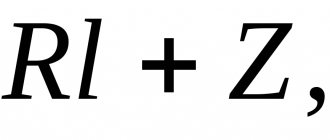FAQ about boilers and heating
The “Warm House” coolant is available in the following brands.
- Based on ethylene glycol (red): “Warm House -65” (concentrated); “Warm house -30” (ready for use).
- Based on propylene glycol (green): “Warm House-ECO -30” (ready for use); “Warm House-ECO -20” (ready for use).
Ethylene glycol- based coolants are used as a working fluid in heating and air conditioning systems of large industrial facilities, as well as individual houses and cottages (in single-circuit gas, heating element and solid fuel boilers).
Propylene glycol- based coolants are also used in any system as a working fluid, but primarily in facilities with increased environmental safety requirements (in double-circuit boilers, heat pumps).
Operating temperature ranges from -20(-30oC) to +104(+106oC).
A specially selected package of additives in the “Warm House” reliably protects equipment from scale, foaming and corrosion.
Coolants do not have an aggressive effect on plastic and metal-plastic, rubber, paronite and flax, which eliminates the possibility of leaks. However, you should know that all coolants have a slightly higher fluidity than water, so it is necessary to carefully assemble all connecting units and be sure to pre-pressure test the system. If necessary, joints in systems can be treated with sealants resistant to glycol mixtures (Hermesil, ABRO, LOCTITE), and silky flax can be used without smearing with oil paint.
Coolants when heated have a high coefficient of volumetric expansion and, as a consequence of this, the expansion tank in the systems must be at least 15% of their volume. The power of the circulation pump should be higher than when working on water: in terms of productivity - by 10%, in terms of pressure - by 60%.
Concentrated coolant (-65oC) must be diluted! This allows you to increase its heat capacity and reduce viscosity, that is, improve circulation. It is considered optimal to dilute the coolant at a temperature of -25oC or -30oC. For electric and gas double-circuit boilers at -20oC.
For information: the coolant, diluted even to -15oC, is guaranteed to protect the system from destruction in the event of an emergency stop and at lower (up to -60oC) temperatures, since glycol solutions do not expand in volume when cooled. Using a mixture with a higher (above the optimal value) concentration of glycols can lead to carbon deposits on heating elements or in the burner area, which will lead to the formation of tarry deposits, burnout of heating elements, etc.
To obtain a working fluid with the crystallization onset temperature indicated below, the “Warm House” should be diluted with water (distilled or tap water with a total hardness of no more than 6 mEq/l) in accordance with the table below.
Coolant and water consumption for a 100-liter heating system
| "Warm home -65" | Water | Crystallization start temperature | “Warm home -30” and “Warm home-ECO -30” | Water |
| 77l | 23l | -40oC | — | — |
| 65l | 35l | -30oC | 100l | 0 |
| 60l | 40l | -25oC | 90l | 10l |
| 54l | 60l | -20oC | 80l | 20l |
For heating systems of a different volume, the values of coolant and water in liters given in the table are proportionally increased or decreased (if the system is 70 l - coefficient 0.7; if the system is 250 l - coefficient 2.5).
Note:
Since the coolant is packaged in kilograms in canisters, this must be taken into account when calculating:
| "Warm home -65" | — | 1l = 1.087kg, | 1kg = 0.92l |
| "Warm home -30" | — | 1l = 1.062kg, | 1kg = 0.95l |
| "Warm house ECO -30" | — | 1l = 1.04kg, | 1kg = 0.96l |
| "Warm house ECO -20" | — | 1l = 1.032kg, | 1kg = 0.97l |
If water from wells, boreholes, etc., where there may be a high content of salts and metals, is used to dilute the coolant, it is recommended to first mix it with water in the required proportion in a transparent container and make sure there is no sediment. Mixing the coolant with water can be done immediately before pouring into the system (especially for systems with natural circulation) or by filling it alternately in small portions.
Considering that in many regions water does not meet the requirements, it is advisable to use ready-to-use coolants.
