A device for metering consumed electricity (meter) is a familiar and mandatory item in any home, private or multi-apartment. Increasingly, in homes and businesses, outdated electric meters with a spinning disk are being replaced by a new generation electronic meter - a two-tariff electricity meter. Feedback from citizens who have already switched to separate metering of consumed electricity is quite contradictory.
An impressive portion of electricity consumers talk about a fairly quick payback for installing a two-tariff meter: they call it a period of 6 to 18 months. However, negative reviews are also found. The main complaint is that the two-tariff metering system did not justify itself and turned out to be less profitable than the energy supply companies claimed. Why does this happen, and to what extent can the installation of such a device as a two-tariff electricity meter be justified?
How to take meter readings correctly?
Counters come in two designs:
- Induction devices are “old-fashioned” bulky devices with a rotating wheel.
- Static - or modern electric.
Many people still have induction ones, but the trend towards switching to electronic models is already clearly visible - they calculate more accurately, look better, and do not make noise.
When taking readings from an induction device, pay attention to the first 5 digits (some models have 4).
The last digit is usually placed slightly separately or highlighted in a different color, it rotates relatively quickly - it is usually not written on the receipt (for an even and simpler counting) - this is the reading after the “decimal point” in the decimal fraction.
It is better to take data on the same day of the month.
In some regions of the country, it is customary to call the MES or RES on your own (on the appointed day) and report your readings.
Otherwise, the organization makes calculations based on average consumption over the past months - this data will be reflected in the receipt.
How to take readings from an electronic meter, multi-tariff readings
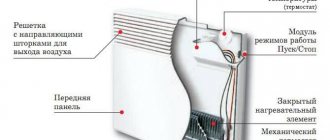
The electronic device can calculate a single tariff, or can be configured to count for several tariffs (different tariffs are introduced for the purpose of saving - during the day they are a little more expensive than usual, and at night they are much cheaper).
The desired mode is selected in the device menu (modes are usually changed by repeatedly pressing the enter button):
- T1 – for single tariff.
- T2 – for separate payment of the grace period from 23:00 to 7:00 am.
- T3 – one standard tariff and two preferential ones.
When these modes (T1 and T2) are displayed alternately, the device will show different readings that have accumulated over the month at a given tariff.
The difference with previous readings is calculated for each tariff separately.
How to take readings from an electric meter when replacing it
Meters are replaced due to their obsolescence, when inaccurate readings are suspected, and for periodic testing in the laboratory. What to do with the readings if the old meter was dismantled and a new one was installed?

Before the old meter is removed, the readings from it are copied onto paper.
You will need to pay off the outstanding balance on the meter.
All other manipulations will be done by the controller.
He will seal the new meter, draw up documents for it and transfer them to the service organization.
Next time the receipt will come with a new number and readings of the installed meter.
By the way, many people are interested in whether it is possible to replace the electric meter yourself? Yes, it is possible, but you must first notify the RES (you can do it by phone).
But the company controller must seal the meter.
When to take meter readings
After the meter installation procedure has been completed completely, you need to figure out how to take readings from a two-tariff electricity meter correctly and in a timely manner in order to avoid overpayment, penalties or incorrect charges.
Energy company specialists most often recommend taking monthly meter readings at the same period - the last days of the current month. This regularity allows you to control your electricity consumption and provide timely data to your electricity supplier.
How to take readings correctly
According to the principle of operation, counters can be induction (they are also called mechanical and disk) or electronic. The first option is already considered outdated, but sometimes occurs. Disk meters can be quite noisy, their accuracy is low, and they can only work in one tariff zone. The readings of induction metering devices, the accuracy class of which is more than 2.0, have long been considered invalid and require mandatory replacement.

