Device diagram
The device is used both in systems of one and two pipes. Regardless, it includes:
- valve;
- static element (thermal head);
- sensitive component;
- spool;
- stock;
- compensator;
- retainer;
- scale.
also several fasteners, a drive and a regulator . The device is filled with working fluid or gas, as desired.
Photo 1. Diagram of a thermostat for radiators. Arrows indicate the components of the structure.
The design and principle of operation of the thermostat
Any automatic radiator valve consists of 2 parts:
- Thermostatic valve with an actuator for shutting off the coolant flow.
- Thermal head with a control element that responds to changes in air temperature.
The valve, made of brass, has a traditional mechanism with a working cone that fits into the seat and thus reduces its flow area. The difference from a conventional manual tap is that the cone is attached to a pressure rod with a spring that extends outward. Pressing on the end of the rod is carried out by the second element - the thermal head. The stronger the pressure, the smaller the flow area. The diagram below shows the assembly of the heating battery regulator:
Inside the thermostatic head is a small sealed container filled with a heat-sensitive medium - liquid or gas. When heated, this medium expands, the container increases in size and presses harder on the rod, blocking the flow of coolant. When cooling, the process goes in the opposite direction, which is the principle of operation of the thermal head. An adjustment knob with a printed scale mechanically limits the maximum opening of the valve.
Important. The thermostat installed on the battery only affects the coolant flow, changing it in one direction or another. The thermostat is not a water temperature regulator, that is, it performs quantitative regulation, but not qualitative one.
Where is the device installed?
The operation of the device is influenced by 4 factors:
- exposure to sunlight on the body;
- temperature outside the room;
- air circulation in the room;
- additional heating sources.
In apartment buildings, thermostats are placed high up, near the roof , as heat rises. This helps balance the temperature differences in the building. In single-story ones, on the contrary, they are mounted near the heater.
Photo 2. Electronic thermostat installed on the heating radiator. The device is connected to the coolant supply circuit.
It is considered most favorable to place a highly sensitive device on the feed. This principle has a limitation: the strapping elements should not be covered with anything. The thermostat is placed in front of the battery, after the branch from the main line. This allows it to regulate the temperature of the room without affecting the neighbors below.
Important! Otherwise, you must use a device with a remote sensor.
How to properly install a thermostat on a battery with your own hands
No special skills are required to place the device. The most difficult part of the process is installing a bypass in a system with metal pipes. If problems arise with the latter, you should invite a specialist to help assemble the device.
To work you will need:
- the device itself;
- shut-off valves;
- pipeline cutting, fasteners or welding for its installation ;
- bypass;
- a set of keys;
- tow or any other sealant .
Before starting work, be sure to drain the coolant. To do this, just close the valve located after the branch pipe from the main to the radiator.
It should be taken into account that the bottom tap, if any, must be opened, otherwise the liquid will become stuck in the battery.
Attention! The thermostat should be installed in the warm season . For example, in the summer, before the start of the heating season.
After draining the coolant, proceed to installing the taps. A vertical cut is made in the pipe section near the radiator, disconnecting the line. Then do the following:
- If the thermostat is metal, then the bypass is simply welded. If electronic, then place a jumper between sections of the pipe.
- Remove the nuts and shank from the shut-off valves . The same is done with the device. The resulting parts are screwed into the radiator plugs.
- and temperature control device are installed one by one
- The pipeline is assembled by tightening the fasteners or by welding.
- The system is filled with working fluid and a test run is carried out.
After carrying out the initial check , they inspect the piping for leaks or defects. The former are eliminated with a sealant, the latter by repeated heat treatment.
Before installation, when choosing a location, it is recommended to consider access to the device in case of repair. To do this, you will need to choose a place in the free space and correctly direct the head of the device.
Sometimes it becomes necessary to adjust the temperature in each specific room. This can be done by installing a thermostat for the heating radiator. This is a small device that regulates the heat transfer of a heating battery. Can be used with all types of radiators, except cast iron. One important point is that the device can lower the initial temperature, but if there is not enough heating power, it cannot increase it.
Design of thermostats for heating radiators
The thermostat for a heating radiator consists of two parts - a valve (thermovalve) and a thermostatic head (thermostatic element, temperature regulator). These products are produced for different pipe sizes and different types of heating systems. The thermostatic head is removable; regulators of different types and even from different manufacturers can be installed on the same valve - the seat is standardized.

