Heating appliances are in great demand, so many consumers are interested in the design of the product, manufacturer and other parameters. The heating radiator design is divided into 2 types: sectional and panel.
Heating radiators for apartments and houses are made of cast iron, steel and various alloys. Nowadays, they have many forms, and this is not their only difference; they also stand out due to their design features.
Radiator design features
Internal filling of a heating radiator
The battery is a separate heating device that contains elements with internal channels for the movement of energy carriers. Heat is removed by convection, radiation and heat transfer.
Sectional types allow you to increase the heating area by adding elements. Panel installations cannot be changed in shape, which is taken into account when calculating and installing the system. The accompanying passport indicates the temperature criteria for the operation of the device, operating pressure parameters, and heat transfer.
Radiator section
The cross-sectional structure of a heating battery consists of a metal pipeline in the form of combined horizontal collectors through which water passes. The channels are connected using small-diameter vertical tubes, and the entire system is housed in a housing made of cast iron, steel or aluminum. The separate sections are screwed together.
Radiators serve to heat the room, so the design of the devices affects the quality of heat exchange. The material of the heat exchanger and housing plays a role, so bimetallic options are used, including 2 types of materials.
Radiators must be able to be cleaned periodically, because... scale deposits on the inner surface reduce heat transfer.
What it is
An electric battery refers to two different designs.
Liquid electric battery
From the verbose descriptions on manufacturers' websites, you can still extract nuggets of useful information and generally understand how this device works.
- The circuit is based on a conventional heating element, a tubular heater. Since the solution is positioned as energy-saving, it usually has low power - up to a kilowatt. Models with peak consumption of 300 - 500 watts dominate.
- Water or oil acts as a coolant. There are both sealed designs with a non-replaceable coolant, and open ones, into which you can pour any liquid through a plug.
- Thanks to the fins, the aluminum body provides a solid heat exchange area, and thanks to the thermal conductivity of this metal, the same temperature over this entire area.
- The electric heating battery operates at full power only until the target temperature is reached. When it is reached, the heating turns off, as soon as the temperature drops, the heating element turns on again.
- Microprocessor control of a miniature electric boiler ensures the most rational operating mode, due to which huge savings are achieved.

The circuit contains a digital thermostat.
The ease of connection makes it easy to install a heating system with your own hands.
Dear Reader: Wait, laugh. For now, we are just quoting the advertising assurances of the manufacturers.
Liquidless electric battery
Manufacturers of the second type of miracle devices explain that the possibility of water or oil leakage always remains with you as long as you use a liquid heating device. The truth is liquid-free, where a low-temperature heating element in an aluminum casing will heat you even more economically and safely.
At the same time, microprocessor control continues to save, save, and save again.
The author will allow himself to quote a few more fragments of technical descriptions.
- The battery housings are made from aircraft aluminum, which allows the use of pressure up to 80 kgf/cm2 and preserves the oxide film that protects the aluminum from corrosion (see article Aluminum heating batteries - a reliable component of the heating system)
- The batteries are assembled on threads, in contrast to low-quality soldered and cast structures.
- Older models are bimetallic heating radiators - obviously with steel core sections.
The price of younger models is about 6,000 rubles. Seniors - 10,000.
If desired, you can assemble a kit from a purchased separate radiator and heating element.
We will try to maintain maximum objectivity to the last and will not comment on any of the four points. The author will say politely: he does not associate any of the points in this section of the article with anything even remotely resembling common sense.
Types of radiators by design

The heating capacity of batteries depends on the exchange area, so the design is important.
The choice of form is influenced by factors:
- ceiling height and room area;
- maximum pressure in the heating line;
- duration of operation (long-term or periodic);
- boiler power, pipe material, characteristics of other devices in the system;
- chemical composition and physical properties of the energy carrier.
Radiators are selected in the form of sections, panels, plate and tubular types. The climate in the region and the required heating conditions, the presence of aggressive factors, and the cost of batteries influence.