Electronic devices for monitoring electricity consumption can have a wide range of options and several tariff zones, they are silent in operation, and the accuracy of readings is several times higher than that of induction analogues.
Electricity meter readings are taken to the decimal point, regardless of whether the device is electronic or mechanical. Usually these are the first five or four digits. Another color, often red, indicates a tenth of one kilowatt, and it does not need to be included in the receipt for payment for lighting.
Some older induction meters may not have a window to display tenths of a kilowatt.
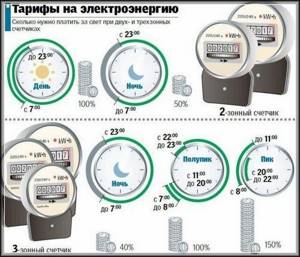
In multi-tariff metering devices, to take data, you must switch according to the readings using the “Enter” button or in another way, depending on the device model. Tariff zones differ by the time of day, when the price for electricity is higher and when it is lower.
At night, electricity is inexpensive, but during the day the cost of one kilowatt is several times higher. There may also be another, third tariff zone, which divides the day into “Peak” and “Half-peak”:
- T1 - “Day” or “Peak”;
- T2 - “Night”;
- T3 - “Half Peak”.
Where should the readings received from a two-tariff meter be transmitted?
Readings, as from a regular meter, must be transmitted once a month, between the 15th and 25th, to the energy sales company. Its details, telephone number and website address are indicated in the payment document, which the subscriber receives by mail every month.
You can also contact the Mosenergosbyt office or the MFC. The State Services website will also help. And if you registered in your personal account, you can submit your readings on the MES website. Regardless of the meter, submit readings once a month. Twice a year, employees of the energy sales organization monitor the meter. Be at home so that an employee can take readings from the meter.
Now you know about all the pros and cons of the system of paying for electricity at two tariffs. Considering the advantages and disadvantages of this saving method, you can make the best decision for yourself by weighing all the pros and cons. And if you already have experience using this calculation scheme, then leave your feedback at the bottom of the article.
According to the standard
If an electric meter is not installed, the consumer pays for the supply of resources according to current standards. Standard indicators and tariffs are approved by local authorities, taking into account the costs of production and transmission of electrical energy, as well as the individual characteristics of the region that affect the cost of resources.
If the absence of an individual meter is explained by the impossibility of installing it for technical reasons, the calculation is performed using the following formula:
P = k × N × T, in which
- P – monthly payment amount;
- k – the number of officially registered residents in the specified living space;
- N – consumption standards established in the region;
- T – the value of the tariff that determines the cost of one kilowatt-hour.
If there are no technical reasons why it is impossible to install an electric meter, an increasing coefficient is additionally included in the formula in addition to the indicated multipliers. Its use is explained by the fact that the authorities are trying to interest owners in installing individual metering devices.
The number of residents is determined according to official registration data. But if, during the inspection, representatives of the management company identify additional persons in the specified living space, the payment amount will be calculated taking into account unregistered residents.
Calculation example
Let's consider an example of calculation for a family from Moscow consisting of 3 people. The two-room apartment is not equipped with an electric stove, and electrical energy is not used to heat the room.
The tariff established for these conditions is 5.47 rubles. for 1 kWh with a consumption rate of 56 kWh per person.
The amount is calculated using the above formula. After substituting the actual values, we get:
P = 3 × 56 × 5.47 = 918.96 rubles,
For a situation where installing a meter is not technically possible. Otherwise, the result must be further multiplied by 1.5. Then the payment will increase to 1378.44 rubles.
What does the tariff depend on?

Electricity tariffs for the population are set by the local executive authority, which has powers in the area of state regulation. The activities of the regional department are monitored by the Federal Tariff Service (FTS), which carries out legal regulation of prices for services and goods and controls their application.
The cost per kilowatt depends on:
- on the type of settlement (urban or rural);
- on the type of stove (gas or electric);
- depending on the type of tariff system (single-tariff, two-tariff, multi-tariff).
ATTENTION! Each subject of the Russian Federation has its own tariffs for electricity. You can find them on the official website of the Federal Tariff Service, the energy sales company in your region, or on your payment receipt.
Types of electricity tariffs
The main types of electricity tariff system are:
- single-rate tariff according to the meter (payment is taken into account only for the kilowatt-hours marked in the meter);
- two-rate tariff with the basic rate for the power of connected electrical receivers (kilowatt-hours marked in the meter and the total power of all power receivers are paid. This tariff was created for large industrial enterprises, because their devices have very high power and the costs of electrical equipment and the power supply system in some cases exceeds 50% of the enterprise value);
- two-part tariff with payment of the maximum load (kilowatt-hours marked in the meter and the maximum load of all power receivers are paid);
- a two-rate tariff with a basic rate for consumer power participating in the maximum power system (payment per kilowatt-hour is taken into account with an additional payment for power during peak hours and at other times at different rates);
- single-rate tariff, differentiated by time of day, day of week, seasons of the year (only kilowatt-hours marked in the meter are paid, but the rate is differentiated by period).
The basis for tariff calculations is the Federal Law on the Use of Electricity, accounting for its consumption in a particular region and the costs of components for supplying electricity to premises.

