The temperature in the house during the cold season should be such that this cold season can only be felt outside. For this, the heat supply infrastructure must be at a decent level. Many countries, including Russia, have chosen cast iron heating radiators as the basis for their heating infrastructure.
The service life of such devices can be decades of reliable operation without additional repair costs, since cast iron is the most resistant to high pressure and to the effects of various impurities that are part of running water.
What should you pay attention to when choosing?
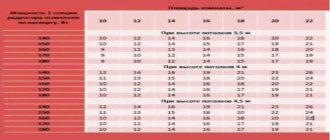
There are many technical criteria to consider when determining which cast iron radiator is best for you. First of all, this is heat transfer, the choice of which takes into account the size of the heated room.
You may also be interested in how much one section weighs, what is the total weight, power, depth, width, height and area of a cast iron radiator. A table of the main characteristics specified by the manufacturer for each type of radiator will help you become more familiar with the main parameters of the devices.
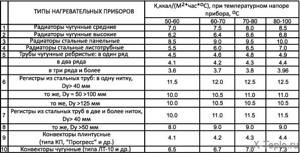
Table of heat transfer characteristics of radiators of various types.
Mini calculation
For country houses, 6 atm devices are suitable. To calculate the thermal power that will be sufficient for each room, you can use a simple rule: if the room has only one external wall and one window, 1 kW (1 kilowatt) of thermal power will be enough for heating 10 square meters. living space; if the room has two external walls, but one window, then for every 10 sq.m. need 1.2 kW; if the room has 2 external walls and 2 windows, then for every 10 sq. m. 1.3 kW will be required.
Of course, the calculation can be performed using a more complex method, but this will be sufficient. Then you will need to find out how many kilowatts one section of the heating device you choose produces in order to determine the required number of sections, the total capacity of which will allow you to effectively heat the room.
Advantages and disadvantages of cast iron radiators
Cast iron radiators are manufactured using casting. The cast iron alloy has a homogeneous composition. Such heating devices are widely used for both central heating systems and autonomous heating systems. The sizes of cast iron radiators can vary.
Among the advantages of cast iron radiators are:
- Possibility of use for coolant of any quality. Suitable even for coolant with a high alkali content. Cast iron is a durable material and is not easy to dissolve or scratch;
- resistance to corrosion processes. Such radiators can withstand coolant temperatures up to +150 degrees;
- excellent heat storage properties. An hour after turning off the heating, the cast iron radiator will radiate 30% of the heat. Therefore, cast iron radiators are ideal for systems with irregular heating of the coolant;
- do not require frequent care. And this is mainly due to the fact that the cross-section of cast iron radiators is quite large;
- long service life - about 50 years. If the coolant is of high quality, then the radiator can last a century;
- reliability and strength. The wall thickness of such batteries is large;
- high heat radiation. For comparison: bimetallic heaters transfer 50% of the heat, and cast iron radiators – 70% of the heat;
- The price for cast iron radiators is quite reasonable.
Among the disadvantages are:
- heavy weight Only one section can weigh about 7 kg;
- installation should be done on a previously prepared, reliable wall;
- Radiators must be coated with paint. If after a while it is necessary to paint the battery again, the old layer of paint must be sanded. Otherwise, heat transfer will decrease;
- increased fuel consumption. One segment of a cast iron battery contains 2-3 times more liquid than other types of batteries.
Differences between imported and domestic brands
A classic example of a cast iron radiator is the MS-140, the operating pressure of which is 9 atm, and the pressure test pressure is 15 atm. These types of cast iron radiators have been used for many years, their quality has been tested by time. Since cast iron has excellent thermal conductivity, and it is also neutral with respect to virtually all coolants, such radiators can be used in heating systems that have poor coolant preparation (contamination, increased aggressiveness, etc.).

The Russian market offers radiators not only from domestic manufacturers, but also various types of devices manufactured in Turkey, the Czech Republic, Italy, England, and Spain. The difference between imported and domestic batteries lies in higher quality surfaces, as a result of which the same power can be obtained from a device with smaller dimensions (for example, the domestic MS-140 has a capacity of 1.3 liters, and the Czech TERMO radiator (Viadrus company) ) volume is 0.8 l, while their power is almost the same).
In addition, imported cast iron heating radiators, as a rule, have smoother internal surfaces, resulting in reduced hydraulic resistance. Also, a distinctive feature of foreign devices is the lower weight of the structure.
High resistance to corrosion allows the use of cast iron batteries in open systems where the oxygen content in the coolant is higher than average, and the high wall thickness prevents abrasive wear, this is especially important if the coolant has a high content of solid particles.

