Features of stove-based heating
Stove heating is the norm for Russian villages, the reliability and practicality of which has been proven for centuries.
And today, many village houses have ovens with a stove for cooking food and a hearth for baking bread. Some of them are equipped with a water circuit for the heating system, while others are not. But rural homeowners are in no hurry to throw them away and replace them with modern boilers. A more trouble-free and problem-free heating method has not yet been invented.
Without a water circuit throughout the house, a wood stove can only heat a small space around it. For heating one or two rooms this option is acceptable, but for a large cottage it is no longer possible.
The following is burned as fuel in such village stoves:
- coal;
- peat;
- firewood;
- briquettes (eurowood).
There is no fundamental difference between these types of fuel from the point of view of the design of the stove inside and the wiring of the water heating system in a private house. Some of them give off more heat, while others take longer to burn out. But the design of the firebox and the layout of pipes with coolant in the rooms are the same in all cases.
When making a choice in favor of stove heating, do not forget about the fire safety standards for the construction of brick stoves - only their strict compliance will reduce the risk of fire to a minimum
Among the advantages of stove heating are:
- no dependence on the availability of electricity in the network;
- relatively low cost of installing a heating system;
- low cost of solid fuel and the possibility of using different types of fuel;
- extreme ease of operation;
- long-term heat transfer (for brick structures);
- versatility - suitable for heating and cooking food at the same time.
If a private house cannot be connected to main gas, then a wood stove will be the best choice for heating it.
The only exception is when coal or firewood is not available in a particular area. But this option in Russia is the exception rather than the norm.
The two main disadvantages of furnaces with a water circuit are the impossibility of automating operation and the difficulty of adjusting heat transfer in individual rooms
Also among the disadvantages of stove heating should be mentioned:
- long warm-up of the system before heat transfer begins;
- loss of useful space in the house due to the massiveness of the stove;
- heavy weight of the brick stove structure;
- low efficiency due to the loss of a significant amount of heat into the pipe;
- high fire hazard if used incorrectly.
A brick heating and cooking stove for a private house with water heating, depending on the design and number of rows, can weigh from 1.5 to 10 tons. Plus the weight of the pipe is added here.
A foundation for such a mass requires a powerful and expensive foundation, which can also be called a disadvantage of the heating systems under consideration.
Miracle stove on water with your own hands, video drawings
Stove heating in Ukraine, as they say, is experiencing a rebirth. The reasons for this phenomenon are clear without any explanation. That is why Kharkov innovator Oleg Petrik proposed using pulverized coal thermal power plant technologies to increase the efficiency of home stoves, and for this it is not at all necessary to have the skills of an experienced mechanic.
How can you increase the efficiency of a coal (wood-burning) stove or solid fuel boiler without the use of additional energy resources.
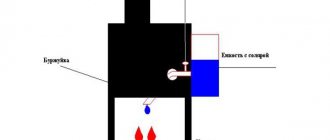
The principle of operation of the technology is quite simple: water from the reservoir (steam generator) is converted into steam at a high temperature (400 - 500 C) and supplied directly to the flame, acting as a kind of combustion catalyst, increasing the productivity of the heating installation.
To create a rationalization system, you will need: a steam generator, which is made from improvised means (a canister or pan, preferably made of stainless steel, will do; even an old moonshine still can be used). A nipple from a car tire is cut into the container. You will also need about half a meter of oxygen hose and about one and a half meters of tube, preferably made of thin-walled stainless steel with an internal diameter of 8 mm, from which the superheater is made.

The rubber tube above the stove must be raised 20-30 centimeters (it is not raised in the photo shown). Although some cooling of the oxygen hose occurs due to water vapor, this must be done for fire safety reasons.

In order, in turn, to speed up the production of steam by the steam generator, when lighting firewood, it is necessary to pour no more than 200 ml of water into the container, it will boil in 5-8 minutes and the device will begin to operate at full power. After this, the steam generator can be completely filled with water for long-term operation of the oven.
Stove water heating device
The furnace for the heating system in question should ideally be calculated and built at the same time as the house. If a residential building has already been erected, then it will be difficult to install a brick stove structure in it. And often this turns out to be completely impossible due to the need to build a solid foundation and rebuild the rafter system.