The thermostat for a heating radiator consists of two parts - a special valve (valve) and a thermostatic head (regulator)
There are different valves and regulators, so before installing a thermostat for a heating radiator, you will have to become at least a little familiar with its structure, functions and types.
Adjustment devices
These are mechanical valves or automatic devices with which you can change the heat transfer of the radiator. Mounted on both single batteries and groups of them.
Ball valves
They are used to open or stop the flow of coolant. They are installed together with bypasses in front of radiators or entire sections of the heating system.

A ball valve consists of a body with an internal metal sphere. There is a hole inside it, which in the “open” position does not create obstacles to the movement of liquid. When the tap is closed, the sphere turns with its blind side and blocks the gap.
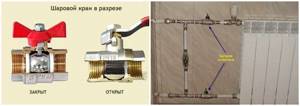
A ball valve can also operate in an intermediate position, but it is not advisable to leave it in a half-open state for a long time. At a high temperature of the coolant, the ball can stick to the walls, which subsequently causes breakdowns.
Needle taps
Valves of this design can smoothly regulate liquid flow, which directly affects the temperature in the heating radiator. The cast body houses a cone-shaped rod driven by a handle. When the handle is rotated, the needle moves into the canal, closing or opening the passage. The tip can be non-rotating, spherical, with a soft nozzle, which allows for smoother adjustment.
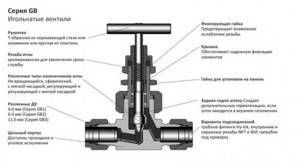
Needle valves can be operated manually or automatically. Additionally equipped with temperature sensors and an electric drive.
Mechanical thermostat
Designed to regulate and constantly maintain the set temperature in the radiator. It is a mechanical valve that cuts into the coolant supply pipe. At the top of the device there is a thermal head for setting the desired mode.
The thermostatic head is an element sensitive to temperature changes. Inside it is an elastic cylindrical bellows filled with gas or liquid with a high coefficient of thermal expansion. When heated, it increases in volume and moves the rod, thereby reducing the clearance of the pipe. The flow intensity drops, the radiator cools.

Mechanical thermostats allow you to control the microclimate in a room without constant human control. The specified mode will be maintained automatically. The main conditions for long-term operation of the valve are that high-quality non-freezing liquid or specially prepared water must circulate in the system, since the device is sensitive to contamination.
Automatic thermostat with remote sensor
Such devices consist of two parts - a mechanical thermal head and a temperature sensor, which are connected by a thin capillary tube 1-10 m long. The capillary mechanical thermal sensor is used to maintain a given temperature in the operating range from 30 to 90 ° C. Can be used both to start valves and to turn on/off the circulation pump.

Electronic thermostat
These are the latest generation devices that allow you to create a favorable temperature in the room using a microprocessor built into the thermal head. Operates on batteries in two control modes:
- as standard, a constant temperature is maintained, which can be set using touch buttons or via radio.
- in programmable mode - the sensor regulates the temperature by hour and day of the week, the temperature schedule is set from a radio remote control or using various applications from a smartphone, tablet or computer.

Automatic thermostats with sensors help remove excess load from the heating system, save on heating the premises in the absence of residents, and make the conditions in each room as comfortable as possible.
Thermal valve - structure, purpose, types
The valve in the thermostat is very similar in structure to a regular valve. There is a seat and a shut-off cone that opens/closes the gap for coolant flow. The temperature of the heating radiator is regulated in this way: by the amount of coolant passing through the radiator.

