How to calculate consumption?
When calculating fuel consumption, many factors are taken into account: quality, brand, duration of coal combustion, average temperature outside, area, material and degree of insulation of the house.
Using calculations, an average value is obtained, since it is difficult to take into account all the criteria, as well as the onset of thaws and frosts. Before starting the calculation, the total area of the house is calculated. The boiler power is calculated using the standard formula: 1 kW per 10 m2. For example, for an average country house of 160 m2, 16 kW equipment will be required. The efficiency of modern boilers ranges from 50 to 90%; for example, we take the average value of 70%. We calculate the duration of the period during which heating is needed (on average 6 months).
Fuel consumption is calculated as follows:
- To operate a boiler with a power of 16 kW with an efficiency of 70%, it will require 11.2 kW/h. To generate 1 kW you need 0.25 kg of coal with average characteristics. 11.2*0.25 = 2.8 kg per hour.
- We calculate the daily amount of fuel: 2.8 * 24 = 67.2 kg.
- We determine the coal consumption for the month: 67.2*30 = 2021 kg.
- To calculate the amount of coal for the winter, multiply the resulting number by the number of cold months: 2016*6 = 12096 kg.
- To calculate the cost of heating for the winter, we multiply the resulting value by the price of coal per 1 kg.
Reference. To get data on consumption, preferred brand and operating time on one tab, look at the technical documentation for the boiler. Instructions are always included with purchase.
What factors need to be considered
When determining the consumption of coal in a boiler for heating a house, the most difficult thing is to select accurate initial data for performing the calculation. The volume of solid fuel required to heat a room depends on many parameters. First of all, you need to take into account the quality of the raw material: brown coal has the lowest heat transfer rates, and anthracite coal has the highest. You also need to consider:
- specifics of the heating system model;
- climate features (average daily temperatures in the cold season, duration of the winter period, etc.);
- materials that were used to build the house;
- the number of windows and doors, as well as what they are made of (wood or PVC);
- age and size of the house (number and area of rooms, ceiling height, number of floors, etc.);
- quality of thermal insulation materials;
- stoker's experience and skills.
At the same time, the listed factors must be considered as a whole. For example, when using the same boiler model, fuel consumption for heating a stone house after a major renovation and a country cottage without high-quality thermal insulation of the walls will differ dramatically.
It is almost impossible to take into account all variables when calculating, therefore, regardless of the type of fuel, only the average value of its consumption during the cold season is determined.

Regardless of the type of fuel, when calculating consumption, only the average value of its consumption during the cold season is determined.
Online fuel consumption calculator
Select city Select city BELARUS Brest Vitebsk Minsk Polotsk KAZAKHSTAN Aktyubinsk Almaty Dzhambul Karaganda Kzyl-Orda Kokchetav Kustanay Pavlodar Petropavlovsk Semipalatinsk Taldy-Kurgan Turgai Ust-Kamenogorsk Fort ShevchenkoMOLDAVIA ChisinauRUSSIA Abakan Arkhangelsk Astrakhan Barnaul Blagoveshchensk B Ryansk Vladivostok Vladikavkaz Vladimir Volgograd Vologda Voronezh Grozny Ekaterinburg Irkutsk Kazan Kaliningrad Kaluga Kemerovo Kostroma Krasnodar Krasnoyarsk Kurgan Kursk Lipetsk Makhachkala Moscow Murmansk Naryan-Mar Nizhny Novgorod Novgorod Novosibirsk Omsk Orenburg Orel Penza Perm Petrozavodsk Petropavlovsk-Kamchatsky Pskov Rostov-on-Don Ryazan Samara St. Petersburg Saratov Smolensk Syktyvkar Tambov Tomsk Tula Tyu men Ulan-Ude Ulyanovsk Ufa Khabarovsk Cheboksary Chelyabinsk Chita Yakutsk YaroslavlUKRAINE Vinnitsa Dnepropetrovsk Zaporozhye Kiev Kirovograd Lugansk Lvov Nikolaev Odessa Poltava Rivne Simferopol Ternopil Uzhgorod Uman Kharkov Kherson Chernigov
Enter the total heat loss of the house, kW
Required amount of thermal energy per heating season, kJ
Which coal do you prefer?

Don't forget about the fuel storage room. You can try to save on coal by choosing an inexpensive type. However, you will need a lot of it, so you will have to overpay for delivery, and also find storage space. And vice versa - you will need less high-quality coal for heating, so you will save money on delivery and storage. This way you can significantly reduce the consumption of coal for heating your home.
Projected coal consumption for home heating
If you live in a populated area where the ubiquitous gas pipe has not yet reached, then the problem of heating your own home is more than relevant for you. If you go through all the possible options, excluding blue fuel that is not available to you, then coal will be the undisputed leader. Strange as it may seem, it is coal heating, which was once abandoned due to many side disadvantages of its use, that is making a comeback today.

Coal stoves work on the same principle as classic Russian heating and cooking brick stoves. You can even boil water or cook food on it (read: “Project of a house with stove heating”). But there is one fundamental difference - the air in such devices is heated not due to air convection, but through its uniform heating in several places at once by radiators. Which supplies the coolant, a preheated heating boiler, with a circulation pump.
Traditional stoves, coal and wood, have one unpleasant feature for a city person who is not accustomed to physical labor - they are labor-intensive to maintain:
- You need to constantly add fuel to the stove
- It is often necessary to remove combustion residues from the stove and clean the chimney of soot.
In addition, traditional stoves require constant monitoring due to uneven combustion of fuel. This leads to the likelihood of frequent temperature changes and the need to constantly check instrument readings to prevent accidental overheating of the boiler.

Solid fuel boilers have successfully evolved and are starting to make a comeback! Now they use different combustion principles. If in traditional models a noticeable part of the materials used did not burn completely, resulting in a lot of smoke, soot and ash, then in new models almost all the fuel burns.
All the different models have common differences from traditional models:
- Versatility. You can burn ANY solid fuel in them almost without leaving a trace - coal, firewood, briquettes, pellets, dry household waste, sawdust, and so on (read: “Fuel briquettes: do-it-yourself production”).
- Long operating time on one fuel load
. The advertisement, of course, exaggerates, claiming that modern top-burning solid fuel boilers can work for weeks from one fill. As practice shows, one portion of fuel lasts from 3 to 8 days. Coal consumption in a solid fuel boiler is directly dependent on the type and quality of coal. High-quality types of coal from low-grade brands with the same volume are distinguished by excellent heat transfer and low waste levels. In second-grade coal, there is generally waste rock, which only wastes the volume of the furnace. - Economical
. Especially if you additionally use free or waste fuel - dry leaves and household waste. On average, solid fuel boilers using new technologies consume 2-3 times less fuel compared to traditional ones. - High heat dissipation
. The fuel burns almost completely due to the high temperature in the firebox. - Easy to use and maintain
. Throwing fuel into the firebox is a task that can be accomplished even by a teenager. And cleaning from ash is a rather rare procedure for modern boilers.