A furnace for water heating in a private house can be made not only of brick, but also of steel in the form of a potbelly stove with heat exchange pipes around the firebox for heating the coolant
Stove-based water heating consists of:
- the stove itself (metal or brick);
- a heat exchanger inside or around the stove firebox, as well as in the form of a coil around the chimney;
- a circuit with coolant distributed throughout the house and an expansion tank in the attic.
Also, in some cases, this heating system is supplemented with a circulation pump and a hydraulic accumulator. However, this extended option is used extremely rarely, since it requires an uninterrupted power supply and leads to an increase in the cost of the entire circuit.
And the main advantage of water stove heating is the low cost of the device. It is not worth supplementing it with expensive and breakage-prone elements.
We suggest you familiarize yourself with How to cover the lining inside a bathhouse
The water heating system in houses is built with natural (gravitational) or forced circulation of the coolant. If it is made on the basis of a wood stove, then it is best to give preference to the first option.
The wiring diagram with natural water circulation is cheaper than the forced analogue, and also, unlike it, does not require power supply
It is recommended to install water stove heating only in one-story houses with an area of up to 150 m2. In this case, it can be made gravitational without additional pumps.
If you need to heat a cottage of a couple or more floors, then it is better to do this using a more powerful boiler. The furnace for such buildings will have to be built simply huge, which is expensive to implement. Yes, and you will have to put considerable amounts of fuel into it each time. But doing this is highly not recommended due to the increased risk of fires.
A classic stove heating system with natural water circulation consists of:
- heat exchanger as part of the stove;
- metal pipeline circuit;
- radiators (usually replaced with thick pipes in rooms);
- expansion tank.
If you decide to do water heating in a country house yourself, then it is better to design it according to this scheme. Installation and calculation of this option is easier than with forced water movement.
A system with a circulation pump is more suitable for boilers; based on a stove, it loses its increased heat transfer efficiency
If the boiler is automated and constantly heats water as needed, then the wood-burning stove is heated once or twice a day. It is at these moments that the coolant in the furnace firebox heats up to release heat into the rooms. Afterwards, driving it with a pump through the pipes of the circuit is pointless. Nothing will heat the water in a cold firebox anyway.
When choosing a wood or coal stove, owners of private houses usually expect to receive an autonomous heating system. If you install pumping equipment in it that requires power from the electrical network for operation, then it will be difficult to talk about autonomy.
A brick oven takes longer to heat up, but it also takes longer to transfer heat to the space around it. The steel counterpart, on the contrary, heats up quickly and cools down just as quickly after the fuel burns out. This problem is partially solved due to the presence of large volumes of coolant in the water circuit.
However, the more water that has to be stored in the system, the more expensive it becomes in terms of materials.
A metal potbelly stove with a water coil for the heating circuit in private homes can be placed directly on a wooden floor without installing a special foundation
A steel furnace for water heating with a power of 5–15 kW - without fuel and water it is a structure weighing 100–300 kg. Such a potbelly stove can be safely placed on reinforced logs. Stove foundations need to be poured when the stove weighs more than 700–800 kg. Now, if it is brick, then you definitely can’t do without concrete work.
We invite you to familiarize yourself with the External and internal decoration of the bathhouse
Compared to a metal stove, a brick stove weighs more, costs more and is more difficult to install. However, it has higher efficiency and less risk of freezing the circuit with pipe rupture due to the formation of ice inside. If you decide to do everything completely for yourself and permanent residence, then it is recommended to choose the brick option.
If the heating system is built on the basis of a hot water boiler, then it can be piped not only with steel pipes, but also with metal-plastic and polypropylene pipes. However, if the water is heated by a wood-burning stove, then the circuit with the coolant from it should be created only from stainless steel.
With a large load of firewood, the water in the furnace coil can quickly heat up to 100 degrees and boil; only steel can withstand such temperatures for a long time
Metal-plastic is designed to work with coolant heated to 90–95 °C. For a short time it can withstand heating up to 110–120 °C. At the same time, the automation of boilers and boilers initially does not allow the water to warm up to such degrees. For heated floors it heats up to 30–45 °C, and for radiators up to 60–65 °C.
However, in the case of a wood-burning stove, temperatures under a hundred are not only possible, but far from uncommon. It is not recommended to take risks and play Russian roulette by piping this stove with metal-plastic pipes. It is best to give preference to more reliable stainless steel.