Sectional radiators
Heat exchangers connect sections of the same type, which inside have 2–4 channels for water movement. Prefabricated elements are made of aluminum, steel, cast iron of various shapes and lengths. Heating of the room is coordinated by the number and size of sections.
Prefabricated batteries transfer heat by convection and radiation, operate economically, and are equipped with manual and automatic temperature controllers, taps, and valves. The products are inexpensive, and the ability to choose the center distance makes them popular for different buildings.
Disadvantages include the risk of leaks due to a sudden surge in pressure, difficulties with cleaning internal channels and external cleaning of the intersection space.
Tubular batteries
Design of tubular batteries.
The power depends on the diameter of the pipes. The cross-sectional design of the radiator includes 1 – 6 vertical collectors, which are connected by an upper and lower pipe; the coolant circulates unhindered. Heat transfer depends on the diameter of the pipes and the dimensions of the heat exchanger (0.3 - 3.0 m). The units can withstand pressures up to 20 atm.
Tubular batteries withstand pressure changes and hydraulic shocks. Smooth interior contours resist the accumulation of dirt and deposits. Welded joints do not leak. The appearance fits into various interiors. Radiators are available in all sizes and differ in body shape. The disadvantage is the high cost.
Panel models

A panel radiator looks like two metal panels welded together. Inside the plates there are vertical channels for circulation of the energy carrier, and ribs are attached to the outside, which increase the heat transfer surface. The panels are arranged in 2 or 3 rows, the material is steel.
Advantages of the models:
- low inertia makes it possible to quickly respond to changes in external temperature;
- due to its lightness, massive fastenings are not required;
- compact devices can be placed in any part of the room;
- low price.
To heat the model, you need half as much water as a sectional battery. The disadvantage is that panel installations cannot withstand high pressure in the main line; purified energy carriers without dirt and impurities must be poured into the system. Poor quality painting of joints leads to corrosion and leaks.
Lamellar

The operating principle of the radiator is convection exchange. The heat exchanger is a core with fixed fins made of thin metal. Inner tubes serve to transfer water. This type of radiator is installed in industrial and public buildings, multi-apartment buildings with a centralized main line.
The degree of heating is regulated by increasing the number of plates. Radiators effectively heat the room, but when the boiler is turned off, cooling occurs quickly. The coolant must be heated to a high temperature and pass under pressure.
Technical features of cast iron batteries
Modern cast iron batteries are largely similar in their technical characteristics to more expensive and innovative devices made of bimetal, aluminum and steel.
The working pressure inside cast iron batteries is eight atmospheres. As for the optimal location of these units, it is best to place them in the space under the window openings, which will increase heat transfer rates.
In order for the volume of transferred heat to be as large as possible, the correct solution would be to periodically wash the inner surface of the batteries to clean it of rust and other harmful substances. This will increase the productivity of the equipment, and at the same time extend the service life of cast iron heating batteries.
Classification by material of manufacture
Radiators must last a long time and withstand various aggressive influences. In a multi-storey building, the operating conditions are not entirely suitable, since the coolant is not of high quality. Aluminum appliances are not installed in the apartment, because... The radiator is wearing out and will quickly fail.
Manufacturers take care of damage to the insides and protect the surface with polymers, but such options are expensive and are not always in demand. Bimetallic and steel installations are less damaged by corrosion. Cast iron batteries are suitable for centralized heating from the city branch.
Cast iron

. A heavy radiator consists of sections and is distinguished by powerful heat transfer. The device tolerates energy contamination, but limescale and scale accumulate on the insides. The units operate for a long time, sometimes they are removed, disassembled and cleaned under pressure to restore the original heat transfer.
At the same time as cleaning, the intersection gaskets are changed, which eventually fail. Cast iron batteries have an outdated design and are not installed in closed automatic heating systems. In apartments that are heated from the central branch, such batteries can withstand pressure changes and water hammer.
Aluminum
The aluminum radiator in the heating system efficiently releases energy and has a large area due to the impressive number of fins. Devices are produced that can withstand a pressure in the system of about 12 atm, and the pressure during pressure testing is at the level of 18 atm.