To understand what tariff you should pay for a service, you need to take into account several factors:
- a gas supply system has been installed in the house;
- is there a meter for electricity consumption in the house or apartment and, if so, what type of device is installed;
*IMPORTANT: When calculating the tariff, you must take into account what mode of utility service consumption is officially assigned to your apartment. For example, the house is connected to a gas supply, but this apartment does not use a gas stove, but this is not officially documented. It would be a mistake to assume that the apartment is charged as if without using a gas stove, but in fact in this case the tariff is the same as with a gas stove.
To find out the rate for payment you need:
- Go to the energy sales website of your region.
- Select the tariffs tab.
- Select a city, district, locality.
- From the table presented, select the desired section: “In houses equipped in the prescribed manner with stationary electric stoves and (or) electric heating installations” - in other words, apartments without gas supply / For apartments and houses equipped with electric stoves / For apartments and houses in rural settlements.”
- Select the section with the tariff plan of your meter (without differentiation by time of consumption, dual-tariff or multi-tariff meter).
Classification of electricity meters
Electricity metering devices differ in the number of tariff zones. Their difference is that they are divided into single-tariff and multi-tariff.
A single-tariff meter records the consumption of electrical energy around the clock at one tariff.
In turn, multi-tariff electricity meters are divided into subtypes:
- accounting for two zones (two tariffs): day (peak) zone T1 and night T2;
- accounting for three zones (three tariffs): peak zone T1, half-peak zone T2 and night T3;
- metering in four zones (four tariffs): designed for metering electricity of large enterprises.
A multi-tariff meter records the volume of electricity at a certain time of day (zones). In Russia, no more than three tariffs are accounted for.
Calculation of power consumption

To do this, all household appliances and light bulbs in the house are rewritten.
The power of each of them is indicated (if it is not visible on the case, it is taken from the technical documents).
Those devices that do not give off heat while they are working are called condenser devices. For them, you need to take into account that the starting power will be 2 - 2.5 times greater than that indicated in the documents.
Add up all the powers of induction appliances (giving off heat - irons, incandescent lamps, stoves, etc.) and condenser appliances (TV, washing machine, refrigerator, etc.), multiplied by 2 - 2.5.
Add 10% to stock. The required power is obtained.
Replacing the device
For a number of reasons, the meter needs to be changed - for example, when switching to differentiated metering (a multi-tariff device is installed). Another reason for replacement is that the existing accounting device is morally outdated (accuracy class 2.5). Electricity meters are also periodically removed for verification.
In cases of replacement, follow the following procedure:
- contact energy sales with a request for a visit from an inspector. His main task is to make sure that the seal on the meter being removed is not broken. The unauthorized breaking of the seal by the owner without a representative of the energy sales company gives reason to suspect him of fraud. For such actions, administrative liability is provided in the form of a fine;
- Having arrived at the place, the inspector checks the integrity of the seal, records the readings on the device display and fills out a certificate of removal of the device;
- the meter is dismantled and a new one is installed in its place. In this case, the controller activates the installation of a new meter, records the readings on it and seals the device.
If the meter is not replaced, but only removed for verification, the controller will transfer the subscriber to pay according to the average indicator.
How to install a three-tariff meter?
There are old meters with a “rotator” - they are all single tariff. There are new meters, electronic ones. They support one-, two-, and three-tariff plans.
In order to replace a meter in Moscow , you need to submit an application to Mosenergosbyt to install a meter that supports two or three tariffs. Together with installation at Mosenergosbyt, a meter for an apartment costs 4,550 rubles, and if the old meter is due for verification, then 3,900 rubles.
The connection happens quite quickly, within a couple of hours or faster, the installer does everything himself. Since the meter is installed through Mosenergosbyt, they register it themselves. It is probably possible to install meters through third-party electricians, but it seems to me that this is easier to do through the sales company itself.
How is heat energy consumption calculated?
How much do housing and communal services cost in different areas of Moscow and the Moscow region?
How to calculate the cost of electricity and its consumption?
Let's look at how to calculate electricity consumption. On meters, the basic unit of measurement is 1 kW/h (kilowatt per hour). Each region has its own prices for this kilowatt.
To calculate the payment , you need to know two indicators: the tariff (how much 1 kW/h costs) and energy consumption (how much “runs up” on your meter).

There are three ways to find out local rates:
- From the receipt that comes to your apartment or house every month.
- By calling the supplier organization.
- On the official website of the relevant electrical networks.
Electricity consumption is calculated by simply subtracting the previous month's figure from the current figure.
By multiplying the expense by the tariff, we get the amount that needs to be paid for light.
Common house meter (ODN)
Another question - how to calculate one-time electricity consumption? The general meter keeps track of electricity for lighting the elevator, entrance and stairs and other joint expenses.
The payment from each owner will be greater, the more m2 of living space he occupies.