In addition, the pipes coming out of the furnace from the coil for connecting the circuit pipes will definitely heat up to very high temperatures. They are separated from an open fire by less than half a meter. It is dangerous to connect any plastic pipes to them due to the risk of them melting.
Heat is supplied from the stove to the heating circuit in portions of several hours, while wood or coal is burning in the firebox. If there is not enough water in the heating system, the house will quickly dry out. Therefore, in villages, such heating is usually made from thick steel pipes, and not on the basis of radiators more familiar to city dwellers. The heating register for wood burning stoves is simply perfect.
The classic scheme of water stove heating with natural circulation involves direct contact of water with the atmosphere through an expansion tank, but air in the coolant is contraindicated for conventional batteries
A stainless steel pipe with a diameter of 80–120 mm laid throughout the house is a heating register, consisting of a supply from the stove and a return to it. In the room farthest from the firebox, these lines are connected together, and in the remaining rooms they are laid in the form of two pipelines along the outer walls.
The register does not look as aesthetically pleasing as the radiator. But the first option is much cheaper and easier to make yourself than the second. To implement it, you just need to have experience in handling a welding machine.
We invite you to familiarize yourself with DIY wiring diagrams in the bathhouse
The heat transfer area for such a circuit is calculated by multiplying the PI number by the diameter and length of the pipe. Plus, in the calculations it is necessary to take into account the thermal pressure in the supply and return, as well as the vertical distance between the pipelines.
However, often such calculations are not made, but a pipe with a diameter of 80–100 mm is taken and laid around the perimeter of the entire residential building with a loop in the back room. In this case, heat transfer is adjusted “by eye” and experimentally as a result of adding a particular volume of fuel to the firebox.
It’s not for nothing that register circuits coupled with water furnaces are so common. You don’t even need to calculate them, just take a suitable pipe and weld it together.
The heat exchanger in the stove can be made of copper, steel or cast iron. It is better to immediately exclude the copper option due to the high price. Soldering such a device yourself is extremely problematic.
Cast iron batteries should be installed inside the firebox with caution - due to temperature shock, individual sections may become detached from adjacent elements
Cast iron is superior to steel in terms of technical parameters. However, making a heat exchanger for a wood-burning stove out of it yourself seems problematic. You can only take an old battery for this. But here we must take into account that the seal between its sections will burn out in the firebox. And this is a direct path to loss of tightness and water escaping into the combustion chamber.
If it is decided to make the heat exchanger from a cast iron battery, then it is best to take the MS-110-300 or MS-90-300 models for this. They are small and will easily fit in the firebox. Their heating surface area for each rib will be about 0.14–0.16 m2.
Based on these numbers, you can estimate how many sections will be required for a particular circuit. For every 10 square meters of house area, 1 kW is needed, which will be approximately equal to 0.1 m2 of heating area of a cast iron heat exchanger.
The fins of a cast iron radiator are usually connected using heat-resistant rubber gaskets. In a stove firebox, such a rubber seal will burn out; it needs to be replaced with an asbestos cord
Another point about using a cast iron battery as a heat exchanger is the difficulty of cleaning it from soot from inside the firebox. From time to time the combustion chamber needs to be cleaned, and the raised ribs of the cast iron will greatly interfere with this.
The most optimal option for a heat exchanger is steel in the form of:
- a coil of several tubes;
- sheet steel shirts.
They are made from low-carbon steel St10...St20 with a thickness of 4–5 mm. If you take tubes, then with a diameter of 30–50 mm.
The easiest way to make a steel heat exchanger is from sheet steel - however, only the surface facing the inside of the firebox towards the fire will participate in heat exchange

The tubular version is more efficient in terms of heat transfer, but it is also more labor-intensive to manufacture.
Qy=K*(Tcp-Tk)
- K is the heat transfer coefficient of the material (15–20 is taken for low-carbon steels, and 50 for gray cast iron);
- Tcp – average temperature of the heating medium in the furnace (Tmax Tmin)/2;
- Tk – average coolant temperature (Tsupply Treturn)/2.
If wood is burned in the stove, then Tcp=(700 300)/2=500 °C and Tk=(80 60)/2=70 °C. As a result, Qy=15*(500-70)=6450 kcal/hour. That is, per square meter of the heat exchanger surface facing the fire will be approximately 7.5 kW/hour.
