Select hot water boilers in the factory catalog
Price from 220,000
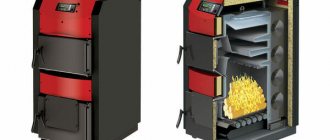
The REP boiler plant produces water-heating steel boilers with a capacity from 150 kW to 4 MW using all types of fuel: coal, wood and wood waste, gas and liquid fuel. Depending on the degree of automation of the fuel combustion process, you will also find a wide choice - manual, automatic, semi-mechanical and mechanical boilers.
Models of steel hot water boilers produced by REP Boiler Plant:
- Hot water boiler 0.15 MW;
- Hot water boiler 0.2 MW;
- Hot water boiler 0.3 MW;
- Hot water boiler 0.4 MW;
- Hot water boiler 0.47 MW;
- Hot water boiler 0.5 MW;
- Hot water boiler 0.58 MW;
- Hot water boiler 0.6 MW;
- Hot water boiler 0.7 MW;
- Hot water boiler 0.8 MW;
- Hot water boiler 1.0 MW;
- Hot water boiler 1.1 MW;
- Hot water boiler 1.16 MW;
- Hot water boiler 1.25 MW;
- Hot water boiler 1.4 MW;
- Hot water boiler 1.5 MW;
- Hot water boiler 1.6 MW;
- Hot water boiler 1.86 MW
- Hot water boiler 2.0 MW;
- Hot water boiler 2.2 MW;
- Hot water boiler 2.5 MW;
- Hot water boiler 3.0 MW;
- Hot water boiler 3.5 MW;
- Hot water boiler 4.0 MW;
Instructions for safety measures when operating the boiler
The KV water heating boiler complies with the safety requirements in accordance with GOST 12.2.096-83, GOST 12.2.003 – 91.
Before putting the boiler into operation, it is necessary to check the sound levels and sound pressure at the workplace, which should not exceed the values allowed in accordance with GOST R ISO 3746-2013
Electrical safety during operation of a hot water boiler is ensured by:
- Constructive selection and placement of electrical equipment;

- Use for control circuits voltage not higher than 36 V;
- Laying electrical wires along the frame in metal hoses;
- Reliable grounding of the boiler at the place of its installation in accordance with the ROM;
- Creating reliable electrical contact between non-current-carrying metal parts of the boiler, which may become energized if the insulation breaks down, and the grounding bolt.
Methods and means of monitoring hazard parameters:
- The sound level is determined in accordance with GOST R ISO 3746-2013;
- Electrical safety during boiler operation is controlled by checking the insulation resistance of the wires, which at an ambient temperature from 283 K (+10 ° C) to 303 K (+30 ° C) and a relative 80% should not be less than 1.0 MOhm for wires and equipment, located outside the control panel;
- Insulation control is carried out according to the PUE;
- Checking the resistance of the electrical contact between metal non-current-carrying parts of the boiler, measured by a DC bridge, should not exceed 0.1 Ohm;

- Inspection of connections of the service area and guards of rotating parts is carried out visually.
- Removal of flanges, as well as repair of boiler elements, is permitted only in the complete absence of pressure and complete removal of water from the pipe systems.
- Work inside combustion devices and gas ducts is allowed only at a temperature not exceeding 50 °C according to the permit.
- Before starting work inside the boiler, it is necessary to ventilate the combustion chamber.
- It is prohibited to carry out any repairs while the boiler is operating.
- It is forbidden to leave the boiler unattended until combustion in the furnace has completely stopped.
It is strictly prohibited:
- operation of a hot water boiler with a faulty pressure gauge;
- operation of a hot water boiler with faulty safety valves.
To avoid steam formation due to water loss from the boiler and high hydraulic resistance, the water flow through the boiler must be in accordance with the data specified in the passport.

The boiler room must be provided with sufficient natural light, and at night - with electric lighting.
Places that, for technical reasons, cannot be provided with natural light must have electric lighting. Illumination must comply with SP 52.13330.
The boiler must be operated in an area free of shadows, interference, glare and stroboscopic effects.
In addition to working lighting, boiler rooms must have emergency electric lighting.
The following places are subject to mandatory installation of emergency lighting:
- the front of the boilers, as well as the passages between the boilers, behind the boilers and above the boilers;
- switchboards and control panels;
- measuring instruments;
- ash rooms;
- fan areas;
- rooms for tanks and deaerators;
- water treatment equipment;
- boiler platforms and stairs;
- pumping rooms.
