I noticed that bimetallic radiators are increasingly used when installing heating systems. I would like to know why they have become so widespread, and what are their strengths and weaknesses? Thanks in advance for your answer.
The correct design and reliable operation of the heating system for housing or administrative and office premises depends on the choice of devices (radiators, convectors, etc.).
The choice of radiators is represented by numerous types, brands and manufacturers, but today we will talk only about the most popular radiators - bimetallic ones. During their production, all the positive qualities were taken into account and the disadvantages of other types of heating devices were eliminated.
Bimetallic radiator in section
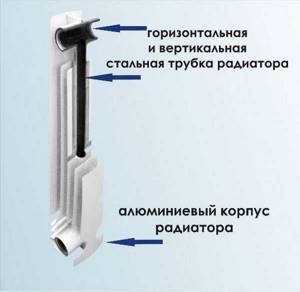
In simple terms, a bimetallic radiator is a heat transfer element of a heating system, which consists of a steel inner part (through which the coolant moves) and an aluminum frame (fins), which does not come into contact with water, and serves only for improved heat transfer.
Less commonly, ribs made of other metals can be used instead of an aluminum top layer. The main idea behind using different metals in one device is the different physical and structural properties of these materials.
Materials used for bimetallic radiators
The housing of the bimetallic radiator section is made of aluminum. This metal has good thermal conductivity and heat dissipation. But it does not withstand changes in pressure and temperature well.
The interior of bimetallic radiators consists of either steel or copper. Steel is used more often due to its low cost. But steel bimetallic radiators have slightly larger sections than those with a copper core. This is because when using copper the thickness of the channel walls is lower.
Good manufacturers use high-quality steel that is resistant to corrosion. In addition, they coat the inside of the tubes with an anti-corrosion coating.
Cheap Asian manufacturers often use low-quality steel, which quickly rusts. But it will take more than one year for the pipes to completely destroy, since they constantly contain water. Do not forget that in Asia there are both cheap non-name manufacturers and high-quality brands. This is evidenced by the variety of reviews about Chinese bimetallic radiators.
Installation of equipment
The installation of bimetallic heating radiators must be carried out in accordance with the instructions given by the manufacturer. And, of course, the installation must be carried out by a specialist who has a license to carry out this type of work.
Before installing batteries, wash the communications.
A valve will need to be installed on each battery; it can be either manual or automatic and designed to release air from the radiator. To prevent the valve from becoming dirty, special filters are installed on the supply risers to protect against dirt.
Aluminum or bimetallic radiators?
Radiator installation procedure:
- Mark the mounting locations for the brackets;
- Attach the brackets using dowels or cement mortar;
- Connect the battery to the supply lines, this is done using a tap or thermostat;
- Install an air bleed valve at the top of the radiator.
The bimetallic heating radiator must be installed so that the horizontal sections of the heads lie directly on the brackets. It is undesirable to cover radiators with various screens and cabinets, as the operating conditions of the equipment may worsen.
Design of bimetallic heating radiators
Each section consists of an aluminum body with flat parts, the so-called “feathers”. The main heat transfer occurs through them.
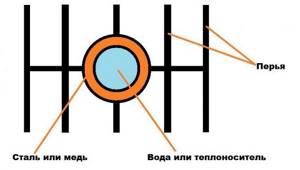
Bimetallic radiator in horizontal section.
At the top and bottom inside the aluminum body there are steel or copper horizontal tubes. On each side they have an internal thread for a nipple nut. the latter is used to fasten the sections together. The nipple nut has an external thread.
The upper and lower parts are connected by a vertical channel, also made of steel or copper. Water or coolant passes through it. The main transfer of thermal energy occurs in these tubes.
Air cutoffs are located at the top of many models. They serve to direct warm air from the wall into the room. They are especially effective when installing batteries in a niche or under a window.
The operating principle of bimetallic radiators is the same as that of others. But there are three main differences from aluminum, cast iron and steel radiators:
- Bimetallic radiators have less heat transfer than aluminum ones. The difference on average is 10-20%.
- Bimetallic batteries are highly durable; some models can withstand pressures of up to 40 bar.
- Bimetal radiators are not subject to corrosion due to the high acidity of the water.

