The heating system is one of the most important aspects on which the comfort of being in the house depends. It is with its correct installation and configuration that the heat transfer will be high and the percentage of energy loss will be minimal. But in addition to these parameters, it is also worth paying attention to the choice of radiator - it is its characteristics that determine the final efficiency and durability of the system.
Bimetallic heating batteries have priority in this segment: the sizes and types of these solutions are varied, and the parameters are most suitable for all possible use scenarios. Installation of radiators of this type is appropriate for both residential premises (private houses and apartments) and offices.
Combining the advantages of other types of batteries, bimetallic solutions look attractive from both a practical and financial point of view. They will save money both on utility bills and on system maintenance. But do these radiators have their own disadvantages and how critical are they? This article will help you make your choice.
Advantages and disadvantages of bimetallic radiators
Let's consider the advantages and disadvantages of bimetallic heating radiators compared to cast iron and aluminum counterparts. For a fair comparison, let’s take the three most popular and best-selling models. Among bimetallic solutions, buyers consider Royal Thermo PianoForte 500/Bianco Traffico for 10 sections to be the most attractive. Aluminum batteries in this comparison will be represented by the Alecord 350/80 model with the same number of segments. Among cast iron radiators, the recognized leader in sales is STI Nova 500.
Choosing a heating radiator
Since the radiator is installed indoors, the aesthetic side of the item often becomes the decisive factor for home owners. And this is acceptable in cases where it is necessary to heat a cottage with its own heating system. But for a city apartment this approach is unacceptable, since a number of certain restrictions in operation immediately arise. When choosing a radiator, you need to look at its strength so that it can withstand the pressure of the heating system.
There are several types of water heating radiators. This is basically:
- cast iron;
- steel;
- aluminum;
- bimetallic.
In this article we will look at the last two types, their best and worst sides, as well as features of use.
Weight
Here the bimitallic Royal Thermo PianoForte 500/Bianco Traffico has no advantage - the weight of a battery of ten sections will be 22 kilograms. Its aluminum competitor wins in this indicator by almost two and a half times, its weight is almost 9 kg. However, this loss does not look so serious against the background of the cast-iron STI Nova 500 - this battery is heavier than both competitors combined. Her weight is 42 kilograms.
Of course, weight is far from the most important parameter if you set out to choose the best coolant. Manufacturers of bimetallic heating radiators do not pay too much attention to this, focusing on the volume of sections and heat capacity. In practical use, this parameter also has little effect - except that a heavier battery requires better installation of the fasteners.
Determining the number of bimetal sections
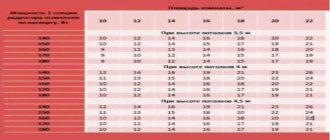
Calculating the required number of sections and correctly determining which bimetallic radiators are best makes it possible to create comfortable living conditions. The calculation is performed using a simple formula, for which it is enough to know the area of the heated room and the power of one section. The second parameter is always indicated by the manufacturer in the device passport; you can also find out the power of one section from the store’s price list.
To achieve maximum effect when heating a room, it is enough to use thermal energy in the amount of 100 W per 1 m2. Based on this, the number of sections of bimetallic radiators is calculated using the formula:
N=S*100/P,
Where N is the required number of sections,
S – room area,
P – power of one section.
For example, you need to determine the number of sections of a bimetallic radiator installed in a room with an area of 20 m2, knowing that the power of one section is 160 W. Substituting the indicated values into the well-known formula, the following is obtained:
20*100/160=12,5.
Consequently, 13 sections are sufficient to effectively heat the specified room.
However, it should be borne in mind that using the specified formula to determine the number of sections may not give an accurate result. To do this, it is necessary to take into account many other factors that can affect the amount of thermal energy required. For example, heating a room with two external walls requires more heat than one with one external wall. A correction factor helps solve the problem in this situation. To calculate the number of sections of a bimetallic radiator in a corner room, a coefficient of 1.2 is used. For a room with two external walls, the calculation will be as follows:
13*1,2=15,6.
That is, 16 sections will be required.
The amount of heat for comfortable living largely depends on the following factors:
- Climatic conditions of the area.
- Predominant wind direction.
- Location of external walls.
- The quality of thermal insulation of the entire house.
- Number of door and window openings.
- Radiator installation location.
In addition, there are many other factors that determine the required amount of heat for a particular room.
Heat capacity
Of course, the main parameter when choosing a radiator is the ability to receive and release heat. The higher it is, the more economical and efficient the system as a whole will be. Heat output is essentially the power of the battery - the same units (watts) are even used to measure it.