Forced circulation system
A system with forced circulation of coolant using a circulation pump does not have these disadvantages. Such piping of a solid fuel boiler allows you to ignore the hydraulic resistance of the system and use control valves to maintain optimal temperature conditions. Negative aspects also include possible power outages, which will cause the circulation pump to stop and the boiler to overheat. To avoid such troubles, you should equip your solid fuel boiler with a built-in emergency heat exchanger.
Important! It should not be overlooked that excessive regulation can lead to overheating of the boiler.
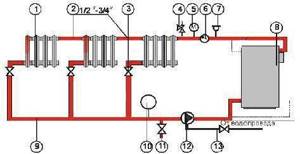
Figure 8: Forced circulation heating system
Fire up the hot water boiler
By the time of the initial or next start-up of the boiler during normal operation, prepare reserves of fuel, materials, tools and spare parts.
The firing time must be known to all boiler room personnel.
Before lighting the boiler, inspect the firebox, convective part of the boiler, air and gas paths for cleanliness, then tightly close the manholes, hatches and hatches. Inspect the outside of the boiler lining and make sure it is in good condition.

Check the serviceability of the boiler fittings, paying special attention to the sufficiency of the gland packing, the reserve for tightening the glands, and the condition of the valve stems and valves. The direction of rotation of valves, cocks, valves and dampers must correspond to the arrows on them. Adjust the safety valves, check for free passage of water from the safety valves through the discharge pipes. Make sure there are no plugs on the boiler supply and water discharge lines.
Make sure that the fan guide vanes and dampers on the gas ducts move easily, that there are position indicators for the dampers and that their drives are in good working order.
Check the tightness and cleanliness of the gas ducts, and the presence of draft. Ventilate the boiler flues for 10-15 minutes by opening all the dampers on the gas flues behind the boiler and the kindling control device, and opening the ash pan door of the combustion (ash) box.
Check the serviceability of all components of the combustion equipment and its readiness for long-term operation. To do this: remove slag and debris from the combustion grate, and ash from the combustion and turning boxes.
Fill the boiler with water: open the drain valves, the vent valves and then the valve at the water inlet to the boiler. Close the vents only after water comes out of them.
It is necessary to drain the boiler until settled sludge, dirt and other foreign matter stop coming out of the drainage system fittings.
The boiler should be fired only if there is an order written in the shift log by the boiler room manager.
Sequence of firing a hot water boiler:
- Fill the boiler with water, purge the upper and lower collectors through the air vents and drainage fittings, respectively (prepare the boiler for lighting);
- Open the valves on the water supply and drainage lines on the boiler, set the nominal water flow;
- Cover the surface of the combustion chamber with an even layer of coal 30 - 40 mm thick;
- Slightly open the damper on the boiler flue, the kindling control device and ventilate the firebox at low draft;
- Place wood on top of the coal layer and light it (without starting the fan) with the ash door open;
- Spread the wood coke formed after the wood burns out over the grate in an even layer, close the ash door, turn on the fan and give a gentle blow under the grate. The air supply under the grate should be as small as possible to ensure a normal excess in the firebox;
- As the layer of coal on the grate burns and the boiler warms up, it is necessary to gradually increase the supply of fuel and air and, successively increasing the draft and blast, to raise the load to the required level.
- Maintaining a stable draft and uniform heating of the boiler is controlled by a kindling control device - a bypass flue with shut-off and control valves and a measuring device that records the temperature of the flue gases at the outlet of the combustion chamber. When lighting up, the shut-off and control valves are moved to the “open” position, and the temperature of the flue gases in the bypass flue (200 – 380°C) is monitored according to the thermometer readings, as the boiler, flues behind the boiler and the chimney warm up, to ensure stable draft, valve are moved to the “closed” position to bring the boiler to the nominal operating mode.
If the boiler is started from reserve, make sure that there is no air in the water volume of the boiler by sequentially opening the air vents.
The boiler is fired at low heat and moderate draft.
When lighting the boiler, it is necessary to ensure uniform heating of its parts. Lighting the boiler with water supplied and a pressure that does not correspond to the data specified in the passport is prohibited.
Gravity type system
The simplest version of such piping is considered to be a gravity-type system, where water circulation occurs naturally by convection. Everything here is extremely simple, but an indispensable condition for the successful functioning of such a system is the location of the boiler at least half a meter below the water heating devices. It would be ideal to place the boiler in a basement or semi-basement.