Bimetallic radiator in section (steel core)
Description and principle of operation
The peculiarities of the domestic climate dictate their conditions, because people are forced to spend a considerable part of their lives in heated rooms. The problem of lack of heat during the harsh seasons in modern multi-storey buildings can be solved by powerful and reliable heating radiators, which can return home comfort to apartments in cold weather.
Such devices, which, if necessary, regulate the temperature in the room, are designed to maintain optimal comfort. The main thing is to be able to find a winning option, to acquire ideal batteries, whose characteristics will best provide heating for an apartment, residential building, or office.

These can be bimetal heating radiators . But what are their convenience and advantages over other heat exchangers? Let's try to evaluate everything in order.
When choosing a radiator, of course, its cost and possible service life are taken into account. But the most important feature of a heating device is the level of heat transfer.
It all depends on the physical properties of the material that forms the basis of the battery case. For example, to operate a cast-iron structure that was common in the recent past, an excessive amount of coolant is required. Its role is played by hot water. It is supplied from one side and, heating the sections, comes out from the other, this is the principle of operation of almost any battery.
Aluminum radiators, which have replaced cast iron designs on the market, although they have poor resistance to corrosion, are attractive due to their high heat transfer, at the same time they have a nice design and are easy to install.

The listed advantages also apply to steel structures, which, together with the previous type of heat exchangers, came into use in our everyday life relatively recently. But having reliability, durability, and structural stability when in contact with chemicals: acid, alkali, which serve as additives to the coolant, at low temperatures, they can create big problems.
The reason is the high thermal conductivity of this material, so the steel heating system too quickly releases both heat and cold into the surrounding space. This greatly reduces the efficiency of such radiators.
Bimetallic heating devices, created from aluminum and durable steel, as a result, have the useful characteristics of both of these materials at once. Therefore, their thermal conductivity is high, as is their durability.
A bimetal radiator will be an excellent option for solving many problems; it is suitable for homes and offices, being corrosion-resistant, constructive and compact.

Such a heat exchanger consists of vertical steel tubes, the outer coating of which is aluminum, which helps to gently regulate the process of heat transfer.
In this case, the role of coolant is, as before, water and other liquid substances; they transfer the required amount of energy to the steel base.
Harmful additives do not corrode the structure, which is protected by the properties of a substance such as steel, and do not affect the external coating, which is prone to corrosion. Next, the heat is supplied to the aluminum shell, which heats the room according to its valuable physical properties.
Having replaced cast iron batteries, which do not have a very impressive appearance, as well as other monometallic devices, bimetallic heating devices have a very attractive design and are also resistant to hydraulic and air shocks.
Initially intended for working systems with enormous pressure and low-quality coolant, they are increasingly used as individual heating devices. As can be understood from the above, using the valuable properties of a combination of metals, they significantly increase the efficiency and quality of heating the room.

