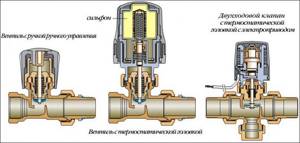
Installing a thermal head on a heating radiator: principle of operation, installation, rating
The operating principle of a thermal head for a heating radiator allows you to make room heating autonomous. The device eliminates the need to manually control the operating mode of the heating device, reduces energy costs and maintains a comfortable room temperature. The ability to install a thermostat is provided for all radiator models of recent years.
- Is it worth installing thermal heads on heating radiators?
- The operating principle of a thermal head for a heating radiator
- Types of radiator thermal heads
- Manual thermal heads
- Mechanical
- Electronic
- Which thermal heads are best for radiators?
- How to properly install a thermal head on a heating radiator
- How to set up a thermal head on a heating radiator
- Rating of thermal heads for heating radiators
- Danfoss
- Thermo
- Caleffi
- Oventrop
- Honeywell
- Conclusion
- Reviews of the thermal head on the heating radiator
How to select and install thermostats on radiators
A prominent representative of the control valves of heating systems is a thermostat for the battery, otherwise known as a radiator valve or thermostatic valve. Like other innovations in the field of heating, it came to us from Europe, and almost immediately it was included in state building codes as a mandatory element of any water heating system. Accordingly, the purpose of this article is to reveal the principle of operation of the thermostat and tell users how to select, install and configure it in a home heating system.
- 1 What is a thermostat used for?
- 2 Design and principle of operation of the thermostat
- 3 Types and choice of thermostats
- 4 Installation and configuration 4.1 Installation of thermal head
Structural features
The thermal head consists of the following parts:
- frame;
- bellows;
- locking mechanism;
- pusher;
- stock;
- spring;
- seals;
- fasteners.
The valve is responsible for the amount of coolant passed through.
Typically the housing material is transparent or colored plastic. The bellows is made of brass or steel. Stainless steel springs are responsible for opening and closing the rod. One sets the stem to its original position after closing the valve, and the other after opening.
There is a locking part on the top of the housing. It allows you to fix settings. To prevent the element from sticking, it is recommended to dismantle the thermal heads after the end of the heating season.
Selection of shut-off and control valves
For the functions described above, one of three types of control valves is used:
- cone valve;
- ball valve;
- automatic regulator.
Ball valves do not cope well with temperature regulation, since they operate in two positions: open or closed. If you install the faucet in an intermediate position, its tightness will be lost, since the coolant will destroy the ball element.
A cone valve is a more efficient way to control temperature. It can be in a half-open position. At the same time, we must not forget about the need to return it to the starting position. This method of temperature control is inconvenient and labor-intensive.
The best option for temperature control is the use of automatic thermostats mounted next to the batteries. Another name for these devices is thermostats.
How to choose
When choosing a thermal valve, you need to take into account all the available features of the heating system.
Based on the characteristics of the heating system, as well as the conditions of its installation, in order to control the temperature, it is possible to use various combinations of valves and thermal heads.
So, for example, for use in single-pipe systems it is worth using valves with a higher throughput.
The same applies to those two-pipe systems in which water circulation is carried out by gravity, that is, naturally, without forced mechanisms. In cases where a two-pipe system is used where there is a circulation pump, it is recommended to choose those types of valves where it is possible to adjust the throughput.
After selecting the valve, you need to select the thermal head.
The most common options that can be purchased today are:
- having an internal thermoelement;
- electronic (which can be programmed);
- having an external temperature sensor;
- anti-vandal;
- having an external regulator.
Most often, classic thermostats with an internal sensor version are installed in cases where their axis will be in a horizontal position.
In cases where it is not possible to install the head horizontally, it is best to install an additional remote temperature sensor with a special capillary tube.
In addition to vertical installation options, there are also other reasons to purchase a remote version of the sensor:
- if heating radiators with a temperature regulator located on them will be located behind the curtains;
- when there is any other heat source next to the installed thermal head;
- if the location of the battery is under a large window sill.
Very often, in rooms where interior requirements are increased, batteries are covered with decorative screens. Due to this, the internal thermostat will only register the temperature that is inside this casing. In this case, access to the thermal head adjustments will be blocked. Therefore, in such cases, it is recommended to opt for a remote controller with a temperature sensor.
If we talk about electronic thermostats with a display, then they come in several types; the first have a built-in control unit, and the second have a removable control unit. The latter have the peculiarity of being able to be disconnected from the thermal head, while it will continue to operate in the same mode. The purpose of such models is to regulate the temperature in different modes at different times of the day. This makes it possible to reduce the heat level during the day, and at night, when everyone in the house is sleeping, to raise it to the desired level. Due to this, it is possible to significantly save energy.
If there are small children in the family who always want to touch and twirl everything, it is recommended to install anti-vandal thermostats. This will protect the device settings from unauthorized intervention. The same situation applies to options installed in various public buildings, from kindergartens to hospitals.
What are the criteria for choosing a thermal head?
Thermostatic devices are produced by many manufacturers.
To make the right choice, you need to be guided by the following criteria:
- Thermal valve to which the head will be attached . Since the connection can be clip or threaded, you need to pay attention to this point. If the manufacturer is the same, there will be no problems.
- View of the threaded connection on the head itself . It can be in the form of a nut with curtains or simply round. In the first case, during installation you need an additional tool to crimp the connection. In the second, everything is much simpler.
- The presence of a “skirt” . The head looks better with it, because... it covers the work area.
- Material of manufacture . The cheapest are thermal heads in a plastic case. Expensive models have a metal body.
- Plastic quality . Some manufacturers, in order to reduce the cost of their products, use the cheapest type of plastic. The strength of the structure suffers from this, and over time the plastic turns yellow and loses its aesthetic appearance.
- Work item type . The choice will have to be made between liquid, gas, electronic and paraffin.
- Smooth rotation . The handle should rotate smoothly. This is a sign of good quality. Any cracking, squeaking or jamming indicates a not entirely high-quality product.
- Graduation and scale length . For most models it is in the range of +5 – +30 °C. If the graduation scale is located around the entire perimeter of the head, it can quickly wear out.
- Availability of anti-vandal casing . It protects against unauthorized access to settings.
- Design . Since thermal heads are mainly located in plain sight, their appearance and color scheme are important.
It is not necessary to purchase a ready-made kit consisting of a thermal valve and a thermal head. These devices can be purchased separately.

