Home / Heating
Back
Published: 03/08/2021
Reading time: 3 min
0
383
To efficiently warm up rooms, many different types of additional equipment are used. I would like to consider the principle of operation of the convector and its design, because this unit is very popular among consumers, it is capable of not only heating the air, but also creating its circulation in the room.
In the article I will touch on important design elements, describe in detail the heating element and the functionality of the thermostat. It will be equally interesting to carefully study the calculations that need to be made long before purchasing a particular model. There are two options for determining power to achieve maximum productivity; the area of the building or its volume are taken into account.
- 1 Convector design 1.1 Heating element
- 1.2 Thermostat
- 3.1 By room area
Principle of operation
The very word “convector” indicates that the principle of its operation is based on such a physical phenomenon as convection. Cold air, being more dense, is located in the lower layers - near the floor of the room. Having passed through the convector, the air warms up, its density decreases, as a result of which it rises.
Convection can be not only natural, but also forced. The built-in fan will help increase the convection air flow and thereby increase the efficiency of the heating device.
Some general information about the device
In Europe, many people have been using electric heating for quite some time. In our country, due to high prices for electricity, this is problematic. Nevertheless, you need to warm up somehow, and therefore buying a convector is one of the best solutions. The principle of operation of the device is quite simple. The essence is the natural convection of air passing through the heating element. This type of heating equipment has a small shape, which allows it to be placed where it is convenient. Today there are both floor and wall-mounted options. The shape in most cases is rectangular, although there are also square, etc. So what are convectors, you ask? This is a device that has many holes in its body. Cold air enters the sides and bottom, then it heats up and exits through the holes on the front side.

Water heating convector device
The main working element of the convector is the heat exchanger. It is with its help that heat is transferred from the coolant, the function of which is performed by hot water circulating in the heating system, to the surrounding air. The heat exchanger is a pipe on which many metal plates (lamellas) are mounted, increasing the heat exchange area. Depending on the required power, the convector can be equipped with either one or two heat exchangers.
The distance between the lamellas of the heat exchanger is not set arbitrarily, but is clearly calculated. It would seem that the more plates are mounted on the pipe, the better the heat transfer. However, if their density is too high, air circulation through the device will be difficult. It is necessary to achieve the “golden mean” - so that the lamellas do not interfere with air movement, but at the same time ensure the most efficient heat transfer.

1. Convector housing. 2. Heat exchanger. 3. Decorative lattice. 4. Tangential fan. 5. Large decorative cover.
6. Small decorative cover. 7. Decorative edging. 8. Mounting leg. 9. Adjustment screws. 10. Mounting bolt.
11. Ball valve. 12. Shut-off and control valve. 13. Flexible eyeliner. 14. Gaskets.
There is also an alternative type of heat exchanger from a design point of view, in which wire is used instead of lamellas. Wire convectors are somewhat more efficient, but at the same time much more expensive, and therefore less common than plate convectors, so we will not talk about them in more detail.

Water convector with wire heat exchanger.
Many technical characteristics of the convector are determined by the material from which its heat exchanger is made. It can be steel, copper or a combination of copper and aluminum. The use of non-ferrous metals for the manufacture of a heat exchanger, due to their high thermal conductivity, leads to an increase in the efficiency of the device in comparison with its analogue made of ferrous metal. By the way, aluminum lamellas are very thin, and if handled carelessly they easily become jammed, which impairs aerodynamics.
Heat exchangers can differ not only in the material of manufacture, but also in the shape of the metal fins. Along with smooth lamellas, corrugated ones are also used: wavy, U-shaped, meander, etc. Corrugated lamellas have a clear advantage: the relief increases the area of the plate, and therefore heat transfer.

Heat exchanger with wave-shaped lamellas.
The efficiency of heat transfer from the coolant to the lamellas largely depends on the tightness of the plates to the pipe: even a small gap can cause large heat losses. If the heat exchanger is made of steel, welding is usually used to connect the lamellas to the pipe; if it is made of copper, soldering is used.
In the case of bimetallic heat exchangers, in which aluminum plates are in contact with copper pipes, neither welding nor soldering is applicable. However, even here it is possible to achieve a tight fit of the elements. In this case, either lamellas with special cuffs are used, or the mandrel method is used - plates are placed on a pipe, and then this pipe is expanded using a mandrel.
Some convectors are equipped with a fan that draws air into the heat exchanger and, thereby, speeds up air exchange, and therefore the process of heating the room. The fan can be tangential or axial. The first has an impeller that extends along the entire length of the heat exchanger.

The axial fan propeller is located at the end of the heat exchanger and directs air along it.