Having decided to buy a bimetal radiator , when choosing it, you should take into account that it is visually difficult for a non-professional to distinguish it from purely aluminum devices. More precisely, this can be done if the device is not yet connected to the heating system.
The main visual difference between bimetallic structures is the presence of a steel core inside the body. Another indicator will be the weight characteristics of the radiator, because pure aluminum structures are much lighter.
Weight and heat dissipation
There are two stereotypes about bimetallic radiators:
- They are light and do not heat well;
- They are heavy and keep you warm.
This seems stupid
But in fact everything is true. The lighter the radiator, the less energy it can take from the coolant. Accordingly, it will release less heat into the room. And vice versa - the more aluminum in the radiator, the more thermal energy the water or coolant gives to it. And it warms better.
It's just that different people encounter different makes and models. Some options are made lightweight, but have poor heat dissipation. And some are heavy, but produce more kilowatts of heat.
Many manufacturers artificially increase the heat output of bimetallic radiators. Sometimes the numbers differ by 1.5-2 times. To know the actual heat transfer of bimetallic heating radiators, you can read the article “How many real kW of heat are in one radiator section.”
Popular manufacturers
Three manufacturers have gained the most popularity on the Russian market: Global, Sira, RIFAR.
Heating devices from Sira group appeared on the Russian market about 20 years ago. Three types of height sizes are available: 30, 50, 80 cm . Each section has two vertical channels, connected to each other using threads, which allows you to add or remove sections at any time. is required for assembly . The cost of one section is from 700 rubles.
Global offers devices with a height of 35 and 50 cm. When connecting sections, special steel nipples and paronite gaskets , which significantly reduces the possibility of leaks. An installation kit is provided with the radiators. There are several design options: Global Style is conservative, Global Style Plus is elegant, Global Style Extra is simple. The cost of one section is from 620−670 rubles (depending on height).
Sira radiators are not suitable for a house in which the heating system was installed more than 30-40 years ago, since the diameter of the vertical sections is only 5-6 mm. For older houses, Global devices with a diameter of 10 mm are more suitable.
The domestic manufacturer RIFAR recently released a new MONOLIT with non-separable channels welded into a single system. This design completely eliminates the possibility of leakage. The main feature is the ability to use coolant with a temperature of 135°C. The cost of one section is from 610−620 rubles.
Bimetallic radiators are ideal for Russian conditions. They easily withstand the abundance of impurities in the coolant and frequent, sudden pressure surges . Aluminum radiators deteriorate much faster. Steel appliances are, of course, more durable, but they are heavy and rust.
Semi-metallic radiators
Some manufacturers produce semi-bimetallic radiators. Not all of their interiors have steel or copper inserts. Most often, only vertical channels are made using bimetal technology. But sometimes cores for horizontal channels are made from copper or steel.
Semi-bimetallic radiators have worse characteristics than bimetallic and aluminum ones. Here are their differences:
- Parts of the ducts not protected by steel or copper are sensitive to temperature changes, like aluminum radiators;
- Bimetal channels give off heat worse than aluminum radiators;
- The cost of semi-bimetallic radiators is higher than aluminum ones, but they are no better.
Semi-bimetallic radiators are often passed off as bimetallic if they only have steel or copper top tubes. After all, you won’t be able to look at what the inner vertical part of the section is made of.
In the same way, aluminum radiators are passed off as semi-bimetallic. Dishonest sellers say that the vertical part is made of copper or steel, but in reality this is not the case. Again, there is no way for you to check this.
The design of bimetallic heating radiators is designed in such a way as to protect aluminum from pressure, water hammer and temperature. We hope that the article was useful to you. Don't forget to share it with your friends!
How to calculate the number of radiator sections
Thanks to a simple mathematical formula, you can make a calculation and find out how many radiator sections are needed to heat the room.
Before making calculations, you need to know the area of the heated room and the power of the radiator. The second value is indicated on product packaging or provided by radiator manufacturers in price lists.
So, to find out the number of radiator sections (A), you should multiply the area of the room (S) by 100 and divide by the radiator power (P).
A = S ×100÷ P
With a room area of 20 sq.m and a radiator power of 180 watts, we get:
A = 20×100÷180
A = 11.11
Accordingly, the number of sections can be 11 or 12. But, since radiators with a number of sections exceeding 10 heat up less efficiently, it is better to install two or three radiators with fewer sections.

Option for connecting radiators in an apartment
Specifications
The technical characteristics of batteries include dimensions. The height of radiators ranges from 20 to 80 cm. To select a radiator of the right size, you need to take into account the distance between the base of the window and the floor and subtract 20 cm from this number. The width is directly dependent on the location where the device will be installed.
Another important indicator is the working pressure, which varies between 15-35 atm. For centralized heating systems, it is better to choose the maximum values; for autonomous ones, the minimum values are also possible.
One of the most important and significant criteria affecting the efficiency of radiators is power. This indicator is determined based on the power of one section (it is indicated in the data sheet).
Types of bimetallic batteries
First of all, it must be said that not all bimetallic heating devices are made of steel and aluminum. Copper is sometimes used instead of steel. But then they are made not in sectional form, but in panel form. And they cost quite a lot, but they have excellent heat dissipation.
There are also models in which the manifold is made of stainless steel. They are suitable for networks with high pH levels, as well as for those who like to take all system components with a large margin of safety.
In a fully bimetallic radiator, the entire frame is made of steel, in some - stainless steel
The “steel + aluminum” option is the most common, and when they talk about bimetal, they usually mean it. But radiators made of these metals can be of two types: full or partial.
If inside the sections both horizontal and vertical collectors are made of steel, they speak of “full bimetal”, sometimes the name “reinforced bimetallic radiator” is also found. This is also about him. To increase the heat transfer of the section, two vertical tubes can be placed in it. This is usually done in models with great depth.

There are models with one and two vertical collectors
If only the vertical tube is made of steel, this option is called "partial" or "semi" bimetallic.