The cast iron radiator STI Nova 500 for 10 sections boasts a power rating of 1500 W. With a slight margin, which can be attributed to an error, it is ahead of the aluminum solution from Alerecord with an indicator of 1550 watts. It is the bimetallic solution that gets the palm - this radiator is capable of delivering 1850 W. It would seem that we can already say with confidence which battery is better: aluminum or bimetallic, but we should not rush to conclusions. A huge role in the operation of the radiator is also played by the ability to withstand high temperature changes, as well as the ability to withstand high pressure.
How they work
The difference between bimetallic radiators and other types of batteries is the combination of steel pipes with aluminum panels. The steel pipe ensures the movement of coolant under pressure due to its strength, and aluminum, which has high thermal conductivity, increases the transfer of thermal energy to the environment.
The following bimetallic batteries are currently produced:
- Fully bimetallic construction. All of her steel pipes are surrounded by aluminum. Only steel has direct contact with the coolant, through which heat is transferred to the aluminum panels. This type is durable and reliable.
- Semi-bimetallic construction. In such radiators, only the vertical, most mechanically loaded, pipes are made of steel. Part of the line is made of aluminum; in these areas the coolant is in direct contact with it. The cost of such batteries is noticeably lower and has more efficient heat dissipation, but they are less durable.

According to the design, there are 2 types:
- Sectional radiators. This is the most popular type. First, non-separable sections are made, which are connected to each other with nipples in production conditions. You can disconnect and, conversely, add sections.
- Solid batteries. They have a monolithic design, and therefore have their own dimensions and power. Due to the lack of joints, the batteries are very durable. The choice depends on conditions and finances. Often you have to choose between durability, cost, and appearance.
Working with coolant
As for working with coolant, there are two main characteristics that should be taken into account first: the boundary pressure at which the radiator will operate and the maximum temperature of the liquid.
For the STI Nova 500, these figures are 14 atmospheres and 130 degrees Celsius, respectively. The aluminum radiator Royal Thermo PianoForte 500/Bianco Traffico can please you with a working pressure of 16 atm, and in critical situations it can withstand 24 atmospheres. In this case, the limit temperature will be a more modest 95 degrees - this is the standard for this type of battery.
The bimetallic solution also emerges as the winner from this comparison: its operating temperature is a comfortable 110 degrees, but the operating pressure reaches 30 atmospheres. Moreover, for short periods of time such a battery is capable of operating at 45 atm.
Main negative factors affecting batteries
- Acidity and alkalinity of water . One of the problems with our central heating system is that the water that is “driven” through it is not treated. The same liquid circulates for a long time in long-term pipelines, as a result of which the composition of acids and alkalis in it increases. These substances come into contact with the metal of the radiator, destroying it and gradually thinning it. Over time, when the diameter of the pipe becomes less than critical, the battery breaks through.
- Materials dissolved in water . Sand, rocks and pieces of metal are constantly circulating in our pipelines. Gaining high speed in a turbulent fluid flow, they collide with the inner surface of the pipes (especially at turns), making holes and microcracks in the metal, which then grow favorably under the influence of the same acids and alkalis, but mainly sand.
- Frequent maintenance work : purges, shutdowns, etc. To reduce the risk of burst pipes, utilities periodically release air through them at increased pressure. It is believed that if the battery does not rupture, then it will not rupture even when water is turned on, and if a breakdown does occur, nothing terrible will happen, since only air will come out of the radiator.

Practical nuances of operation
In addition to the characteristics that can be expressed in numbers, there are also nuances associated with the practical use of this or that type of radiator. Here it is worth considering the main pros and cons of bimetallic batteries compared to aluminum and cast iron. Let's start with the positive features:
- Bimetallic radiators have high heat transfer.
- Having steel pipes, they can easily withstand a decrease in the quality of the coolant.
- These solutions boast maximum operating pressure.
- Bimetallic batteries have an extremely long service life, and the manufacturer’s warranty for them is the longest.
- These radiators can operate with coolant volumes that are several times smaller than those of competitors. This increases the efficiency of the heating system.
- Due to their small size, bimetallic batteries generally benefit from aesthetic indicators, and their dimensions are acceptable.
- This type of radiator is least susceptible to corrosion (including when draining the coolant).
- Bimetallic batteries do not suffer from leaks in inter-threaded connections.
- When using them, there is no need to remove air through a special valve.
