Heat dissipation of a cast iron radiator
The power of a cast iron radiator directly depends on the area of its outer surface and lies in the ability to release heat energy at the highest possible coolant temperature. Basically, this value ranges from 80 to 200 watts per section . To calculate the required power, the following formula is used: for 25-30 cubic meters. m. battery power should be 1 kW . If there are several external walls, the power indicator increases.
How many cast iron radiators are needed to heat a house?
Before discussing how to calculate the number of heating radiators required for a particular home, you need to calculate the number of sections for heating each room in the house.
You can use the services of specialized companies. Who will perform this type of service with pleasure and for money. You can calculate the amount of heating equipment for free using an online calculator, of which there are a great many on the Internet. There is a third option - independent payment.
There is a proven calculation algorithm: you need to multiply the area of the room by one hundred and divide by the power of one section of the model you have chosen.
Important! You should know that when calculating, it is necessary to make adjustments for the presence of windows and walls bordering the street, and an unheated attic. (It is necessary to increase the value by 20 - 30%).
For example: a corner room of 20 m2 on the top floor of a high-rise building; two windows; section power 160 W.
So: 20 x 100/160 = 12.5. We add at least 30% to the windows, two load-bearing walls and the attic. We get that in a room with an area of 20 m2 you need to install 16.25 sections. We round up to 17 and divide it into 2 radiators, which will be located under the windows. Carry out similar operations for each heated room in the home.
Dimensions of a cast iron radiator.
In the Soviet Union, the overall dimensions of cast iron radiators had a certain standard. In one section, the distance between the centers of the coolant supply and discharge pipes ranged from 30 to 50 cm. The width of the section was not standardized and varied among different manufacturers. Almost all modern batteries also have these standards. The most popular model among cast iron products is MS-140. (installed in many “Khrushchev” and 9-story buildings of the 60-80s). The distance between the centers of the pipes is 50 cm; battery height 58.8 cm; width 9.3 cm; depth - 14 cm. The variety of overall dimensions of batteries is explained by the needs of customers.
Styles, sizes, varieties
When choosing the type of heating device, aesthetic considerations play an important role. This is understandable: every day in front of our eyes. And if the appearance is annoying, then what kind of rest and good mood can we talk about? So let's start with the appearance.
Old style
Most of us remember old batteries that were far from perfect. Today there are such people. Despite their unattractive appearance, they have very good characteristics, and in a modern interpretation, with a slightly reduced intersection distance, they don’t look so bad. Moreover, today everyone is trying to hide heating devices behind a screen, in a niche or box. In this case, it is generally unclear what role appearance plays: it is still not visible.

MS-140 and MS-90 - difference in section depth
And the cost of one section of this type is the lowest: Russian-made from 270 to 350 rubles. Those brought from other countries cost more, but they differ in size - the standards are different, some manufacturers have higher heat transfer. For Belarusian cast iron radiators the price per section starts from 300 rubles, for Lugansk ones from 410 rubles.
The name of cast iron radiators of the old type is simple - “MS”, and then through the dash there are numbers that indicate the depth of the section (first) and the center distance (second). For example, MS-140 500 means that the section depth is 140 mm, the center-to-center distance (also called inter-nipple) is 500 mm. Another example: MS-110 300. Depth 110 mm, center distance 300 mm.
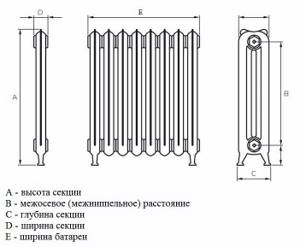
How to understand what the overall dimensions mean
From these numbers you can at least roughly understand whether the modification is right for you or not. The depth determines whether the radiator will fit under the window sill or will stick out. Only to the value itself you need to add another 30-50 mm for the distance from the back wall of the heater to the wall. In total, it turns out that the MS-140 will cover a window sill that protrudes by at least 18-20 cm.
The center-to-center distance determines how far apart the inlet and outlet pipes should be. With a bottom connection, this parameter can only suggest the approximate height of the section. Why not accurate? Because with an interaxal distance of 500 mm, it can be either 552 mm or 585 mm, and in cases with retro-style radiators, more than 600 mm. The difference may not be very big, but sometimes it is significant: the height to the window sill may not be enough.
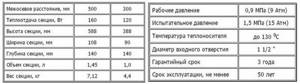
Technical characteristics of MS-140 radiators (click on the picture to enlarge)
New generation
But not everyone wants to install screens on radiators. Some interiors allow aluminum and bimetallic models to fit well. For this reason, many installed new products for themselves. Today there are models made of cast iron, which from a distance cannot be distinguished from aluminum ones. They have the same modern look, flat front panel, smooth surface. Some are covered with factory enamel, others you have to paint yourself.

