An electrode boiler is one of the options for organizing electric heating. It is usually used for heating private and country houses.
The main feature of such a unit is the replacement of the heating element in the form of a heating element with a block of electrodes that directly heat the coolant. This has a positive effect on increasing such basic indicators of electric heat generators as maximum service life and productivity.
An electrode boiler, unlike conventional electric or gas heat generators, is a direct-acting unit. That is, to heat the coolant, it uses a special heating block of electrodes.
Moreover, heating occurs not due to the flow of water near the “hot” rods, but because through them, electric current passes directly through the coolant, thereby causing random movement of ions in it with a frequency of 50 hertz.
As they move, they collide en masse, and as a result, the water becomes hot. The degree of its heating in relation to the energy expended on this is largely determined by the characteristics of the composition of the liquid. But in any case, such a unit is 40% more economical compared to similar devices operating from the mains.
Such units are classified according to several parameters:
- Power.
- placement diagram .
- Supply current – single- or three-phase.
- Single or double circuit heating system.
In terms of power, such devices can vary from 2 to 50 kW, taking into account the fact that units up to 6 kW are used only in private buildings with a volume of no more than 80 cubic meters, and operate from a conventional single-phase network. High-power units, consuming more than 9 kW and capable of heating tasks with a volume of up to 1600 cubic meters, are powered only from three-phase networks.
The coolant in the electrode circuits can only be heated to 75 degrees Celsius, otherwise the equipment begins to consume increased power, reducing its efficiency.
According to the method of placing the coolant, boilers are divided into closed and open. The former require installation on the circuit of an expansion tank and a circulation pump, which will ensure the movement of water in the system. The second involves the natural flow of coolant without additional equipment.
The design of all electrode systems includes a metal pipe with an internal dielectric coating, for example, polyamide, pipes welded into it for coolant inlet and outlet, power and grounding marks, and, finally, an electrode block inserted into one of the sides of the pipe, fixed again on polyamide insulating nuts.
The opposite side of the cylinder is simply sealed tightly.
Advantages of electrode boilers
Obvious advantages of electrode units over other heating devices:
- High performance – the efficiency of electrode boilers is 96%.
- Energy savings - to heat a house, the equipment uses 40% less electricity than other electrical units.
- Safety - the device is designed in such a way that the slightest risk of electrical leakage is completely eliminated. Sparks and other negative phenomena are impossible here, so households are protected from fire situations.
- Heating efficiency - thanks to the high power of the unit, ensured by the absence of any barriers in the process of moving heat to the energy carrier, the heating system heats up in a short period of time.

Electrode heater
- No scale – current passes through the carrier with a frequency of 50 Hertz, so electrolysis is impossible here, which protects the internal walls of the boiler from scale.
- Ease of installation - electrode models are compact in size and do not require a chimney or boiler room, so you can install them yourself.
- Ease of use - the device operates silently and without the formation of any contamination: be it soot or ash.
General aspects of electric heating
With the exception of boilers, all types of electric heating do not require external heating and auxiliary devices (heating circuits and radiators, chimneys), which is their undoubted advantage. They are quite easy to operate and install, and have low inertia. It is often possible to connect electronic control units and operate them remotely.
Again, most of the considered types of electric heating are quite expensive to operate. The power of almost all devices required to heat a room of a certain area is approximately the same, and it is quite large. It is generally accepted that for heating 100 sq. meters with a ceiling height of 2.5-3 m, 12-16 kW of electrical appliance power is required.
The geographical location of the heated house also plays a role here. In the southern regions of the country, the cost of electric heating will be much lower than in the northern regions. The design and insulation of the house also play an important role. The warmer and smaller the house itself, the less electricity will be required to heat it. Typically, electricity is used to heat small one-story houses or apartments in urban buildings with powerful wiring. In other cases, electric heating is used as auxiliary heating.
And most importantly, this type of heating makes you completely dependent on the availability of electricity itself, i.e. it makes the system energy-dependent.
Great savings come from the use of electrode boilers, warm infrared heaters and devices with automatic mode and temperature regulators (the so-called smart home).
An electric boiler with three heating elements mounted in the basement of my house (see photo) was used initially, from the design stage, as a backup option. I almost never turn it on. The total boiler power is 6 kW (3*2 kW).
This power is for a well-insulated house (interior decoration, foam blocks, insulating foam layer, brick cladding) with an area of 95 square meters. meters in the Urals are only enough to maintain the temperature in the rooms within 15-18 degrees, and in severe frosts it is only enough to keep the water heating circuit from defrosting.
The situation is also the same with my neighbors: one of them used the same boiler for heating a new house with an area of 64 square meters for one month. meters, which cost him 6 thousand rubles. Later (and now), after connecting the gas, he spends 1-1.5 thousand rubles per month on heating. The difference is noticeable.
At the same time, common electrode boilers with automatic adjustment and non-freezing liquid in our area “consume” 2-3 thousand rubles per month, which is comparable to the cost of gas heating.
From the author.