The gas-filled bellows is not too sensitive to external heat sources. This is a definite plus, but its cost is much higher than that of a liquid bellows
A thermal head equipped with automation benefits a lot, but it is not always effective. There is no point in mounting it on cast iron radiators. This material is very heat-intensive, and since the mass of the battery is large, it has great inertia. Only a manual type of head can work correctly here.
Rules for choosing a thermostatic head
You need to choose a device taking into account the characteristics of the heating system and its installation. Based on this, a valve and thermostatic head for radiators are used to control the temperature. Moreover, they can be combined in different ways.
For example, for single-pipe systems it is better to use high-flow valves. Similar elements are suitable for two-pipe systems with natural circulation of the working medium. For two-pipe systems with forced movement of coolant, the best option would be to install a thermal head on radiators, which allows you to regulate the throughput.

The choice of thermal head for a radiator should also be approached responsibly. The most common options are the following:
- With a thermocouple installed inside.
- Programmable.
- With external temperature sensor.
- Anti-vandal.
- With external regulator.
Servo+two-way valve
The use of servos and two-way valves allows you to regulate the temperature in the room more efficiently. Most often, this combination is used in “smart home” systems, but the general principle can be used in completely ordinary homes.
To implement the scheme, perform the following actions:
- a number of temperature sensors are installed in the house;
- temperature sensor data is transmitted to the processor;
- a special program processes the data;
- in accordance with the specified parameters, the coolant supply to the radiator is turned on/off.
Such a system allows you to control not only an individual radiator, but also an entire group of radiators, for example, a part of a heating circuit intended for a specific room.
If, when using a thermal head, the valve stem is affected by a compound poured inside, then in this case a servo drive is used, i.e., an electric motor operating at very low speeds. It allows the valve to open/close very smoothly. When the valve opens abruptly, there is a high probability of a water hammer that is dangerous for the system. As a result, both individual components and the entire heating system can be damaged.
If it is not practical to install a smart home system with a large number of temperature sensors, you can use a regular room temperature sensor, a servo drive and a two-way valve. This solution is especially convenient if the room is heated by a radiator, which is installed in a niche and covered with a special decorative screen. In this case, it will be inconvenient to regulate the temperature using a valve or thermal head, since you will have to dismantle the screen each time.