Sectional design options for an aluminum heating radiator:
- one-piece structures with cast sections;
- extruded type with elements connected mechanically;
- combined options.
The advantages of aluminum radiators include small dimensions, lightness, and large area. The disadvantage is the destruction of metal in an aqueous environment, especially in the presence of stray currents in the main line. The oxide film inside is damaged by an aggressive energy carrier; during the reaction, gas is released, which in a closed circuit leads to rupture of the battery.
Bimetal

Bimetallic installations are of higher quality. The purpose and design of the radiator allows the device to operate under high pressure conditions and with the danger of water hammer.
Batteries are produced sectional or cast, and come in two types:
- made of aluminum and steel;
- made of aluminum and copper.
In bimetallic devices, contact of water with aluminum is not provided. This design improves thermal conductivity, reduces weight and increases strength. Radiators made of two metals can withstand pressure up to 100 atm, no corrosion is observed.
Variety of heating radiators
The most traditional are cast iron models of heating radiators, which are familiar to everyone.
Today, these units are used extremely rarely due to their large weight and the impossibility of installation in heating systems that operate automatically. However, these devices also have their own advantages, which distinguish them from batteries made from other materials. First of all, the design of the heating radiator made of cast iron allows it to withstand severe pressure changes. In addition, such batteries are resistant to the appearance of corrosive deposits on them and withstand the effects of harmful impurities in the coolant, which is also important.
The design of a panel-type heating radiator is somewhat different. First of all, these devices are significantly lighter than cast iron batteries. In addition, their walls are less thick, which reduces their inertia. The operating principle of a panel-type steel heating radiator is based on greater heat transfer compared to other models. In addition, the appearance of these devices is much more modern.
Many consumers appreciate aluminum heating radiators. These radiators are also very light in weight, their heat dissipation is quite acceptable, and the design can be very different.

In inexpensive devices, silicon is added as an addition, preventing rupture of the structure in the event of serious changes in pressure and temperature. And those devices that are more expensive may contain zinc and titanium, since these substances are designed to provide the structure with increased resistance to various types of mechanical damage and protection against corrosion.
Design and operating principle
The principle of operation of a radiator is that the heated energy carrier moves through a pipe system and enters the batteries, transfers heat, then moves along the return branch to the heating source. A radiator heats the air in a room using radiation and convection. Different types of devices have different ratios of thermal radiation and convection.
Steel and cast iron radiators heat the room by radiation, and plate and panel heaters transfer energy by convection due to the large total area of ribs and strips. The warm flow tends upward; in return, cold air is drawn in, which heats up.
How to calculate the power of radiators and the number of sections
The purchase of effective, high-quality equipment should be complemented by correct calculations of the number of sections.
SNiP consists of design rules and operating standards for heating systems. Radiators need to be installed taking this into account. For the calculations to be effective, the following rules should be used:
- the maximum width of the structure should not exceed 70% of the size of the window opening;
- the product must be mounted along the center line of the window;
- the distance between the wall and the device is 3-5 cm;
- the product should rise above the floor no more than 12 cm;
- the distance from the battery to the window sill is 5 cm.
In some cases, for better heat transfer, the wall surface is covered with a special reflective material. Such rules promote the free movement of air masses. For correct calculation you need to know the following parameters:
- room sizes;
- number and area of entrance doors and windows;
- materials for building a house;
- placement of rooms relative to cardinal directions;
- technical parameters of the heating design.