Each cast iron heating device is supplied already painted, or coated with an anti-corrosion coating as a primer. Radiators can be installed either by hanging them on the wall or using special legs.
Minuses
The only disadvantage of cast iron radiators is that they do not always withstand hydraulic shocks well. All Russian radiators, unlike imported analogues, require additional painting and drawing of intersection connections. But if you consider that their cost is three to four times cheaper than imported analogues, and the thermal output characteristics are not inferior to more expensive products, you can come to terms with this drawback.
It is also worth noting that in the case of combustion with solid fuels, which have massive dimensions, cast iron radiators are characterized by increased inertia. If abroad this may be considered a minus, then in Russia, with its cold winters, the high heat of the radiator is, of course, a plus.
The heat that is emitted by a cast iron radiator is much more beneficial for the human body than the thermal energy generated by other types. If you want stylish cast iron radiators that will fit perfectly into your interior, you can choose the retro style produced by many manufacturers.
Types and methods of installation
Most cast iron radiators are sectional models. This means that you can select any heating power depending on the heat loss of the room. Its expansion occurs section by section. As many as needed are collected into one battery.
There is another type - these are solid radiators. They have very high reliability: leaks are only possible if the cast iron breaks down, and this can happen after several decades. But this type is rare: this is how most designer models are cast, in a “retro” style or of non-standard height - from a meter and above.
How cast iron radiators are assembled/disassembled
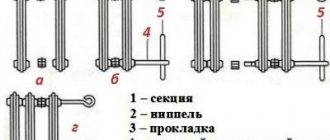
The sections are connected to each other by nipples, the tightness of the joints is ensured by gaskets made of heat-resistant rubber. The nipples have threads on the right and left, the same thread is on the inner surface of the vertical collectors (upper and lower). They are twisted and untwisted using a special mounting wrench.
The mounting key for radiators is a rod with one end flattened. The second one often has a ring into which the lever is inserted. A lever is usually needed when dismantling old radiators: they boil, become overgrown, and it is often very difficult to remove the thread from its place. A crowbar or rod is inserted into this ring, which serves as a lever.

In order to assemble or disassemble a cast iron battery you will need a special key and physical strength
The key is inserted into the manifold to the required depth (try it on from the outside first). The end of the blade rests on the groove in the nipple. Then, turning the key and nipple in the desired direction, the section is unscrewed or tightened. In this case, you need to alternately turn it a couple of revolutions, either in the upper or in the lower manifold. You need to be especially careful with cast iron: it is fragile and excessive force can cause the section to burst. Therefore, there are no distortions: they turned a little at the top, moved down, then up again, etc.
Read more about how to build up, assemble or disassemble sections here.
In the case of cast iron, leaks often occur at the joints: over time, the gaskets lose their elasticity. But for dismountable models this is not a problem: you need to unscrew the nipples, change the gaskets and put everything back together. This is not such a difficult operation. The duration of trouble-free operation depends on the quality of the nipples and gaskets. So when choosing, pay close attention to these “minor” details.
Installation methods
Cast iron batteries are either hung on the wall or placed on legs. Everything is clear with the legs: they come complete with the radiator (retro models) or are ordered separately (with other models). But there is one problem with installation on the wall: a cast iron battery has a serious weight. Therefore, it can only be mounted on a solid wall. In principle, installation on partitions is also possible, but then a reinforcement system must be provided that can withstand this weight.
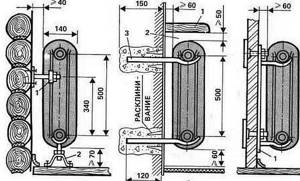
When choosing an installation method, make the main fastening reliable
You can hang it on special brackets, pins, or hooks. Two are placed on top, one on the bottom. The main weight falls on the upper holders. The bottom one serves to give direction. The method of installing holders is any available. The main thing is that it is strong and reliable.
New generation sectional cast iron radiators
Special attention should be paid to the compact cast iron one-, two- and three-channel domestic sectional radiators of the new generation of the ChM series, which have an original design.