Coolants "Warm House" are highly stable and provide continuous operation for 5 years. After five years of operation, the coolant will remain a low-freezing liquid, but will exhaust the life of additives to counteract corrosion and scale. It must be drained and disposed of. Before pouring new coolant into the heating system, it must be flushed with water.
NOT RECOMMENDED
- pour coolants into systems with galvanized pipes, as precipitation is possible;
- use coolants in heating systems with electrolysis boilers of the “Galan” type;
- mix “Warm House” with other coolants without prior testing, as this may lead to a deterioration in the performance characteristics of the latter;
- bring coolants to a boil during operation.
Coolants “Warm House -65” and “Warm House -30” are intended for technical use only (ethylene glycol is poisonous!). To avoid poisoning, do not allow it to get into food or drinking water. In case of contact with skin, wash off with soap and water.
The coolant "Warm House-ECO" is approved for use as a refrigerant in the food industry. However, this does not mean that it is safe to drink.
All “Warm House” are fire- and explosion-proof, have certificates of conformity and state registration certificates, have been tested at the Plumbing Research Institute and are approved for widespread use. On the market since 2001.
Coolants should be stored out of the reach of children, in sealed containers, away from food products, and away from direct sunlight.
TO AVOID BUYING A FAKE, CHECK FOR THE PRESENCE OF THE EXPRESSED INscription “WARM HOME” ON THE CANISTER ITSELF!
information about the manufacturer: Our own modern production allows us to produce efficient, consistently high-quality and environmentally friendly products.
The list of objects where “WARM HOUSE” is used speaks for itself: the Kremlin, the State Duma, the Bolshoi Theater, Moscow State University, the Olympic venues in Sochi. LLC "GELENA KHIMAVTO" production base: Moscow, Shcherbinka, st. Yuzhnaya, 14 WEB: https://teplonostd.ru
What are the advantages and disadvantages of water coolant?
Water can rightfully be called the cheapest and most accessible coolant. Moreover, almost all modern heating boilers, shut-off valves, pipelines and other structural elements are designed specifically for water circulation . Plus, if an emergency occurs and the coolant leaks outside, it will be ordinary water, which will not harm human health in any way. But in addition to its advantages, such a universal coolant has a number of equally significant disadvantages:
- In the event of a sudden onset of frost and the heating system is not started, this can lead to rupture of the pipeline, and in some cases, the central boiler. But regardless of the extent of the damage, repairing them will require a lot of money and time.
- If water is used as the main coolant for a long period, then scale will form on the inner walls of all heating units, which leads to excessive consumption of energy resources by up to 30%. This, in turn, leads to additional costs for heating the home.
If we consider home heating assembled using metal pipes, then during prolonged contact of water and metal, especially if the batteries are not completely filled with coolant and there is air in them, corrosion will occur and, as a result, breakdown of the heating system.
Features of choosing a heat transfer fluid
Before choosing any coolant, you must pay special attention to the main characteristics of the substances included in its composition.
- Indicators at which the coolant turns into ice . Water freezes at 0°C, while antifreeze remains liquid down to -60°C, depending on the type of antifreeze. This parameter is very important in heating systems with irregular frequency of use.
- The ability of boiler equipment to work with non-freezing coolant “warm home”. Many manufacturers provide recommendations on the type of coolant to use in the accompanying documentation for the boiler.
- Cost of non-freezing liquid . Everything here is quite simple - the homeowner practically does not have to pay for water. In turn, high-quality antifreeze is quite expensive.
- Coolant toxicity parameters . If a double-circuit boiler is used as the main heat source, then it is better to use water. First of all, this is due to the fact that antifreeze is toxic and when mixed with water heated in the tap water, it can cause harm to human health. In turn, for a single-circuit boiler, the non-freezing liquid “warm house” is the best coolant.
- Materials used for the manufacture of pipelines and heating radiators . You need to pay special attention to this parameter, since, for example, a steel pipe quickly becomes unusable when exposed to water.
The choice of high-quality coolant for heating homes must be approached with due responsibility and attention. Recently, on the shelves of stores engaged in the sale of heating equipment and related materials, a wide range of non-freezing coolants has been presented. Therefore, the homeowner should not have problems choosing the right liquid. The main thing is to take into account the characteristics of different brands of coolant and the nuances of heating equipment installed in the heating system.