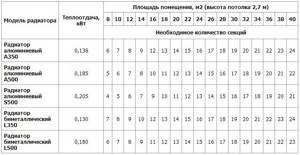
The table shows a simple calculation of the number of sections.
| Power of 1 heating radiator section according to the passport, W | Room area, m² | ||||||
| 10 | 12 | 14 | 16 | 18 | 20 | 22 | |
| 140 | 8 | 9 | 10 | 12 | 13 | 15 | 16 |
| 150 | 7 | 8 | 10 | 11 | 12 | 14 | 15 |
| 160 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 | 12 | 13 | 14 |
| 180 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 | 12 | 13 |
| 190 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 | 11 | 12 |
| 200 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 | 11 |
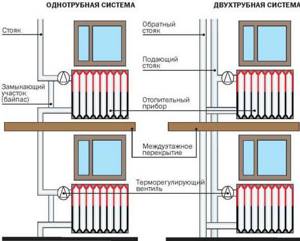
Connecting the radiator yourself
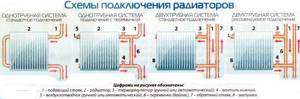
In the multi-apartment sector, the batteries are mounted on one side of the room. The radiator is connected using several methods depending on the pipe layout.
Diagonal or cross connection is used. The underwater pipe is connected to one side of the battery at the top, and the outlet pipe is connected to the other side at the bottom. This scheme is relevant for installations with a large number of sections of considerable length.
The bottom connection involves connecting the inlet and outlet from the radiator from below to two pipes on both sides of the heat exchanger. The scheme is characterized by low efficiency, but this option cannot be avoided if the heat supply system is located in the floor.
Disadvantages of cast iron radiators
Despite all the above advantages, cast iron radiators also have some disadvantages, among which it is especially important to mention the following:
- during long-term operation, rust accumulates inside the units;
- the heat transfer surface of the equipment is small, and the thermal conductivity of cast iron is very low, therefore, in order to efficiently heat a living space, cast iron heating radiators must consist of at least ten sections;
- due to the fact that the mass of the coolant and the cast iron batteries themselves in the centralized heating system in an apartment building is very large, it will be necessary to install a volumetric pipe system that cannot be hidden in the wall;
- Due to the fact that the volume of coolant is very large, it will take a lot of time to heat the room. And the increased inertia of cast iron equipment will not allow equipping the radiator with a mechanism for regulating the heat produced;
- such devices are quite difficult to install in ready-made heating systems equipped with automatic devices, which does not allow controlling fuel consumption;
- the rate of heat transfer into a cast iron battery is very small.

Caring for radiators in the absence of heating in the off-season
To carry out work on their equipment, heat supply organizations usually drain water in the off-season. Without a coolant, the corrosion process intensifies in almost all types of radiators (to a lesser extent in cast iron radiators).
According to manufacturers' recommendations, radiators can be kept empty for no more than 15 days. Therefore, measures should be taken to conserve water in heating appliances. Usually, to do this, close the lower shut-off valve - when connecting the radiator to the side.
The top valve is left open - pressure and corrosion products (hydrogen during the oxidation of aluminum) are released through it. When the aluminum radiator is completely turned off, the Mayevsky valve should be opened - the accumulation of hydrogen can lead to an increase in pressure and depressurization of the product.
To maintain the efficiency of heating appliances, especially radiators, it is recommended to flush them. Radiators are washed once every 2–5 years, the frequency of washing is determined by the decrease in heat transfer from the device. The simplest cleaning method is to flush through a hose from a water tap.
To do this, the radiator is emptied of water through a non-passable bottom plug and disconnected from the connections. The hose is connected to the upper hole, and flushing water flows out of the lower hole.
Heating devices removed for cleaning
Washing is carried out until the discharged water is completely clarified. Then the radiator is installed in its place. For ease of removal and maintenance of heating devices, they should be installed on dismountable connections such as the American squeegee - you can read more about this here.
Cast iron radiators should be painted after 5–6 years, and special heat-resistant types of paints and enamels must be used. Painting is carried out after preliminary preparation of the surface of the devices in several layers. Painting is also relevant for steel products - if the coating at the damage site is damaged, the process of metal corrosion is significantly accelerated.
All the recommendations given in this article must definitely be followed in apartments with centralized heating. In autonomous heating systems, the chemical composition of the coolant remains virtually unchanged, and the pressure in the equipment is much lower. But still, it is not recommended to drain water there in the off-season - this will slow down the corrosion process.