Sectional view of thermostatic valve
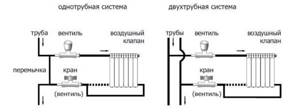
The valves are installed differently for one-pipe and two-pipe wiring. The hydraulic resistance of a valve for a one-pipe system is much lower (at least two times) - this is the only way to balance it. You can't mix up the valves - it won't heat. For systems with natural circulation, valves for single-pipe systems are suitable. When installing them, the hydraulic resistance, of course, increases, but the system will be able to work.
Thermostatic heads
There are three types of thermostatic elements for heating thermostats - manual, mechanical and electronic. They all perform the same functions, but in different ways, provide different levels of comfort, and have different capabilities.
Manual
Manual thermostatic heads work like a regular faucet - you turn the regulator in one direction or another, allowing more or less coolant to flow through. The cheapest and most reliable, but not the most convenient devices. To change the heat transfer, you must manually turn the valve.

Manual thermal head - the simplest and most reliable option
These devices are quite inexpensive, they can be installed at the inlet and outlet of a heating radiator instead of ball valves. Any of them can be adjusted.
Mechanical
A more complex device that maintains the set temperature automatically. The basis of this type of thermostatic head is a bellows. This is a small elastic cylinder that is filled with a temperature agent. A temperature agent is a gas or liquid that has a high coefficient of expansion - when heated, it greatly increases in volume.
Thermostat device for a heating radiator with a mechanical thermostatic head
The bellows supports the rod, which blocks the flow area of the valve. Until the substance in the bellows heats up, the rod is raised. As the temperature rises, the cylinder begins to increase in size (gas or liquid expands), it puts pressure on the rod, which increasingly blocks the flow area. Less and less coolant passes through the radiator, and it gradually cools down. The substance in the bellows also cools down, due to which the cylinder decreases in size, the rod rises, more coolant passes through the radiator, and it begins to warm up a little. Then the cycle repeats.
Gas or liquid
With such a device, the room temperature is fairly maintained at exactly +- 1°C, but in general the delta depends on how inert the substance in the bellows is. It can be filled with some kind of gas or liquid. Gases react faster to temperature changes, but are technologically more difficult to produce.

Liquid or gas bellows - not much difference
Liquids change volumes a little more slowly, but are easier to produce. In general, the difference in the accuracy of temperature maintenance is about half a degree, which is almost impossible to notice. As a result, most of the presented thermostats for heating radiators are equipped with thermal heads with liquid bellows.
With remote sensor
The mechanical thermostatic head should be installed so that it faces the room. This way the temperature is measured more accurately. Since they are quite large in size, this installation method is not always possible. For these cases, you can install a thermostat for the heating radiator with a remote sensor. The temperature sensor is connected to the head using a capillary tube. You can place it at any point where you prefer to measure air temperature.