How does modern coal heating work at home?
A simple example to understand how a top-burning boiler differs from a traditional boiler is an ordinary match and a thermometer:
- If you light a match under a thermometer and turn it with the sulfur head down, it will burn quickly and will hardly have time to heat the thermometer (traditional stove).
- If you do the same thing, but place the match with the sulfur head facing up, the match will burn much longer and will greatly heat up the thermometer (top-burning stove).

Heating with coal in a private house works like this:
- Coal is loaded into a voluminous combustion chamber (capacity up to 500 liters).
- The fuel is ignited.
- A lot of air is supplied from above into the combustion chamber through a pipe using a fan to heat the firebox to a temperature that ensures almost complete combustion of the fuel.
- The heat enters the heat exchanger, in which the coolant circulating through the pipes and radiators is constantly heated.
How much coal is needed to heat a house? Coal heat supply, experience
Heating residential houses with coal is not a thing of the past, since the more preferable heating with gas is still not available in all regions and not to everyone, and, moreover, technological heating systems that run on coal are quite productive and the most balanced in quality and cost. Modern heating boilers for private buildings have been improved to such an extent that:
- they can burn a wide variety of fuels, including garbage;
- fuel consumption is several times less than in conventional stoves;
- due to the high temperature, the fuel burns almost without waste;
- do not require constant maintenance and are easy to use.
- what is the residential building made of?
- how insulated it is;
- what is the heated area;
- what type of heat supply is used;
- what kind of boiler is in operation;
- will be purchased;
- what are the average monthly outside air temperatures in this area;
- how long does the heating season last, etc.
The answers to all these questions determine how much coal is needed to heat a house, and what standards of coal consumption for heat supply should be applied.
For example, it is much easier to heat a wooden or block house than a brick house of similar size. Coal heating price
In both first cases it will be approximately a third less than in the last.
To supply heat to a well-insulated foam concrete house with an area of 100 square meters. m.,
As practice says, you will need 3 tons of coal (a third of it is coal, the rest is long-flame), and you can’t heat a poorly warm one with six tons.
In the south, a ton of coal is purchased for the entire heating season for a country house of 200 square meters. m., and in the northern regions, where frosts can sometimes reach 40 degrees, even a small wooden house with an area of 50 square meters. m.
over the winter it will “eat” three tons.
So coal consumption for home heating (
actually yours) will need to be done in a functional way. The very first. Of course, talk to your neighbors who have a home similar to yours to decide on the quantity in the most general terms: three or five tons will be needed, this is already a significant difference.
The trading organization will also guide you - they have a lot of experience. But you still don’t need to buy a decent amount of coal at once. Take, as they say, for testing, several bags of coal of different brands and try with it, remembering which one burns better, gives more heat, leaves a little ash and which one is most comfortable in the house.
You will most likely be conducting your own experiment in September, so make an adjustment for the outside air temperature. Having understood how many days the purchased volume lasted, you will be able to calculate the need for coal for the entire heating period.
In the first year, purchase fuel with a reserve; if there is any left, it will be useful next year; coal does not lose its qualities for a long time. It will be worse if there is not enough for the whole season.
For a more accurate calculation of coal consumption for home heating
(for example,
with an area of 150 sq. m.)
, you can listen to the advice of professionals. As is clear, to generate 1 kilowatt of heat energy, you will need to burn 0.2 kg of coal for an hour. For the heating period, this area requires approximately 40 thousand kW, or 8000 kg (40,000 x 0.2). In other words, you will have to purchase at least 8 tons of coal, which contains good heat output. You will need more brown, less coal.
An even clearer way to count is using a bucket. From many years of practice it is known that the heating supply of a house with an area of 150 sq. m approximately during the season, 450 buckets weighing 18 kilograms each are used. We multiply 450 x 18, we get 8100 kg, in other words the same 8 tons with less.
Having found out the quantitative need for fuel, and knowing the prices for it, it is easy to calculate how much it costs to supply coal with heat.
for the coming heating season
.
Nowadays, the need to use coal for heating very often appears when living outside the city limits in a non-gas supply house. In this case, coal is considered the most successful replacement, which is better than electric heating both in terms of costs and final efficiency.
This publication discusses coal heating. We will get acquainted with its theoretical and functional qualities, study the types of coal and give advice on its choice. Approximate fuel consumption in a variety of situations will also be given and equipment for heating a home will be demonstrated.
Coal for heating - varieties, tips for choosing
There are only 3 types of coal suitable for use in heating systems - coal (marked with the nomenclature “A”), brown (“B”) and hard coal, while hard coal, for its part, is divided into 5 varieties:
- long-flame - “D”;
- gas - “G”;
- skinny - “T”;
- coke - “K”;
- bold - "F".
Coal is considered the most widely used fuel in industry. It is better than other varieties in terms of consumption, heat transfer and combustion duration. Also, when burning coal, a minimal amount of slag waste is formed.
Anthracite contains 10% ash and 1% sulfur, therefore, during its combustion, the smallest volume of sulfur dioxide is released, which, upon contact with water, forms sulfuric acid - a substance that has a bad effect on the condition of metal structures (inner walls of boilers, chimney pipes).
However, it is impossible to offer coal for heating a home, because despite all the advantages, this material has major disadvantages. There are two of them - the highest cost and complexity of ignition among all types of coal.
What material should I choose? A suitable option for heating a house with coal is long-flame fuel - “DPK”; this type of coal is perfect for burning in solid fuel boilers, as well as for ordinary potbelly stoves, fireplaces and stoves. In terms of quality/cost ratio, “DPK” is considered an excellent option; it simply ignites, burns for a long time (does not require third-party blowing) and emits a relatively decent amount of heat energy.
Depending on the size of the fractions, “DPK” and other types of coal are classified into the following types:
- ordinary “P” - the size of the factions can be very different;
- seed “C” - fraction size 6-13 mm;
- pin “W” - up to 6 mm;
- small “M” - 13-25 mm;
- nut “O” - 26-40 mm;
- large “K” - 50-100 mm;
- slab “P” - more than 100 mm.
For domestic use, it is better to use fuel of classes “M” and “O”; the size of such fractions burns well both in layer and dust combustion.
1.1 Fuel consumption
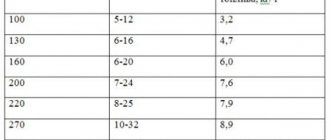
Coal consumption is mainly calculated using standard 10-liter buckets (the usual capacity of a solid fuel boiler firebox); one bucket of this size contains 18 kg of material. According to average statistics, coal consumption for heating a house with an area of 200 m2 at different periods of the season is:
- September—October — 1 bucket/day;
- November—February - up to 10 buckets/day;
- March/April—1-2 buckets/day.
Having summed up the monthly consumption, we acquire total fuel consumption of the same 580 buckets, which is equal to 10.5 tons of coal. This figure is given without taking into account air temperature, so practical fuel consumption differs from region to region.
1.2 Pros and cons of coal heating, alternatives
Coal heating has the following advantages:
- the smallest cash expenses, frugality;
- availability of coal;
- ease of storage and transportation of the material (mainly supplied to the consumer in bags, coal briquettes for heating are also in demand);
- the ability to burn household waste simultaneously with fuel;
- autonomy - there is no need to connect outsiders to the house;
- low material consumption due to its high heat transfer.
But this method of heat supply also has its own disadvantages, which include:
- the need to continuously maintain the functionality of the system - you need to add fuel to the boiler or stove 2-3 times a day;
- the need for constant maintenance of the equipment - removing ash every 2 days, completely cleaning the firebox - once a week;
- When coal burns, dangerous gases are released, which, if the chimney system is poor, usually end up inside the house;
- burning coal has a distinctive, unpleasant aroma for most people.
As a replacement for coal as a material for heating a private home, you can consider fuel pellets - a granular material that consists of a mixture of peat and wood shavings. Fuel pellets are divided into two types - simple (white) and torrified (black).
Torrified fuel granules at the production stage are fired at a temperature of 300 degrees in vacuum chambers, which gives them a number of positive performance qualities. Such fuel pellets do not absorb moisture (they can be stored in damp rooms or under clear skies), do not rot and have a combustion efficiency comparable to coal, which is why black fuel pellets are often called bio-coal.
Fuel pellets are environmentally friendly fuel, in which the ash content will not exceed 3%. However, in terms of material costs, heating with simple “WPC” coal is more profitable, since its price will be approximately 5 thousand per ton, while the cost of pressed fuel pellets starts from 6.5 thousand, while the consumption of materials is almost the same.
1.3 How to choose a coal heating boiler? (video)
Features of use
A popular question is which coal is best for heating a home. Experts in this field say - anthracite or coal. Anthracite is able to ensure long-term and uniform combustion of a batch of coal loaded into the boiler, the highest thermal output and a small amount of waste. A popular type of coal, which is intended for combustion in low-power boilers, is considered to be long-flame ordinary coal, seed, nut.
p, blockquote 8,0,0,0,0 —>
In recent years, anthracite has become increasingly popular due to its low sulfur content (up to 1%) and ash (up to 10%). Due to the low sulfur content, the combustion products formed during the combustion of anthracite contain less sulfur dioxide. In addition to benefits for the environment, this has a beneficial effect on the service life of boiler parts and chimney pipes, which are exposed to the least amount of sulfurous and sulfuric acid, which appear as a result of the interaction of sulfur and water vapor.
p, blockquote 9,0,0,0,0 —>
If you decide to purchase coal for a heating boiler, take note that the amount of fuel will directly depend on its quality characteristics. Therefore, make a purchase only from manufacturers who have the appropriate quality documents.
p, blockquote 10,0,0,0,0 —>
Methodology for calculating the amount of fuel for the season
Let's figure out how to calculate the consumption of any type of fuel for a room. First, we will calculate how much heat is needed to heat the entire house per hour. Multiplying by 24, we get the daily value, then multiplying by 30 and 111 days, what is the consumption per month and for the entire heating period.