We recommend: Installing a toilet: connection diagram, installation with a plastic pipe, at what minimum distance from the sink is it possible to install it and how to connect the structure to the water supply?
Coolant production and standards
TeploDom complies with GOST 28084-89 on Low-freezing cooling liquids and is manufactured according to TU 2422-012-72021999-2011. (ethylene glycol based coolant and propylene glycol based coolant). TeploDom antifreeze is explosion- and fire-proof, has passed quality control and is approved for widespread use (certificate of conformity ROSS RU.AI 28.NO1907, state registration certificate RU.77.99.32.008.E038860.09.11).
Restrictions and disposal
It is not recommended to heat TeploDom to boiling temperature (+112°C), since when heated to 170 degrees, additives and ethylene glycol decompose.
After the expiration date, drain the coolant and dispose of it in accordance with current legislation in your region.
Correct Application
To obtain a working composition, the original antifreeze is diluted with water. When adding 10% liquid, the crystallization start indicator changes, it becomes equal to -25 °C , with an increase to 20% - the start of crystallization begins at -20 °C .
When replacing a coolant that has exhausted its resources, you should flush the system with water or a special liquid.
Important! A special condition for preserving the original qualities of this type of antifreeze is not bringing it to a temperature of +170 ° C , when the additives decompose and the working qualities of the solution are significantly reduced.
Some recommendations
Before using the composition for the heating system, you should take into account some of the features of such compositions. The use of the product is not always justified, and in some cases it can lead to breakdown of system elements. The coolant has a more viscous consistency than water, so a more powerful pump is required to circulate it. Equipment that is designed only to work with water will not be able to ensure good circulation of antifreeze in the system.

Warm House liquid should not be brought into contact with galvanized materials, as this will lead to the release of toxic substances into the air, which is unsafe for health.
Also, the product is not recommended for use in open heating systems. This is especially true for the “Warm House – 30” and “Warm House – 65” modifications, which are not environmentally friendly compounds.
When using such a mixture, it is desirable that the radiators are made of thin material with good thermal conductivity. This is due to the fact that the heat transfer rate of the composition is thirty percent lower than that of water.

When the use of antifreeze is prohibited
Despite the fact that manufacturers strongly recommend using antifreeze for heating, in some cases it is simply dangerous. To be honest, you won't find this information on the packaging, as it simply isn't economical for production. However, before choosing one or another coolant, it is worth learning in more detail why antifreeze is dangerous.
- In double-circuit boilers, the non-freezing liquid is gradually mixed with hot water. Direct skin contact with antifreeze will not do you any good. It is prohibited to use it as a coolant in those houses where double-circuit boilers are used.
- It is strictly forbidden to use anti-freeze in an open heating system, since during the entire period it gradually evaporates and enters the air.
- Ethylene glycol, as well as propylene glycol, react with galvanizing and release toxic substances into the atmosphere.
- Antifreeze is much more viscous than water, so a more powerful pump is needed to force it through the pipes. Than the one that comes with the kit.
- The heat transfer coefficient of antifreeze is 30% less than that of water; accordingly, the radiator material should be thinner.
We will not definitely recommend or dissuade you from using the “Warm House” heating fluid, since everything depends on the specific operating conditions.
VIDEO: Water or anti-freeze, which is better for the heating system?
Characteristics and types of coolant
The following brands of coolant are produced:
- “Warm House ECO-20” is an antifreeze made from propylene glycol. Ideal for dual-circuit heating devices;
- “Warm House -30” is an antifreeze made from ethylene glycol, used for heating with single-circuit boilers, but it is also suitable for other designs. When filling systems of double-circuit and tensile boilers, dilution is required;
- “Warm House ECO-30” is made from propylene glycol. When filling systems of double-circuit and tensile boilers, dilution is required;
- “Warm House -65” is a high-concentration composition made from ethylene glycol.
Completely prepared compositions are already diluted to the required concentration - the composition is of high concentration, produced from ethylene glycol