If a heating radiator installed in a niche is hidden by a screen, it may be inconvenient to regulate the temperature using a thermal head. A servo-driven system will be more efficient
It is also worth noting that the temperature sensor or thermostatic head should not be installed in a niche covered with a screen, since excess temperature is created in such a space. As a result, it will be impossible to obtain correct readings from measuring instruments.
What types of servos are there?
Servo drives are widely used in the automation of heating, water supply and sewerage systems. There are two types of such devices:
- open;
- closed.
The first ones remain open in an inactive state and close when voltage is applied to the device. The latter, on the contrary, are closed and open when power is supplied. For heating systems, only closed type servo drives are used.
What does the unit consist of?
The design is a compact equipment consisting of two main parts: a brass valve and a thermostat, which is highly sensitive to temperature changes. The element functions independently, as a single mechanism, which does not require additional wiring of any type of energy.
Device and design diagram
The inside of the head is filled with a special mixture that reacts to the temperature of the air in the house or room. This substance is often used as a gaseous or liquid material.
What else is included in the package of the thermal head?
- Cap with temperature gradation;
- Safety installation;
- Oil seals;
- valves;
- Pass-through element connected to the battery and supply pipeline.
VIDEO: Room thermostat. Comparison of temperature control methods
How the device works
Thermostatic heads for radiators are a sealed corrugated body, also called a bellows. It is filled with thermal substances in the form of gas or liquid mixture.
During operation, as the temperature increases, the gaseous substance expands, as a result of which the bellows changes shape and becomes more straight. After this, the thermostatic valve for the heating radiator is activated, which is regulated directly by the thermal head. When the temperature of the coolant rises, the element closes the flow of water going into the pipes, which leads to a decrease in the temperature in the room.
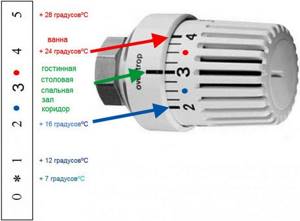
Basic indoor modes
In the case of a lower temperature, the opposite principle of operation is triggered - when the element located on the battery is compressed, the valves open, which leads to an increased flow of water into the system.
Type and technical features
We have found out how a thermal head works on a heating radiator; now we need to understand the different types of devices in order to ultimately choose the most suitable option.
There are two main criteria by which thermostatic devices differ.
Elements can be:
- Liquid;
- Gas-filled.
Each type has its pros and cons; in short, the first type reveals more accurate toC readings, the second are distinguished by their reliability and fast operation.
In addition to the type of filler, the system differs in the type of control - mechanical or electronic.
Mechanical thermostat
The installation does not require additional power from external electricity.

One of the mechanical device options
Thermostatic heads for mechanical radiators have the following advantages:
- low cost compared to an electronic mechanism;
- ease of operation;
- independence from any type of energy.
The main disadvantage of a mechanical device is the manual adjustment method using a valve.
Electronic installation
The automatic element is capable of adjusting the water flow without user control. In the place where the valve should be located there is a liquid crystal screen and control panel.

An electronic variety that makes it convenient to set the desired mode in a room or home
Electronic devices have two remote and built-in sensors that detect temperature conditions and convert it into a digital value on the screen.
In addition to the ability to program the temperature in the house for certain hours, thermostatic heads for radiators can lower the temperature in the room in the absence of the owners and raise it in a few hours so that the house has time to warm up when they arrive. Also, if the property is “idle” for a long time, you can set the cool microclimate mode, which will not allow the heating system to freeze in the winter.
This type of shut-off valve, regardless of type, has a choice of two regulation systems.
Closed logic
Open logic
The system has built-in standard readings that were set during production development. You can only manage basic parameters.
It works based on the type of equipment and the entire system in general. Can adjust its functionality to any heating installation. Often used in industrial areas. To adjust the settings, you should call a specialist, since this process requires certain skills and takes a long time.
Disadvantages of the automated system include the need for frequent battery replacement. It is recommended to immediately purchase rechargeable batteries so that they can be easily charged.
How to properly install shut-off valves?
If the device has already been selected and purchased, the next step is to figure out how to install the thermal head on the radiator. Naturally, first of all you need to choose the place where the device will be located.