With remote sensor
All changes in heat transfer from the radiator will occur depending on the air temperature in the room. The only disadvantage of this solution is the high cost of such models. But the temperature is maintained more accurately.
| Name/Company | Setting range | Operating temperature range | Control type | Functions/purpose | Connection type | Price |
| Danfoss living eco | from 6°C to 28°C | from 0°C to 40°C | Electronic | Programmable | RA AND M30X1.5 | 70$ |
| Danfoss RA 2994 with gas bellows | from 6°C to 26°C | from 0°C to 40°C | Mechanical | For any radiators | clip-on | 20$ |
| Danfoss RAW-K with liquid sponge | from 8°C to 28°C | from 0°C to 40°C | Mechanical | For steel panel radiators | M30x1.5 | 20$ |
| Danfoss RAX with liquid sponge | from 8°C to 28°C | from 0°C to 40°C | Mechanical | For design radiators white, black, chrome | M30x1.5 | 25$ |
| HERZ H 1 7260 98 with liquid sponge | from 6°C to 28°C | Mechanical | M 30 x 1.5 | 11$ | ||
| Oventrop "Uni XH" with liquid sponge | from 7°C to 28°C | Mechanical | with zero mark | M 30 x 1.5 | 18$ | |
| Oventrop "Uni CH" with liquid sponge | from 7°C to 28°C | Mechanical | without zero mark | M 30 x 1.5 | 20$ |
Types of thermostats
Thermostats for heating radiators can be classified according to several criteria:
- depending on the material of the case;
- depending on the execution;
- depending on the type of thermostatic head;
- depending on the location of the thermostat sensor.
Let's look at all types in more detail.
Case material
The thermostat housing is made of four types of metal compounds:
- stainless steel;
- made of brass coated with a nickel layer;
- made of bronze protected by nickel plating;
- made of bronze with chrome plating.
The best option is a thermostat with a stainless steel housing. Due to its chemical properties, steel does not corrode and is not affected by other metals. Therefore, such radiator valves are the most durable and reliable in operation. On the negative side, they are characterized only by a relatively high price and the fact that they are more difficult to find on sale.

The characteristics of brass and bronze devices are approximately similar: they hardly differ in price and service life. But when choosing these valves you need to be as careful as possible. Often you come across devices, usually at a low price and from unknown manufacturers, the production technology of which was violated. This concerns, first of all, the manufacture of the alloy. But there are manufacturers who neglect even basic things. For example, their products often lack an arrow that indicates the direction of movement of the coolant. You need to stay away from such thermostats.
Execution option
Depending on the version, thermostatic valves are divided into:
- Angular;
- Straight;
- With fittings for connection to the heating system.
The name of angular and straight, also called through, thermostats comes from their shape. The figure below shows both of these devices.

Both straight and angle valves are suitable for heating systems that are made using a two-pipe design that includes a circulation pump. And for a single-pipe circuit it is better to choose a through-pass device. In this case, the cross-sectional diameter of the saddle must be selected as large as possible. This will ensure that the thermostat, when open, provides less resistance to the coolant current and minimizes energy losses.
A heating set with a built-in valve is needed, first of all, for ease of installation, and secondly, such a scheme looks more aesthetically pleasing than if the assembly was carried out from separate elements. Like everything beautiful, the headset is distinguished by a higher price compared to a set of separately purchased hoses and a radiator valve. But the convenience, quality and aesthetics outweigh this drawback.
The headset can be immediately attached to the radiator and heating pipes coming out of the floor.
Separation by thermostatic head type
Depending on which thermostatic head is installed in the thermostat, they are divided into:
- Manual;
- Mechanical, divided into: gas;
- liquid;
Briefly about each type.
Manual
Such thermostats have the simplest thermostatic head in their design. It works on the principle of a regular water tap. When the regulator is tightened, the flow area decreases, and when unscrewed, it increases. This allows you to regulate the volume of coolant entering the radiator and, consequently, the temperature of the battery.
The advantages of such devices are:
- Minimum price;
- Maximum reliability and durability.

The only downside is the inconvenience of manual temperature control. However, these devices can be used instead of conventional ball valves. Such a regulator is installed both at the inlet and outlet, and sometimes on both sides of the heating radiator.
Mechanical
Such devices are able to automatically maintain the set temperature of the liquid in the radiators of the heating system. This is ensured by a bellows filled with gas or liquid, depending on which mechanical heads are divided into:
- Liquid;
- Gas.
The bellows itself is a cylindrical elastic container. It rests on the rod, which presses on the seat valve. Under the influence of heat, the temperature agent expands or contracts and, accordingly, the valve stem lowers or rises. The stem lowering limit, set using a rotating handle, determines the maximum level to which the valve can block the coolant flow.