Installation of radiators of this type allows them to be placed in any buildings, including those with improved heat-shielding properties, covering the maximum length of the window sill space. Even in rooms where the depth of the window sill niche is very small or nonexistent, a device of this type minimizes the space occupied by heating devices.
The optimal ratio of design and main indicators of the ChM series batteries allows us to consider them the most promising heating devices of domestic production, which are used for heating various types of buildings.
Sections of radiators of the ChM series are made from gray cast iron by casting into sand-clay molds in modern furnaces, which ensures stable quality and the best technical characteristics of the devices. Vertically located ribs ensure high heat transfer, and the absence of cavities where dust can accumulate helps to improve the aesthetics and hygiene of heating devices.
Main advantages
The advantages of a cast iron radiator traditionally include:
- Corrosion resistance. A feature of cast iron is its resistance to oxygen, due to which such heating devices can be used as part of open heating systems, as well as operate in the mode of regular filling and draining of coolant. Steel radiators quickly rust from the inside after the system is emptied and fail after 2–3 years of operation in “ragged” mode.
- Undemanding to the acidity level of the coolant. Cast iron batteries are not afraid of acidic or alkaline environments and are suitable for systems filled with antifreeze.
- High temperature resistance. The batteries can withstand heating of the coolant up to 150 C°. Such technical characteristics make the heating device suitable for gravity systems with a solid fuel boiler, where it is difficult to regulate the heating of the liquid.
- Quite a large internal cross-section. Thanks to this, washing is not required very often.
- Heat storage properties. Thick-walled cast iron radiators have an important property - they retain heat for a long time. After turning off the heating, the radiator will cool down gradually, and after an hour the thermal radiation will be approximately 30% of what it was when the boiler was stopped. The ability to retain heat in cast iron heating devices is several times higher than that of batteries made from other materials, which makes them the preferred choice for autonomous systems with a solid fuel boiler that requires loading fuel more than once a day.
- Durability. The thickness of the walls of cast iron batteries contributes to long-term operation, provided that the material is of high quality and optimal operating conditions. There are examples of successful operation of radiators made a hundred years ago, and examples with Soviet batteries that begin to “crumble” after 20–30 years of operation. Manufacturers estimate the service life of their products at 10–30 years, but in fact it can be much longer.
Basic properties of cast iron radiators

When choosing a cast iron battery, it is recommended to take into account all technical characteristics, a reliable and detailed table with which is indicated in the instructions offered by the manufacturer. This will help you install cast iron radiators without tearing the material at the joints and seams. The operating characteristics of this equipment are such that 70% of the heat released into the air is distributed by radiation, and 30% by convection.
How to choose cast iron heaters
When choosing radiators, we follow the standard algorithm. We determine the required thermal power, calculate the number of sections, and assemble heating devices for each room from them. Then - the purchase of heaters, installation kits and control valves.
What type of radiators is better to choose:
- For heating technical, utility and utility rooms of a private house, the MS-140M series or its variants are quite suitable.
- In residential premises, “accordions” are clearly inappropriate. Buy nicer “aluminum-look” batteries.
- If your budget allows, install designer appliances - domestic or imported, there is practically no difference. Find out the weight of the sectional heater in advance and consider the installation method - wall or floor.

Vintage taps for retro batteries from Carlo Poletti - Conventional ball valves and balancing valves are not suitable for retro radiators purely visually. We need similar Carlo Poletti fittings.
- Place any batteries you like in a private cottage; they will easily withstand the pressure of an autonomous system.
- What devices are best for an apartment? The answer depends on the method of heat supply. With a centralized supply, it is not recommended to install cast iron due to periodic testing of the network. If the pressure “jumps” to 12 bar, the sections may crack.
Note. Before purchasing radiators, you can contact the heat supply organization and formally request the operating parameters of the pipeline network. But if the pressure is exceeded and the cast iron is destroyed, you will suffer losses that are difficult to compensate.
Where is it better to use
Cast iron radiators are optimal for heating rooms for many reasons. Cast iron is quite inert in thermal terms. Of course, this is the reason for the increased heating time of the battery at the beginning of the heating season, but, on the other hand, due to its inertia, cast iron batteries can retain and transfer heat to the air space of the room for a significant time after an emergency shutdown.
In a similar situation, aluminum, bimetallic or steel batteries will stop heating much faster.
For this reason, cast iron radiators are the best choice for apartments in multi-storey buildings. After all, a sudden shutdown of centralized heating supply is a common occurrence in our realities. And only the installation of a high-inertia cast iron battery can make this unpleasant phenomenon almost unnoticeable.
They are also often chosen due to their design features. Many interiors decorated in retro style (Soviet or Tsarist) simply will not look good if you use any other types of heating devices.
Types of heating devices
There is no official classification of cast iron batteries. We can roughly divide heaters into 3 types:
- Soviet-style “accordion” type MS-140;
- devices with an increased heat exchange area, simulating new bimetallic and aluminum heaters, only cast from cast iron;
- designer batteries made in retro, modern style.
Comment. Let us remind you: all cast iron heating devices are sectional, that is, stacked.