Recommendation for correct installation, taking into account the location of the battery itself and external factors
Often, the battery itself is chosen as the installation location, not covered with curtains, panels and other decorative devices. The presence of interference is a very important factor that can negatively affect the accuracy of the readings.
In addition, the temperature of the device can be affected by:
- Sun rays;
- drafts;
- climate control equipment installed nearby.
There is another option for the location of the equipment - an area on the horizontal section of the system, located in front of the battery itself.
If the heating system is of a two-pipe type, stepping back a little from the battery, you need to install a bypass. In a two-pipe device, installation is carried out directly on the upper supply pipeline.
Main installation steps:
- All coolant is drained.
- A bypass is installed on a single-pipe device; otherwise, the stage is skipped.
- The thermal head is installed into the threaded hole in the battery.
- The thread is wrapped with FUM tape to improve tightness.
- The device is being installed. It is important to position the device correctly, following the designating arrows on the body, which must be in the same direction as the water flow, otherwise the thermostatic valve for the heating radiator may fail or simply lose its operational features.
How important and necessary is a thermal head?
The thermostatic head for a heating radiator allows you to optimize energy consumption, which can bring significant savings in thermal energy throughout the heating season. Using a heating boiler, you can raise or lower the heating temperature in all heating radiators at the same time.
However, this is not always necessary, since different rooms have different needs for the level of heating. The bedroom, children's, living room, dining room and hall need a temperature of 200 - 220, in the bathroom a comfortable level of air heating is desirable around 240 C, and in utility rooms 160 C is sufficient.
Level 120 and 70 for special occasions. By installing thermostatic heads, homeowners can adjust the temperature in each room according to their wishes.
The design and principle of operation of the thermal valve
The first thermal head was manufactured by the Danish company Danfoss in 1943. Both the first devices and modern equipment consist of the following parts:
- housing, which in most cases is made of plastic;
- a metal bellows filled with a medium sensitive to changes in temperature;
- valve body designed to change the coolant supply level;
- a pressure rod, a return spring and a valve, with the help of which the temperature is adjusted.
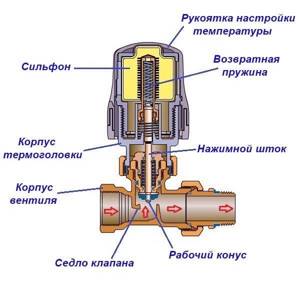
Internal structure of a standard thermal valve
The operating principle of the device is as follows:
- the user determines the optimal temperature and adjusts the thermal head;
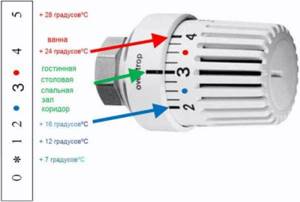
Setting the temperature
- when the temperature inside the radiator increases, the substance inside the bellows expands and acts on the valve seat, which shuts off the coolant supply;
- When the temperature-sensitive substance is cooled, the reverse process occurs.
How to choose a thermal head yourself
Thermal heads for batteries come in three main types:
- manual;
- mechanical;
- electronic.
Manual thermal heads
A manual thermal head is, in fact, an analogue of a ball valve, since the level of coolant flow is adjusted by the user independently based on the data of a thermometer installed in the room or his own feelings.

Manual controller
The advantages of this type are the simplicity of the device and low cost. Among the disadvantages is a short service life, since when the handle is rotated over time, the internal mechanism weakens and its tightness is lost.
Mechanical thermal heads
More popular are mechanical models that work according to the principle described earlier. The thermosensitive medium can be:
- liquid. The liquid thermal head is less expensive and has a simpler design, which extends the useful life of the device. But along with this comes lower performance;
- gas. The production of gas-filled thermal heads is more complex, which is reflected in the price of the equipment.
The connection must be made in such a way that the device is directed indoors. This will increase the accuracy of the device and temperature conditions accordingly.
In order to be able to install the equipment correctly in any situation, manufacturers produce:
- with built-in temperature sensor (pictures above);
- with a remote sensor, which is installed in the most optimal location and connected to the main device with a capillary tube.

Regulator with separate temperature sensor
Electronic thermal heads
The most modern electronic thermal head is equipped with a microprocess that acts on the valve. The equipment requires autonomous power supply (batteries) to operate.

Device with microprocessor for autonomous operation
The cost of this equipment is as high as possible, but the device allows:
- set a certain temperature regime during the day and at night, which allows you to achieve comfort when sleeping;
- set the temperature on certain days of the week, which is necessary, for example, in a country house with temporary residence.
Manufacturers
When choosing a thermal head, it is important to determine not only the type of device, but also the manufacturer of the equipment, on which the reliability and durability of operation depends. Experts recommend:
- Danish company Danfoss, which manufactures thermal heads of all types. The most popular devices are the danfoss RA and RTD series (now partly the RTR series) - universal equipment for all types of systems;