After this, we calculate the heat transfer of the accepted unit of measurement for each type of solid fuel. By dividing the amount of heat required per month and season by heat transfer, we will see how much of this type of combustible material is needed per month and for the whole year. This will show us how much fuel we need to store for the winter and allow us to compare the efficiency of different devices.
What you need to know to calculate
Before calculating fuel for the entire season, you need to clarify a number of points, since firewood consumption depends on several factors. Here is a list of questions that require answers:
- How much heat is needed to heat a country house in your area of residence?
- What type of wood is planned to be burned?
- What is the moisture content of this wood? Is it freshly cut, semi-dry, or has it been around for a year or two?
- What is the efficiency (COP) of your heating unit? Indicated in the passport for a solid fuel boiler or stove.

Thermal energy consumption for heating a private home is determined by calculations performed by specialists or by an aggregated calculation method. For most homeowners, the second option is more acceptable, since you have to pay for the first. Its essence is this: on the coldest days, 10 kW/h of heat is allocated to heat 100 m² of building area located in a temperate climate zone. Taking into account the temperature change during the heating period, the average consumption during the season will be 5 kW/h.
Different types of wood release different amounts of thermal energy when burned, which is why it is important to know this in advance. The table below shows the calorific value of firewood of different types, referred to a measure of volume - 1 m³:
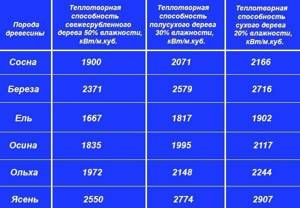
As can be seen from the table, the moisture content of wood fuel also affects the calorific value. The drier the wood, the more energy can be obtained per unit volume. This is understandable: when raw wood burns, part of the heat is spent on evaporating moisture and is not used to heat the house.
The efficiency indicator (EI) makes it clear what part of the thermal energy from burning fuel the boiler is able to direct into the heating system, throwing the rest into the chimney. This value is specified in the technical data sheet of each heat generator. For those who have not yet purchased a wood-burning heat source, here are the efficiency indicators for various heaters:
- when burning in a classic solid fuel boiler, 70 to 75% of the heat is used;
- the same, in a pyrolysis boiler - 80%;
- Russian brick or bell-type oven – 65%;
- steel or cast iron stove – no more than 55%.
The nuances of buying coal
The retail trade offers many types of barbecue coals directly from the manufacturer: birch, coconut, oak, aspen or special briquettes.

Each type of coal has its own specific application and has distinct characteristics.
Birch trees are the cheapest and safest option. High-quality coals from this wood provide uniform heat, do not emit unpleasant odors when smoldering, burn for a long time and are excellent for any culinary devices: barbecues, barbecues, grill ovens, and so on. They do not contain phosphorus, sulfur and other harmful substances. Experts advise using birch charcoal.
Coconut charcoal is a good imported product, but quite expensive compared to its birch counterpart. It is made from coconut shells and has several advantages:
- Increased heat transfer.
- No harmful chemicals.
- Burns without smoking and has no odors.
- Quite a long combustion time.
- Its consumption is five times less than when using any other varieties.
Briquettes are a good option for barbecues, however, they are also more expensive than the usual birch coals. It is produced by briquetting small pieces of wood.
Main advantages:
- High heat transfer and calorie content.
- Impressive burning time.
- Minimum amount of residual ash.
- Economical consumption of briquettes, which exceeds the consumption of wood (for similar purposes) several times.

Oak adhesive components are used - although a worthy combustion product for cooking, it is not entirely suitable for home kebabs. It is difficult to light and will require some skill to achieve its maximum effectiveness. The main purpose of this representative of the coal family is to use it in professional kebab shops, bars and restaurants.
Charcoal - this name on the packaging clearly indicates that there are softwood coals inside, which are absolutely not acceptable for barbecue. They always contain resins, which, when burned, will certainly spoil the taste of kebabs.
Stone - absolutely cannot be used in barbecues, even if the packaging says that it has undergone special treatment. When it burns, a whole bunch of harmful substances and specific odors are released, which will certainly transfer into the cooking kebab.
Sometimes aspen or pine trees are passed off as birch trees. It is quite easy to expose the deception - only birch ones have a brilliant anthracite color. Aspen and pine have no shine. They're just black.
When purchasing coal, first of all, you need to be concerned with the question: “How much does the product offered cost?” It should be remembered that even the cheapest birch charcoal cannot cost less than 100 rubles per 3 kg package. Lower prices are simply not possible.
The product packaging itself will help you choose the best option. It must contain min = 8 positions required by law: reliable name of the product, contact information of the manufacturer, information about certification, purpose of the product, and so on.