The bellows allows you to regulate the temperature in the room with an accuracy of 1 °C. In this case, it almost does not matter what it is filled with: gas or liquid. Gas reacts more quickly to temperature fluctuations, beginning to contract or expand faster than a liquid filler. But this is almost imperceptible to humans, as is the difference in the accuracy of the maintained temperature regime. Heads with gas and liquid have a difference in this indicator within 0.5 °C. Most thermostatic heads are equipped with liquid bellows simply because they are easier to manufacture.
Electronic
These are the most “advanced” devices. All actions here are controlled by a programmable microprocessor. This allows you to set not only the temperature, but also the time when it will change up or down. This mode is useful during sleep, when it is more comfortable to be in a cooler room. And it’s more pleasant to wake up and get out of a warm bed when the air has already warmed up. In addition, you can set a reduced temperature mode while you are at work, so as not to spend money on unnecessary heating of empty rooms.

A relative inconvenience is the size, which is slightly larger than that of manual and mechanical regulators. However, this pays off in functionality and ease of use, as well as maximum accuracy in maintaining the air temperature in the room. Among the negative aspects are the high cost and the need for energy supply. You have to buy batteries and monitor their charge level. This drawback can be eliminated by purchasing an electronic thermostat that can operate from home AC power.
By sensor location
Based on this feature, a distinction is made between thermostats with a remote sensor and those with a sensor installed directly on the device.

Remote sensors are the preferred option when heating system radiators are mounted in places that prevent them from interacting with the indoor air. These can be decorative screens or thick curtains. In this case, a temperature sensor placed on the radiator will regulate the operation of the thermostat depending on the temperature of the battery, enclosed by a screen, and not in the room. When placed indoors, the sensor will inform the thermostat about the actual temperature in the places where it will be installed.
If, however, the mechanical sensor is not remote, then it is installed in such a way that the head is directed towards the room, and not the wall or window sill. This will allow you to more accurately measure the room temperature. However, the size of the temperature sensor and the parameters of the heating system do not always allow this rule to be observed. A remote device comes to the rescue again. As with anything, increased convenience comes at the cost of higher prices for remote temperature control.
How to install correctly
They install a thermostat for a heating radiator at the inlet or outlet of the heating device - there is no difference, they work with equal success in both positions. How to choose a place to install?
According to the recommended installation height. There is such a clause in the technical specifications. Each device is configured at the factory - they are calibrated to control the temperature at a certain height and usually this is the upper radiator manifold. In this case, the heat regulator is installed at a height of 60-80 cm; it is convenient to adjust it manually if necessary.
Installation diagrams for heat regulators for radiators
If you have a bottom saddle connection (pipes fit only from the bottom), there are three options - look for a device that can be installed at the bottom, install a model with a remote sensor, or reconfigure the thermal head. The procedure is simple; the description must be in the passport. All you need is to have a thermometer and at certain moments turn the head in one direction, then in the other direction.

Installation is standard - on fum tape or linen winding with packaging paste
The installation process itself is standard. The valve has a thread. The appropriate fittings are selected for it or a matching thread is cut on the metal pipe.
One important point that those who want to install a thermostat for a heating radiator in apartment buildings should remember. If you have a single-pipe installation, they can only be installed if there is a bypass - a section of pipe that stands in front of the battery and connects the two pipes to each other.

If you have a similar wiring (there may not be a pipe on the right), a bypass is required. The thermostat should be installed immediately behind the radiator
Otherwise, you will regulate the entire riser, which your neighbors will definitely not like. For such a violation, a very substantial fine can be issued. Therefore, it is better to install a bypass (if not).
Reasons why the battery in one of the rooms does not heat:
No heating at all

If you have lost heating in the network, then you need to try to find out if your neighbors have it, or at least on the staircase. If in any doubt, call the emergency service and find out if there was an accident on the main heating pipeline due to which your heating was turned off. In a private home, the cause may be a failed circulation pump, a disconnected power supply for such a pump, or a non-working heater or coolant boiler. There can be many reasons and all of them are in the boiler room. Only a specialist can understand most of them.
When accepting the boiler room of a private home, receive instructions from the installers on what to do if the heating goes out in the entire house.
Airing