Thermal head from a Danish company
- German companies Heimeier, which produces equipment under the RTL brand, Buderus, part of the Bosch Thermotechnik GmbH concern, and Oventrop;
- Russian-Italian company Valtec (Valtek).
Device Description
Essential elements
The thermal head valve for the radiator has a rather complex design.
Its main elements are:
- Thermal sensor.
- Sensor drive mechanism.
- A valve that opens and closes the lumen of a pipe.
Today, there are models with both remote and built-in sensors.
Devices of the second type are more common (and, importantly, are cheaper), so we will focus in detail on their description:
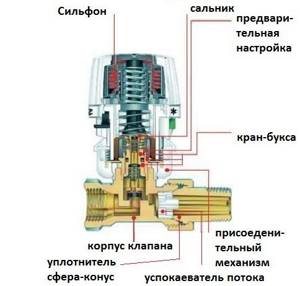
Main design elements
- The basis of the temperature sensor in such systems is a bellows - a sealed and elastic container filled with liquid or gas.
- The bellows is connected to a setting spring, which allows you to set the response temperature of the mechanism.
- A spring-loaded rod is attached to the bellows chamber, which actuates the valve spool.
- The spool is located in the saddle - a chamber inside the thermal head body. When moved to the lowest position, the gasket completely blocks the lumen of the saddle, blocking the flow of coolant into the radiator.
The thermal head for a heating radiator, operating under the control of a remote valve, functions differently:
Two-component device: head + sensor
- The bellows function is performed by a temperature sensor, which is located at a distance from the radiator.
- Inside the temperature sensor there is a sensitive element that responds to changes in room temperature.
- The sensor is connected to the actuator either by wires or by capillary tubes (hydraulic models).
- When the temperature changes, information from the sensor enters the thermal head, inside of which there is a rod connected to an adjustment spring.
Mechanism of operation
So, we have figured out the basic design elements, now we need to analyze how the thermal head on a heating radiator works:
- The main sensor is a bellows, in which the liquid or gas is under a certain pressure. The adjustment spring is responsible for balancing the device, which compresses the bellows when we set the temperature we need by rotating the rotary handle.
The temperature is set on the side scale
Note! The better the calibration of the device, the more accurately it will respond to temperature changes. At the same time, the price of such high-precision thermal heads will be appropriate.
- As the temperature rises, the volume of the bellows increases (mainly due to gas expansion or partial evaporation of the working fluid).
- An increase in the volume of the bellows leads to the fact that the spring fixing the rod is released, and the valve gradually closes the gap in the pipe.
- This continues until equilibrium is established inside the device, or until the radiator valve under the thermal head is completely closed, i.e. the rod will not go to its lowest position.
Models with remote elements work according to a similar scheme. The only difference is that either special programmable devices (climate control systems) or remote sensors (liquid, gas or electronic) react to temperature changes. Only after this the information reaches the thermal valve mechanism and activates the rod.
Key varieties
Before installing the thermal head on the radiator, we need to figure out which model is right for us. In addition to matching the connection diameter (this point must be taken into account), it is also important to select the valve according to the operating principle and layout.
Bottom line
In order to get pleasure and savings from thermal heads, you need to get used to them, get used to them, literally with each one separately. During this process of getting used to it, you need to be patient, persistent and never give up (just like in family life). Only after this will you be able to make friends with your heads and save well with their help.
I confirm! The heads are working! For example, a cold radiator becomes hot if a window is opened above it. And on the contrary, if it’s February and the sun is outside, then the radiators in the sunny room turn off to zero. This is real alternative energy!
On the other hand, if a strong wind blows at night, the room becomes cool. It feels like even my very good heads can’t open 100%! These days we have to open the heads a quarter or even half a division. But agree! If the heads worked perfectly, there would be no need to invent Smart Home computers and computer-controlled boilers!
Article created 01/26/2016
Video: operation of a thermostatic valve on a steel panel radiator
Separately from the valve, the thermal head for the heating radiator is completely useless, since there is a sensor inside it that is triggered by changes in the temperature in the room. The bellows chamber contains a solid, liquid or gaseous substance that changes volume.

Thermal head and valve separately
The chamber is connected to a rod that either completely closes the thermostatic valve or opens it to an adjusted level. This is the main difference between a thermal valve and a control valve, which can be used to slightly reduce/increase the flow of coolant inside the heating register.

Thermal head and valve in section
Attention! A thermal head for a heating radiator with a valve can only be installed in bypass systems of single-pipe systems. When the valve is activated, the flow is completely blocked, so the circulation in the heating circuits stops. The bypass bypass pipe completely solves the problem.
Thus, a valve is first cut into the coolant supply pipe to the heating radiator, and the thermal head is screwed onto it perpendicular to the liquid flow. There are several modifications of the thermal head:
- for single-pipe systems - produced by a limited number of companies, for example, models RA-G, RTD-G from Danfoss;
- for two-pipe systems - in any store, 97% of the assortment of heads are of this type.