Which coal is better is decided purely individually, since each type of this product has its own specific specifics
Unfortunately, buying excellent charcoal for the barbecue is quite problematic. There are a lot of fakes in this segment of production and trade. And even Moscow cannot guarantee that the coal purchased at its retail outlets will be a quality product.
Therefore, it is much more practical and profitable for the average person to prepare good charcoal with his own hands.
Coal heating equipment
Coal ovens
A conventional stove can only heat one or two rooms, even if you use coal rather than wood to heat the house. True, it can be improved by embedding a heat exchanger for water heating inside the brickwork. The stove is good in its own way, but sometimes it can be dangerous due to the fact that it provokes carbon monoxide poisoning.
Important. The stove chimney valve can be closed only after the coal has completely burned and the flames have disappeared from the firebox.
For heating a cottage with coal, a heating unit such as a boiler is much more efficient, reliable and safe.
Coal solid fuel heating boilers
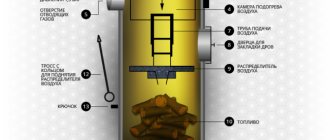
The diagram shows the design of an improved coal boiler
The design of a coal heating boiler is simple, but very effective. Its cast iron heat exchanger and powerful grate are resistant to burnout and corrosion. Even the simplest of these devices have been regularly heating homes for many decades. But still, old-style boilers are inferior in performance and heat transfer to their current competitors.
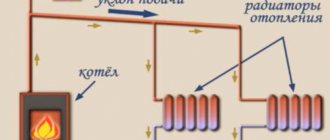
The operating principle of a heating boiler looks like this:
- as soon as a fire is lit in the firebox, a draft is created in the chimney and air is drawn into the fuel chamber;
- the coal heats up and partially burns;
- gaseous products of coal combustion are mixed with the secondary air supplied inside and finally burn;
- the resulting gases give up their temperature to the coolant and are then discharged through the chimney.
Modern coal-fired heating boilers consistently heat residential premises and outbuildings. They consume 2 times less fuel compared to outdated models. Advanced technologies have improved not only the design and design of heating units, but also the very principle of fuel combustion. As a result, now the homeowner does not have to load the next portion of coal into the boiler several times a day and remove accumulated slag.
The enlarged combustion chamber is designed for simultaneous loading of a large amount of coal, which gradually burns out over 6–12 hours. Forced air injection promotes the most complete combustion of fuel. Thanks to this, coal consumption for heating the house is significantly reduced.
Especially for automatic models of heating equipment, it is recommended to purchase eco-pea coal, which has optimal dimensions and is free from dust.
The large bunker of the automated heating boiler ensures long burning of coal
Automated fuel supply from the bunker to the boiler “frees the user’s hands.” He becomes free from the obligation to constantly monitor the operating heating device. The capacity of the bunker is enough for non-stop burning of coal for a week.
Reviews of coal heating demonstrate how satisfied users are with the practicality of automated coal boilers. It is very convenient to start the boiler at the beginning of the heating season, and throughout the winter just add coal to the bunker as it is emptied. You also don’t have to remove ash and slag too often, just a couple of times a month.
Lighting coal for heating in a boiler, especially anthracite, can be difficult for an unaccustomed person. First, the boiler is heated with wood or a special mixture, and then fine coal is added little by little. When combustion becomes stable, you can add anthracite in large portions. Exactly how much and how often will depend on the boiler model and will be more accurately determined in the practice of its use.
Do not use gasoline to ignite coal in a heating boiler!
What to do if the electricity in the house goes out? In this case, the automatic supply of coal to the fuel chamber of the boiler will be stopped. At the same time, the circulation pump will stop working, and water will stagnate in the heat exchanger. But the boiler will not boil, because coal combustion will go into low mode. Then, when power is restored, the coal will reignite.
Solid fuel boiler maintenance
Boiler maintenance measures boil down to the need to clean the heat exchanger and smoke exhaust channels. Soot settles on their surfaces, and this phenomenon reduces the efficiency of the heating unit by 15%. The frequency of cleaning a coal heating boiler can vary: old cast iron models have to be cleaned 2-3 times per season, and modern ones once every 2 years.
For unhindered maintenance of the boiler, there must be free access to it in the room where it is installed.
Activated carbon for industrial water treatment
This coconut shell activated carbon is a medium activity carbon used in various water treatment applications, usually in stationary absorbers. It is more highly effective at dechlorination compared to coal-based activated carbon. Thanks to the many micropores, this activated carbon adsorbs trihalomethanes or methyl tert-butyl ether, as well as other disinfectants, well. This grade of activated carbon is widely used in soft drink filling machines, breweries and water treatment companies.
| Standard analysis | Characteristics | Method of analysis |
| Iodine number, mg/g | 1000–1500 | ASTM D4607-94 |
| CTC (Carbon tetrachloride activity), % | 50–100 | ASTM D3467-88 |
| Bulk density, g/cm³ | 0.45–0.55 | ASTM D2854-96 |
| Hardness,% | 95–98 | ASTM D3820-79 |
| Humidity, % | ASTM D2867-99 | |
| Ash content, % | ASTM D2866-94 | |
| pH value | 6–11 | JIS K1474 ASTM D2862-82 |
Particle size distribution 4×8 USS, 6×12 USS, 8×16 USS, 12×30 USS, 20×40 USS, 40×100 USS
| Mesh | more (+4, +6, +8, +12, +20, +40) | |
| Mesh | in the range (4–8, 6–12, 8–16, 12–30, 20–40, 40–100) | > 90% |
| Mesh | less than (−8, −12, −16, −30, −40, −100) |
70×325USS: According to report
Note: the standard analysis is an average analysis, the data is based on practical production experience, and may vary depending on the raw materials and customer requirements.
Areas of application
- dechlorination;
- ozone removal;
- elimination of trihalomethane or methyl tert-butyl ether;
- elimination of odors and tastes;
- elimination of pesticides and other dissolved pollutants;
- protection of reverse ostomy membranes and resins.
Advantages
- Pore structure. Each carbon-containing material has the properties to form internal pores of varying sizes. Typically peat and lignite have fairly large pores. In coals based on bituminous coal, pores with different sizes are mainly formed. Coconut shell-based coals have more micropores and fewer macropores.
- Necessary pore structure for maximum adsorption.
- Effective for backwashing.
- Capable of regeneration.
- Highly effective in dechlorination.
Which is better, coal or gas?