How the boiler will work
First, the resulting “glass” is filled with liquid; most likely, you will use ordinary water. After some time, the water will begin to boil. In this case, steam will form, it will rise up the pipeline, give up its heat to the heating devices and again turn into an ordinary liquid. The water, in turn, will flow down a specially installed pipe at a slope, after which it will move back into the “glass”. The cycle will repeat again and again without stopping.
Regardless of what volumes need to be heated, a do-it-yourself electrode boiler will still be a cost-effective asset. All this makes it possible to produce a boiler of small dimensions, which can be called another advantage of this design.
If your goal is to heat a large room, then you can make several such boilers at once, place them in places convenient for you in any order, thereby obtaining the required outlet temperature of the coolant. Another advantage is that the manufacture of ion boilers, as well as their installation and operation, does not require obtaining any permits.
So, what we end up with is the most economical equipment that is highly efficient in creating thermal energy. Isn't this what we all need for high-quality heating of the house in the winter? But the heating problem also has its other side - we are talking about achieving the most comfortable microclimate in the house with minimal energy consumption. That is why you should additionally take care of the thermal insulation of your home and ensure that all energy-saving technologies are followed during construction/improvement.
As a conclusion
Now you have been able to see for yourself that assembling an electrode boiler with your own hands is quite easy and within the capabilities of almost all of us. The most important thing is that you need, firstly, to become familiar with the operating principle of the device, and secondly, to follow all the instructions given here. Only in this case everything will be as successful as possible. Have a warm winter, gentlemen!
Device and technical characteristics
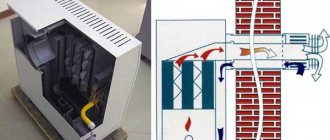
This method of instantly heating the coolant is not some kind of modern development; it has existed for several decades, so today models are produced by several companies. The designs are basically similar and differ only in minor details.

This is usually a vertically mounted cylinder, with a wide lower part where the electrical switching unit is located. The design contains two pipes for supply and return coolant.
Electrodes are installed inside the device. When working in a 220 V line, there is one electrode in the center, and in a 360 V line, there are three insulated electrodes made of specialized alloys, secured with protected polyamide nuts.
In addition, the design contains:
- control unit;
- control unit controller;
- low quality voltage protection;
- power and ground terminals;
- rubber gaskets for insulation
- insulating.
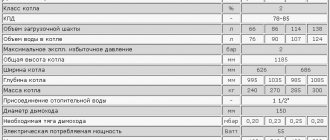
Average characteristics of a domestic ion boiler:
- diameter of the electrode boiler – up to 300-350 mm;
- length – approximately 600 mm;
- weight of one installation is from 10 to 12 kg;
- thermal power from 2.0 to 55.0 kW.
An indispensable component of an ion boiler unit is a special coolant, which must necessarily meet the conditions specified in the technical instructions of the manufacturer.
Electric boiler on heating elements
The do-it-yourself electric boiler circuit with a heater is the easiest to implement and has been known for quite a long time.
Operating principle of a heating element boiler
The design of all household appliances in which heating elements (heating elements) are installed is the same. When the power is turned on, voltage is applied to the heating element, which gradually heats up and transfers thermal energy to the liquid located around it.

The advantages of such devices:
- a wide range of heating elements of various shapes and power;
- Possibility of use in any heating system with liquid coolants;
- insulation is installed on the boiler body, so that voltage is supplied exclusively to the heating element;
- do not require complex maintenance;
- The heating level is very easy to control, even with a minimal set of automatic controls.
Among the disadvantages of a homemade electric boiler of this type are:
- “gluttony” in electricity consumption, since heating 10 m² of area requires 1 kW of power;
- impurities in the coolant accumulate on the heating element in the form of scale, so it needs to be cleaned approximately once a year;
- The heating element can only function in the presence of liquid; it is recommended to install an idle speed sensor with it.
Heating electric boilers
In boilers of this type, tubular heating elements (heating elements) are used to heat the coolant. Essentially, these are electrical conductors with very high resistance. Electric current flowing through the element causes its heating, which is transferred to the coolant.
The heating element itself is surrounded by dielectric material and placed in a metal tube of various shapes. The connection contacts are located at the ends of the tube. The tube itself (heating element body) is electrically safe.
At the household level, heating elements are well known from old electric kettles and portable water heaters.
The disadvantage of this type of boiler is the same disadvantage as in a kettle - the formation of lime on the surface of the heating element and the walls of the boiler. This lime formation occurs when using so-called hard water. Therefore, when servicing the boiler, an element of cleaning lime deposits is introduced by adding various additives to the coolant. Or before use, water is artificially brought to a normal hardness level of 7–10 mEq. per liter
The main ways to soften water are pre-boiling, distillation or the use of special filters. This also needs to be taken into account before purchasing an electric heating element type boiler.
Another problem with the boiler heating element may be a coolant leak. A heating element that is not immersed in water overheats and, as a result, burns out, which in turn leads to a fire.
Therefore, there is no need to skimp on boiler automation and pay special attention to its automation.
Adaptability to working with heated floors
Most boilers are designed for traditional heating systems, that is, they produce coolant with a temperature of 60-95 ° C. The peculiarity of water floor heating is that much lower temperatures are required: about 35-50°C. Only under such conditions the floor will not burn, but will be pleasantly warm.