Thermal head for one-pipe and two-pipe heating distribution systems
Heads for a 2-pipe system can be visually distinguished by the size of the adjusting cap and color. Devices for single-pipe heating circuits are larger and have a gray or white color. Small diameter red caps are installed on heads for two-pipe systems with high pressure, low flow.
Arrows on the housing indicate the direction of coolant flow; installation against the arrow is prohibited. Therefore, when choosing, you need to take into account whether hot water flows from below or from above into the radiators of different rooms of the apartment.
The operating principle of a thermal head for a heating radiator is extremely simple:
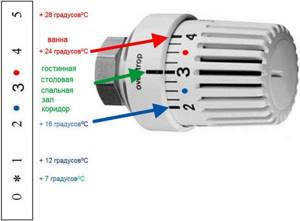
- the user sets the required value for the air temperature in the room, for which the device has a scale with divisions (for example, 21 degrees usually corresponds to value 3);
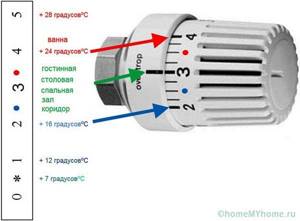
Adjusting the thermal head scale
- when the temperature rises by 1 degree, the substance inside the bellows chamber will heat up, increase in volume, and press on the valve stem;
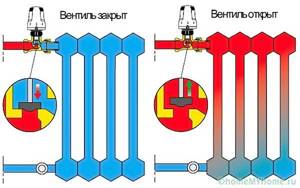
Thermal head operation in a system without bypass
- the supply of hot water to the battery will be completely shut off, but circulation in the heating circuits will continue through the bypass;
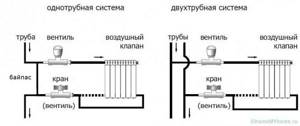
Design differences between one-pipe and two-pipe systems
- an inoperative register will lead to a decrease in temperature, the volume of the substance in the bellows will decrease, the pressure on the rod will disappear, and the valve will open.
The technology for regulating the room temperature in this case is effective only for radiators with minimal inertia. Bimetallic, aluminum, and steel batteries cool/heat faster, so they are optimally suited for automatic adjustments by thermal heads. Cast iron radiators take a long time to heat up, accumulate heat, and take longer to cool down, so the effectiveness of adjustments by thermal heads is reduced.

Using thermostats on cast iron radiators is not the best option
Installation options and recommendations
In order for the thermal head for a heating radiator to have maximum efficiency in regulating the microclimate in the rooms, it must be installed correctly. The main mistakes of home craftsmen are traditionally:
- vertical placement on the valve - so that the device does not stick out to the side, does not interfere with walking near the battery, wet cleaning, it is mounted vertically, and the bellows is heated by heat flows rising from the valve, so the head should be placed horizontally outward;

Incorrect installation of the thermal head on the radiator valve
- installation in niches - in confined spaces, convection is reduced, heat accumulates behind curtains, under window sills, the operating temperature of the head is not reflected correctly;

Installing a thermostat behind curtains leads to incorrect temperature determination
- installation in downdrafts near the window sill - the bellows is intensively cooled by the draft from the window, vent, and stops working.
It is considered optimal to adjust the thermal head for a heating radiator using a remote sensor placed on the walls. The industry produces heads with tubes within 2 m, which allows the sensor to be normally removed from the heating device or drafts from the window.

Device with remote sensor

Thermostatic head remote control
Related article:
Thermostats with air temperature sensor. A separate material provides practical guidance on the selection and installation of thermostats.
Self-installation of a thermal head on a heating radiator should be done on the supply line after the bypass in front of the register. For ease of use, manufacturers produce heads of several types, classified by the following characteristics:
- adjustment - manual or preliminary settings (set with a special key by a specialist plumber);

Adjustment with a special key
- installation – to the left/right of the battery, axial, angular, straight, three-way for installation in the bypass;
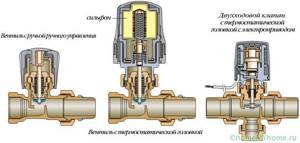
Different types of thermostatic elements
- thermocouple - wall sensor, remote controller or built-in bellows;

Electronically controlled thermal head for heating radiator
- the working substance of the bellows is budget paraffin heads, medium-cost liquid devices, expensive gas thermoelements;
- heating system - the throughput of heads for single-pipe systems is an order of magnitude higher.
Expert's point of view
Andrey Starpovsky
Head of the Heating, Ventilation and Air Conditioning Group, GRAST LLC
Ask a Question
“The thermal head is used in 90% of cases to lower the air temperature. However, in a country cottage, by installing heads with valves on all registers, the temperature can be raised. In the rooms farthest from the boiler, heat loss in the heating circuit is maximum. Therefore, when the supply to nearby registers is shut off, hot water better heats those furthest from the boiler room.”