Important! In order to operate the system safely and protect it from overheating, it is necessary to ensure that at least one of them is not accidentally disconnected from the heating radiators.
And at the top point of the room, place an open or membrane type expansion tank to ensure the uninterrupted presence of coolant in the system. It should be remembered that the higher the expansion tank is, the higher the pressure in the boiler. You should not lose sight of monitoring the water level in the expansion tank; in the event of leaks in the system and loss of liquid, the consequences can be devastating for the heating system.
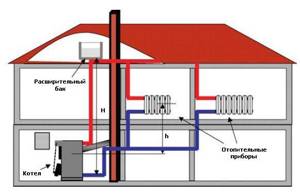
Figure 6: Heating system based on a solid fuel boiler
Boiler operation
Make sure that the water parameters correspond to the specified operating mode; do not allow them to be changed within the limits specified in the boiler passport.
The circulation in the boiler is forced. The water chemistry regime must ensure operation of the boiler without the deposition of scale and sludge on heat-receiving surfaces. Quality standards and quality control of boiler feed water must comply with the “Rules for the technical operation of thermal power plants (approved by order of the Ministry of Energy of the Russian Federation dated March 24, 2003 N 115)”, SP 124.13330.2012 SNiP 41-02-2003 “Heat networks” and GOST R 51232-98. An extract from SP 124.13330.2012 SNiP 41-02-2003 “Heating networks” with quality standards for network and make-up water for hot water boilers is presented below.
Normal values of feed water indicator
Free carbon dioxide content - 0
pH value for heating systems:
- open - 8.5–9.0
- closed - 8.5-10.5
Content of iron compounds, mg/dm3, no more, for heat supply systems:
- open — 0.3*
- closed - 0.5
Dissolved oxygen content, mg/dm3, no more than — 20
Suspended solids content, mg/dm3, no more than — 5
Content of petroleum products, mg/dm3, no more, for heat supply systems:
- open -0.1
- closed -1.0
Standard value of the carbonate index of supply water (X) when heating supply water 70-100°, (mg-equiv/dm3)2, no more, at pH values:
- not higher than 8.5 -3.2
- 8,51 – 8,8 -2,3
- 8,81 – 9,2 -1,8
- 9,21 – 10,0* -1,5
The standard value of the carbonate index of network water (X) when heating the network water is 101-120°, (mg-equiv/dm3)2, no more, at pH values:
- not higher than 8.5 -2.0
- 8,51 – 8,8 -1,5
- 8,81 – 9,2 -1,2
- 9,21 – 10,0* -1,0
* at pH of supply water above 10.0, the X value should not exceed 0.1 (mg-equiv/dm3)2
It is prohibited to use liquids such as “Antifreeze” and similar ones as a coolant.

The frequency of chemical control of the water-chemical regime of equipment is established by a specialized commissioning organization, taking into account the quality of the source water and the condition of the operating equipment.
The frequency of quality control of source, make-up and network water, as well as water at points in the distribution network of heat sources and heating networks with an open heat supply system, is determined in accordance with the requirements of sanitary standards and regulations. Based on the frequency, a chemical control schedule for the water chemistry regime is drawn up.
The choice of methods for deaerating the make-up water of a heating network, methods of preparing water for feeding boilers and making up heat supply systems, and developing water treatment technologies must be carried out by a specialized (design, commissioning) organization, taking into account the quality of the source (raw) water, the purpose of the boiler room, sanitary requirements for the coolant, requirements, determined by the design of heat-consuming equipment, safe operating conditions, technical and economic indicators and in accordance with the requirements of manufacturers.
Operation of a hot water boiler without pre-boiler water treatment is not allowed.
Before putting the boiler into operation, it is necessary to inspect the heating networks. Eliminate leaks and flush the heating system. Washing methods and methods are established by a specialized design organization, depending on local conditions.
While on duty, boiler room personnel must monitor the serviceability of the boiler and all its boiler room equipment and strictly adhere to the established operating mode of the boiler.
Detected malfunctions must be recorded in the shift log. Personnel must take immediate measures to eliminate malfunctions that threaten the safe operation and operation of the boiler.
To ensure normal operation, the operator must maintain the specified temperature of the water leaving the boiler.
Operating a hot water boiler with a closed valve on the gas duct is prohibited!
To ensure the normal process of fuel burnout in the combustion device, as well as sufficient cooling of the grate, operating the boiler without the blower fan turned on is prohibited!