There are two solutions: find an installation that can dispense warm rather than hot water, or mix cold water with the hot water, and only then dispense it into the pipes. The second solution requires additional equipment - a collector unit, in which mixing occurs. This is not the cheapest technology, as it requires measuring the temperature of the hot water and return water, mixing them until the temperature drops to the desired level. Of course, collector units are different, more or less expensive, but they still need to be purchased and installed.
Let's start with boilers for water floors, which can themselves produce coolant at the required temperature. Here in the first place are electric thermal units. You can set the temperature yourself from 25°C and above. That is, no additional costs and comfortable work with heated floors. In addition, induction and electrode (ion) boilers have very small dimensions, which makes them easier to install. If you have only one circuit, you can connect it directly to the output. If there are several circuits, a heated floor comb will be needed, but the simplest one, without mixing and temperature controllers. In principle, you can make it yourself from pipes and fittings. Other equipment may require (or not, depending on the configuration) an expansion tank, a drain valve and a circulation pump.
There is another option that simply shows excellent efficiency when working with low-temperature networks - these are condensing gas boilers. They are most effective when the temperature of the coolant in the return pipeline does not exceed 35°C. That is, this is an excellent option for a water floor.
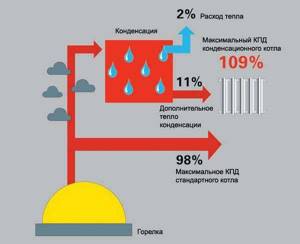
The best choice is a condensing gas boiler for heated floors
Gas boilers using traditional heat extraction technology require the installation of a mixing unit with control elements. If you decide to use such equipment, try to choose a model that can work with two or more circuits simultaneously. Usually one of them is high-temperature for radiators, and the rest are for low-temperature systems such as underfloor heating. In this case, monitoring the temperature and mixing the coolant is done automatically and everything happens inside the installation. So if your water heated floor works simultaneously with radiator heating, such equipment is an excellent solution.
The situation is more complicated with boilers using pellets and liquid fuel: for them, a collector (mixing) unit is required. And with all the stuffing: thermometers, controllers and thermal heads.

Wiring high-temperature boilers for heated floors is not the easiest task
Design features
In order to understand what we are talking about, let us recall the student and/or military background of many of those who are now reading this article. We are talking about a method of boiling water, for which some used a boiler, while others used a simple homemade design. These are two blades, fixed at a short distance from each other and connected by a 220V power cord. When this “boiler” was placed in water, heating occurred literally within 2-3 seconds and violent boiling began. This is precisely the principle on which an anode heating boiler works.
Please note that conducting experiments with heating water is dangerous to life and health. On the one hand, a short circuit may occur, on the other hand, a person runs the risk of electrical injury (electric shock).
The convenience of using such devices lies in the fact that parallel installation of electrode heating boilers into an already existing heating system, which works, for example, with a gas boiler, is allowed. The coolant in both cases remains the same. But manufacturing companies produce not quite standard heaters, in which water is simultaneously used as both a coolant and a heating element.
The main elements of the module are:
- steel tube;
- inlet/outlet pipes;
- terminal for connecting wiring;
- heating electrodes;
- high quality insulation.
Cathode heating boilers have a powerful steel body on the outside. The walls are made of sheet metal up to 4 mm thick. Several electrodes up to 20 mm are located inside the household structure. They are made of a refractory alloy that has a long service life.
Modern electrode ion boilers do not have an intermediary material between the anode and cathode. Heating from both terminals occurs directly from the coolant itself, water. Accordingly, there is practically nothing to “burn out” inside the cavity. The scale that appears on the tubes in electric electrode boilers after long-term operation is cleaned off with ordinary sandpaper.
What is the difference between electrode and heating element boilers?
The individual characteristics endowed with electrode heating boilers allow them to be distinguished from heating elements:
- in heating elements, at the initial stage of start-up, the working tubes are heated, and electrode boilers, made by hand or purchased in a specialized store, begin to heat the water immediately after start, which reduces inertia;
- ion heating boilers have positive reviews, as they are 20-0% more economical than devices with heating elements;
- thanks to alternating current with a frequency of 50 Hz, the electrodes move between the terminals and create a chaotic movement that promotes heating; this feature reduces the starting current for the electrode heating boiler, reducing the load on the electrical network
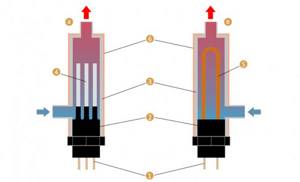
The difference between electrode boilers and heating elements
- A do-it-yourself electrode boiler made or produced at a factory has smaller overall parameters than other household analogues.
Such features ensure significant distribution of this heating system.
What are the advantages of using
Homeowners do not have to completely give up gas if the premises already have wiring from radiators and mains installed. Often such ion heating boilers play a duplicate role in finished systems. Although, if the cost of gas rises faster, then they can be used as the main source of heating.