Timely care and proper operation of heating radiators significantly extend the service life of products and maintain the quality of their work at a high level. Maintenance activities take little time, but the result will show itself - the radiators will last a long time, they will not require replacement for a long time (and, accordingly, financial expenses).
( , 1 today)
We recommend reading:
Heating
Autonomous water heating system
Electric heating methods
Cottage heating system
Types of aluminum heating radiators
Laying heating pipes
How to disassemble an aluminum battery?
Sometimes situations arise when you need to disassemble the battery. For example, it is necessary to add additional sections to the radiator or replace one of the sections that has leaked. In any case, you need to know how to disassemble an aluminum heating radiator correctly.
Battery parsing algorithm:
- dismantle the radiator. To do this, you must first shut off the flow of coolant into the system. The threaded connection is unscrewed using a wrench;
- remove the radiator and place it face up on the floor;
- disassemble the device into separate sections. The sections can be disconnected using a radiator wrench. Insert it into the grooves of the nipple nut of the upper hole and make several turns counterclockwise. Do the same with the bottom hole. Section disconnected.
Installation of bimetallic radiators
special key
Even before installation begins, you should decide on the wiring diagram and connection method. The wiring can be serial or parallel. In a private house, two-pipe parallel wiring is more often chosen; in a city apartment, only single-pipe serial wiring is possible. The radiators themselves are most often connected diagonally.
The entire tool can usually be purchased together with heating appliances. However, there are situations when special fasteners are necessary due to the design of the walls (too thin or too hard). Installation recommendations are contained in the instructions.
First, the fastenings are marked, then a Mayevsky crane is mounted on each device. It should be taken into account that the distance from the floor to the device should be 8-10 cm, from the window sill to the device - 5-10 cm, from the wall to the radiator - 2-5 cm. The protective film from the radiators is removed only after they are connected to the heating system.
Immediately after installation, connections are made and air is released from the devices. Experts believe that approximately a bucket of water should be drained from each battery. If no leaks are detected at startup, they will not appear later. If leaks do exist, they should be repaired immediately.
A little history
The history of the creation of radiators goes far back, several thousand years ago, when people began to think about how to make their home warm and comfortable for living in the cold season. Then they heated themselves using an open fire, the smoke from which escaped through a special hole. The first heating battery appeared already in Ancient Rome in the form of a stove with a pipe. Interestingly, some modern houses still use this type of heating system to this day.
In 1855, German entrepreneur Franz San-Gali created the first cast iron radiator and called this device a “hot box”. The cast iron radiator has become widespread throughout the world and was used in steam heating systems. This was a serious start for new inventions in the field of heating. The first tubular steel radiator, invented by Rubert Zehnder, appeared in 1930. This discovery was a triumph. The battery was named Zehnder and demonstrated excellent technical characteristics: lighter weight than cast iron units and high heat transfer.
A little later, bimetallic radiators appear that combine both steel and aluminum, embodying all the advantages of steel and aluminum batteries. Subsequently, many companies mastered this technology, and it is still successfully used in the modern world for the production of radiators. Cast iron batteries came to Russia in the 20s, and already in the 40s all Soviet apartments had cast iron heaters. Aluminum and bimetallic radiators in Russia became popular much later than in Europe.
How the heating system works in multi-storey buildings
The heating system in high-rise buildings was carried out according to standard designs. And if neighboring five-story Khrushchev-era buildings (or nine-story buildings, etc.) look like twins, this does not mean that the heating in them should be as identical as their appearance. And the reason is not at all that
Houses built three to five years apart can be made according to different designs. So it turns out that in one house people on the fifth floor complain about the heat, and in another house on the first floor the windows are not closed for the same reason.
With top wiring, heat flows from top to bottom. At the same time, in order for it to reach the top (the pipes go to the basement), the main riser is installed in one of the entrances, closer to the middle of the house. It is through this that all the heat is transferred upward (to the attic or to the ceiling of the apartments on the top floor) and is supplied.
According to the project, the diameter of this riser is the same as the pipes in the basement, which are used to heat the entire house. But sometimes, in order to save money, it is reduced, and then the commissions spend the whole winter looking for warmth in this house.