It is generally accepted that the most profitable option for heating is main gas.
However, having learned the cost of supply and connection, many residents are looking for alternative heating options. It is better to compare these types of fuel according to three criteria:
- Energy. When burning 1 m3 (0.62 kg) of natural gas, you will receive 9.45 kW/h of heat without taking into account the boiler efficiency. A kilogram of anthracite will give 7.16 kW/h.
- Economic. Tariffs for the population for gas supplies are taken into account, as well as the cost of transporting coal and the efficiency of boilers.
- Ease of use. In all cases, a chimney and ventilation will be required. Storage of coal fuel requires space; it will have to be stored manually, while gas is supplied through a pipeline.
Reference. If the house is already connected to the gas main, then you don’t have to look for a more profitable heating method. If there is no connection, the best option is coal boilers operating in automatic mode.
The cheaper way to heat your home
The price of fuel for heating a private home is of great importance, but it is pointless to consider it in isolation from heat transfer. We will calculate the cost of heating taking into account both parameters.

Combustion of peat fuel 3 hours after laying
In the area where our expert lives, the following prices are asked for proven types of fuel:
- Freshly cut firewood – 20 USD. e. for 1 m³. Let's tie the price to the weight: 20 dollars for 600 kg or 33 cu. e. for 1 ton.
- Briquettes made from pressed sunflower husks – $57 per ton.
- Peat briquette – 84 USD. e./1 t.
It is easy to calculate that 10 kg of wood will cost 33 cents, the rest of the fuel - 57 and 84 cents, respectively. Then 1 hour of heating on wooden logs costs 33 / 1.5 = 22 cents (remember, the wood burned out in an hour and a half).
In a similar way, we determine the hourly rate for burning briquettes:
- pressed husk: 57 / 2.17 (2 hours 10 minutes) = 26 cents;
- briquetted peat: 84 / 3 = 28 cents.

Burning briquetted sunflower seed husks. Interesting result, right? In our case, heating up an absolutely cold building costs 5.28 USD. e. per day for wood, 6.24 dollars for pressed husks and 6.72 cu. e. - on peat “bricks”.
Please note that we took the cost of raw wood (and it will decay sooner) and divided it by the time of full combustion of dry wood. That is, the difference between traditional fuel and briquettes is minimized. We suggest watching the progress of the experiment on video and listening to an expert’s opinion on this matter:
Coal and coal consumption for heating
Of course, an important question is the problem that affects everyone who has already installed coal heating - which coal is better for heating? Many experts say that the most acceptable type of coal is anthracite - hard or brown coal. These types of coal for heating can be purchased almost everywhere and in any quantity. You can buy coal for heating in bags, and even order several tons with delivery to your storage location.

For ease of transportation, coal is often transported in bags.
What kind of coal is used for heating?
Note that the concept of “hard coal” includes several types of minerals:
- Brown coal: has the lowest combustion temperature and is not currently used for heating because it is inefficient.
- Hard coal, grade D: is ideal for heating a house with coal, as it has a long flame.
- DPK coal: very often this type of coal is called long-flame “nut” and “fist”. Typically used for heating small boiler rooms in private houses.
- TPKO coal: lean coal, usually used for private purposes.
- Anthracite: ideal for powerful boilers.
|
|
Pressed coal is also used for heating.
Undoubtedly, all experts will say that anthracite is the best option. But why? And all because of its properties, since this type of coal is very hard and has excellent heat transfer during combustion. It has a glassy luster and a bright black color. The carbon content in this coal is almost 90%, and impurities are only a small amount. When burned, anthracite produces almost no odor or smoke. It is also non-flammable.
Coal consumption
As for coal consumption, a scheme is used to calculate the amount of firewood for one heating season, since coal is the same solid fuel. This calculation of coal consumption for heating is the most accurate and simplest. So, the simplest unit of measurement in everyday life is a bucket. On average, a bucket filled with coal weighs about 18 kilograms. If you believe those who constantly use solid fuel heating, then based on their readings for coal heating of a house of 200 sq.m., the consumption is:
- September-October – 1 bucket per day (18 kg);
- November-February – 10 buckets per day (180 kg);
- March-April – 1-2 buckets per day (22-24 kg).
Now we will calculate the total consumption of coal for heating a house in buckets:
60+120+400=580
But if you don’t like such a simple method for determining coal consumption for heating, then you can use a more “scientific” method using coal consumption standards for heating. To get 1 kW of energy, you will need about 0.2 kg of coal. On average, approximately 50,000 kW of energy is consumed per heating season. So, we multiply 0.2 kg by 50,000. We get a result similar to the previous one - 10,000 kg (10 tons).
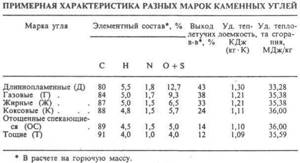
Characteristics of different grades of coal
But it is worth noting that when purchasing coal, be sure to take into account its grade, since each type of coal has a different level of energy output.
How much coal should I buy to heat a private home? What varieties?
How many tons, kg, of coal are needed per season to heat a private house?
What determines its quantity?
What parameters should be provided?
What if this is a living space? (it happens that apartments are heated with coal)
What types of coal are better?
How to practically spend coal?
Let's start with the fact that houses can be very different in size and building materials.
Let me give you my own home as an example.
Approximately 90 sq. meters area.
During the winter, we spend 2.5 - 3.5 tons of coal on heat supply.
We purchase a ton of nuts (coal) and two tons of seeds .
Of course, you need firewood for kindling. Then we add the nut - it flares up faster and gives a quick temperature, and then we drown it with the seed - it burns longer, it just maintains the required temperature.
How to save coal . This is no small matter. First of all, we have a warm house . On the outside there is brick, but the main thing is slag, burnt coal with a concrete solution. This material retains heat well. And the thickness of the walls is about 45 cm. Also, everything possible is insulated . All cracks are sealed, windows are insulated. There is also slag and a specialized heat insulator in the attic. Heating is water - heating radiators in any room and in the bathroom. But still, we built a rough wall - a warm wall. This makes it very possible to maintain the temperature. This rug is warm all day long even if you don’t turn on the stove.
Another means of saving. When we select burnt coal, we do not throw it away (many do this), but sift the ash and ash through a sieve, and what remains in the sieve goes back into the stove. Moreover, when there is a good wind outside, it burns perfectly.
There should also be valves that can be used to adjust the draft, and, naturally, the rate of coal combustion and the temperature in the rooms. If there is no valve, then with a strong draft the coal will quickly burn, the house will be hot (which is completely unnecessary) and then everything will quickly cool down.
For example, neighbors, having a house of similar size, use 6-7 tons of coal per season. However, they have walls made of blocks made of concrete (cold), and there are no valves or rough walls in the house.
My father-in-law uses one and a half to two tons of coal per season. The house is smaller there. Note 65 square meters
Friends who live in apartments use approximately the same amount of coal. Our village is not gasified and many have installed autonomous heating and installed boilers. One and a half to two tons is enough for a 2-3 room living space.
Of course, it is necessary to take into account the weather factor - cold winter or warm. Based on this, in severe winter the consumption becomes somewhat higher. But, as you can see, this can always be improved.
Coal heating: pros and cons
Coal-fired heating systems cope well with increased heating demands in severe frosts. One of its main advantages is its ability to retain heat for a long time. In addition, coal stove heating has other advantages:

- independence from the availability of main energy resources (electricity, gas);
- availability: coal, like the boilers themselves, is domestic and inexpensive;
- efficiency: average efficiency for different types of equipment - 70%;
- autonomy: if you purchase the appropriate model, you will not depend on electricity and gas;
- simplicity of design ensures long-term uninterrupted operation of the device;
- automation: many models themselves solve issues of fuel supply and thermoregulation.
Despite the improvement of technology, coal devices are not without drawbacks:
- In order for combustion to bring maximum efficiency, special conditions will have to be observed: requirements for the brand, quality, and humidity of the burned raw materials.
- The need to allocate a utility room for storing fuel and installing the unit.
- The cyclical nature of the process means different loading frequencies (depending on the type of device). Coal will have to be loaded into any boiler.
- Maintenance required: removal of soot, soot, ash, cleaning.
Many devices require the installation of auxiliary devices such as pumps and forced ventilation units. Despite the automation of many systems, coal generators require constant monitoring.
Choosing coal as a fuel and a boiler for it
Unfortunately, sometimes there are errors in publications, they are corrected, publications are updated, developed, and new ones are prepared. Subscribe to the news to stay informed.
If anything is unclear, ask first! Ask a Question. Review of publication.
Why does the boiler smoke? A coal-fired heating boiler was installed. Nowadays it started to smoke. What could it be?
How to add coal, top up a coal heating boiler. Refilling coal. Heat supply. Sequence of actions when refueling. Before.
Heat supply to a wooden house with heated floors. Functional experience. Review. Review of underfloor heating for heating a country house made of wood. Functional experience.
A heating stove is an unusual stove design. An interesting design of a heating stove with adjustable room heating.
Ignition of the oil burner using propane (cylinder-type gas). Design of a gas ignition system for a burner during production. Reliable ignition.
Calculation of firewood consumption by a long-burning boiler
To calculate the consumption of firewood in a long-burning solid fuel boiler per day, use the following formula.
V = 24Q / (q x 0.01 efficiency) V – means the volume of firewood required for 1 hour, m³; Q – required power for heating, kW; q is the thermal output of a certain type of wood with a specific degree of humidity, kW/m³; Efficiency is the efficiency of the boiler, in%.
Let's say you purchase a solid fuel pyrolysis boiler with a heat transfer rate of 75%. Load dry pine logs. The calculation will look like this:
V = 24 x 5 / (2166 x 0.01 x 75) = 0.074 m³.
When trying to correctly calculate fuel consumption in a pyrolysis boiler, you need to remember the nuances of its operation. An efficiency factor of 75-80% is displayed in the formula if the firewood has a maximum moisture content of 25%. If the indicator is higher, the boiler efficiency decreases to 70%.
The consumption of firewood in a long-burning solid fuel boiler for a month is done as follows:
0.074 x 30 = 2.22 m³
However, this is not the final result, since the formula involves the calorific value for a “clean” m³, and in fact, firewood in a woodpile takes up more space due to the packing density. To correctly calculate firewood in cubes, you need to know the number of storage meters.
GOST 3242-88, where the standard is specified, will help you carry out these calculations. In connection with this, stacked firewood must be measured, folding meters calculated, and then converted into dense meters, m³. the translation is made by multiplying the volume of the woodpile by the value of full wood.
Full wood coefficients for transferring folding measures back to back
| Length, m | Conifers | Hardwood | ||||||
| Round | Shattered | A mixture of chopped and round | Round | Shattered | A mixture of chopped and round | |||
| Thin | Average | Thin | Average | |||||
| 0,25 0,33 0,50 0,75 1,00 1,25 1,50 2,00 2,50 3,00 | 0,79 0,77 0,74 0,71 0,69 0,67 0,66 0,64 0,62 0,61 | 0,81 0,79 0,76 0,74 0,72 0,71 0,703 0,68 0,67 0,65 | 0,77 0,75 0,73 0,71 0,70 0,69 0,68 0,66 0,64 0,63 | 0,77 0,75 0,73 0,72 0,70 0,69 0,68 0,67 0,66 0,65 | 0,75 0,72 0,69 0,65 0,63 0,61 0,60 0,58 0,56 0,55 | 0,80 0,78 0,75 0,72 0,70 0,68 0,67 0,65 0,63 0,62 | 0,76 0,74 0,71 0,69 0,68 0,67 0,65 0,63 0,62 0,60 | 0,76 0,74 0,71 0,69 0,68 0,67 0,66 0,65 0,64 0,63 |
Since in our case there is an inverse problem, the fuel volume calculated above must be divided by one of the coefficients that corresponds to the present conditions.
Let's say we take chopped firewood 0.5 m long. For coniferous species, we need to take an indicator of 0.73. At the end, we calculate the real consumption of solid fuel from dry pine per month for a dwelling with an area of 100 m²:
2.22 m³ / 0.73 = 3.04 m³
https://youtube.com/watch?v=lmSAbJsWmpQ
Wood briquettes for the boiler
Wood briquettes are the predecessors of pellets. The technological process for producing both types of fuel is almost identical. Pellets were created to automate the operation of solid fuel units. Briquettes, originally intended for manual laying, resembled logs or beams in their appearance, and weighed from 0.5-2 kg.
At the moment, the production technology has been changed. Consumers began to be offered cylindrical fuel, up to several centimeters long, which made it possible to use wood fuel briquettes in automatic boilers.
How and from what are wood briquettes made?
Heating wood briquettes for boilers are produced in three different ways, each of which has its own characteristics and markings:
- Rectangular RUF briquettes - received the marking due to the fact that the first compressed fuel was created on equipment manufactured by the German manufacturer RUF. In shape, the finished product resembles a small brick. The production principle is based on pressing sawdust and waste using hydraulic presses at a pressure of 300-400 bar.
Cylindrical briquette – pressing of briquettes for solid fuel boilers of this type is carried out using hydraulic or shock-mechanical equipment. When pressing, the pressure increases to 600 bar. The disadvantage of the cylindrical type of fuel is the fear of moisture and susceptibility to mechanical damage.
Pini&Kay – pressing of wood briquettes for heating boilers is carried out using mechanical screw equipment. The difference between production is the simultaneous use of high pressure (up to 1100 bar) and thermal firing. The resulting “logs” have edges and a characteristic dark brown color.
The washers are similar in structure to Pini&Kay, have four or six edges and a radial hole in the center. The length of the briquette is only a few centimeters.
The briquette production technology used affects the quality and cost of fuel. Pini&Kay have the highest calorific value; they are resistant to moisture and mechanical stress, and also burn longer when fired.
Briquette consumption in the boiler
Solid fuel for boilers in briquettes is made from various types of wood. The burning time and fuel consumption depend on the type and type of wood:
- Coniferous briquettes flare up quickly and create a high temperature in the firebox, but quickly burn out due to the large amount of resin released. Heating with pine briquettes is not profitable due to high fuel consumption, but it is advisable to use them to light the boiler.
Pressed hardwood slabs have a high calorific value, are difficult to ignite and burn out slowly. The average consumption is 10 kg for 6-7 hours.
Another type of briquettes that has not found widespread use are slabs made exclusively from bark. This type of fuel burns hard, but during combustion it has practically no flame and smolders slowly. At the same time, the temperature is maintained until the slabs burn out. The average burning time is 12 hours.
Cost of wood briquettes
The cost of wood briquettes for a solid fuel boiler varies depending on the type of production and the type of wood waste used in production:
- RUF is the cheapest type of compressed fuel made exclusively from soft wood. Price per ton, about 5-8 thousand rubles.
Pini&Kay - costs between 7-10 thousand rubles per ton. Universal fuel type. Used to ignite open and closed fireplaces, as well as pyrolysis boilers.
It is economically profitable to use fuel briquettes due to their high calorific value and low content of non-combustible residue.
It is advisable to heat long-burning solid fuel boilers with wood briquetted fuel, due to the moisture content of no more than 10%, which significantly facilitates the gas generation process. Firewood stored for 2 years has a moisture content of at least 20%.
Long-burning coal boilers - advantages of use
coal boilers for heating a private home These include:
- Consumption of a significant amount of fuel. The combustion of the material in the firebox is akin to smoldering. In this case, fuel begins to be burned from its lower layers in the upward direction. The air required for combustion is supplied in strictly dosed quantities. The automatically controlled injection process promotes almost complete combustion of coal - only one or two percent of its total volume remains.
- Unlike conventional models of solid fuel boilers, long-burning systems do not require constant maintenance. Capable of holding up to five hundred liters of fuel, the container makes it possible to increase the burning time from one load to several days. Cleaning combustion chamber boilers requires significantly less time - controlled combustion reduces the amount of soot formed.
- The temperature regime of a conventional long-burning solid fuel boiler is quite difficult to control, which can cause the system to overheat. An uneven combustion process is much more difficult to control. A long-burning solid fuel coal boiler is free from this drawback - the fully controlled process of burning the fuel material and heating the coolant ensures the stability of the initially established temperature.
Approximate calculation of solid fuel for a house with an area of 100 square meters
To heat a house of 100 square meters, we need 100 square meters. m. * 100 W = 10 kilowatts of thermal energy per hour. Accordingly, per day it will be 10 kW/h * 24 hours = 240 kW. We will need 240 kW/day per month * 30 days = 7200 kilowatts, for the entire heating period 240 kW/day * 111 days = 26,640 kW.
Sometimes, calculations are based on the fact that the flame burns actively only 10 hours a day, which is enough to maintain the set temperature. Then the required amount of heat is 10 kW/h * 10 h = 100 kW. Often, based on this parameter, the consumption is written in the operating instructions.
On average, when burning 1 kg of oak wood, 3.4 kW is released. 240 / 3.4 = 70.6 kg of firewood will be burned per day, 7200 / 3.4 = 2117.64 kg per month, 26,640 / 3.4 = 7835.29 kg per winter. That is, in one winter, a solid fuel device burns almost 8 tons of wood.

