Don’t forget to drain the water from the summer water pipes at your summer cottage before winter. This process is simple, until the first frost.
Tips for preparing your pipeline for winter:
- The pump must be carefully removed from the well and preserved for the cold period;
- With a storage system in a container, you need to open a special drain valve.
- In places where water is consumed, you must also turn the tap valve to the open position.
- Blow out the pipeline to remove residual water (detailed instructions).
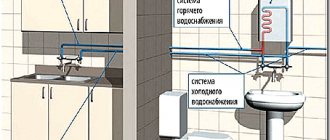
An example of drainage in the presence of a centralized water supply for a dacha
How to drain water from a hydraulic accumulator for the winter
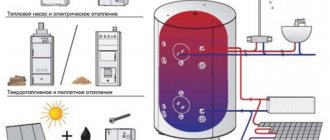
A hydraulic accumulator (hydraulic tank) is a metal container designed for connection to water supply pumps, inside which a reserve amount of water is stored at a given pressure.
By equipping the pump with a hydraulic accumulator, you will always have a small supply of drinking water in your house, even in the absence of electricity. In this article we will look at a hydraulic accumulator for water supply systems, study its purpose, design and principle of operation.
You will also learn about the types of such equipment, the features of its selection, calculation and connection.
Treat basement and cellar for mold
The end of the summer season is the right time to treat the cellar and basement so that a “mold kingdom” does not develop in them over the winter. First of all, in dry weather, take all the jars outside and dry the room, and then treat the walls and other structures with an antiseptic (this procedure must be repeated every few years).
As an antiseptic, you can use a solution of copper sulfate (100 g per 1 liter of water).
Those who like to solve problems in a radical way recommend using a sulfur smoke bomb to treat the basement. Seal all ventilation holes in the empty room, cover metal parts (if any) with polyethylene. Check that there is no one in the house (you will have to leave it for a day), and then light the fuse of the checker, go out and close the doors tightly. Upon return, thoroughly ventilate all areas.
Purpose, device, principle of operation
First, let's clarify the terms - the hydraulic tank and expansion tank are not the same devices. A hydraulic accumulator is used in water supply systems of a private home, designed to supply water using a pump from an external source, while an expansion tank is installed in heating and hot water supply systems in order to stabilize their pressure and prevent the occurrence of water hammer.
Let's consider the main functions of a hydraulic tank in water supply systems:
- the device prevents wear and tear on the pump due to frequent activation - since the tank constantly contains water, the pump will only start when it is empty, which will have a positive effect on the durability of the unit;
- the hydraulic accumulator reduces the likelihood of water hammer occurring in the pipeline when the pump is turned on; it also maintains stable pressure in the system, preventing pressure fluctuations when several taps are used simultaneously;
- The tank provides a constant supply of water, which is especially important in country houses with problematic power supply.
Pumping station with hydraulic accumulator
The hydraulic tank device consists of a metal tank itself and a membrane located inside it, which divides the tank into two chambers - one for water, the second for air. The water chamber is made of butyl, a sanitary-safe type of rubber; the liquid stored in it does not come into contact with the metal walls of the tank. Water is supplied and drained through two threaded pipes to which pipelines are connected; the pipes have identical diameters.
A pneumatic valve is responsible for regulating the pressure in the air chamber. Large volume hydraulic accumulators (100 liters and above) are equipped with a check valve, which is needed to bleed air from the water chamber. A similar function in small tanks is performed by a shut-off valve. The standard air pressure in the hydraulic accumulator is 1.5-2 Bar.
The operating principle of the hydraulic tank is quite simple. Initially, the pump pumps water into the tank, and when the storage tank is filled, the pressure switch detects this and turns off the pump, stopping the supply. Then, as the water reserve is used, the relay detects a decrease in pressure, turns on the pump and the cycle repeats.
Types of hydraulic tanks and features of their calculation
Depending on the shape of the body, this equipment is divided into two types - horizontal and vertical hydraulic accumulator. There is only one design difference between them - vertical tanks with a volume of more than 50 liters are equipped with a valve to bleed air, which accumulates in the water chamber and reduces the efficiency of the device. In horizontal tanks with a volume of 50-100 liters, the tap is located in the end part on the side of the body.
In all hydraulic accumulators with a volume of less than 50 liters, air is bled from the water chamber by completely draining the water. The shape of the tank is selected based on the size of the room where it will be installed. There are no tricks here - you need to take the tank that best fits into the space allocated for it.