The procedure for installing the thermostatic head
Useful tips
To ensure that installing a thermostat does not turn into problems for you, we present some useful tips:
- When purchasing a thermostat for a heating radiator, make sure that the warranty period for the device is at least 3 years;
- Do not believe the labels on the packages and check the country of origin solely by the barcode numbers, since most often thermostats are assembled in China or Korea;
- Purchase thermostats only in specialized stores or departments;
- Make sure that there are no additional heating devices in the room where the thermostat is installed, as this may interfere with its operation and you will not achieve the desired temperature;
- It is not recommended to install thermostats in niches, or to cover them with any objects or curtains.
You can install the thermostat for a heating radiator yourself, because all you need is a wrench and the installation instructions included with the device. Only you can decide what the temperature should be in the room!
Types and selection of thermostats
Based on their design, radiator valves are divided into 3 groups:
- straight;
- corner;
- as part of a set for connecting heating devices.

If everything is clear with straight and angular thermostats, then we should say something about the headset separately. It allows you to simultaneously install a thermostat on the radiator and connect it to pipes coming directly from the floor. Although the price of such a headset will be more than traditional pipe connections, such a connection will look much more aesthetically pleasing.
Advantages and disadvantages
Advantages of using thermal valves for heating radiators:
- The ability to automatically regulate the heating of the room and create comfortable conditions for the residents of the house.
- Ability to adjust the heating level of the radiator.
- Reducing the temperature in unused rooms to minimum positive values.
The most significant advantages of thermal cranes are the ability to save fuel. They limit the heating of rooms and make it possible to minimally heat unused rooms. The use of heating control in a private house saves approximately 20% of fuel; when preserving the second floor or part of the rooms, even more (for example, bedrooms, guest rooms, saunas, cinema rooms, billiard rooms, gyms, etc.). Even turning off the heating in one room for five days a week (in the “student bedroom”) produces noticeable savings. But you shouldn’t think that one unheated room will freeze the whole house - with the doors closed, the temperature in one room does not drop below +10 °C.
Any heating system, even designed by an experienced plumber, is not ideal. The possibility of not entirely uniform heating of rooms is possible - thermal valves are also used to compensate for uneven heating. They are also used to lower the temperature in buffer zones that do not require constant heating at 20 °C (in storerooms, boiler rooms, vestibules, hallways, verandas). Often, prudent owners increase the heating of the bathrooms only before the evening bathing of the family and especially children, and the rest of the time they maintain an acceptable 20...21 ° C.

