Water heating device
Heating is the process of heating indoor air, which compensates for heat loss in the house due to lower temperatures outside.
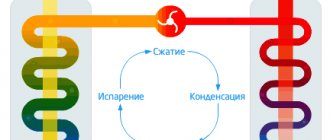
Heating of the house occurs due to the movement of coolant throughout the room. In the case of water heating, the coolant, heated water, moves through a pipeline and enters heating radiators, which, when heated, release heat into the premises.
The general layout of the heating system is as follows. The water is heated in the heat generator. Under its own pressure or under the influence of circulation pumps, water moves along a closed circuit of the heat pipeline. During its circulation, the water cools, transferring heat to the room, and returns back to the heat generator. This process is repeated as long as the water heating system is turned on and all its components are working properly.
Choosing a boiler
* Heating of a country house can be based on the use of one of the following types of boiler:
- Gas device. If there is a gas main nearby, then there are simply no alternatives to this choice, which is explained by the cost of a cubic meter of fuel. Of course, you will have to spend time and effort obtaining numerous permits, but the result justifies the means.
- Solid fuel. A good option for rural areas where firewood is always abundant. From an economical point of view, it is also a very worthy choice. Unfortunately, you will have to put up with certain operational inconveniences and the need to regularly add firewood to the firebox.
- Electrical modification. A compact, reliable and easy-to-use option, which, unfortunately, is not very economical; the price per kilowatt is growing every year. In addition, in the private sector, the network is often worn out and does not have stable voltage, which is detrimental to a modern device.
- Liquid fuel. Not the best option for a summer residence. Firstly, the combustion of diesel provokes the formation of large volumes of combustion products that settle on the soil used for growing crops. Secondly, problems may arise with the supply of fuel.
If we talk about power, then for regions with a cold climate, about 1.75 kW per 10 square meters of area is required. For warm areas, this parameter is limited to kilowatts.
Single-pipe and two-pipe water heating systems
There is also a difference between single-pipe and two-pipe water heating systems. In a one-pipe system, radiators are connected to the heating system in series, in two pipes in parallel.
That's all about the basic principles of water heating! Warmth for your home.
Several visually designed drawings of water heating systems:
Closed, double-circuit closed water heating system with hot water boiler with Expansomat

Closed, double-circuit closed water heating system

Closed single-circuit heating system

Open water heating system with artificial circulation and expansion tank

Open water heating system with natural circulation and expansion tank

©Obotoplenii.ru
Features of country heating

In most cases, the dacha is not a place of permanent residence, so heating a country house has the following specifics.
As a rule, a holiday village is located far from the main gas supply line. This circumstance forces us to look for another source of thermal energy and practically excludes the installation of gas boilers.
If the dacha has an organized electricity supply, then there are limitations on power and wiring installation. If, when the air temperature drops in the warm season, it is possible to use an air conditioner for heating, then in cold weather it will not help.
It is advisable to heat the cottage periodically. In this case, the risk of the system defrosting in extreme cold must be taken into account.
Heating of the premises should occur as quickly as possible.
Pipe layout project
After the heating engineering design has been prepared, it is necessary to create pipe layout diagrams in the premises. To do this, you need to decide on the step and layout scheme.
To determine the layout step, it is necessary to take into account zones of active heat loss, namely: external walls, windows and doors. It is advisable to shorten your stride in the immediate vicinity of these zones. In order to obtain the most comfortable heating possible, it is worth designing the underfloor heating supply in such a way that the circuit pipe coming from the supply manifold with heated water passes along the active heat loss zones first.
To heat the central part of the room, a pipe pitch of 20-30 cm is used, and in zones of active heat loss, a pipe pitch of 10-15 cm is used. This is done in order to increase the heat transfer of the floor surface without changing temperatures and to eliminate duplicate heating sources. However, make sure that in all rooms you set the same step ratio, for example, for the central zones 25 cm, and for zones of active heat loss 10 cm, in this case the calculation of the dependence of heat transfer on the coolant temperature for the entire floor surface of the building will be the same.
For direct pipe laying, there are 2 main schemes: “snake” and “spiral”. Depending on the room, the priority of using one or another scheme changes. To determine the step, you will have to decide how much power is needed to heat a particular room. In cases where it is necessary to organize heating for a small room, it is advisable to lay the pipe in a “snake”. In principle, this installation option is the simplest and most versatile, but it has several disadvantages. Firstly, the difference in temperature of the floor surface in different corners of the room will be most noticeable, and secondly, if it is necessary to lay the pipe with a small pitch (<15 cm), there is a possibility of encountering a bending problem - the pipe may not withstand the overload and break.
In this case, it is necessary to provide for the use of wide fold loops. If it is necessary to heat living rooms of medium size (12-16 m2), it is better to use the “spiral” laying method.
In this case, the temperature at different ends of the room will tend to the average value, since next to the pipe with the cooled coolant there is always a pipe on the supply side with the heated coolant. In addition, all bending angles are directed at 900, which greatly facilitates the installation of a rigid pipe, especially if it is necessary to make installation in small increments (18-20 m2) and there is a need to lay two or more contours, then it is still advisable to use several “spirals” .
Helpful advice The distance from the wall to the nearest part of the pipe of the underfloor heating circuit should be at least 15 cm.
Heating with water heated floors
A new approach to solving heating problems
A modern solution to the problem of heating in a country house with periodic residence is a thermal fireplace with a water circuit. It will not only allow you to make romantic evenings near a live fire, but also perfectly heats a house of up to 100 square meters. m. With its help, there will be plenty to enjoy about water heating in your dacha - the boiler is considered not only reliable and practical, but also adds sophistication to the interior of a dacha house.
A thermal fireplace is essentially a solid fuel boiler. But its lower part is designed like a fireplace. Its double walls are made of steel 6 mm thick, in the space between which there is a water circuit (also called a “water jacket”) filled with water. Hot water heated by the fireplace is distributed through the heating system pipes to all rooms.
Essential elements
What does a water heating system in a private house consist of? If in a city apartment we move, as a rule, into housing with already functioning heating, then here we will have to draw up a project from scratch.
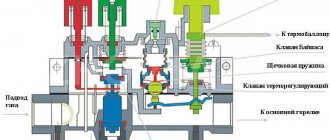
Boiler
A heat source that converts fuel combustion energy or electricity into thermal energy transported by a coolant. The list of main types of boilers looks like this:
- Gas engines currently provide the lowest operating costs. Of course, when working on mains gas: bottled gas will increase the cost of a kilowatt-hour of heat several times.