The second most common cause is the airing of the radiator or heating riser. This is when there is air in the radiator or in the entire riser that was not released when the system was started (filled with water).
If there is heating in the riser, but there is none in the radiator, then this is one of the possible reasons. A Mayevsky valve is used to bleed air from the radiator. If the riser is cold and the radiator does not heat, but the neighboring ones are hot, then most likely there is air in the entire riser. In order to bleed the air from the riser, a specialist from a service company is invited. He should do the same manipulation with the air vent at the top of the riser, most likely in the attic.
The taps on the radiator are closed
A common cause is closed taps on the radiator or a closed thermostat. Their internal parts turn sour and do not turn. To check whether the valve or thermostat is open, turn the knob or thermostatic head. They must not move separately from the damper stem or valve ball.
If this still happens, then you need to remove the handle or thermal head and use a wrench rather than pliers, for example, carefully try to turn the valve stem or thermostat. If unsuccessful, call a specialist to replace the failed fitting.
The three-way thermostat valve is clogged
The next reason may be clogged internal parts of the three-way valve of the thermostat. Once installed on the radiator, you can try to remove dirt by turning the valve in both directions several times. Friction inside can help the water flow to break away accumulated sediment.
The radiator itself is clogged

Even modern radiators can become clogged with debris carried by the water from the centralized heating network. In our practice, there may be large quantities of sand, as well as pieces of metal or rust. A blockage is determined when one section heats at the entrance, the rest do not, only the upper or lower parts warm up, or the central part is cold. To eliminate this cause, it is necessary to flush the radiator and dismantle it.
How to adjust (reconfigure)
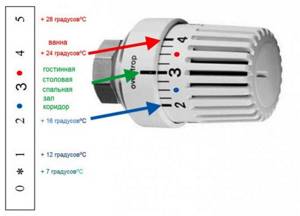
All thermostats are factory adjusted. But their settings are standard and may not match your desired parameters. If you are not satisfied with something in the work - you want it to be warmer/colder, you can reconfigure the thermostat for the heating radiator. This must be done with the heating running. You will need a thermometer. You hang it at the point where you will control the state of the atmosphere.
- Close the doors, put the thermostat head in the extreme left position - completely open. The room temperature will begin to rise. When it becomes 5-6 degrees higher than what you want, turn the regulator all the way to the right.
- The radiator begins to cool down. When the temperature drops to a value that you consider comfortable, begin to slowly turn the knob to the right and listen. When you hear the coolant making noise and the radiator starting to warm up, stop. Remember what number is on the handle. It will need to be set to achieve the required temperature.
Adjusting the thermostat for a radiator is not difficult at all. And you can repeat this action several times, changing the settings.
Regulating the heating operating temperature is an important task both from the point of view of ensuring a comfortable temperature in the room and in terms of fuel economy. Excessive overheating of the air leads to increased fuel consumption and uncomfortable sensations for the inhabitants of the home. There are several ways and stages of adjusting the operation of the heating complex. Thermostatic temperature control of heating devices is considered the most effective. It is implemented using temperature control devices. How to install a thermostat on a heating radiator - the material in this article will answer this question.
Types and selection of thermostats
Based on their design, radiator valves are divided into 3 groups:
- straight;
- corner;
- as part of a set for connecting heating devices.