Boiler performance can be adjusted by changing the amount of fuel supplied to the furnace for combustion and by changing the amount of air supplied to combustion. If there is a planned reduction in heating output, do not overload fuel into the boiler.
In the event of a power outage or poor traction, immediately scrape the coals from the grate onto the floor and fill them with water.
All boiler control and safety devices and devices must be maintained in good condition and checked regularly.
To ensure reliable operation, the water flow through the boiler and the water pressure in the boiler must clearly correspond to the parameters specified in the boiler passport!

To avoid clogging of convective heating surfaces with ash and soot deposits, the distribution of fuel over the grate should be uniform, the layer height when burning coal should be no more than 200 mm (2 - 3 diameters of a medium-fraction piece of fuel), when burning fine-grained wood waste, the layer height should be no more than 200 mm; loading of large firewood and briquetted wood waste in height is allowed up to the lower edge of the opening of the upper loading door.
To prevent the condensation of water vapor from the flue gases and, as a result, the adhesion of ash particles to the convective heating surface, it is recommended to keep the temperature of the water entering the boiler at least 55°C when operating at reduced load.
Uneven loading of fuel into the boiler furnace and variable operating modes are not allowed. This causes temporary overloads or leads to burnouts.
It is necessary to regularly purge the upper and lower boiler collectors. At least twice a shift, the lower ones through the drainage fittings, the upper ones through the air vents. When the water flow rate drops below the nominal value, it is necessary to increase the frequency of blowdowns (the lower the water supply and the lower the water pressure, the more often the blowdown). Record the time and results of the purge in the logbook.
The heat load of the boiler can vary between 50 – 100% of the rated power of the boiler. Operating the hot water boiler at a higher heat load is prohibited.
During operation of the boiler, it is not allowed to allow active combustion of the fuel in the combustion chamber under the layer grate, as well as excessive accumulation of ash and slag. This can cause deformation of the box, grates and burnout of the grates (if a grate is installed).
At least once every two weeks, inspect and clean the turntable from ash particles.

The air supply is adjusted in accordance with changes in the fuel supply, changes in the opening value of the air dampers or the guide vane of the blower fan.
With proper air supply, the color of the flame should be light straw, and the smoke coming out of the chimney should be gray.
When chemically cleaning the internal surfaces of collectors and boiler screen pipes, cleaning reagents are introduced through a fitting welded into the water supply pipeline to the boiler or through a drain fitting.
Periodically, but at least every 12 months, it is necessary to carry out a preventive inspection of the boiler and its elements. At the same time, pay special attention to identifying possible cracks, bulges, bulges and corrosion on the outer and inner surfaces of the walls, violations of the density and strength of welded joints, as well as damage to the lining. The most vulnerable areas due to unregulated combustion and violation of operating conditions are: the bottom part of the boiler; places of installation of combustion doors, doors for cleaning the convective beam, part of the screens subjected to the most intense heating, at the level of the combustion door; convective beams.
Stopping the boiler
Stopping the boiler in all cases, except emergency, should be carried out only upon receipt of a written order from the administration.
When stopping the boiler, it is necessary to stop the fuel supply to the furnace. Turn off the blower fan and smoke exhauster only after the fuel has completely burned out.
It is forbidden to leave the boiler unattended until combustion in the furnace has completely stopped.
Emergency stop of the boiler
Boiler room maintenance personnel are obliged to immediately stop the boiler if the following emergencies occur:
- The pressure has risen above the permitted value on the boiler and continues to increase;
- Cracks, bulging, leaks, sweating, etc. were found in the main elements of the boiler;
- The power supply has been interrupted;
- A fire has occurred in the boiler room, which threatens the life of operating personnel or the safety of the boiler.
- The water supply has fallen below the permissible values according to the boiler data sheet.
If it is necessary to emergency stop the boiler, turn off the fan and remove the burning coal from the grate with a scraper. Being careful, fill the coal thrown from the grate with water, turn off the smoke exhauster, remove the voltage from the control panel, and then reduce the water flow through the boiler; if necessary, stop the water supply by completely closing the shut-off valves at the inlet and outlet.
The reason for the emergency stop must be reflected in the shift log.
If damage or malfunctions of the boiler and auxiliary equipment occur that do not require immediate shutdown of the boiler, maintenance personnel are obliged to immediately notify the administration.