It is unrealistic to classify products according to other criteria. Technical characteristics - weight, dimensions, heat transfer - vary widely. Let's look at the properties of batteries by group.
Pros and cons of traditional accordions
To begin with, we present the technical parameters of one fin of the MS-140M radiator, taken from the technical data sheet:
- total height – 588 mm, between holes – 500 mm, depth – 14 cm (the number is included in the marking);
- heat flow (power) – 160 W, surface area – 0.21 m²;
- working pressure – no higher than 10 Bar;
- the volume of water inside the section is 1.45 liters, the maximum temperature is 130 °C;
- weight – 7.12 kg;
- material – gray cast iron SCh-10, plugs – malleable cast iron KCh-30 or steel;
- gaskets - rubber.
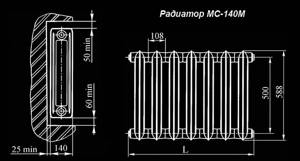
Dimensions of the MS-140 heater and recommended installation distances
Note. The amount of heat flow is indicated under certain operating conditions: the difference Δt between the temperature of the room air and the coolant is 70 degrees. The calculation of heat transfer of section 1 is described in a separate instruction. The letter "M" in the marking means "modernized".
“Accordions” are produced by several Russian enterprises and the Minsk Heating Equipment Plant. The average price for a MS-140M battery section is 10 USD. e., minimum – 6 cu. e.
The mentioned Belarusian plant also produces modified versions of “accordions”, shown in the photo below:
- lightweight model 2K60 with a power of 120 W, the fin weighs 5.1 kg;
- 2KP100-90-500 depth 9 cm, heat output - 140 W;
- modification BZ-140-300 with an interaxial distance of 30 cm, power - 120 W.
The undoubted advantages of radiators remain their affordable price, durability and corrosion resistance to chemically active substances. However, the latter advantage is inherent in all batteries made of cast iron.

Flaws:
- Soviet “accordions” of the MC type do not meet current interior design requirements. The new modifications look better.
- Fragility. A slight impact can cause a microcrack to form in the metal, and then a leak. Freezing of the coolant definitely leads to destruction; the expansion of water causes cast iron to split.
- Significant mass of the heating device, aggravated by spaciousness. Due to the coolant, each section is made heavier by 1-1.5 kg. The multi-section heater cannot be hung on a wall made of aerated concrete or a plasterboard partition, only placed on the floor.
- Limited scope. Due to the maximum operating pressure of 10 Bar, the radiator cannot be used in an apartment with central heating, where the water pressure reaches 12 Bar (at the time of testing the network).
- There is no bottom connection to the heating system, pipes are connected only from the side.
Inertia (long heating and cooling) cannot be attributed to the pros or cons of radiators. This is a feature of thick cast iron walls that does not affect the quality of heating.
Important note. The efficiency of the boiler and the efficiency of the system do not depend on the amount of water in the batteries. The load on the circulation pump is like fairy tales. If the volume of coolant is large, then only the time of initial heating and final cooling will change. Listen to the expert's opinion in the video:
It is worth mentioning one more advantage of the M-140 series batteries. Since “accordions” were previously used everywhere, working sections can be found for free or purchased from scrap metal. According to reviews from owners of private houses, used cast iron radiators are often used for heating outbuildings and utility rooms.
Radiators with increased heat transfer area
The uniformity of the shapes of cast iron appliances is due to the manufacturing technology - casting. The extrusion method used to produce aluminum sections is not applicable here. But in recent years the picture has improved - products with a flat front panel and side ribs, reminiscent of light alloy heaters, have appeared on the market.
Reference. The aluminum-look batteries shown in the photo are produced by Russian, Belarusian and Chinese companies: Konner, STI NOVA, Minsk Plant.
As an example, we list the characteristics of the KONNER Modern section with a standard center distance of 500 mm:
- total height – 60 cm, depth – 96 mm;
- heat transfer at Δt = 70 °C is 150 W;
- maximum water pressure in operating mode – 12 Bar;
- capacity – 0.9 liters;
- weight – 4.1 kg.
The outside of the heater is covered with polymer enamel (usually white). Gaskets are EPDM rubber, the kit includes 4 end plugs. The cost of one KONNER Modern rib is 500 – 12 USD. That is, at least 4 pieces are sold. For rooms with low window sills there is a series of low KONNER G1 batteries with a center distance of 300 mm and a power of 120 W.