Old cast iron radiators are being replaced by new models in a modern style.
Just a few years ago, such new generation cast iron radiators were supplied only from European countries: Italy, Czech Republic, Turkey, and of course from China. Today they are also available in Belarusian, Russian, and Ukrainian versions.
Unfortunately, the quality of coverage among Europeans remains better, but the price is also much higher. If we talk about new cast iron heating radiators made in Russia, they are 100-150 rubles more expensive than the “old” form. Compared to them, the price for “Europeans” is several times higher. But you need to take into account the following features:
- “ours” are supplied primed, not painted;
- “Europeans” have a smoother internal and external surface, which is why there is less hydraulic resistance;
- “import” has higher heat transfer and a smaller volume of sections;
- “ours” weigh more and have larger dimensions (at approximately the same operating pressure).

Cast iron radiators in a modern style
There is a difference in all respects and is quite noticeable. So the choice is not easy.
Designer radiators in “Retro” style
These heating devices will not fit into any interior. Most likely, you need to choose a model together with the designer: they are definitely not hidden, but used as a decorative element. Cast iron radiators “Retro” are stylized as products of past centuries; there are different patterns and bas-reliefs on the surface, protrusions at the top and bottom. Often such “antique” batteries have legs designed in the same style.

European cast iron radiators can be like this
If we talk about manufacturers, then there are already products from Russia. The RetroStyle and Exemet campaigns specialize in the release of this particular group. They have a large selection of models of different designs. They also paint, tint and polish their products to match your interior (not free, of course).
There are quite a large number of batteries in this style:
- German Guratec,
- Czech Viadrus;
- Turkish Demir Dokum;
- Spanish Roca;
- English Rococo;
- Polish F
The size range is quite wide: center distance from 300 mm to 900 mm, section width from 40 mm to 81 mm, depth from 100 mm to 235 mm. A wide variety of designs, styles and shapes.

Cast iron radiators made in Russia from the RetroStyle campaign
As you can see, there are more cast iron radiators of different types and designs than aluminum and bimetallic ones combined. There's definitely plenty to choose from here.
Manufacturers of cast iron radiators