What is a potbelly stove with a water circuit: the advantages and disadvantages of a popular stove
A potbelly stove is characterized by high heat transfer and fuel burning rate. These qualities are given to it by the materials from which the firebox is made (cast iron, steel, iron). The potbelly stove quickly flares up and heats up, and if a water circuit is connected to it, then the warm flue gases along the way also manage to heat the water for domestic needs.
When choosing the material from which it is best to make a potbelly stove, you need to be guided by the following indicators:
- Thermal conductivity is the property of metals, liquids and gases to conduct heat through themselves. The faster heat is transferred, the faster the object heats up or cools down. Foam plastic has low thermal conductivity - 0.036–0.050 W/m*C. Taking it in our hands, we will immediately feel that it is warm, because the foam does not transfer heat, but accumulates it. If you take a metal bar, you will feel the cold due to the high heat transfer.
- Heat capacity is the property of a material to accumulate heat. Water has the highest heat capacity, air is in second place, and cast iron, steel and iron are at the end of the list. Therefore, a metal stove heats up quickly and cools down just as quickly. In city houses, central heating radiators are filled with water, which gives off heat for a long time, heating the home.
List of materials used to create a potbelly stove:
- Steel.
- Cast iron.
- Iron.
- Brass.
- Aluminum.
- Copper.
There are many articles on our website that describe instructions for making stoves. In the following material you will find installation instructions for a potbelly stove operating on waste oil:.
Table: thermal conductivity, heat capacity and melting point of popular materials for creating a potbelly stove
| Material | Thermal conductivity, W/m*oС | Heat capacity, J/kg*oС | Melting point, oС |
| copper | 382–390 | 400 | 1085 |
| aluminum | 232–236 | 920 | 660 |
| brass | 97–117 | 400 | 900 |
| iron | 74 | 460 | 1539 |
| cast iron | 62,8 | 500 | 1200 |
| steel | 47 | 540 | 1500 |
| water | 0,6 | 4200 | — |
| building brick | 0,2–0,7 | 880 | 1000–1100 |
| Styrofoam | 0,036–0,050 | — | 150–200 |
| air | 0,025 | 1100 | — |
Copper is the most thermally conductive material of all those listed in the table. Its disadvantages are cost and melting point. Aluminum and brass have the same limitations. At high temperatures, a cast iron or steel stove will only turn red, but will do its job, while a copper, aluminum or brass stove will melt.

Potbelly stoves are most often made of steel because it has a high melting point and the highest heat capacity among all available materials
Making a stove from steel, iron and cast iron is justified due to the prevalence of these materials. From the point of view of thermal conductivity and heat capacity, they need fine-tuning. It is more expedient to use the thermal energy of the stove to heat water, otherwise it will simply go down the chimney. To limit heat loss, it is also very important to achieve complete combustion of the fuel.
The ideal way for a potbelly stove to work is when barely warm air comes out of the pipe, and all the energy is directed into hot water supply and heating the house.
Table: advantages and disadvantages of a potbelly stove
| Advantages | Flaws |
|
|
As can be seen from the table, a potbelly stove has a lot of disadvantages, so if you decide to install this design, you will have to take into account all its weaknesses.
You can also make a simple diesel stove for the garage. Our material offers three designs. More details here: .
Choosing the best option
It will be difficult to install a massive brick stove in an already built house. In this case, water heating is best organized on the basis of a metal potbelly stove, which can be placed on a reinforced wooden floor without pouring the foundation.
However, if it is possible to make the foundation as it should be, then preference should be given to a more reliable brick stove structure.

The water circuit around the house for a wood-burning stove is best made from thick steel pipes and with natural circulation of coolant
Installing a circulation pump and/or accumulator in the heating circuit in question is a waste of money and zero additional benefit. They will only complicate the installation of the system. And if the lights go out, these devices will create problems. Whereas the heating option without them will continue to calmly heat the house if there are problems in the electrical network.
Device design
Having decided to equip an economical water stove with their own hands, many are faced with the problem of where to get the drawings for the device of this design. In our age of technology, obtaining such information is a mere trifle. Moreover, having understood the operating principle of such a furnace, many try to create their own version, and sometimes such attempts lead to the appearance of very effective samples.
Details may vary, but the main components of such a device remain unchanged.