- Such radiators are not sensitive to oxygen accidentally entering the system.
Do not forget that such radiators are not a universal solution - they have their disadvantages:
- The price of bimetallic batteries is usually higher than that of aluminum and cast iron (although not always).
- This class of solutions has a lower flow area, which slightly reduces heat transfer.
- Such batteries have higher hydraulic resistance, which requires more power to pump the same volume of coolant through the system.
Technical parameters of bimetal radiators
The technical characteristics of devices of this kind far exceed the analogue indicators of other more traditional batteries and registers. A fairly important indicator, especially for centralized heating systems, is the ability of heat exchangers to withstand high operating pressure. And it is worth noting that bimetallic radiators have the highest indicator for this parameter, namely, their internal design can withstand up to 40 atmospheres.
The power of such heating equipment is measured in Watts, the number of which is indicated in the technical documentation. The power indicator is closely related to the radiator sections, the number of which is calculated individually for each living space.
Bimetallic radiators have completely different heights and widths, which allows you to choose the best option that best suits the area of the room, the width of the windows and the distance from the window sills to the floor surface. They are much lighter in weight than cast iron batteries and registers and therefore are easier to transport and carry out installation work.
Such equipment can be connected to both single-pipe and two-pipe heating systems in two ways through:
- side channels;
- lower channels.
In The appearance of such radiators is quite modern, so they will fit into absolutely any interior.
Cost and conclusions
Comparing the three best-selling radiators from different classes is meaningless without mentioning the financial side of the issue. A cast iron solution from STI Nova for 10 sections will cost about 7,000 rubles. An aluminum radiator will be much cheaper - Royal Thermo PianoForte 500 of the same volume will cost just under 3,000 rubles. The bimetallic battery is significantly superior to them - its price is just over 11 thousand.
It is worth mentioning the guarantee provided by the manufacturers:
- for a bimetallic battery – 25 years;
- for aluminum – 10;
- for cast iron – 2.
If we recalculate the price for a year of warranty, then Royal Thermo PianoForte is the most profitable investment, while benefiting from other characteristics.
Recommendations for choosing the best option
In order to make a choice, you should analyze the technical characteristics of both types of heaters. The table below shows the parameters of products from a well-known Italian manufacturer of heating equipment sold under the RADENA brand.
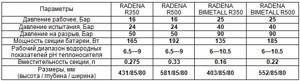
Note: the bimetallic radiator designated R350 has a center distance of 350 mm, respectively, in the R500 the size is 500 mm.
Having studied the technical data in the table, we can conclude that the introduction of a metal frame into the heater design helped to increase their strength characteristics, but reduced the heat transfer performance of the radiator. At the same time, the cost of radiators has increased significantly. Therefore, there is no question about which batteries are better; there is a scope for each type.
The scope of use of aluminum radiators is individual heating systems for houses, apartments or entire buildings, where the coolant pressure is low and, in the worst case, its quality is no worse than drinking water. In apartments whose systems are connected to centralized heating networks with all the disadvantages described above, it is better to install bimetallic devices, although this will cost you more.
Brief descriptions of bimetallic battery models
As it turned out during the review, it is heating systems based on bimetallic batteries that are the most durable and efficient in their class. At the same time, it is worth considering which models in this segment are the most popular and have earned the trust of customers.
- Royal Thermo PianoForte 500/ Bianco Traffico. The radiator in the review has excellent heat dissipation (1850 watts) and a pleasant aesthetic appearance. Sold only in a version with 10 sections - this option reduces the number of installation options, but also increases reliability (bimetallic batteries, due to their solid design, are much less likely to leak at the joints). Exclusive technologies patented by the company were used in the production of the battery. Also among the advantages of the model is environmentally friendly paint, which is applied using a special spraying method. The company also states that it insures each customer against defects and malfunctions for up to one million dollars.
- Royal Thermo BiLiner 500 Noire Sable. To produce the collector of this battery, a high-tech grade of carbon steel was used - the most durable and reliable material used on the market. The heat output here is also higher than any aluminum or cast iron counterpart (just over 1700 watts). In this case, the volume of coolant contained in one section is less than 0.2 liters. The radiator is also notable for its design and dimensions - with all its outstanding characteristics, it has dimensions of only 8x57x8 (for one section). The mass of a standard battery is 15 kilograms.