Their positive properties include:
- high degree of reliability;
- temperature is controlled automatically;
- real efficiency reaches 99%;
- installation of additional equipment may not be carried out;
- startup and operation in systems designed to operate on gas;
- increased efficiency.
An electric electrode boiler operates exclusively on alternating current. Switching to constant voltage is not allowed.
Thanks to the built-in automation, the set optimal temperature is maintained for the specified time. You can increase energy efficiency by programming the system to lower the temperature on weekdays when no one is home, and raise it in the evening and on weekends.
Thermostat block
According to reviews, electrode boilers have a good emergency shutdown system. If a possible coolant leak is detected, the device will automatically turn off. Also, short circuits do not occur in these heating devices.
The coolant for such equipment can be purchased directly from the manufacturer, who will provide the appropriate quality composition.
Coolant-electrolyte
What are the disadvantages of using
In addition to the advantages, each system has its disadvantages. Ion electrode boilers have the following disadvantages:
- increased requirements for electrolytic water quality;
- it is necessary to carry out mandatory grounding of the device in order to reduce possible risks of working with an electrical device;
- it is advisable to maintain the water temperature in the system no higher than 70-750C in order to reduce energy consumption;
- the cathode and anode need periodic descaling to ensure greater efficiency for the ionization process;
- the system requires mandatory coolant circulation, so a water pump must be installed in it.
Voltage drops are not dangerous for the boiler itself, but they are necessary for the accompanying automation. A UPS or, at a minimum, a surge protector will help you avoid damage from an unstable network.

Rules for safe operation
The optimal water temperature for operation is 50-75ºС. This information is indicated in the device passport. In closed and open systems, expansion tanks must be used.
The outlet from the boiler to the expansion tank in an open system should not have any shut-off valves.
Do-it-yourself installation of an electrode boiler into the system must be accompanied by the installation of an automatic air valve, a pressure gauge for measuring the operating pressure and an explosion safety valve at the highest point of the system.
It is possible to install it in the heating circuit as an additional heating source, but in this case it is necessary to bring the quality and type of coolant into proper condition.

Not all radiators can work with ion boilers, and the quality of the coolant is suitable for some. With very big reservations, cast iron radiators can be used.
Read with this article: Types of heating radiators and their performance characteristics
When installing, one and a half meters of supply pipes to the boiler must be made of non-galvanized metal. After this section, the use of metal-plastic is allowed.
Grounding according to PUE standards is mandatory. The cable should have a cross-section of 4-6 mm. Its minimum electrical resistance must be no higher than 4 Ohms.
If possible, the entire system of pipelines and consumers should be flushed with clean water before installation. It is allowed to use special chemicals to help clean the lines.
After the coolant has been used up, it must be properly disposed of. It is not allowed to discharge it into sewers, water bodies or into the ground.
When making calculations, they are guided by the following parameter: 8 liters of coolant must correspond to 1 kW. To operate in the 10 l per 1 kW mode, the device will be turned on almost constantly, which may negatively affect its performance properties.
Let's make a brief overview of the most popular models of electrode heating boilers, which have already been rated by consumers and identified their strengths and weaknesses. When choosing such equipment, the brand name itself means little. Only in operation can you understand how well the boiler copes with the task, how often it breaks down, and what problems there are in operation. The purpose of this rating is to name the best Russian and European brands.
Electrode boilers
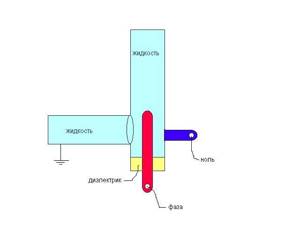
Ionic boilers are another name for these boilers. The principle of their operation is to use a coolant that has electrical conductivity. Electrodes to which a voltage of 50 Hz is applied are integral structural elements of such a device. A two-phase or three-phase AC network ensures the operation of such heaters. The three-phase version is used for devices of higher power and increased dimensions.
The housing is grounded and plays the role of one electrode. Reliable grounding is an indispensable condition for safe operation of the boiler. Grounding is expensive.
The second electrode is a metal rod. It is placed in a container where the electrolyte circulates.
After connecting the alternating voltage, the coolant molecules begin to move chaotically and collide. The released energy heats the electrolyte. It is then distributed among the heating devices and, having transferred heat, again enters the heating zone.
In Table 1, the lower limits of specific power parameters refer to small units. The lower limits of the unit cost, on the contrary, apply to powerful devices. The data is provided without taking into account the costs of automatic control systems, which significantly save electricity.
| Parameter | Meaning |
| Length | up to 60 cm |
| Diameter | up to 32 cm |
| Power | 2-50 kW |
| Optimal temperature | 75 C |
| Specific power | 0.35 + 0.5 kW/kg |
| Unit cost | 0.28 + 2 thousand rubles/kW |
When heating, the boiler power increases due to a decrease in the resistance of the electrolyte as its temperature increases. Continued heating requires more and more power. The temperature of the liquid is therefore limited by design. The maximum permissible value is determined by the properties of the liquids and the parameters of the boilers. Low temperatures of the heat transfer fluid compared to the norms for heating radiators (for example, 50ºC for boilers versus 90ºC for aluminum radiators) increase the radiator area. The costs associated with this are the fee for using the electrode boiler.