If everything is clear with straight and angular thermostats, then we should say something about the headset separately. It allows you to simultaneously install a thermostat on the radiator and connect it to pipes coming directly from the floor. Although the price of such a headset will be more than traditional pipe connections, such a connection will look much more aesthetically pleasing.
Radiator connection set with built-in thermostat
For two-pipe systems with a heating circulation pump, any of the valves listed is suitable; the only question is how to connect the heating device, and from a technical point of view, they are all the same. Another thing is a single-pipe circuit; for it it is better to buy a special battery temperature regulator with an increased flow area of the seat. Such thermostats have less hydraulic resistance, which is clearly visible in the diagram:

In addition to valves, you should also choose thermal heads for batteries, and here is an immediate recommendation: the valve and head must be from the same manufacturer, and the connecting threads must match. The standard thread on the valve is M28 and M30. In general, the choice of head designs is not too wide - in addition to conventional elements with a built-in bellows, there are also products with an electronic control unit and display. These thermostats are programmable and can be set to maintain different room temperatures throughout the day.
Advice. When choosing a programmable thermostatic head, remember that it requires power from batteries or mains. In order for the thermostat to work correctly, you will have to monitor the availability of power.
In cases where it is planned to install heating devices behind screens or the windows of the room are intended to be covered with thick curtains, conventional thermocouples may not function correctly. Due to weak air movement in the radiator area, the temperature behind the screen and in front of it may differ by a couple of degrees, so in addition to the thermostat, it is worth buying a remote sensor with a capillary tube.
The sensor behind the screen will control the thermostat via a capillary tube, focusing on the correct temperature in the room. There is also a more advanced version in the form of a remote regulator, which is also connected by a capillary tube. But here you need to be more careful: not all valves are suitable for such thermal heads, so when choosing a thermostat you need to consult with the seller.

Finally, a few words about radiator valve manufacturers. Quite a lot of them have appeared, especially Chinese ones, whose quality is more than doubtful. The following brands of thermostats are definitely recommended for use; their reliability is beyond doubt:
- DANFOSS;
- HERZ ARMATUREN;
- OVENTROP.
Advice. You should not buy and install thermostats on all radiators in the house. The rule is this: in order to ensure normal regulation, in each room it is necessary to equip with thermostats only those batteries whose total power is 50% of the total or more. In simple words: with 2 heaters in the room, the valve must be installed on one (which is larger), with 3 - on two radiators, and so on.
Is a thermostat needed in a heating system?
The use of temperature control is caused by the need to provide comfortable conditions in rooms according to individual requests. Temperature adjustment directly affects fuel consumption during autonomous heating. In the absence of regulation and monitoring, the room will be hot and there will be a need for constant ventilation. High temperatures contribute to increased humidity and the occurrence of fungal diseases.
There are several stages of temperature control:
- Control on the boiler (in autonomous heating version);
- Control on the distribution manifold or individual branches of the heating system;
- Adjustment on heating devices.
How to regulate battery temperature
If the radiators heat well, but the room is too hot, you need to adjust the coolant supply. Overheating not only negatively affects a person’s well-being, but also leads to excessive energy consumption. To escape the heat, residents open vents, windows and balcony doors, warming the street at their own expense.