The advantage of a heating device with forced convection is obvious - increased efficiency. But it also has obvious disadvantages: firstly, the need to connect to the mains, which may not always be easy to implement, and secondly, the noise that the fan makes during operation.
The heat exchanger, as well as the fan (if provided for by the design), connection points to the heating system, coolant supply regulator, and air release valve are hidden behind the walls of the stainless steel housing. The upper end of the case is covered with a grille, which does not interfere with the movement of air flows, but at the same time prevents foreign objects from getting inside. Some convectors have an air damper that allows you to control the intensity of air flow.
How to choose a gas convector
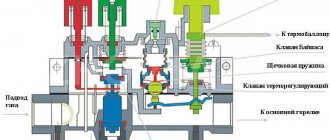
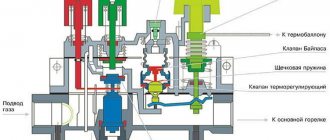
You should pay attention to the technical characteristics of heaters. The best option is to choose a convector with a closed cast iron heat exchanger and a programmable control unit
When choosing equipment you will need to consider the following:
- Power calculation. When heating a room, air convection is used. Consequently, heaters are only effective in limited spaces. For each room you will need to install a separate convector. Power calculation is carried out according to the formula 100 W per 1 m².
- Housing type. Heaters with a closed combustion chamber and exhaust of combustion products through a coaxial chimney are suitable for apartments. You can install any type of equipment in your home. But when installing a heater with a closed chamber, it is necessary to take care of a constant and intense flow of fresh air.
- Fuel type. A gas heating convector running on liquefied gas is prohibited from being installed in an apartment in a multi-storey building, due to the high explosion hazard of the cylinders.
All convectors are initially manufactured with the ability to connect to the main gas pipeline. If you plan to connect the gas convector to the cylinder in the future, you need to purchase a special reducer (in some modifications it is included in the kit).
Wall and floor water heating convectors
According to the installation method, all heating convectors are divided into wall-mounted, floor-mounted and in-floor. The first two types are very similar to each other, so we will consider them together.
The main difference between wall and floor convectors, which are very similar in appearance, is their dimensions. Wall-mounted ones are usually quite high, while floor-mounted ones are low and compact. The latter, due to their modest size, are less conspicuous and can be easily hidden behind furniture.

Wall-mounted water convector.

Floor water convector.
There are even baseboard models with a height of less than 200 mm, which can serve as a replacement for baseboards and heat the room along the entire perimeter.

Skirting water convector.
All wall and floor convectors are divided into models with a casing and models without it. The casing does not perform a decorative role, as one might expect: it helps create additional traction to improve air circulation. Often the height of the casing significantly exceeds the dimensions of the heat exchanger. This discrepancy is not at all a defect of the manufacturer; it is done intentionally: the higher the casing, the stronger the thrust. As for convectors without a casing, they also have a casing, but it only masks the heat exchanger and protects it from mechanical damage.
It should be noted that the surface of the functional casing or decorative housing does not heat up too much. This distinguishes convectors from radiators - in this case you cannot get burned by accidentally touching the surface of the housing.
Most often, convector bodies are made of steel, regardless of the heat exchanger material. The fact is that steel is easy to paint, and this gives the buyer the opportunity to choose a heating device that will fit perfectly into the interior of the room. However, steel, although the most common, is not the only option. If you wish, you can find something more exotic, for example, a convector in a wooden case.
Water heating convectors built into the floor
There is another type of heating convectors, which is very different from those discussed above and therefore stands apart. They are unusual in the location of their installation - in a niche located below floor level. With a high degree of probability, you can find such heating devices in commercial or office premises with large panoramic windows, against which ordinary radiators or convectors will not look entirely appropriate.
In cottages and apartments, such convectors are also installed, but usually only in cases where the lower edge of the window is located no higher than 150-300 mm from the floor level. It is allowed to install heating convectors into the window sill.

Water heating convector built into the floor.
The height of the body of convectors built into the floor can vary from 50 to 130 mm, and the length can reach 3 m. But the user, unless he himself has been involved in design and installation, can only guess about the true dimensions of the heating device, because he will only be able to see the decorative grille at the level floor through which heated air rises upward.

Most often, such gratings are made of steel, aluminum or plastic, but sometimes you can find cast iron, marble or, for example, wood. Whatever material the grille is made of, it must be strong enough so that you are not afraid to step on it when passing by.
In the case of large French windows, in-floor convectors are an indispensable option for heating equipment. On the one hand, and we have already mentioned this, they, being located below floor level, do not interfere with the view. On the other hand, it is precisely such convectors that most effectively heat a room with floor-to-ceiling windows. Cold air from the window enters the convector through the grille, and from there it comes out the same way as warm air.
To install an in-floor convector, it is necessary to prepare in advance a niche in the floor with a depth of 100 to 300 mm. However, installation can also be carried out at the stage of floor screeding. It should be borne in mind that not every convector can be used for in-floor installation.
The limiting factor in this case will be the height of the device body. Powerful models with a height of several tens of centimeters are not intended for installation in rooms located on the upper floors of a building. Of course, the installation of in-floor convectors should be planned in advance - even at the stage of building construction. The exception is low-power, low-rise models that allow installation in a screed.
In-floor water heating convectors, unlike wall-mounted or floor-mounted ones, often have a fan in their design for forced air supply to the heat exchanger, as well as a drainage system for collecting and removing condensate from the device body.
Possibility of temperature control
Sometimes, especially in the spring, when it is still cold at night, and the sun is already beginning to noticeably warm up during the day, you periodically have a desire to reduce the heat coming from the heating device. Water heating convectors are easy to adjust their power. When the coolant supply to the convector is shut off, it will cool down quite quickly, which is due to the small volume of water inside it compared to the radiator.
All you need to maintain the room temperature at a given level is to equip the convector with thermostatic fittings with mechanical or electronic control.