Working processes in electrode boilers cause changes in the properties of the coolant. It has to be changed in a timely manner so that power consumption does not increase. This is another cost item.
Stray currents appearing in electrode boilers cause electrochemical corrosion of structural elements even made of stainless steel. The gradual dissolution of the electrode rod adds to the worries. Increased operating costs are a consequence of these circumstances.
Electrode boilers are easy to operate, very reliable, take up little space, do not make noise, are equipped with advanced automation devices, have a wide power range, and are safe to operate. Choosing an electrode boiler is the best solution for those who need to quickly heat up a residential building (for example, when visiting their country house in winter). This is a champion in terms of heating speed. These boilers can be assembled in cascades, increasing the total power to the required limits.
Electrode boilers are innovative products. They are produced by venture producers. Well-known companies prefer heating elements.
Advantages and disadvantages
There is a lot of conflicting information in the technical literature about the operation of ion boilers. However, the achieved technological parameters of the operation of such a heating system indicate its significant advantages compared to similar heating devices operating on electricity:
- The highest efficiency level is 90-98%, higher than that of conventional heating elements structures.
- High speed of ion heating boilers reaching operating power.
- Small dimensions and weight, which simplifies the piping of the ion boiler.
- There is no need to install a smoke ventilation system. heated room.
- There is no overheating or coolant leakage.
- Voltage drops in the network slightly reduce the power of ion heating boilers, but do not stop the process of heating the coolant.
- Can be placed in a heating circuit with a traditional boiler running on any fuel as an additional source of heating at night or during peak load hours.
- Cascade installation of several ion units with stepwise adjustment of heating power is allowed.
- With proper disposal of waste coolant, ion boilers absolutely do not pose a threat to the environment.
- They have a low cost compared to traditional units.
Disadvantages of ion boilers:
- Specific parameters for the quality of the heating medium.
- Not all heating devices can work in tandem with ion electrode boilers. Experts recommend using bimetallic or aluminum batteries. Moreover, the latter should not contain oxides, which can change the chemical composition of the electrolyte and imbalance the operation of the entire system.
- High requirements for electrical grounding.
- The maximum temperature limit is up to 70 C.
- The electrodes quickly become covered with scale and require periodic replacement.
- It is unacceptable to work in the DHW heating circuit.
ELECTRODE HEATING BOILERS
Electrode boilers are the most compact of the entire family of electric water heating systems. They are reliable due to their simple design. The principle of their operation differs from all other classic electric heaters. Heating of the coolant is realized using two electrodes through which alternating current flows.
An electrolyte that meets a number of requirements is used as a coolant. The coolant must have a certain density (amount of salts), on which the ion content and series resistance of the electrolyte depend. The salt solution itself must be clean - free from mechanical impurities.
Manufacturers recommend using “branded” liquids with strictly defined characteristics. Sometimes users buy a concentrate, which is diluted to the required consistency. Electrode electric boilers can be either single or three-phase, their power does not exceed 16 kW.
Advantages of electrode technologies:
Compactness - the outer diameter of the housing is not much larger than the diameter of the main main pipe of the heating system of the house.
- Affordable price - the cheapest of all electric boilers.
- They have a simple design and high reliability.
- In the event of a coolant leak and a critical decrease in its level, the electrode boiler remains operational.
- When using an electrolyte with non-optimal operating values, scale appears on the electrodes. It leads to a slight decrease in power, but does not lead to failure.
- The heating system has low inertia. This allows you to heat the room more intensively and effectively carry out automatic regulation.
- The equipment is highly resistant to voltage changes in the power supply network. A voltage drop of a critical value for other types of boilers leads to a slight decrease in power.
Disadvantages of electrode boilers:
This type of electric heaters cannot be connected through a residual current device (RCD) since significant leakage currents arise as a result of operation. Therefore, the probability of electric shock is higher than with heating elements and induction boilers.
It is necessary to control the level of fluid resistance. For the same reason, it is impossible to use antifreeze. The price of a special electrolyte or its concentrate is high.
As a result of operation, the electrodes wear out and the characteristics of the coolant change. This requires periodic replacement of consumables, approximately once every three to four seasons. During the electrolysis process, a small amount of gases are formed, which are released through an automatic air vent.
Some of these gases are toxic, so the area where the heater is installed must be thoroughly ventilated.
The electricity consumption of such a boiler depends on the electrical conductivity of the liquid. As the temperature rises, electrical conductivity increases, so the coolant temperature should be 55°C-65°C. If it is exceeded, electricity consumption will increase many times over. This equipment is difficult to control in terms of heating parameters. Control is carried out by adjusting the current consumption.
Principle of operation

The principle of operation of such systems involves the use of ordinary water as a current conductor, which has undergone preliminary preparation, which consists of saturating it with salt. Its required concentration is determined in the passport of each specific unit.
Since current flows through both the electrodes and the water in which they are located, such an installation cannot be connected through an RCD, which significantly reduces the electrical stability of the entire system. The flow of current through water creates electrolysis, which promotes the accumulation of the corresponding gas in the coolant, which complicates the operation of the system and requires periodic release from the heating circuit.