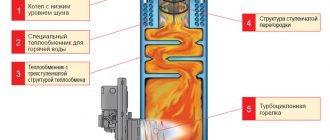
Advantages and disadvantages

The advantages of long-burning boilers include:
- efficient use of the combustion chamber - this is achieved due to the fact that the fuel inside the unit does not burn, but slowly smolders;
- high efficiency, which for some samples is close to 85%;
- significant volumes of the loading chamber;
- ability to work on one load of solid fuel for more than 12 hours;
- the ability to concentrate heat within the boiler, allowing it to heat large spaces.
In most KDG models, up to 50 kg of fuel can be loaded at a time, so owners of boiler products are freed from the need to constantly add firewood to the firebox.
There were no complaints from users regarding the operation and quality of the equipment. The only problem when deciding to purchase it is the high cost of the heating complex - from 100,000 rubles. If you purchase a not very prestigious and cheap unit, no one can guarantee the high quality of work of such a “stove”.
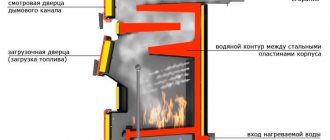
Internal cleaning of hot water boilers
The operation of a hot water boiler must be accompanied by regular, at least twice a shift, removal of sludge from the boiler. To do this, open the valves on the drainage fittings and drain the water until the settled sludge stops coming out of the drainage system fittings. In this case, the system's makeup must be turned on.

Cleaning of internal heating surfaces from scale should be carried out chemically with the involvement of a specialized organization.
Clean internal surfaces between heating seasons. If the boiler operates all year round, clean the internal surfaces at least once a year.
In the boiler room, it is necessary to keep a log (statement) on water treatment and the water-chemical regime of boilers to record the results of analyzes of water, steam, condensate, reagents, on boiler purging and maintenance operations of water treatment equipment in accordance with the approved regime map and the frequency of chemical control. Each time the boiler is stopped to clean the internal surfaces of its elements, a description of the physical and mechanical properties and thickness of deposits, scale and sludge is made in the water treatment log.
Cleaning convective heating surfaces from soot deposits
When burning organic fuel (coal) in boiler plants of any capacity, issues inevitably arise in cleaning heating surfaces from external ash and soot deposits.
Contamination of the external heating surfaces leads to: an increase in the temperature of the flue gases, the aerodynamic resistance of the gas path and, as a consequence,
- to a decrease in the productivity and efficiency of the boiler unit;
- to excessive fuel consumption,
- increasing costs for own needs,
- deterioration of environmental indicators due to overestimation of thermal emissions and nitrogen and sulfur oxides, in the latter case due to a violation of the aerodynamics of the combustion space.
- After 3000 hours but not later than 6000 hours of operation of the hot water boiler, monitor the operation of the gas-air duct of the boiler installation according to the readings of the control and measuring instruments. In the event of a decrease in the vacuum in the combustion chamber or loss of the developed pressure of the smoke exhauster, the boiler should be stopped to carry out work to clean the boiler flues and chimney from settled ash and soot.
Clean the convective part of the boiler by washing with cold water or blowing with compressed air using a compressor until the heating surfaces are completely clean.
Operation of hot water boilers after washing with water begins only after the thermal insulation of the convective part has completely dried.
How to properly install supply and exhaust ventilation
There are several objective reasons why ventilation in the boiler room is necessary:
- supplying a sufficient amount of oxygen to the boiler to maintain the combustion process;
- removal of carbon monoxide that accidentally entered the room from the furnace outside the premises;
- compensation of the amount of air used during the combustion process.
Please note that to burn 1 kg of firewood you will need 4.6 m3 of air, and burning coal requires about 8-9 m3, based on the quality of the fuel.
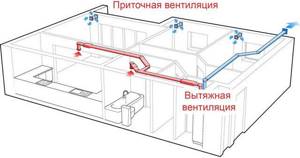
- Openings for air inflow and outflow should be located on different sides of the boiler room. The supply opening is made at the bottom of the wall as close as possible to the heat generator, and the exhaust opening is under the ceiling.
- If the boiler is equipped with a smoke exhauster or a blower fan, you should not place the hood next to it (read: “How to choose a smoke exhauster for a solid fuel boiler - types, differences”). Otherwise, the draft will reverse, and the exhaust hole will become a supply hole.
- If the door from a residential building opens into a furnace room, then it is advisable to install a grille for the inlet opening in the door leaf. Warm air entering the boiler will improve the combustion process.
- The size of the exhaust opening should be smaller than the supply opening, since most of the incoming air enters into a thermochemical reaction and exits through the chimney in the form of CO2.
