or diesel boiler. For solid fuel heaters, installing a compensating vessel on the supply side is undesirable; it is better to connect it to the return line. Well, at the end, adjustment is required, for which the device of the expansion membrane tank provides a special spool on top.
The fully assembled system must be filled with water and the air vented. Then measure the pressure near the boiler and compare it with the pressure in the air chamber of the tank. In the latter it should be 0.2 bar less than in the network. If this is not the case, it must be ensured by bleeding or pumping air into the membrane water tank through the spool.
Checking the functionality of the lid
Simplified test: are the valves working?
We start the engine and, being careful, unscrew the cap: if you hear the hissing sound of a deflated chamber, the bypass valve is working (however, whether it is correct or not is unknown).
After removing the cover, squeeze any hose of the cooling system with your hand. Continuing to hold it in this way, put the cover in place. If it then regains its shape, the vacuum appears to have been filled. But if, even before starting the engine, the hoses look like they are flattened, the vacuum valve is definitely not working.
More accurately, the safety valve can be checked using a pump and pressure gauge. We connect the pump to the lower supply pipe of the tank, and plug the upper one using improvised means: a bolt or a cylindrical drill that fits tightly into the supply hose.
We create pressure with the pump and control the moment when the safety valve is activated (hissing sound). The pressure value recorded on the device scale shows the actual response pressure.
If the safety valve is too tight, it can be repaired. Why spend extra money when it is enough to shorten the pressure spring by one or two turns, and the spring will become softer. The assembly is easy to disassemble, the main thing is not to lose small parts. And don't overdo it by biting off the coils. Do this little by little and check the results.
Purpose of an additional tank of a double-circuit boiler
As a rule, built-in compensation tanks in gas boilers have a volume of about 6-8 liters. They are designed to compensate for the expansion of 120 liters of coolant circulating in the heating system. Under normal operating conditions, such an expansion tank is enough for a small apartment or house.

When installing radiators of non-standard shape and size, the heating system must be equipped with an additional expansion tank. Because these batteries hold more water
If the heating area is large, heated floors are installed or there are many radiators in the rooms, the volume of the standard built-in tank will be small, since more water is used.
When heated, excess coolant completely fills the tank. And since there is no free space left in the tank, the water pressure increases in the heating system itself and an emergency release occurs by the safety valve. After this, it is unlikely that the gas boiler will be able to start working automatically.
To avoid such negative consequences, an additional expansion tank with a membrane is installed in the heating system in a design for a double-circuit gas boiler. When the standard tank is completely filled, the water goes into the reserve hydraulic tank. After cooling, the liquid returns to the radiators.
Place of the reservoir in the cooling system
A container to compensate for expanding antifreeze can be installed in different places, the location depends on the make of the car. The reservoir is attached to body parts - side members and the interior partition using a rubber clamp or a special bracket. As a rule, the tank is placed on the side where the upper radiator pipe for its connection is located.
Typically the container is installed closer to the radiator pipe
There are containers with 2 and 3 fittings. The latter are connected by three hoses to the following units:
Excess antifreeze from three units enters the reservoir with 3 fittings.
The tanks, equipped with two fittings, are connected to the small circulation circuit and the main cooling radiator; there is no connection to the stove.
The expansion tank is the highest point of the engine cooling system. This is done so that the liquid from the tank can flow into the circuit according to the law of communicating vessels. When the antifreeze level in the container is 3-4 cm above the Min mark on the body, all pipes and units are filled with antifreeze. Including the highest of them - the throttle cooling circuit.
Liquids for filling into the tank
Today's cars, built with the widespread use of new technologies, are very demanding of all process fluids, including coolant. The list of requirements is as follows:
Antifreeze is a purely domestic product, synthesized during the USSR
All of the above requirements are met by antifreeze or antifreeze, which is the same thing. The name antifreeze comes from the English word antifreeze, which means “non-freezing”. Antifreeze is a substance created on the same basis from ethylene glycol in the former USSR. The word consists of the abbreviation TOS (technology of organic synthesis) and the ending “ol”, inherent in the names of chemical preparations.
The base of antifreeze and antifreeze is the same - water + ethylene glycol in different ratios. Differences between products from different manufacturers may lie in the package of inhibitory additives, so it is not advisable to confuse liquids. There will be no fatal consequences, but some substances can neutralize the effect of others and the anti-freeze properties will deteriorate. In this case, the color of the liquid does not matter - it is just a dye.
You can use distilled water to fill the tank in the following situations:
The color of antifreeze does not affect its properties; the additive package is important
Distilled (desalted) water does not meet the above requirements: it freezes at zero temperature and boils at 100 °C. Therefore, it is poured temporarily or as a solvent for antifreeze.
It is unacceptable to pour tap water saturated with salts into the expansion tank. An exception is the breakdown and loss of antifreeze on the way and the absence of a car shop nearby. Fix the leak, fill the cooling system with tap water and get to a garage or service station, then drain it immediately. Otherwise, deposits will form on the inner walls of the water jacket of the engine and other units, impairing heat transfer.