Externally, Konner heaters are very similar to products made of aluminum alloy - the front section is flat, heat exchange fins are cast on the sides
How are these batteries better than accordions:
- The heat transfer surface has increased thanks to the side fins and flat front panel.
- Accordingly, the share of infrared heating has increased. That is, the radiator began to transfer more heat through radiation.
- The depth of the fins has decreased without reducing heat transfer.
- The operating pressure is increased to 12 atmospheres.
The disadvantages of batteries are typical - the products are fragile and limited in coolant pressure. But we managed to solve the problem of appearance - now the heaters look no worse than bimetal. Prices have increased slightly - a section costs between 10...17 USD. e.
Note. The cost of a Belarusian radiator 2K60PP, equipped with a flat panel, is 21 USD. e. by the rib. The reason is the complication of the manufacturing process; mechanical processing of the frontal plane and painting were added.
Designer retro batteries
The selection of antique radiators is impressive in variety. In this case, technical parameters fade into the background, giving way to other characteristics:
- beauty;
- compliance with the design of the rooms;
- overall dimensions.

In addition to traditional two-channel devices, you can choose heaters with 3-4-5 channels. There are radiators with smooth surfaces and a relief pattern, designed for floor installation. Batteries in the Art Nouveau style have angular outlines, while retro ones are more rounded.
Explanation. Two-channel radiators have 2 vertical coolant flows, three-channel radiators have 3, and so on.
High-quality retro batteries are produced in the Czech Republic, Germany, Turkey, the Russian Federation, and more recently in China. Famous brands:
- Viadrus;
- Guratec;
- Demir Dokum;
- EXEMET;
- Retro Style;
- Iron Lion;
- taps and other retro-style fittings are produced by the Italian brand Carlo Poletti.
It is pointless to provide technical data for heaters, since the variation in power, dimensions and weight is too great. Prices also vary widely - from 20 to 250 USD. e. per section. Chinese and some Czech devices cost 20...30 USD. That is, Turkish and German are significantly more expensive. The cost greatly depends on the massiveness and design of the product.

The only parameter that remains unchanged is the operating pressure. In this regard, designer heating radiators are no better than “accordions”, since cast iron walls can withstand 15 Bar (maximum). The average value is 8…10 Bar. The table below shows the characteristics of several models:
| Radiator brand and model | A country | Weight, kg | Coolant volume, l | Thermal power, W | Price, y. e. |
| Viadrus KALOR 500/70 | Czech | 4 | 0.8 | 70.3 | 20.05 |
| Viadrus Bohemia 450/220 | Czech | 9.9 | 2.4 | 110 | 78.25 |
| Demir Dokum Nostalgia 500/200 | Türkiye | 9.6 | 2.3 | 163 | 52.20 |
| Retro Style Anerli 560/230 | Russia | 17 | 3.29 | 189 | 229.60 |
| EXEMET Modern 600/100 | Türkiye | 4.3 | 0.7 | 102 | 32 |
| EXEMET Classica 500/176 | Türkiye | 9.3 | 1.95 | 145 | 76.85 |
The negative and positive properties of retro heating devices in general repeat the advantages of previous varieties. The main difference is the high cost and massiveness of some batteries; the weight of 1 rib reaches 17...20 kg.
Tips and tricks
Comfort in the home, as well as lower energy costs, depend on the efficiency of heating. A couple of useful tips will help resolve pressing issues:
- If there are already cast iron radiators in the house, and they have become worse at heating, there is no need to change them for this. The heating system may be clogged. Silt has settled inside the sections, preventing the normal circulation of the coolant. Heating devices can simply be washed and they will work perfectly.
- When installing new heating for a private home or cottage, cast iron heating devices will be a good choice. They maintain heat for a long time, even if the fuel in the boiler has gone out.
Before purchasing radiators, you need to make sure that this is the only correct solution. Finally, it is worth noting that it is not advisable to paint them often. With each layer of paint, heat transfer decreases, since it is a kind of insulator.
Recommendations for selection
To achieve efficient heating of a room, you need to understand not only the types of batteries. As you know, each has its own level of heat transfer, which largely depends on the number of sections. Let's look at this issue in more detail.
Calculation of the number of sections
At the moment, there are several ways to calculate how many battery sections are needed for the heating to be effective. Let's get acquainted with a technique that takes into account the area of the room. The statement here is that to heat 1 m2 you need 100 W of device power.
The formula is as follows: N = (100 x S)/Q where:
- N—number of sections;
- S—room area (m2);
- Q is the heat transfer level of one section (W).
For more accurate calculations, it is recommended to take into account the following features: the number of double-glazed windows, doors, wall thickness.