Most of the Russian market is represented by domestic models. This can be explained by the fact that the cost of transporting cast iron batteries makes up a large part of its final cost. The main manufacturers include:
- CHAZ – Cheboksary Aggregate Plant (Russia)
- Minsk Heating Equipment Plant (Belarus)
- Kiran (Ukraine)
- Viadrus (Czech Republic)
Design features of plate radiators
Modern plate convectors are designed with the same simplicity of design as the previous “Soviet” models.
Such radiators consist of the following structural elements:
- A curved - most often U-shaped - piece of pipe, at the ends of which two ball valves are installed.
- A set of plates “strung” on a pipe. Moreover, in most cases, the plates are made of the same material as the pipes.
- Protective casing - a metal box with an open top and bottom. Moreover, inside the casing you can accommodate not just one piece of pipe (thread), but several such “packages” at once.
Sectional and plate batteries arranged in a similar way operate according to the following scheme:
- The coolant moves through the pipe under high pressure, practically without cooling.
- Thin plates heat up to high temperatures in just a matter of seconds.
- The temperature of the air inside the case instantly rises by several degrees.
- Warm air rises up through the perforations in the casing cover, and cold air is “sucked” into the housing through holes in the bottom.
As a result, plate heating radiators provide a high rate of thermal convection of air masses, warming up a small room in literally a matter of minutes. However, when heating really large rooms, naturally convection will not be enough. In this case, a tangential fan is installed on the bottom side of the plate convector housing, providing forced convection .
Design and principle of operation of the radiator
Moreover, the intake of air masses is carried out not from the bottom, but through the perforations in the lower part of the side edges of the casing, which makes it possible to “drown” the plate battery in the floor slab, leaving only the upper grid at the level of the floor covering.
Advantages and disadvantages of plate batteries
The undoubted advantage of such heating devices is their high structural strength.
Through such a radiator, coolant can be pumped under a pressure of 20 atmospheres or more - the strength of the structure depends only on the annular rigidity of the pipe, which can withstand pressures of up to 40 bar.
In addition, such a radiator will not leak - it has no internal joints. Other advantages include low cost and good compatibility with cheap thermostats, the operating principle of which is based on dosing the flow of coolant into the heating device.
The obvious “disadvantages” of such heating devices include, firstly, the uniformity of the exterior, the shape of which is determined by the contours of the box-shaped casing, and, secondly, the loss of thermal power due to contact with dust - a significantly smaller volume of air passes through the “clogged” plates.
However, both drawbacks can be easily eliminated - the box-shaped body can be “recessed” into the floor covering or designed as a baseboard, and dust can be easily cleaned with a regular vacuum cleaner.
Types of plate radiators
The classification of the range of plate batteries in most cases is organized according to the following design features:
- By type of pipe and plate material.
- According to the number of “threads” in the casing body.
- According to the diagram for connecting the radiator to the wiring.
- According to the scheme of fastening the casing to the supporting surface.
Based on the first method of classification - Based on the type of material of the pipe and plates - we can distinguish the following types of batteries:
- Steel plate radiators, the main elements of which are made of the same metal. Such heating devices are relatively cheap, but their thermal output leaves much to be desired. Therefore, in combination with high-strength steel tubes, it is customary to use plates made of metals with higher thermal conductivity.
- Copper plate batteries, the elements of which are made of this non-ferrous metal. This radiator provides maximum thermal output. However, not all homeowners can afford such products. Therefore, to reduce the cost of construction, only internal pipes are made from copper, onto which plates of cheaper metal are strung.
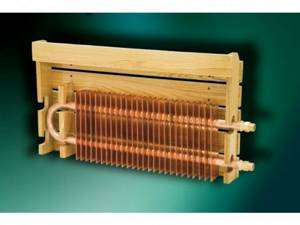
Copper plate radiator
The second method of classification - according to the number of “threads” in the body - distinguishes the following types from the assortment:
- Radiators with one heating element - a “package” of one pipe and one set of plates.
- Batteries with two or more heating elements , the design of which includes a pressure manifold that distributes the coolant flow over several “packages”, and a return manifold that collects the “outgoing” coolant for subsequent transfer to the distribution system.