Mechanical thermostatic valves.

Electronic thermostatic valves.
The installed thermostatic valve must have high flow capacity so that significant hydraulic resistance does not create at the inlet. Some convector manufacturers initially equip their products with thermostatic fittings. If the device you purchased is not equipped with a thermostatic valve, you can purchase and install it yourself.
You can also regulate the air temperature in the room manually. Some models of convectors have a damper, which the user can, if desired, turn and thereby block the path of heated air.
Inverter heater
Operating principle
The inverter with which this type of device is equipped converts alternating current into direct current, changing the voltage and frequency. This physical process is called inversion. The inverter looks like a periodic voltage generator. It is similar in form to a discrete signal. Inversion has a strong impact on the power of the device, and all electrical appliances with it become less noisy and more economical.
Advantages and disadvantages
This type of device has quite a few advantages:
- Economical. When the inverter system of the device reaches the desired temperature level, the mechanism of the device does not turn off, but continues to operate at low speeds. This leads to maintaining a favorable climate in the room. The heater does not require energy consumption for switching on and off functions. When using an inverter, there is no such thing as “high current” for starting. When starting the device, the current is no more than the rated current, which has a positive effect on the service life of the entire device. The device does not need to be constantly in the on and off mode. After all, these cycles significantly reduce the service life of the device. Compared to conventional appliances, energy savings are about 40%.
- Practical and productive. This device is capable of heating even at very low temperatures, while the beneficial effect is expressed by a high coefficient. During operation, the heater shows the ratio of heat generated to energy expended, designated as EER. This indicator for the device is equal to four. For example, with a consumption of 250 W, you get more than 1 kW of heat. This is a good indicator.
- The heater has high safety and environmental friendliness characteristics during operation.
- Operation is carried out with a low noise level, this is due to a decrease in rotation speed at part load. Without a doubt, this indicator has a positive impact on the life of the consumer.
The large number of advantages of the device does not deprive it of its disadvantages, but there is only one. This is a considerable cost of the heater compared to other similar devices.
Use in heating systems
Today, the inverter device is successfully used in heating systems whose power source is electricity.
This innovation has earned many positive reviews. It is installed wherever there is an electrical connection. You can use inverter heating without permits; in particular, you do not need to obtain permission to install a heating system. A pleasant moment for consumers is the cost of the equipment, which turned out to be much lower than other heating systems. A conventional gas boiler these days can easily be replaced by an inverter heater. Then the operation of the heating system with an integrated inverter device will be as follows: passing through the heater, electricity enters the boiler. In this case, the inverter boiler constantly produces an induction current. If a power outage occurs, the boiler will continue to operate from the battery. The heater includes a magnetic part and a heat exchanger.
Can be used for room cooling
A convector can be called universal climate control equipment, since it can perform different tasks in different seasons: heating in winter, cooling in summer. True, not every device is adapted for cooling; manufacturers usually indicate that one or another of their models has this capability.
It should be borne in mind that convectors generate cold much worse than heat, so when calculating the power of the device, you need to rely on your needs for cold, because reducing the heating power, as you now know, is not difficult.
In order for your convector to start cooling, rather than heating, the air in the room, you need to empty it, fill it with a special liquid and connect it to the chiller. However, there are models in which the process of transition from one mode to another is much simpler and faster. They have two unconnected circuits at once: one for the coolant, the other for the refrigerant. To change the operating mode, you will only need to turn off the fluid circulation in one circuit and turn it on in the other.

And a couple more comments regarding the possibility of using this type of climate control equipment for cooling a room. Remembering the principle of operation of a convector, you will understand that in natural mode it is not able to work for cooling. That is why all models designed to operate in two modes are equipped with fans. In addition, the fan helps reduce the amount of condensate formed on the heat exchanger when the convector is operating for cooling.
Types of convectors

All models on the market can be divided into two types - liquid and dry. Liquid units are distinguished by a submersible heating element. Since heat from the heating element is first transferred to the liquid, radiators are quite large. They can even be used as a permanent heating source. In everyday life, dry electric convectors are more often used as an additional source of heating.
Provided you choose the right type and model of electric convector, you can create the optimal temperature regime in the house. The devices can be installed in any room, including bathrooms and kitchens, characterized by high humidity.