You can calculate the required size of the hood if you multiply the boiler power by 8 - we get the hole area in cm2.
Hot water boiler maintenance
Check the tightness of the boiler lining once a week.

At least once a shift, check the operation of the safety valve by manually lifting the levers until water appears from the flow line.
When stopping the boiler at the end of the season, you should drain the water from the boiler, rinse, clean the boiler of dirt and scale, the flues of ash and soot, then fill the boiler and system with water, removing remaining air through the air valve. Completely clearing the combustion chamber, rotary box and grate from slag and ash.
The water heating boiler must be subject to technical inspection by the administration before being put into operation, periodically during operation (according to the established deadlines) and, if necessary, ahead of schedule.
Technical inspection of boilers must be carried out by a person responsible for the good condition and safe operation of the boiler.
External and internal inspections are aimed at:
- during the initial inspection, establish that the boiler was manufactured, installed and equipped in accordance with the “Rules for the design and safe operation of steam boilers with a steam pressure of not more than 0.07 MPa (0.7 kgf/cm2), water heating boilers and water heaters with a water heating temperature not above 388 K (115 °C)” approved by the Ministry of Construction of Russia on August 28, 1992 and the documents submitted during registration, and also that it and its elements are in good condition;
- during periodic and extraordinary inspections, establish the serviceability of the boiler and its elements and the reliability of its further safe operation.
- During external and internal inspections of the boiler and its elements, attention should be paid to identifying possible cracks, tears, bulges, bulges and corrosion on the internal and external surfaces of the walls, violations of the density and strength of welded joints, as well as damage to the lining, which can cause overheating of the metal elements boiler
Hydraulic testing of boilers is aimed at checking the strength of the boiler elements and the tightness of their connections and is carried out in the manner established by paragraphs. 3.16 and 3.17 “Rules for the design and safe operation of steam boilers with a steam pressure of no more than 0.07 MPa (0.7 kgf/cm2), hot water boilers and water heaters with a water heating temperature not higher than 388 K (115 °C)” approved by the Ministry of Construction of Russia 08/28/92
The administration is obliged to carry out inspections of boilers within the following periods:
- external and internal inspections - after each cleaning of internal surfaces or repair of boiler elements, but not less than after 12 months;
- hydraulic test with working pressure - every time after cleaning internal surfaces or repairing boiler elements;
- hydraulic test with test pressure - at least once every two years.
Early (extraordinary) technical inspection of the boiler must be carried out in cases where:
- the boiler was inactive for more than a year;
- the boiler was dismantled and installed in another place;
- bulges or dents were straightened, as well as repairs using welding of the main elements of the boiler;
- more than 50% of the total number of screen pipes were replaced at the same time;
such inspection is necessary at the discretion of the person responsible for the good condition and safe operation of the boiler.
Before hydraulic testing, external and internal inspections must be carried out.
Before internal inspection and hydraulic testing, the boiler must be cooled and thoroughly cleaned of scale, soot and ash. If there is any doubt about the good condition of the walls or seams, the person responsible for the safe operation of hot water boilers must open the lining or remove the insulation in whole or in part.
If during the technical examination of the boiler no defects are found that reduce its strength, operation of the water heating boiler is allowed under operating parameters.
If, during a technical examination of the boiler, it turns out that it has defects that cast doubt on its strength, further operation of such a boiler should be prohibited until these defects are eliminated.
The results of the inspection and the conclusion on the possibility of operating the boiler, indicating the permitted parameters (pressure, temperature) and the timing of the next inspection, must be recorded in the boiler passport by the person performing the inspection.
During an early inspection of the boiler, the reason that necessitated such an inspection is indicated.
Technical inspection of the boiler consists of external, internal inspections and hydraulic testing.
Natural circulation system
If you have chosen a system with natural circulation, it is necessary to minimize all hydraulic resistance in the path of the coolant, minimize all corner and elbow elements and ensure that the diameter of the pipeline is maximum. Systems with natural coolant circulation are good due to the simplicity of their design and independence from the power supply, but their disadvantages include relatively high fuel consumption and the difficulty of maintaining optimal thermal conditions in a heated room.
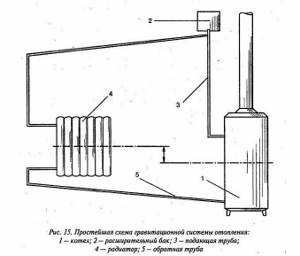
Figure 7: Natural circulation heating system