The first type of radiator is cheaper and more compact than the second type. However, the latter option will provide higher thermal power, explained by the larger area of the heating elements (plates and pipes).
The third classification option - according to the wiring diagram - distinguishes the following types of batteries:
- Radiators with side connection . In this case, the battery connections are located on the side surface of the casing. Because of this, the buyer of the battery will have to install special fittings - corners that ensure the pairing of the horizontal heating element (pipe) and the vertical section of the fittings extending from the horizontal pressure or return branch of the wiring. However, if the distribution pipes are laid vertically, then corners are not needed.
- Radiators with bottom connection . In this case, the battery fittings are located in the lower part of the casing, on the bottom side, which makes it easier to connect the radiator to horizontal wiring, while at the same time making installation to a vertical riser difficult.
As a result, owners of heating systems with horizontal wiring are recommended to use batteries with a bottom connection, and owners of systems with vertical risers are recommended to use batteries with a side connection. Although the latter option can be adapted to horizontal wiring using a cheap fitting - an angle.
The fourth classification option - according to the method of attachment to the supporting surface - distinguishes the following types of radiators:
- Mounted batteries , the housing of which is attached to the wall using special brackets.
- Built-in batteries , the housing of which is “recessed” into the floor, resting on the floor slab at the bottom.
Moreover, it is the mounted radiators that are most widespread. After all, the installation of batteries “recessed” into the floor requires a lot of effort aimed at arranging a niche and hidden wiring.
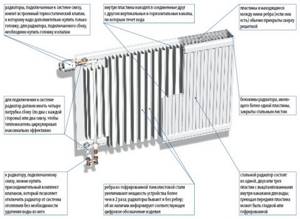
Installation of cast iron radiators.
Gray cast iron is used in their manufacture. Paronite gaskets are installed between the individual sections. Horizontally, the flow of water always goes in one direction. Vertically, the current flows through channels, of which there are one or more. Depending on the number of vertical channels, the area and power of the battery increases. Due to the need to maintain strength and surface area, manufacturers cannot change the weight-to-power ratio much. The large weight of the battery means reinforced fastenings.
Determination of thermal power of plate heating devices
The formula for determining the thermal power that a steel plate heating radiator can produce, and a real example of calculating this parameter, are given below. To calculate the power of the device, it is enough to know the heat loss coefficient of the heated room, the area of the room and its total volume. The passport of any radiator indicates its calculated power at a hot water temperature in the system of 60 0 C. Also, the attached documentation indicates recommendations for the heated area for a specific radiator model.
The thermal output (power) of heating devices depends on the length of the body and the number of plates. The standard height of radiators is 200 mm, the number of plates varies. For example, heat transfer for a radiator with one tube and a body length of 600 mm will be equal to ≈ 347 W. When the length is increased to 3000 mm, the heat transfer will increase to 1730 W. But with the same body length (3000 mm) and an increase in pipes to 4, heat transfer there will already be 4179 W, and with a body length of 1000 mm, four tubes with coolant will give 1393 W of power. Therefore, which radiator is best to buy for a specific room is determined based on the following requirements:
- To heat 1 m2 of a room with a ceiling height of 3 m, you need to spend 100 W;
- For a room with an area of 16 m2, the radiator must have a thermal power of 1600 W, provided that the room has no more than one window, the room is not corner and the ceiling has a height of no more than 3 m. For other initial conditions, correction factors Kp are introduced:
- For two windows Kp = 1.8 / 1600 x 1.8 = 2880 W;
- For a corner room Kp = 1.8 / 2880 x 1.8 = 5184 W;
- For a ceiling 2.65 meters high Kp = 2.65 / 3.0 = 0.88 / 5148 W x 0.88 = 4547 W;
- For PVC windows Kp = 0.8 / 4547 W x 3637 W.
A standard metal-plastic window is 1400 mm wide, so to fully block cold air flows, a radiator of four sections 1400 mm long, with a power of 1950 W, is installed underneath it.
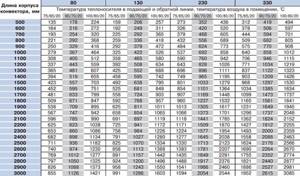
Power table
The heating radiator works like this:
- Under pressure or gravity, the coolant moves through the battery tubes, heating them;
- The tubes heat the plates welded to them, and together the structure heats the air between the radiator elements, which rises up to the ceiling of the room;