With lower wiring in the basement, two pipes of the same diameter are laid side by side along both facades of the house. From one of them, pipelines rise to the very top floor (these are supply risers, they are hotter to the touch). The other is connected to return risers, through which the coolant returns from the upper floors.
In this regard, is it any wonder that in one apartment one radiator will be hot, and the other almost cold; after all, they are connected to risers with different temperatures.
For lower wiring there are U-shaped and T-shaped circuits. Previously, two-pipe systems existed, but they were abandoned in order to save money.
In addition, the project also determined the connection diagram for the house: elevator (or with a pump), elevator-free (direct connection), independent (via a boiler).
Needless to say, the diameters of all pipelines and the number of sections of heating devices were determined by calculation and indicated in standard designs. Are there many houses left in which additional sections are not installed, heating is not installed on the loggia, “warm floor” is not connected, or something else?
All this makes it difficult to regulate the heating system of houses and uniform distribution of heat throughout the risers of apartments.
Heating systems are different. Especially now that multi-level houses have come into operation.
The latest models have individual heating, and this is justified. Who wants it hot and expensive, who wears a vest and will live frugally.
There are also houses with an individual boiler room on the roof. Such mini boiler houses must operate without human control. In the sense that commissioning and further monitoring via a computer. At first, people were insured and worked there. The essence of how these mini boiler houses work is that water is heated on the roof of the house, and then pumped down through pipes. This method, with forced water supply, makes it possible to evenly heat radiators throughout the house. This heating system was borrowed from France. It’s just a pity that everything is not completely in French; we included our rationale for reducing the cost. But in principle, the system works. In Belgorod, quite a lot of 12-18 storey houses are heated in this way. They are served by a technical ambulance type team. If there is a failure, they receive a signal and a team leaves. In normal times it works automatically, without the presence of an operator.
add to favorites link thank
How to choose radiators for autonomous heating?
It is important to know which radiators are best for autonomous heating in your own home. When choosing batteries for a custom home system, you also need to consider a lot of factors.
The heating system of a private house or apartment with an autonomous heating system can be air or water. In the first case, special electrical devices are used, which include infrared heaters, or the room is heated using stove heaters.
But a more common option for individual heating are water-type heating systems, which heat the room by transferring heat from heated water, which circulates well through pipes and radiators.
Advantages of autonomous heating
Individual heating of apartments significantly benefits from a central heating system:
- autonomy;
- ability to regulate heating;
- when using a double-circuit heating boiler, it becomes possible to provide the house with hot water all year round;
- the opportunity to save on payment;
- low operating pressure and absence of water hammer;
- higher quality coolant compared to central heating.
How to clean a heating device for a house or apartment
How to calculate the required number of heating radiator sections? It is clear that a radiator installed in the room (one or more) must provide heating to a comfortable temperature and compensate for the inevitable heat loss, regardless of the weather outside.
The basic value for calculations is always the area or volume of the room. The professional calculations themselves are very complex and take into account a very large number of criteria. But for household needs you can use simplified methods.
The simplest methods of calculation
It is generally accepted that to create normal conditions in a standard living space, 100 W per square meter of area is sufficient. Thus, you just need to calculate the area of the room and multiply it by 100.
Q = S × 100
Q – required heat transfer from heating radiators.
S – area of the heated room.
If you plan to install a non-separable radiator, then this value will become a guideline for selecting the required model. In the case where batteries are installed that allow the number of sections to be changed, another calculation should be made:
N = Q/ Qсy
N – calculated number of sections.
Qс – specific thermal power of one section. This value must be indicated in the technical data sheet of the product.
As you can see, these calculations are extremely simple and do not require any special knowledge of mathematics - just a tape measure to measure the room and a piece of paper for calculations. In addition, you can use the table below - it shows already calculated values for rooms of different sizes and certain capacities of heating sections.
However, you need to remember that these values are for the standard ceiling height (2.7 m) of a high-rise building. If the height of the room is different, then it is better to calculate the number of battery sections based on the volume of the room. For this, an average indicator is used - 41 W of thermal power per 1 m³ of volume in a panel house, or 34 W in a brick house.