In the event of a coolant leak from the circuit, a short circuit will not occur, since the circuit from the liquid will break. During the startup of the boiler, a voltage surge occurs, which requires an autonomous supply of power to it.
As water heats up, its electrolytic resistance decreases, so proper preparation and checking the salt content is required before work. If there is a significant decrease in the resistance of the coolant in the circuit, an electric arc breakdown may occur, the consequences of which are comparable to a short circuit.
The principle of operation of a homemade electrode boiler
The liquid poured into the “glass”, in our case it is water, begins to boil after a while. The steam that gradually forms will begin to rise through the pipe and give off heat, turning into water. The water will flow down the inclined pipe and slowly end up in the “glass”. Then the cycle will begin again.
The high level of efficiency of such heating with large heating volumes allows them to be small in size, which is another advantage.
If you need to heat a large volume of premises, you can create several electrode boilers in different orders to obtain the desired output characteristics. An additional advantage is that such boilers can be mounted and installed without obtaining special permission.
Obtaining highly efficient equipment in the process of heat production is only one of the goals of heating premises in the winter season. The other side of the problem is the small heat consumption to achieve a comfortable microclimate in rooms of different types and purposes
It is also important to take care of the thermal insulation of a house or apartment, and to comply with energy-saving design technologies during the construction of the house as a whole.
Heater design
The design of the device is quite simple. Firstly, this is a device of small overall dimensions.
Secondly, the boiler is a pipe that simply cuts into the pipe junction system by means of a threaded connection using American fittings. Thirdly, electrodes are inserted from one of the ends of the device. The coolant enters through the side pipe, and exits through the free end.
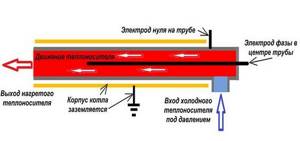
The dimensions of the unit depend on its power. For example, a single-phase Galan boiler is 30 cm long (diameter 6 cm), a three-phase boiler is 40 cm. For a small private house, the first option is suitable. If the house is large enough, multi-story, then it is better to install a three-phase device.
Design of a heating element for a heating boiler
Let's look at the design of a boiler heating element using the example of the Proterm "Skat" boiler, power 6, 9, 12,14,18, 21, 24.28 kW. This is a model of a wall-mounted electric boiler with equithermal regulation.
Water (coolant) comes from the heating system (arrow A), passing through the hydraulic group (3), the boiler tank enters. In it, it is heated by three installed heating elements. When heated, the water rises to the top of the tank and enters the return (supply line B) of the heating system.
A very simple and understandable scheme. There are no complicated burners, nozzles, heat exchangers, everything is as simple as in a samovar. Equithermal temperature control involves connecting an external temperature sensor to the boiler control group.
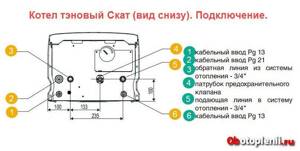
This boiler can operate with a heated floor system by connecting an emergency thermostat to regulate the boiler water temperature. The boiler's hydraulic group includes a two-speed circulation pump that circulates the coolant.
The boiler has a lot of protection:
- From freezing of the coolant;
- From freezing of an indirect heating boiler;
- Pump protection against jamming;
- Safety valve 3 bar.
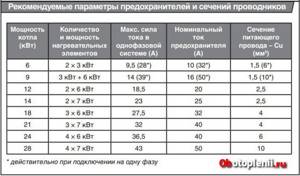
The connection of the electric boiler is made by a separate group of electrical wiring with a separate circuit breaker from the electrical panel. The cross-section of the wires and the rating of the circuit breakers are shown in the table (photo).
What you should know
When you create a heating system that will use cathode heating boilers, it is worth paying attention to several aspects:
- The electrical energy consumption of such a boiler will be much higher if you install the boiler in a previously used system. It is best to install the electrode boiler in a system that is created specifically for it.
- If you use antifreeze as a coolant, you need to pay special attention to detachable connections, since antifreeze has a higher fluidity than water.
- All pipes in the system should be wrapped with a thermal insulation layer - this will allow anode heating boilers to work more efficiently.
- If the radiators are located on different floors of the building, then a more effective option would be to install independent ion boilers for each group.
For lovers of non-traditional systems, we note that do-it-yourself or factory-made electrode heating boilers are not suitable for Warm Floor and Warm Baseboard systems. The temperature in such systems should not be more than 45 degrees - therefore the boiler will not be able to give full efficiency.
Advantages of an ion boiler
How to install an ion boiler

Most often, a gas or solid fuel boiler is used to heat a private home. If none of the options suits you, choose ion heating boilers. The technical characteristics of this type of boiler will pleasantly surprise you, because this device works thanks to a special method of heating water in the heating system.
Technical characteristics of the ion boiler
During operation, water ions move in chaos between the anode and cathode located inside the boiler. The current generated between them helps accelerate the ions and thus heats the coolant. Cathodes and anodes are made from a special durable material that does not rust.