The optimal temperature in living rooms is considered to be about 20°C, in non-residential corridors and lobbies - ±18°C.
There are several methods to maintain a given mode:
- change in coolant temperature, which is only possible with individual heating;
- reducing the supply of coolant to radiators using control devices.
The latter method is popular in apartments with central heating, since you can create comfortable conditions for yourself regardless of the operation of the thermal power plant or boiler room.
Types of thermostats
Thermostatic regulators have a general design principle and various actuators. The overall design consists of a body, stem, seals, valve and connecting threads. The body is made of brass or stainless steel. The housing is equipped with threads for the inlet and outlet of the working medium. The direction of movement is marked on the surface of the valve with an arrow. At the water outlet, instead of a thread, for ease of installation and assembly, an “American” type fitting is usually installed. On the top of the housing there is a connecting terminal with a rod. The output has a thread or special clamps for installing a thermal head.
The rod is equipped with a spring and is in the raised position without applying force to it from the control mechanism (thermal head or handle). At the lower end of the rod there is an actuator - a valve with a rubber (or fluoroplastic) lining. Under the influence of the drive force, the rod lowers and the valve closes (or opens) the coolant flow channel.
This device is called a thermostatic valve. Based on the control mechanism acting on the rod, the following types of thermostats are distinguished:
- Mechanical;
- Electronic;
- Liquid and gas-filled;
- Thermostatic mixers.
Thermostatic mixers are a special type of thermostatic fittings. They are the basis of the operating principle of water heated floors. They set the water temperature in the heating circuits (usually does not exceed 50 degrees Celsius). To reduce the temperature of the coolant supplied from the boiler, the mixer mixes cooled water from the return pipeline of the underfloor heating circuits into the flow.
Mechanical thermostats
Mechanical thermostats are the basic model of thermostatic control valves. A detailed description of the thermostatic valve is given in the previous section. The main feature of a mechanical thermostat is manual control of the valve. This is done with a plastic handle that comes with the product. Manual adjustment does not allow achieving the required accuracy in controlling the heating device. In addition, the durability of the plastic cap leaves much to be desired. Connecting mechanical thermostats to the battery is the first step towards quality control.
Electronic thermostats
An electronic thermostat is a thermostatic valve with a servo-driven stem. The servo drive, based on sensor data, moves the valve stem and regulates the flow rate. There are different layouts of electronic thermostats:
- Thermostat with built-in sensor, display and key control;
- Device with a remote sensor;
- Thermostat with remote control.
The first model is installed directly on the thermostatic valve. The model with a remote sensor has an actuator and control device installed on the valve and a remote temperature sensor. The sensor is installed at a distance from the radiator in order to objectively assess the air temperature in the room. It can also be installed outside the building - adjustment takes place depending on the ambient air temperature.
An electronic thermostat with remote control has a common unit that integrates the control of a group of thermostats using a remote principle.
Liquid and gas-filled thermostats
Temperature regulators of this type are the most popular. They are cheaper than electronic ones and are not inferior to them in reliability. The principle of their operation is based on the use of the thermophysical properties of certain liquids and gases.
The housing contains a flexible vessel filled with a liquid or gas with certain properties. When the air heats up, the working medium of the tank expands and the vessel puts pressure on the valve stem - the valve begins to close. When cooling, everything happens in the reverse order - the vessel narrows, the spring lifts the stem with the valve.
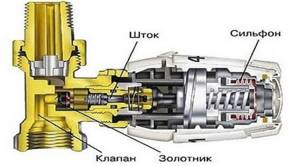
How does a thermostat work?

Thermal head device for heating batteries
The main elements are:
- thermostatic valve;
- thermostat (thermal head).
The first of them allows you to connect to any heating system, since the size of the outlet hole can be different. Thermostat or thermal head is a device for adjusting the thermostatic valve depending on the ambient temperature and the set settings. The required result is ensured provided that a certain level is set, upon reaching which the device will turn off. The coolant supply changes, and as a result, the temperature of the radiator also changes, which will lead to a change in the ambient temperature. The main stages of this process:
- when the temperature setting knob is rotated, the position of the spring changes;
- the pressure rod is lowered into the valve seat, and the working cone closes the hole through which the coolant passes and enters the radiator;
- when necessary, return the thermostat to its original position, the return spring will be installed in place, and the air temperature in the room will begin to increase.
The operating principle of the valve is based on changing the properties of the working medium inside it. A sealed container filled with a gaseous or liquid medium is provided. When the temperature rises, the substance expands, which leads to the blocking of the coolant flow (the rod is subjected to greater pressure and lowers).
Important: The coolant temperature does not change when the position of the thermostat (thermostat) changes. For adjustment, not a qualitative, but a quantitative value is used.
Operating principle of a thermostat for radiators
When you plan to install a thermostat, take into account the position of the arrow on it. It corresponds to the direction of the coolant. In order for the device to function without failures, it must be installed taking into account the position of the arrow. It should coincide with the flow inside the pipe.