It is also important to take into account that the calculation of consumption is also greatly influenced by the quality of the firewood, in particular its humidity, the type of wood it is made of, as well as the conditions of its storage. To heat such a house with firewood, a Zota 15a device is suitable.
One kilogram of coal emits 7.75 kilowatts when burned. Coal-fired equipment consumes 240 /7.75 = 31 kg of fuel per day. 7200 / 7.75 = 929 kg of coal will be required per month, for the entire heating season 26,640 / 7.75 = 3437.5 kg.
How much coal you will have to stock up and load at each load is greatly influenced by its type, ash content and the amount of foreign impurities. For heating this room with coal, the Teplodar Kupper OVK 10 solid fuel boiler model is suitable.
For industrial premises with an area of 5000 sq.m. m., a cast iron hot water boiler from Bratsk, running on coal with pieces of up to 100 mm in size, or Universal 5 and Universal 6 equipment are suitable.
A kilogram of briquettes, when burned, emits an average of 6.2 kilowatts. In one day 240 / 6.2 = 38.7 kg will be consumed, in a month 7200 / 6.2 = 1161 kg, in the winter season 4297 kg of briquettes. You can heat such a house with briquettes using the Peresvet T 10 device.

How to calculate the number of cubes of firewood
Firewood is most often sold in bulk in a car or in a pile. How to correctly calculate the number of cubes of firewood in this option. First you need to calculate the entire volume of firewood. In relation to a car, for example, you can multiply the length, width and height of the body. The conversion coefficient of the embankment into folding meters is 0.82, folding meters into cubes is 0.7. Thus, a ZIL of firewood with a body width of 2.2 m, a length of 3 m, and a side height of 1.2 m will contain 4.5 cubic meters of firewood. (3*2.2*1.2) * 0.82 * 0.7 = 4.5 cubic meters.
For residents of the private sector, issues related to the operation of an autonomous heating system are not particularly difficult. At first glance, everything is very simple. There is a boiler, there is fuel for it, so you just need to put wood in the firebox and set it on fire. It may work, but most often in such situations you will have to simultaneously solve several problems at once, each of which threatens to negatively affect the quality of heating. The many years of practical experience that old-timers have will tell you how to properly heat, how to fill a solid fuel boiler with wood correctly in order to achieve a better combustion effect.

Let's try to figure it out ourselves
How to heat heating units using solid fuel from a scientific and technical point of view, how important it is for the operation of the boiler to what it is heated with and how it is heated
How to store coal
Coal of different brands and even different deposits behaves differently during storage. Some can be stored for years with virtually no loss of quality, while others turn into dust and dust after six months. It all depends on the composition and quality of the fuel, as well as on storage conditions.
The shelf life of coal depends on the brand and deposit
Depending on its resistance to oxidation (which is what causes changes in characteristics and “weathering”), coal is divided into four categories:
- The most stable . This group includes anthracite and semi-anthracite, which in large pieces (the size of a soccer ball and up to the size of the “P” fraction) can be stored without noticeable loss of quality for up to 36 months , smaller fractions from “K” and smaller - up to 24 months . This category includes coals from pools:
- Suchanskoye - TR, GR - stored for 36 months;
- Cheremkhovskoye - DR, DKO - 36 months;
- Pechorsky - ZhR, ZhSSh, ZhSh - 24 months;
- Donetsk – TR, KR – 24 months;
- Podgorodnenskoye – TR – 24 months.
- Resistant to oxidation. Shelf life: 18 months
- Donetsk basin - GK, GKO, GO, GM;
- Kuznetskoe field - TR, TK, TO, SS K, SSKO, SSM;
- Irtysh (Ekibastuz) - SSR;
- Karaganda - KR, KZhR;
- Sakhalin ZhR, KR GR, GKO;
- Ural GR
- Shartunsky SSS
- Kuu-Chekinskoe K2R
- Bukakachinskoye GR
- Medium stability. They are stored for 12 months.
- Kuznetsky - DKO, DM, KR, KZhR, ZhR, K2R, GK, GKO, GO, GM, GKOM;
- Kizelovsky - GR, GMSSH, GSSH, ZHE;
- Donetsk - DKO, DM, DK, DO, GR, GMSShch, GSShch, GShch, R, Zh;
- Pechorsky - DKO;
- Sakhalinskoye - DR, DSS;
- Lvivsko-Vsyaynskoe - GR, GK, GMSSH, GSSH;
- Egorshinskoye - GR;
- Shargunskoe - coal briquettes;
- Tuvinskoe, Neryunfinskoe - KR;
- Zyryanskoye, Chulmanskoye - ZhR.
- Unstable. They are stored for 6 months.
The best brands of coal
Among the coal offered on the market, anthracite is the most preferred for heating a private home. It burns very well and hot, and has a low ash content. The following grades of coal are usually on sale: AK (anthracite “large”, also known as “fist”), AO (anthracite “nut”), AM (anthracite “small”), AS (anthracite “seed”), AS (anthracite “ shtyb").
AK grade coal is the most expensive, but in many cases it is inconvenient to burn with it due to the large size of the pieces. Before use, large pieces often have to be broken with a hammer, which requires extra time and effort. The most preferred brands are AO, AM and AC.
How the heating system is installed.