- Cold air masses, under the pressure of warm air, fall down to the radiator, where they heat up;
- Then the cycle repeats.
Advantages of cast iron heating radiators
Heating appliances made of cast iron are very resistant to aggressive coolant environments. This is explained by the physical parameters of this metal. Cast iron radiators can remain corrosion-free for a very long time, even at elevated temperatures. In addition, virtually no harm is caused to cast iron and various chemicals added to the coolant.
If the device becomes clogged or leaks, they can be easily repaired. Blockages that occur in the radiator can be caused by the properties of the coolant with a high content of Ca and Mg salts. As a result of deposits on the inner wall of the device, it narrows, which leads to a deterioration in the heating rate and normal heat transfer. A leak in a cast iron battery can occur as a result of wear of the gaskets between the sections. It is better to eliminate all the problems described above during the summer preventive shutdown of water supply.
The cost of a cast iron battery is approximately equal to the cost of analogues made of aluminum and steel. But at the same time, it is worth noting that cast iron withstands water shocks much better and can withstand pressure surges of about 16 bar.
Cast iron devices can be used at high temperatures and pressures, due to their low coefficient of thermal expansion.
The heat output of the heater is quite high. To achieve the greatest effect from this property, special reflectors should be placed behind the cast iron radiator.
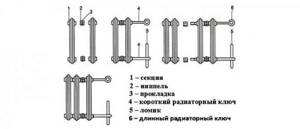
Installation of a cast iron radiator is easy, due to the fact that the radiator sections are connected using a threaded connection and paronite gaskets. The battery is connected to the ends of the pipes in the same way. A special key is used for threading, which can be used to disconnect any section without removing the side ones.
Very long product life of more than 50 years. The only thing is that during this time it is necessary to regularly remove deposits and replace gaskets.
Old batteries: a second life for their intended purpose
What makes old cast-iron batteries attractive is their, dare I say it, enormous service life - these are practically eternal batteries that cannot be demolished. Judge for yourself - today in houses and apartments you can still find working batteries installed under Stalin. Is it a joke? Almost a century old batteries. Radiators made before the collapse of the USSR have almost the same quality - at least they can still work for half a century for their intended purpose.
I agree that by modern standards they are ugly and inconvenient to maintain, but who will stop you from bringing them into divine form and enjoying the warmth they emit for the rest of your days? This is very easy to do, and it is this fact that many restorers use, buying old batteries for cheap, bringing them into proper shape and selling them at a much higher price, thereby earning a living. To be specific, this work looks like this.
- First, the inside of the batteries is washed using chemicals that remove all contaminants from the batteries, including rust.
- Then the battery is disassembled into sections. This is perhaps the most difficult stage of the work - in order to unscrew the old threaded nipples connecting the sections, you need to resort to high heat. The heated metal expands and releases the nipple a little - at this moment the batteries need to be disassembled.
- And then mechanical cleaning - sandblasting, after which the old heating radiators become new. No paint, no rust, no scale - just pure metal with its characteristic shine.

Old batteries photo
After this, the creative process begins, thanks to which it is possible to give the sections a unique and inimitable look. Even simply painting them with the same hammer paints will make old batteries very attractive. People who are familiar with the benefits of old cast iron batteries will pick them up with their hands and feet.
Steel plate radiators - general information
Steel plate radiators are commonly called “accordions”. The appearance of an accordion is created by plates strung on a coolant pipe.

A distinctive feature of such radiators is their high reliability. There are no connections in a plate radiator except for the coolant inlet and outlet. As a result, the radiator itself simply cannot leak; there is nowhere for the coolant to break through.
Thanks to the large number of plates and the direct movement of the coolant, the convector heats up to a high temperature. To protect against touches, the main frame of the radiator is covered with a decorative casing. Convection holes are made in the top cover of the casing.

Convectors have low thermal inertia, which means they can be controlled automatically, that is, thermostats can be installed in systems with plate radiators.