If you try, you can easily make such a stove in your dacha
Here is a list of these parts:
Whatever design is chosen, it is so simple that any craftsman can make a water stove with his own hands.
“REVIVAL OF SPRINGS OF RUSSIA”
Vladimir Nikolaevich Pocheevsky Tel: 8-965-289-96-76
Email: [email protected]
Water consists of hydrogen and oxygen, H2O. Hydrogen H2 is a volatile explosive gas that, when burned, releases 2 times more energy than ordinary natural gas (heavy hydrocarbon) found in pipelines and gas stoves. Colossal heat of combustion! Oxygen O2 is a natural oxidizer, anything burns with it, for example, firewood, as a result we get carbon dioxide CO2...
In general, the idea is not new - to split water into 2H2 and O2 and obtain components for a very, very calorific fuel that burns better (releases more energy) than anything that was previously burned for heating houses. Hence the tempting nature of the process - how to create a boiler in a house on the water, or an engine that runs for free...
The main way out of the technical complexity, which is offered by inventors of all stripes, is to mix water into ordinary fuel, or it is extremely difficult in mixing pressure chambers, or it is extremely simple - by shaking it in a bottle...
Pros and cons of various heat exchangers
Installing a tank inside a brick kiln has been practiced by craftsmen for decades.
This is a proven and reliable method that allows you to constantly heat water and even organize its natural circulation, you just need to lay large diameter pipes (about 50 mm) in compliance with the slopes. A properly made boiler tank very rarely burns out, because it contains a large volume of coolant that cools it. The disadvantage of this option is the large size of the container. It will only fit into a heater made of brick, and there is too little space in metal potbelly stoves. Unlike a tank, the size and shape of a register made of steel pipes can be changed and built into any stove, but other problems arise here:
- When installed inside the firebox, the coil is constantly exposed to high temperatures (up to 1000 °C at its peak) and condensation with soot, and therefore will last 4-6 years, after which it will burn out. Stainless or heat-resistant pipes will last longer - up to 10 years.
- A more reliable way is to install the water circuit inside the chimney duct, where the temperature is lower. But then the heating intensity will drop and to organize normal heating the heat exchanger will have to be increased in size. It turns out to be a vicious circle.
- The coolant circulation inside the register must be non-stop. Otherwise, the water will boil, turn into steam, and its pressure will rupture the pipeline in a weak spot - somewhere at the junction. This means that it is unrealistic to organize gravity flow, and the operation of the circulation pump will have to be secured with an uninterruptible power supply unit in case of a power outage.
- The capacity of metal heaters is very limited, so it will not be possible to insert a high-quality heat exchanger there. Practice shows that a steel factory furnace with a water circuit can serve no more than 2 radiators with a total power of up to 4 kW.

Types of welded registers

Economizer (left) and a conventional tank for installation on a chimney (right)
The samovar heat exchanger (economizer) is free from all of the listed disadvantages. It is a water jacket for the chimney and takes away the heat of the exhaust gases. And their temperature in furnaces operating on wood or waste reaches 300 °C. This solution is often used in sauna heaters to heat water for washing. A combined option is a tank through which a chimney pipe is passed.
For obvious reasons, the idea with an economizer cannot be implemented on a brick stove. But for Buleryan, Breneran or another steel potbelly stove, regardless of its size, this option is well suited. And the last, most effective method is to install a water jacket around the heater body. Essentially, it turns any metal stove or fireplace into a heating boiler. One problem is that the option is quite difficult to implement.
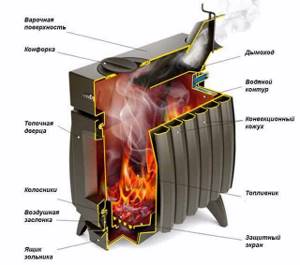
Iron stove designed by Butakov with a convection casing and a water circuit on the rear wall of the firebox
The original design of an external heat exchanger with an improvised economizer is demonstrated in the video:
Some design features of furnaces of this type
A typical wood burning stove with a water circuit consists of the following main parts:
- Directly to the oven;
- A cast iron or steel heat exchanger with a developed contact surface integrated into the combustion space;
- Heating radiators;
- Coolant flow lines, consisting of metal or plastic pipes, shut-off valves, a set of valves and splitters;
- Control and safety group equipped with temperature, pressure monitoring devices, as well as emergency valves;
- An expansion tank that compensates for the excess volume of water resulting from its heating and subsequent expansion.