- Royal Thermo BiLiner 500 Bianco Traffico. An analogue of the radiator described above with absolutely the same set of advantages, but in a classic color. The heat transfer of the section is the same 171 watts, while the dimensions of the models are also absolutely identical. The maximum operating pressure is 20 bar - not a record for bimetallic batteries, but this is quite enough for comfortable operation of the system.
- ROMMER Optima BM 500. A budget solution from a Chinese manufacturer with dimensions that are even slightly inferior to their Italian counterparts. It is for this reason that the heat transfer is lower - here this figure for one section will be only 160 watts. On the other hand, the weight of the battery is extremely small (12 kilograms), and the operating pressure of 18 bar allows you to comfortably use the radiator. The manufacturer claims high resistance to aggressive environments.
- Royal Thermo PianoForte NoirSable 2200. The flagship model from the Italian company in a dark color, which will seriously diversify the interior of the room. The warranty is the same 25 years, and the operating pressure is an impressive 30 bar. The thickness of the section has changed slightly - it is 10 centimeters, not 8, as in the white model.
How to choose and what to pay attention to
To decide which radiator to choose, it is necessary to take into account the peculiarities of organizing the heating supply of the house and the following characteristics of the heaters themselves:
- the value of the testing pressure, which is determined when testing the product - this indicator should not be less than the peak values of the heating network;
- if there is a high content of alkali or acids in the heating network, you should choose a heater with a stainless steel or copper core;
- the outer aluminum casing must be of sufficient thickness and not bend under mechanical stress, and the thickness of the rib protruding from the base must be 1 mm or more;
- recommended core wall thickness - more than 3 mm;
- in sectional batteries it is advisable to check the connecting gaskets for elasticity;
- the edge of the battery must have a width of at least 7 cm, this size gives maximum heat transfer;
- the minimum warranty period (less than two years) indicates the unreliability of this device, since the average service life of radiators of this type is 20 years.
Monolithic or sectional
Monolithic cast products can withstand significant pressure and hydraulic shocks, so they should be installed in multi-story buildings. Sectional products are not able to withstand such tests due to the weakening of the structure by the threaded connections of individual parts, but such heaters are easy to maintain and, if necessary, expand, which is impossible in the case of cast batteries in a private home.
Bimetallic or semi-bimetallic
In addition to standard radiators made of steel (or copper) and aluminum, semi-bimetallic heaters are produced. In these products, the inner core is made not only of steel - it also contains elements of aluminum. Typically, aluminum is used to install vertical pipes.
Such a replacement of the base material significantly reduces the strength characteristics of the product, and in terms of durability in aggressive heating systems, semi-bimetallic radiators differ little from conventional aluminum batteries. The joints between an aluminum pipe and a steel pipe very quickly become unusable due to the difference in the expansion coefficient of these metals when heated.

Semi-bimetallic radiators are slightly lighter than the original, so when purchasing, you should pay attention to this point, since unscrupulous manufacturers may not indicate the exact parameters of the product. These heaters are closer in characteristics to aluminum ones, so it is better to install them in a private home.
Axle distance
All types of manufactured bimetallic radiators are divided according to the distance between the inlet and outlet. Most often, the distance between the axles is 350 or 500 mm, but some manufacturers produce batteries with an interaxle distance of 200 and 800 mm.
Material of manufacture
Most bimetallic batteries are manufactured with a steel frame and an aluminum shell. The steel core copes well with excess network pressure, resists corrosion, and the aluminum shell serves as an excellent heat dissipator. Some manufacturers use high-carbon steel grades, which allows them to achieve higher strength characteristics and durability of the product.

Core.
A more expensive, but best option for bimetal radiators includes batteries with a copper core. This is actually an eternal material with high strength. The service life of such products is at least 50 years.
How to increase sections
Extension of radiator sections is done when there are insufficient numbers of them in the finished product. You will need adjustable wrenches, radiator wrenches, a sharp knife, scissors, and pliers. The following consumables should be prepared: nipples, plugs with right and left threads, elastic gaskets, paronite gaskets, sandpaper.
The extension process includes the following steps:
- Preparatory work. The radiator sections are washed under running water to eliminate blockages. This operation is especially important for used batteries. All threaded connections are carefully checked and wiped with a rag.
- The radiator is placed on a flat, hard, horizontal surface.
- The section approaches the battery, a nipple and a paronite gasket are inserted between them.
- The connection is ensured by smoothly, uniformly tightening the nipple with a radiator wrench. When tightening, ensure an equal number of turns in each section to avoid distortions.
- Checking the tightness of the extended sections. To do this, the pump creates an air pressure of about 1 atm.