In order:
- Readings are taken in the same way as on a home device.
- The last paid data for the last month is subtracted.
- The resulting readings are divided by the area of all apartments.
- What happens is multiplied by the number of m2 of your apartment.
- Your expense is multiplied by the local rate.
How is payment calculated if there is no meter?
How to calculate electricity without a meter? There may not be an individual metering device. In this case, the average consumption rate for the region is taken.
The number of people living in the apartment is multiplied by the average consumption rate (each region has its own) and multiplied by the local tariff.
How to calculate electricity if there is no meter
However, not everyone has installed meters in their apartments yet. Therefore, there is an option in which you can calculate the tariff for paying utility bills, even if you do not have an electricity calculation device.
The option when your home does not have a meter is convenient when your monthly electricity consumption exceeds the norm. In this case, your payments will be lower. However, if you do not spend much electricity, then without installing a meter, you will overpay. So let's look at an example of how to correctly calculate electricity if you don't have a meter.
If two people live in your house, and each of them is provided with 60 kW of electricity per month, and the tariff price is two rubles, then your monthly cost of payment for the receipt will be 240 rubles.
How to calculate the service in this case? This formula is not as simple as the previous one, but if you pick up a calculator, you can easily cope with such calculations.

How to make a calculation to find out how much to pay for electricity this month:
- First of all, you need to calculate the number of people living in your home. Both adults and children are taken into account.
- Next, you need to find out how much electricity per month per person. Rates may vary by region.
- Now you need to make calculations using the formula P = nxNxT. In this case, n is the number of people living in the apartment, N is the volume of kilowatts calculated for each person, and T is the cost of one kilowatt.
Using this formula, you do not need to calculate monthly payments for electricity. You only need to figure out the amount once, and it will remain that way until one of the indicators in your formula changes.
How to take readings from three-phase meters
There are two types of three-phase electricity meters - the old type, which requires transformers, and electronic direct connection (without transformers). If an electronic one is installed, the electricity meter readings must be taken in the same way as described above. Simply write down the values, wait until the necessary information is displayed on the screen, or “scroll” the data to the required page.
Connecting an electric meter in a three-phase network via current transformers

If a large amount of power is allocated or an old-style meter is installed, a transformer is installed on each of the phases. To take readings in this case, you need to know the transformation ratio. The readings taken must be multiplied by this coefficient. The resulting figure will be the actual expense.
But in general, you need to read the contract. The calculation procedure must be prescribed there - in some organizations they write out readings, put down the transformer data or transformation ratio, and the actual calculations are made by the operator himself. So, if you have a 3-phase meter, check the form and procedure for calculations when installing and sealing the metering device and putting it into operation.
Where to submit readings
It is necessary to take data from the electricity meter within a specified period, which precedes or includes the period allotted for sending information; the exact interval is specified in the contract.
Testimony from the public is received by the utility service provider. This role may be played by a supplying organization, a management company or a homeowners' association. It is taken into account that these powers can be delegated to special settlement organizations or auxiliary institutions.
You can transmit electricity meter readings using different methods:
- Enter the information on the receipt and bring it to the billing department.
- Send via Internet. To do this, you need to fill out the appropriate table on the organization’s website or in your personal account.
- Indicate on the form that you want to put it in a special box installed in various institutions.
There are also other modern methods that involve the use of technical devices.
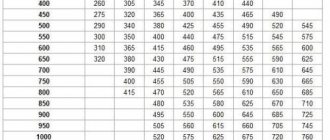
How to calculate electricity consumption using a two-tariff meter
Calculation of electricity using a two-tariff meter is carried out as follows:
- The previous T1 readings are subtracted from the T1 readings for the current month. The result obtained is multiplied by the price of kW at the “day” tariff.
- The previous T2 readings are subtracted from the “T2” readings for the current month. The result obtained is multiplied by the price of kW at the “night” tariff.
- If the energy supply company sends a separate receipt for each tariff, then the results are entered into the “day” and “night” receipts, respectively. If payment is made using a single receipt, the amount for the day and night rates is included in the general receipt and is summed up upon payment.