Video: liquids for pouring into the car cooling circuit
Selecting a membrane tank
To choose the most optimal expansion tank for the heating system in your home, you should consider several recommendations given by experts.
If your home has a natural circulation circuit installed, then the best option would be an open type expansion tank. You can either purchase an open container or make it yourself. The main thing is to make the correct calculations of the tank volume.

Expansion (membrane) tank for heating 24 l
The question of choosing a membrane expansion tank is a little more complicated. When choosing a container, the main thing is not to confuse a heating tank with a hydraulic accumulator for water supply. There are practically no external differences between these containers, so be careful and be sure to read the inscriptions on the nameplate. The heating tank will indicate an operating temperature of up to 120°C and a pressure of up to 3 Bar. On the hydraulic accumulator the temperature is up to 70°C and the pressure is up to 10 Bar.
In addition to the above, when choosing an expansion tank for a heating system, you should pay attention to such a component as the ability to replace the “pear” if it breaks. The dimensions of the device are selected only after preliminary calculation of the closed tank.
Why did it happen so?
Perhaps the automatic requests do not belong to you, but to another user accessing the network from the same IP address as you. You need to enter the characters into the form once, after which we will remember you and be able to distinguish you from other users exiting from this IP. In this case, the page with the captcha will not bother you for quite a long time.
You may have add-ons installed in your browser that can make automatic search requests. In this case, we recommend that you disable them.
It is also possible that your computer is infected with a virus program that is using it to collect information. Maybe you should check your system for viruses.
If you have any problems or would like our support team, please use the feedback form.
And so, let's continue.
As you remember, the inspection did not inspire optimism and reduced the ardor, plus, on top of everything, certain financial problems made adjustments, but there are urgent problems that cannot be abandoned because operating a car is not just uncomfortable, but simply dangerous both for the driver and others, and for the car itself , plus, operating a car in this condition becomes extremely expensive and uncomfortable.
I consider these 6 main problems to be: Fuel leakage Antifreeze leakage Washer fluid leakage Battery terminals falling off Lack of heat in the cabin Incorrect operation of the climate control.
As you might guess, watering the Kostroma lands with such slurries is extremely expensive, and without heat in the cabin it is more than uncomfortable. I’m simply silent about battery terminals flying off while driving. We will begin by eliminating these problems. In this post I will talk about the first four points, because the First War for Heat is worthy of a separate post.
So, having decided on the tasks and spare parts, I went to bow to my friend and part-time mechanic Andrey. Now I can’t afford paid repairs, so I need at least a warm garage to do everything myself, and good advice in addition when I break something. :))) My conscience won’t allow me to just come and occupy the garage for a day, or maybe two, and even for free, because the person in this garage works himself and has enough work. Andryukha, of course, won’t refuse, but he always helps me anyway and if he takes money, it’s like God, we haven’t had such prices for five years now, but we need him to have free time, and then we’ll agree on the price.
CHAPTER FOUR. BACK TO THE FUTURE.
First steps into a new life...
We eliminate fuel leaks.
As you remember, tire fitter Karen planted a jack in the bowels of this horse, don’t spoil it
, which resulted in “tears of happiness” for me and a copious flow of gasoline when the ignition was turned on.
In the pit, they found the cause very quickly; this craftsman pushed the heel of the jack under the fuel filter, crushing it and, as a result, making a crease, which caused the nuts to come off the filter threads, with which the line is screwed to it. There was no iscess filter in the stash , so we simply straightened the filter as much as possible (it turned out to be surprisingly intact and airtight) and secured it in its place. Surprisingly, the carving did not wrinkle either. The test showed that nothing was leaking , the fuel supply was normal, the engine was running smoothly and without failures. A new filter has been ordered . _____________________________________________
How does an open expansion tank work?
An open expansion tank is simply a container partially filled with coolant. Sometimes there is not even a valve for air to escape, but just a hole.
Open expansion tanks have two big disadvantages. First, they are susceptible to corrosion because they come into contact with open air. Secondly, they can only be installed in systems with natural circulation.
If you have a circulation pump installed that circulates coolant through the system, then it will not go further than the open expansion tank. The coolant will simply fill the tank and overflow.
About malfunctions and tank repairs
During operation of the machine, the following breakdowns of the expansion tank may occur;
The tank wall ruptures when the internal pressure is too high
The leakage of the lid is characterized by the appearance of multi-colored streaks on the body
Most car enthusiasts, when a valve or body breaks down, simply replace the part with a new one. This is justified by the lack of time for repairs and the low cost of these spare parts. Although, if desired, the burst plastic of the tank can be soldered, and the lid can be disassembled and cleaned.
Leaks from under the cork occur when the seal is not tight or due to the design features of the container. For example, on VAZ 2110 cars, a stream from the upper small fitting connected to the radiator hits directly into the neck, causing a leak. The solution is to install a more advanced tank from Priora.