Q = S × h × 40 (34)
h – ceiling height above floor level.
Selection of sections by heat transfer
- Open the official website of the manufacturer of the battery you like and download the operating instructions for the device. It indicates exactly at what temperature difference DT the radiator produces the nominal amount of heat. Focus on the 70/50 °C mode.
- If there are no instructions, take the manufacturer's data as truth and multiply the heat transfer by an increasing factor of 1.5-1.8. If you make a one and a half supply, you definitely won’t go wrong.
- Select the latest radiators of a single-pipe system with a double reserve, since they receive the least amount of thermal energy.
How to take into account effective power
When determining the parameters of a heating system or its individual circuit, one should not discount one of the most important parameters, namely the thermal pressure. It often happens that the calculations are done correctly, and the boiler heats well, but somehow the heat in the house does not work out. One of the reasons for the decrease in thermal efficiency may be the temperature regime of the coolant. The thing is that most manufacturers indicate the power value for a pressure of 60 °C, which occurs in high-temperature systems with a coolant temperature of 80-90 °C. In practice, it often turns out that the temperature in the heating circuits is in the range of 40-70 °C, which means that the temperature pressure value does not rise above 30-50 °C. For this reason, the heat transfer values obtained in the previous sections should be multiplied by the actual pressure, and then the resulting number divided by the value specified by the manufacturer in the data sheet. Of course, the figure obtained as a result of these calculations will be lower than that obtained when calculating using the above formulas.
It remains to calculate the actual temperature difference. It can be found in tables on the Internet, or calculated independently using the formula ΔT = ½ x (Tn + Tk) – Tvn). In it, Tn is the initial temperature of water at the inlet to the battery, Tk is the final temperature of water at the outlet of the radiator, Twn is the temperature of the external environment. If we substitute into this formula the values Tn = 90 °C (high-temperature heating system, which was mentioned above), Tk = 70 °C and Tvn = 20 °C (room temperature), then it is not difficult to understand why the manufacturer focuses on this particular thermal pressure value . Substituting these numbers into the formula for ΔT, we get the “standard” value of 60 °C.
Taking into account not the nameplate, but the real power of thermal equipment, it is possible to calculate the parameters of the system with an acceptable error. All that remains to be done is to make an adjustment of 10-15% in case of abnormally low temperatures and provide in the design of the heating system the possibility of manual or automatic adjustment. In the first case, experts recommend installing ball valves on the bypass and coolant supply branch to the radiator, and in the second, installing thermostatic heads on the radiators. They will allow you to set the most comfortable temperature in each room without releasing heat to the street.
Review of aluminum battery manufacturers
Today, many models of aluminum radiators from different manufacturers are sold on the market. Therefore, you can easily select the aluminum heating radiators that best suit your technical parameters, external design and financial capabilities.
You can purchase the desired model on the market, in a specialized store. Aluminum heating radiators are also sold via the Internet. The advantage of such a purchase is that it saves time. If you have any questions regarding the parameters of the equipment, you can ask them to an online consultant or call the phone number listed on the website and chat with the manager.
It should be noted that for heating radiators, prices for aluminum, steel or cast iron models in the online store are usually lower than the market average. Therefore, many people prefer to order heating devices online.
Both imported and domestic products are available for sale. Naturally, prices for domestically produced aluminum heating radiators are lower than for foreign analogues. But this does not affect the quality of the product. Since many modern domestic batteries are produced using Italian technology. Among domestic manufacturers, it is necessary to highlight the companies Rifar and Thermal. They produce durable aluminum heating devices at reasonable prices.
Since Italian aluminum heating radiators have always been famous for the highest quality, they are very popular on the market, despite their high cost. Here we should note the products of Fondital, Sira and Global. These companies also produce bimetallic heating radiators. Hungarian-made heating devices are also popular. True, they are inferior in quality to Italian models. Good aluminum batteries are produced by the Hungarian company NAMI.