Modern gas boiler.
- Solid fuel boilers are the second cheapest heating option. Firewood, coal, peat, sawdust, etc. are used as fuel. The main problem is the need for frequent fuel loading.
- Solar boilers can operate in fully automatic mode; However, solarium is very expensive and continues to rise in price.
- Finally, electricity is the most convenient, safe and... expensive way to heat your home.
In addition: the very idea of using a coolant in this case seems strange. Separate electric radiators or convectors look like a much more sensible solution.
Pipes
Black steel pipes are also used in the installation of central heating; however, when independently moving radiators and designing heating systems for cottages, the focus is, as a rule, on other materials.
- Galvanized steel has the strength of black steel pipes and does not have their main drawback - susceptibility to corrosion.
- Corrugated stainless steel, in addition to its strength, also bends easily. Connections are made with fittings with silicone seals, without threads, which makes assembly quick and easy.
- Polypropylene pipes are cheap and can be installed using a simple low-temperature soldering iron. Typically, pipes reinforced with aluminum or fiber are used for hot water and heating: they are stronger and have a much lower coefficient of thermal expansion.
- Cross-linked polyethylene is an excellent material for beam distribution and laying in a screed. Temperature resistance and tensile strength are combined with flexibility and the ability to be purchased in coils up to 500 meters long.

The wiring from the collectors is made of cross-linked polyethylene.
Armature
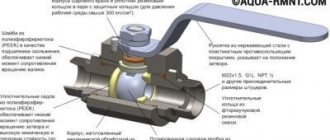
- If you need to shut off the water, the best tool for this is a modern ball valve. Reliability is combined with ease of use and low hydraulic resistance when open.
- Throttles are used for manual adjustment of the heat transfer of heating devices and their balancing.
- Thermostatic heads, after calibration, are able to regulate the throughput so that the set temperature is maintained in the room with acceptable accuracy.
- Automatic air vents are most convenient for removing air. However, instead of them, both Mayevsky taps and ordinary valves and even water taps can be used.
Safety
It is provided by devices called the security group:
- The expansion tank compensates for the increase in coolant volume when heated. Water is practically incompressible and can simply rupture pipes or radiators; but air, separated from water by a rubber membrane, is easily compressed. The volume of the membrane tank is taken approximately equal to 10% of the amount of coolant in the system.
- A safety valve is needed in case the expansion tank capacity is not enough during strong heating. When critical pressure is reached, it releases excess water.
- The pressure gauge allows you to monitor the current pressure in the system.

The pressure gauge, air vent and safety valve are often sold as one unit.
Heating devices
- Cast iron radiators are quite heat resistant and not subject to corrosion. The sections have a large internal volume and, due to the slow movement of the coolant, easily silt into them when connected to the side.
- Steel heating devices are divided into several types: plate, tubular, convectors and registers. Made from corrosion-resistant steels, they are vulnerable to rust, and the thin walls of plate radiators are also extremely mechanically fragile.
- Aluminum radiators are cheap and have excellent heat transfer, but they are afraid of excess pressure and galvanic processes that are generated by the combination of different metals in one circuit (in particular, aluminum and copper).
- Bimetallic heating devices are aluminum radiators with steel cores that increase tensile strength, and copper-aluminum convectors. The latter are a copper tube with aluminum plates pressed to increase heat transfer.

Unlike aluminum, bimetallic radiators can be connected with a copper pipe.
Collector (beam) system
It consists of supply and return collectors, to which two pipes go from each radiator. The collectors are equipped with flow meters to control each heating device connected to the collector. Inlet and outlet pipes are laid under the floor and there is no need to think about how to hide them. The disadvantages include the large length of the pipeline and, consequently, increased cost of work. In addition, the collector system cannot operate without an electric pump, and when installing it, it is worth providing an autonomous power source (battery, electric generator).