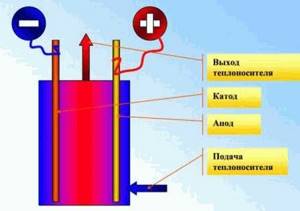
The housing is made hermetically sealed to avoid a breakthrough if the system is connected incorrectly. The complete set of the heating device consists of a heating element, a relay protecting the boiler and a special thermostat that allows you to regulate the temperature.

An ion boiler allows you to install several closed heating systems in one room. This heating device is compact and can be mounted in any more suitable place. The efficiency of such a boiler is almost 100 percent.
Installing a cathode and anode in the system allows energy losses to be reduced to zero. 20 square meters per hour consumes about one kilowatt. During boiler operation, the water in the system heats up much faster compared to other types of boilers. The low start-up inertia allows the coolant in the radiators to be heated to the required level in a short period of time. In addition, the boiler has increased protection against power surges. If there is no coolant in the heating system, the boiler does not fail.
Installation of an ion heating boiler
Before purchasing a boiler, you need to calculate the heated area in the room. For example, you can take an area of 48 square meters with ceilings of 2.6 meters and high-quality thermal insulation.
The area, that is, 48, is multiplied by the height from floor to ceiling, that is, by 2.6. From this it is calculated that to warm up one meter it will be 0.025 kilowatts. A boiler with a power of 3 kilowatts is enough to heat the entire room.

- To shut off the coolant in case of system failure or replacement of the coolant, a ball valve is installed.
- To ensure uniform circulation and distribution of water across the batteries, a circulating pump is installed.
- The filter cleans the incoming coolant into the boiler from scale and rust.
- A drain valve is mounted on the return pipe at the bottom to remove water from the system.
- An expansion tank is required to collect excess water that is generated when it is heated in the system.
- The automatic module for turning on the boiler starts the boiler with the specified parameters.
- After this, the air intake is installed.
For an ion boiler to operate in the correct mode, water must have a certain density. When replacing any boiler with an ion one, you first need to drain the old water from the system and fill it with new one. In addition, an inhibitor is added to it. Distilled water is taken for the heating system.

To connect the boiler to the heating system, steel pipes without galvanization are used. After 120 centimeters from the boiler, the pipeline can be made of a different material.
An ion boiler allows you to quickly and efficiently heat a room, so read the technical specifications carefully. You can install the ion boiler yourself if you carry out the calculations correctly and follow the step-by-step instructions.
Installation and Operation Requirements
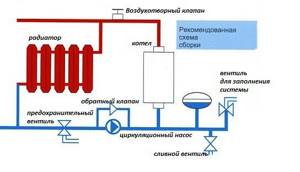
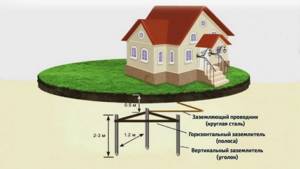
boiler connection diagram
- Installation of such a system requires the installation of automatic air vents, a safety valve and a pressure gauge. Shut-off valves are fixed behind the expansion tank.
- The boiler, due to the nature of its operation , is fixed only vertically on its own mount.
- When designing and installing such a unit , a copper wire with a thickness of 4 mm and a resistance of up to 4 ohms is used to ground it. It is connected to the zero mark, which is most often located at the bottom of the boiler.
- Before installing the heat generator itself , it is necessary to flush the heating pipeline circuit using water with the addition of special agents. If this is not done or if you immediately pour poor quality coolant into it, containing impurities, suspensions and other foreign elements, the efficiency of its heating by the boiler will significantly decrease, and energy costs will increase.
- When choosing radiators for a heating system , it is necessary to correlate them with its total volume, which includes the entire displacement of not only radiators, but also pipes. The optimal ratio is 8 liters of volume per 1 kW of heat generator power. If this threshold is exceeded, the unit for heating the coolant will have to work longer in active mode, and this increases its energy consumption.
- When arranging heating on electrodes, it is necessary to use aluminum or bimetallic alloys, since other materials contain more impurities that reduce the electrical conductivity of the coolant. In an open-type system, it is necessary to install radiators with a polymer internal coating that prevents air from entering and slows down their corrosion. This does not apply to closed loops.
- When using an electrode heat generator , you should avoid installing cast iron radiators that contain various impurities, which affects its efficiency. In addition, cast iron elements are larger in volume, which means that electricity consumption when heating them will be greater.
When choosing an electrode-ionizing system, like any other heating system, it is primarily based on its power, which must correspond to the structural features. These include the total area and volume of the premises heated in it, the volume of coolant in the circuit and the capabilities and limitations of the electrical network.
In practice, each kW of power of such a heat generator is capable of providing heat to a room with an area of no more than 20 square meters and a volume of up to 60 cubic meters with 40 liters of coolant in the heating circuit. If you choose a dual-circuit heating system, the power increases by a quarter.
Conclusion
An electrode boiler is a good solution for dachas and country houses. Its installation does not require permits or a separate room, and its operation does not require increased safety requirements. You can make such a device yourself, but how practical it is is up to you to decide. Although the water heater has a very high efficiency, its use is still much more expensive than the operation of its gas counterpart. It is also worth noting that the ion boiler is demanding on the coolant and heating system. If you do not comply with the mandatory requirements, the device will work ineffectively and will last much less than the stated period.