How is electricity calculated using an individual meter: calculator, formulas
You always have to pay for the utilities you consume according to the tariff set by the state. For apartments with an installed electric stove, the cost of electricity is slightly lower. Thanks to installed meters, users of the electricity network can pay only for the energy that they actually spent. This allows you to rationally use electrical appliances and save your family budget. The process of calculating payment for electricity by meter is quite simple, and anyone can understand it. Especially if you use our online calculator.
If you use the simplest - single-tariff - calculation system, then you only need to fill out the first three fields. With a two-tariff system - the first six. If you have a three-tariff system and the calculations take into account the half-peak tariff, then you need to fill in all the fields and then click “calculate”.
Tariffs can be found in your management company or on official regional websites.
If you don’t trust calculators or just want to figure out what the amount of payment for electricity consists of, then use the formulas given below.
Single tariff device
The simplest models of electricity meters record the consumed kilowatt-hours at one tariff. It is very easy to calculate payment for such a device. To do this, you need to record the electric meter readings to tenths and calculate the previous result from them. The resulting data is multiplied by the tariff.
Pi = ViP x Tcr
Where ViP is the volume (quantity) of electricity consumed during the billing period in a residential or non-residential premises, determined according to the readings of an individual meter.
Tkr is the electricity supply tariff established in accordance with the legislation of the Russian Federation.
It should be taken into account that in some regions the standard for electricity consumption is 150 kW per month. If this indicator is exceeded, then everything that is above the norm is calculated at an increased rate.
For example: The difference between new and old data is 250 kW. This means that 150 kW is paid at one rate, conditionally 3 rubles, and the remaining 100 kW is paid at a higher rate, for example, 3.5 rubles.
You need to carefully count kilowatts on the meter. Sometimes people get confused in calculations and enter the decimal part of the data as a whole number, and get the wrong result.

Two-tariff device
The two-tariff accounting system is a little more complicated than the single-tariff one. But with reasonable self-discipline in terms of using powerful electrical appliances, the apartment owner will be able to save a significant amount on electricity. The daytime tariff can be several times higher than the night tariff, so with such a system it is better to try to turn on the equipment at night. Then electricity will cost less per month.
To calculate the consumed kilowatts for two tariff periods, you need to record the current readings from both time zones and subtract the previous data from them. Next, both resulting numbers must be multiplied by the cost of the corresponding tariff and their sum added. This will be the bill for individually consumed electricity.
Pi = (ViП1 x Ткр1)+ (ViП2 x Ткр2),
where ViP1 is the volume (quantity) of electricity consumed during the billing period in a residential or non-residential premises during the DAY, determined according to the readings of an individual meter.
Tkr1 – tariff for electricity supply during the DAY, established in accordance with the legislation of the Russian Federation.
ViП2 – volume (quantity) of electricity consumed during the billing period in residential or non-residential premises at NIGHT.
Tkr2 – tariff for electricity supply at NIGHT.
Three-tariff device
Payment for electricity under the three-tariff system is slightly different from the previous one. In metering devices working with three time zones, the day is divided into “Peak” - from 7:00 to 10:00, and from 17:00 to 21:00, as well as “Half-peak” - from 10:00 to 17:00, and from 21:00 to 23:00. Peak time is expensive and during this period it is better to use only low-power electricity consumers. During half-peak, the cost per kilowatt-hour decreases slightly, but the best time to use powerful household appliances is at night.
The calculation example is similar to the previous one. However, now the meter switches across three tariff zones. For each of them, you need to subtract the previous data from the current indicators. After this, you need to multiply the kilowatt-hours used by the tariff in accordance with the time zone and sum them up.
It is not difficult to calculate the consumed electricity, although there are some nuances depending on the type of meter. If necessary, you can use special online calculators, which are usually available on the official websites of energy supply organizations.
Useful article? Rate and share with friends!
The principle of operation of a two-tariff meter
It is not difficult to understand how a two-tariff electricity meter works and what is the difference between a single-tariff and multi-tariff electricity meter. It records energy consumption in two periods: during the day from 7.00 to 23.00 and at night - from 23.00 to 7.00. This differentiated metering by zone is what distinguishes a two-tariff meter from a conventional single-tariff meter, which records data around the clock at one tariff.
Electrical energy consumed in private or apartment buildings during the day varies greatly, which can be clearly seen on the load graph of an apartment building.
An example of a daily load schedule for an apartment building.
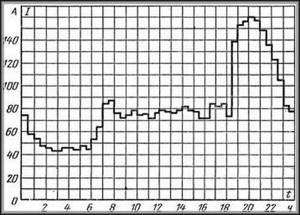
The graph shows that at night, from approximately 1.30 to 6.00, the amount of electricity consumed is the lowest. And the peak load occurs in the evening from 18.00 to 22.00.
Such a schedule can be a strong motivation to use electrical appliances at night. Household appliances with high energy consumption (washing machine, dishwasher, electric kettle, microwave oven, iron, air conditioner) are preferably used during lower peak loads, and their use at night will allow you to save a lot of money.