In fairly complex and expensive “smart home” systems, the heating is generally programmed in such a way that the temperature in the house decreases during the day, when the family runs off to work, school, or kindergarten, and increases in the evening, when everyone is gathered. In such a system, the advantages of using thermal valves increase to the maximum, and the disadvantages are almost unnoticeable.
The disadvantages of using regulators are some complication of installation, a slight increase in hydraulic resistance. Additional thread resistance increases the possibility of leakage. In addition, thermal valves require maintenance - they become clogged, and sometimes (in a private house once every few years, in an apartment - annually) they need to be removed and cleaned.
Installation sequence
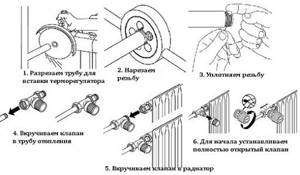
Installation of the thermal head begins with cutting the pipes. It must be performed at a short distance from the radiator. Next, the old shut-off valves are demonstrated, the valve shanks are separated and screwed into the battery plugs.
Then the piping is assembled and installed and the pipes on the sides of the batteries are connected. By turning the lever, the required temperature is set. The thermostatic head for radiators can be mounted at the inlet or outlet of the system.
When choosing an installation location, the manufacturer's recommendations must be followed. Basically, the installation height is 0.4-0.6 meters from the floor. It is to this value that the temperature regime is calibrated. Such criteria are met with top feed. If it is lower, you need to adjust the thermal head to a colder temperature.
Types of thermal agent
Most often, liquid and gas are used in its role. Because of this, the following types of thermal heads are distinguished:
The first type of regulators are cheaper and simpler. For this reason, they are represented by a very large number of models. However, they manage the battery more slowly.
The gas regulator for the heating battery has less inertia, due to which it is able to react quickly enough to changes in room temperature.
In practice, the difference between the two types of reactions is very small
Therefore, when choosing, it is better to focus on the quality of performance. It also depends on the manufacturer. Almost all types of thermostats are capable of setting the temperature, the range of which is +6...+28 °C
Of course, there are options designed to set other temperature levels. However, as the temperature range increases, the price rises
Almost all types of thermostats are capable of setting the temperature, the range of which is +6...+28 °C. Of course, there are options designed to set other temperature levels. However, as the temperature range increases, the price rises.
Choosing the optimal thermal head
The thermal head for heating radiators must be installed correctly.
The first parameter on the basis of which the choice is made is the type of filler if the regulator is automatic. According to this principle, thermostats are divided into two types: liquid and gas. Devices of the first type more accurately adjust the valve to the needs of residents, but the thermal inertia of such devices is higher than that of gas regulators. Gas-filled thermal heads balance the temperature less accurately, but faster.
The second principle of choice is the type of signal supplied to the valve. Thermal heads for radiators can be activated based on temperature:
- water in pipes;
- air in the room;
- outdoor air.
Regulators of the first type are less accurate - the adjustment error can vary from 1 to 7 degrees. Often such a spread does not suit the consumer, so most often they use regulators that receive information from the air. They react sensitively to changes in the temperature balance between the radiator and the air in the room and adjust the water flow, maintaining the desired conditions automatically.
Control can be direct or electrical. In the first case, the thermostat will receive information about changes in temperature conditions from the coolant. The mode is changed by rotating the valve handle, which has a scale on it.
Electrical control is divided into two subtypes:
- control of a circulation pump or heating boiler;
- sending a signal to mechanical valves, which are installed next to the radiator - in this case, you can configure all radiators in one motion.
Common Mistakes
Correct installation requires attentiveness from the master at every stage of work in order to avoid mistakes. The most common problem is the vertical position of the head. This leads to the fact that the room stops heating, since the thermostat itself heats up from the incoming air.
Often the wrong installation location is chosen. You cannot install the regulator at a point where the air temperature is very different from the average in the room. Due to the wrong choice of installation location, the use of a thermal head loses its meaning.
Conclusions and useful video on the topic
The design and purpose of the thermal head is discussed in detail in the following video:
Is it worth installing a thermal head on batteries? One of the users talks about this in detail in his video review:
Thermostatic valve and head in action:
A heating circuit with a thermal head is more convenient to use. This device increases the service life of the equipment included in the heating system and increases its fire safety level.
Based on the benefits of these relatively simple devices and their 20-year service life, they are inexpensive. To buy a truly high-quality product, find out if there is a certificate for the selected device.
Do you use thermal heads for your heating equipment? If yes, then share your personal experience of installation and operation, add photos, tell us whether you are satisfied with these devices and how much more comfortable the microclimate in your home has become after installing thermal heads.
If you still have questions, do not hesitate to ask them in the comments block - our experts and competent users will try to cover complex issues as clearly as possible.
Installing a thermal valve

The first step is to insert the element into the pipeline. To do this, you need to stop the radiator and remove it, as well as turn off the circuit. Initially, the fittings are installed, and later the device is equipped with a remote thermostat.
The position of the valve is extremely important for its further operation. It is important to install it with the sensor in the opposite direction from the radiator and the drive pipe so that the fluid temperatures do not affect the readings. After installing the thermostat, the regulator is mounted without additional elements
Having connected the required marks, it is fixed manually. After this, the device is ready to turn on the boiler. The thermal valve starts working immediately; no additional adjustment is required. All that is important is correct installation, which will ensure the efficiency of the device in the future.
After installing the thermostat, the regulator is mounted without additional elements. Having connected the required marks, it is fixed manually. After this, the device is ready to turn on the boiler. The thermal valve starts working immediately; no additional adjustment is required. All that is important is correct installation, which will further ensure the efficiency of the device.
The three-way valve is installed in the same way. It is only necessary to supplement the system with an additional channel for hot water for its operation and to ensure the operation of the boiler. Because of this change, it is worth carefully calculating the pressure in this area so that it is sufficient for fluid to flow into subsequent elements of the system.