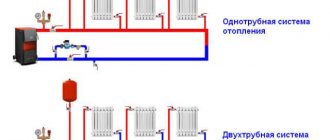
The heating system is the usual Leningradka. At the input there is a 15 kW solid fuel boiler. One of the simplest and most reliable (it is practically omnivorous, it can be heated with any coal). A supply pipe runs from it around the perimeter of the house, to which the batteries are connected. The system is not gravity-fed; it has a circulation pump. The boiler also contains heating elements (3 pieces of 1 kW each), but they are almost never used, since there is always someone to heat the main boiler.

How to store coal
Coal of different brands and even different deposits behaves differently during storage. Some can be stored for years with virtually no loss of quality, while others turn into dust and dust after six months. It all depends on the composition and quality of the fuel, as well as on storage conditions.
The shelf life of coal depends on the brand and deposit
Depending on its resistance to oxidation (which is what causes changes in characteristics and “weathering”), coal is divided into four categories:
- The most stable . This group includes anthracite and semi-anthracite, which in large pieces (the size of a soccer ball and up to the size of the “P” fraction) can be stored without noticeable loss of quality for up to 36 months , smaller fractions from “K” and smaller - up to 24 months . This category includes coals from pools:
- Suchanskoye - TR, GR - stored for 36 months;
- Cheremkhovskoye - DR, DKO - 36 months;
- Pechorsky - ZhR, ZhSSh, ZhSh - 24 months;
- Donetsk – TR, KR – 24 months;
- Podgorodnenskoye – TR – 24 months.
These are storage periods for enterprises selling coal from open areas. Coal will be stored in a private backyard for approximately the same amount of time without losing its characteristics. Then the process of oxidation and weathering begins. You can extend the shelf life of coal if you store it under a roof. The coal shed or basement should have a low temperature and preferably no direct sunlight. Coal oxidation begins at 20-25 o C. At a temperature not higher than 40 o C, the process occurs slowly and is expressed in a decrease in the strength of the pieces, the appearance and deepening of cracks. This process is also called weathering. Since oxidation occurs with the release of heat, the temperature inside a large pile of coal gradually rises, which can lead to spontaneous combustion. This problem is most likely when using low-quality fuel with a high content of fines and/or dust. Brown coals have the highest probability of spontaneous combustion, followed by hard coals with a porous structure (lignites and subbituminous). Anthracites are the least susceptible to oxidation and spontaneous combustion.

Proper coal storage is no easy task.
If you store coal of small fractions such as “seed” or “pile”, you need to periodically check its condition. If the reserves are large, it makes sense to purchase an electronic thermometer, to which you attach a long thermocouple (temperature sensor) and periodically, at least once a week, monitor the condition. Spontaneous combustion temperature of coal:
- Brown – 40-60 o C;
- Fat coals – 60-70 o C;
- Skinny and anthracite – 70 o C.
PS from the author of the blog.
In our new house, we plan to heat it with electricity, since we simply don’t have time to heat it with coal. But if time permits, then in the Altai Territory this is the most budget-friendly heating. But of course everything depends on the price of coal. If you have questions, ask in the comments. I hope this article will help someone decide on a heating system. Thank you for your oh.
And if you are interested in the construction topic, subscribe to
“Samostroy”
. Our channel is about how we build our own house with our own hands. Here's a review article if you're interested:
How we were built. Do-it-yourself frame house 8 by 8 on 2 floors.
More useful articles Go to Source
The principle of operation of a coal boiler
Coal-fired boilers have a slightly different combustion process than other systems. Inside the device, the fire does not burn from bottom to top, but vice versa. This increases the burning time of one batch of coal and ensures its most complete combustion.
In the boiler, almost the same process occurs as the burning of an ordinary candle. Coal burns for a long time, the heat that is produced goes into the heat exchanger. During combustion, air comes from above using a special fan. The combustion chamber in a boiler that uses coal heating in a private house can be quite large and reach a volume of up to 500 liters. This means that at one time you can load a lot of different fuels, which will heat the house for several days.

Such boilers are also equipped with temperature control sensors. The use of coal will reduce the amount of harmful substances that appear as a result of combustion. Coal boilers consist of a firebox, where this process takes place, a heat exchanger for heating coal, and a grate. The heat exchanger can be made of steel or cast iron. Steel boilers for coal are a little cheaper, while cast iron boilers will last longer.
Today, heating with coal has become a practical solution for those people who like to relax in the country.
And one of the most important issues in arranging a heating system is the cost of the equipment. Unfortunately, many will find the cost of the device quite high - after all, even the cheapest boiler models cost at least 20,000 rubles.
For those who have small country houses and other buildings that require heating, domestic models of low-power coal-fired boilers are suitable.

Why is it beneficial to use coal?
The operation of modern solid fuel boilers does not cause any trouble. Especially if the homeowner prefers coal - an efficient, safe, convenient and cost-effective fuel. Compared to other types of the latter, it has many advantages:
- is characterized by high heat transfer, allowing to obtain much more heat per unit of heated area;
- not afraid of humidity;
- does not require special sealed containers for storage;
- It is sold in a convenient package in which it can be easily transported to a city home or to the country.
Installing a coal boiler allows you to not depend on the presence of a gas pipeline within reach, which is especially important for residents of the private sector. In addition, this type of heating equipment can be installed without special permission, which cannot be done, for example, by purchasing a gas boiler.
An additional benefit of using coal as a fuel is provided by the special design of modern boilers. Over the years, not only the appearance of the equipment has improved, but also the method of burning fuel, and, accordingly, its consumption.
Firstly, there was no longer a need to pour coal into the firebox several times a day and clean out the slag. Modern boilers have large combustion chambers and special safe bunkers for storing fuel, from which it is automatically supplied to the firebox via a conveyor as needed. You can immediately load as much coal into the chamber as is necessary for continuous operation of the system for 10-12 hours, and the volume of the bunker is designed for 6-7 days of constant burning of the boiler.
The combustion chambers in modern models of heating equipment are completely sealed and equipped with special ventilation systems, thanks to which the strength of coal combustion and the degree of heating of the system are adjusted. Due to the forced supply of the optimal volume of air, the fuel burns out almost completely, leaving behind a minimal amount of waste, which allows to significantly reduce its consumption.