- As an additional option, you should consider a circulation pump, which is a mandatory part of a system operating on the principle of forced circulation.
A metal or brick oven with a water circuit can be made according to the principle of natural or forced circulation. As a compromise option, a combined system based on the practical application of both principles should be considered.
System with natural coolant circulation
Natural or thermosiphon circulation is provided based on the principle of natural expansion of water when heated and its movement in the required direction, specified by slopes. A number of fundamental principles should be considered a prerequisite for the reliable functioning of such a system:
- The furnace heat exchanger should be located below the level of the radiators.
- The flow area of the main fittings pipes must be at least 57 mm, with the nominal calorific value of the furnace at the level of 15 - 17 kW.
- The system must be equipped with an expansion tank located at a height that ensures reliable circulation of the outgoing flow. As a rule, at least 215 cm from the level of the lower edge of the heat exchanger.
- The return flow line must be installed with strict observance of the slope level, guaranteeing free circulation of the cooled coolant along the way to the furnace heat exchanger.
The natural circulation system is absolutely energy independent, however, it requires a larger amount of coolant in the system. First of all, due to the large flow area of the highway.
System with forced circulation of coolant
Its operation does not require a sufficiently large cross-section of the pipeline, since the coolant is “pushed” under pressure through the operation of a vortex-type circulation pump. It is obvious that modern production also operates with other types of pumps. Reducing the volume of coolant due to a significant reduction in the cross-section of the lines leads to a significantly higher thermal efficiency of the system as a whole and fuel economy in particular. In addition, heating radiators equipped with Mayevsky taps allow you to quickly and effectively eliminate air “locks” by creating excess pressure. The fact of active circulation also determines the presence of an expansion tank of a significantly smaller volume compared to thermosiphon systems. The most significant disadvantage of such furnaces is the fact of direct dependence on uninterrupted power supply. An attempt to combat this disadvantage should be considered the emergence of combined systems.
Combined coolant circulation system
It is a thermosyphon type system equipped with a circulation pump. An additional option is a bypass loop equipped with a rotary tap. Under normal conditions, the pump operates; in the event of a lack of power supply, the inlet pipe with the pump is closed, and circulation is ensured through a bypass loop made of a large cross-section pipe. In essence, this is the same thermosiphon system, with all its inherent disadvantages, however, retrofitted with a pump. In this form, it is rational to see only a double-circuit stove for a bath, where the second circuit is used for hot water supply. Then a large volume of coolant can be used to meet the need for hot water.
https://youtube.com/watch?v=aB1duN9-N4c
PRINCIPLE OF OPERATION:
A self-regulating amount of water is supplied to the hydrogen generator through a tube, which, passing through a converter made of natural material, is saturated with molecular hydrogen and, together with hot air (pulses), is supplied to the furnace firebox under smoldering coals. The coals begin to burn brightly and emit heat, but do not turn into ash for a long time.

In fact, “MIRACLE MEMBRANE No. 01” is an analogue of a wax candle, where the role of wax is played by water, and the coals of burning wood are the wick.
“MIRACLE MEMBRANE No. 01” is completely safe, since the water in the tubes acts as a water seal and prevents the penetration of oxygen from the air and the formation of explosive gas.
“MIRACLE MEMBRANE No. 01” can be used in gas furnaces; hydrogen water must be supplied to an iron plate heated by a gas burner.
The power of “MIRACLE MEMBRANE No. 01” can be calculated for use in industrial furnaces.
Check out the new invention “MIRACLE MEMBRANE No. 02” The operating principle is based on the newly discovered phenomenon of the properties of water: - ignition of supercooled moist air when passing through hot coals.
In ancient Arkaim, our ancestors melted metal using moist air. In the furnace firebox the temperature rose to 1500 degrees C. To achieve such temperatures, they passed moist air from the well through the reactor and fed it into the furnace firebox.
In “Miracle Membrane No. 02”, moist air, passing through the reactor, is converted into “water gas” and, passing through hot coals, ignites. This explains the savings in firewood. “Water gas” burns and gives heat, and the coals of the firewood are a wick (analogous to a candle).
Using our technology, you can make “Miracle Membrane No. 02” yourself and get real fuel savings of 50% due to an increase in the combustion temperature of coals!