Should they be used for heating a private home: we analyze known statements and misconceptions
- An electrode boiler is much simpler and cheaper to install, since there is no need for a chimney or ventilation. In addition, its installation does not require approval.
This is true, however, any electric boiler does not require a separate room for the boiler room, special wall covering, chimney organization, supply and exhaust ventilation. The process of organizing a heating system with an ion-type boiler is indeed simpler, but not as much as when using heating element analogues, which already have in their housing all the necessary components of the heating system (it is enough to connect only the supply and return).

Another example of a complete heating system with an inexpensive electrode boiler.
Regarding coordination, it all depends on power. Any electric boilers with a power of more than 10 kW require mandatory approval from the Energonadzor services. It is also important to understand that any electric boilers with a power over 6 kW must be connected to a three-phase power supply.
- Electrode boilers have a higher efficiency, they are economical and consume 30-50% less electricity.
The efficiency of all modern electric boilers is more than 99%, so such statements are just a marketing technique or a comparison with extremely old models that have not been on sale for at least several years.
However, there is also some truth in the statement, since due to the formation of scale when using hard water as a coolant, the efficiency of heating element models decreases over time to 90 or 80%: heating the coolant through a layer of scale requires more time and energy consumption. The efficiency of ion boilers remains stable for a long time.
Also, the functionality of the automation seriously affects the efficiency. The automation of ion models is simpler and inferior to heating elements, where models in the mid-price segment and above have energy-saving night modes, the ability to program the operating mode for a week in advance, etc. The problem can be solved using a room thermostat costing 2,000-4,000 thousand rubles, but again, these are additional costs that offset the main advantage of electrode boilers - low cost.

Wall-mounted room thermostat for electric boiler.
- The reliability and service life of electrode models is higher.
With proper operation that meets the requirements, this is partly true, since electrode boilers have the simplest possible design and any malfunction in the first 12-15 years of operation is rare.
At the same time, the only vulnerable part of heating element models is the heating element itself - the heating element. When using low-quality coolant, it must be replaced after 3-5 years, when using prepared, purified and softened coolant - up to 8-10 years.
- Ion-type electric boilers are safer.
In an emergency, this is indeed justified by the principle of operation, since in the event of a coolant leak or power outage, the electrodes will simply stop working. When power is applied, they resume operation again without human intervention. Heating element models without overheating protection will not stop working if the coolant leaks, which will lead to destruction.
But the fact is that today even many budget heating electric boilers have protection against overheating, a mode to prevent freezing, and protection against blocking the circulation pump. Therefore, this is an extremely controversial statement.
Efficiency and selection criteria for energy-saving electric heating boilers
- Price
Most electrode models cost between 4-9 thousand rubles, while the cost of heating elements ranges from 19 to 29 thousand for the most common models in the middle price segment.
The low price of ion-type boilers is indeed a significant advantage, but is often overestimated by the buyer. It is worth considering that to organize the system, you will have to separately purchase an expansion tank, a safety group, a circulation pump and other components already present in the housing of models with a tubular electric heater. And this is another 5-10 thousand rubles. To achieve greater comfort and savings, a functional electronic thermostat is also needed - another 2-4 thousand rubles.
Difficulties in operation

Branded coolant from the manufacturer Galan. At the time of writing, the cost of such a canister is about 2,200 rubles.
- Proper operation in accordance with the requirements implies the use of high-quality coolant with a balanced chemical composition and all the qualities of the electrolyte. Manufacturers recommend using liquids specially prepared for these purposes that have good ionization, sufficient heat capacity and anti-corrosion properties. It is possible to pour ordinary tap water into the heating system, but this usually leads to a decrease in efficiency and rapid corrosion of all metal lines of the heating system. In addition, over time, any coolant loses its properties and requires replacement after 3-4 years, which also causes additional hassle and expense.
- As we have already mentioned, the effect of electric current on ferrous metals and stainless steel significantly accelerates the corrosion process, which reduces the life of the heating system. Therefore, in conjunction with electrode boilers, it is generally not recommended to install steel or cast iron radiators - only aluminum or bimetallic ones. Otherwise, the lifespan of radiators is literally reduced several times.
- The phases of the electrical network are connected to the electrodes, and zero is connected to the body of the electric boiler, so reliable universal grounding is required and it is not recommended to limit yourself to installing an RCD. If the grounding is poor, dangerous potentials may appear on pipes and batteries. In addition, it is necessary to ensure the quality of the wiring in the house, since high-power equipment creates a serious load on the electrical network and causes voltage fluctuations. However, this is not a feature of ion electric boilers, but in general of any electrical equipment with a power of 4-6 kW.
To summarize: if you are not ready for additional installation work and operating features of electrode boilers, it is better to pay an additional 20-30% of the cost and choose a heating element electric boiler, which is what we recommend doing. Today they occupy about 90% of the electric boiler market. But with a competent approach, there is also a choice in favor of ion-type boilers, the advantages and disadvantages of which are summarized below.