More difficult is choosing a tank based on performance parameters. Here you need an equipment calculation that will help determine its required volume. The calculation is performed using the formula: O = K*Rmax*(Dmax + 1)*(Dmin+1)/(Dmax-Dmin) - (P + 1), in which:
- K is the power coefficient of the pump connected to the hydraulic tank;
- Rmax - the highest planned flow rate of liters of water per minute;
- Dmax — water pressure level in the tank to turn off the pump (Bar);
- Dmin — water pressure limit for turning on the pump (Bar);
- P - air pressure in the hydraulic tank (Bar).
The pump coefficient depends on the power of its engine:
- power 0.55-1.5 kW - coefficient 0.2;
- 2-3 kW - 0.375;
- 4-5.5 kW - 0.625;
- 5-9 kW - 0.875.
Calculation of almost any hydraulic accumulators for domestic water supply stations will show that it is necessary to use a tank with a volume of 25-50 liters. This is the optimal volume for most pumps for wells and wells, which will be enough for a complete water supply for a private home.
Connection diagrams and installation features
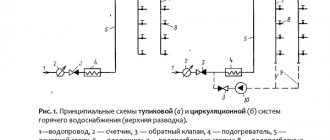
The choice of hydraulic tank connection diagram must be made based on the functions assigned to it. There are 3 connection schemes in total:
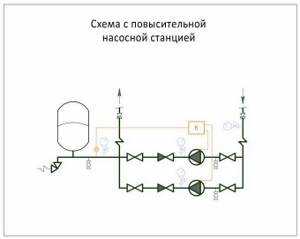
- Diagram of hydraulic tank + booster station. In this case, the hydraulic accumulator is used to stabilize pressure in systems with high levels of water consumption.
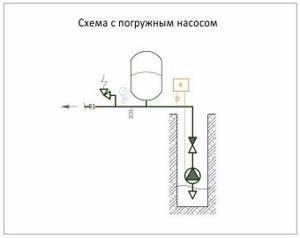
Scheme of hydraulic tank + submersible pump. The most common connection method in systems based on water supply by a pump from an external source.
Reverse circuit: hydraulic tank + booster pump. The hydraulic accumulator is mounted before the booster pump, and not after it, and prevents pressure surges in the pipeline when the pump is turned on.
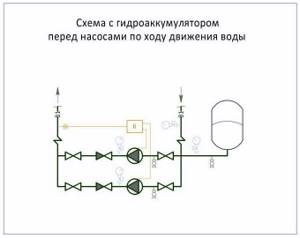
To connect the hydraulic tank and put it into operation, you do not need to call specialists; you can do everything yourself. The tank is attached to the floor or wall using anchors; however, it is necessary to place a spacer made of vibration-isolating material under the mounting plate. The pipes are connected to the branch pipe of the storage tank through special flexible adapters that come with it.
After the installation of the tank is completed, it is adjusted - first you need to determine the pressure in the accumulator, which can be done using a conventional pressure gauge. On the tank body you will find a spool to which the meter is connected. The normal pressure level is considered to be 1.5 Bar; if its actual value differs, then it is necessary to pump up the air using a pump.
Chemical flushing of the system when needed and how to do it
The frequency of chemical flushing depends on the quality of the water used.
Many people do not flush the system at all; in the case of a special coolant, this is normal practice. But the use of water is associated with the formation of scale and other deposits, which reduce the efficiency of heat transfer and significantly increase fuel consumption. Flushing the system is carried out using a special pumping unit, which can be rented for a while. The system is washed with a special solution of cleaning chemicals, which is selected according to the type of pipes, radiators and heat exchanger material in the boiler. In special cases, the boiler is washed separately.
When flushing, it is important to close the taps of all auxiliary equipment: expansion tank, pumps, bleed valves, etc.
At one point, the pipeline ring must be closed, and on both sides of the valve there are pipes for connecting flushing hoses.
Flushing is carried out in two stages: first, the system is pumped with a chemical solution for 40-60 minutes, then the chemical is washed out with clean water several times.
Draining water from pipes for the winter
I plan to dig a well at the dacha and make a normal water supply for the house. Now we have a summer water supply (common well) - water is released in May and drained in the fall. I'm tired of it - I want to come in the fall, winter and spring and at the same time be able to properly wash the dishes and take a shower. Pipes under the foundation have already been installed into the house (polypropylene). Buried underground at a freezing depth (1.5 meters).
But there are a lot of questions. I don’t live in the country all the time. I mostly go there on weekends.
For example, winter, temperature -15 degrees. Let's imagine that there is already a well and everything is connected, but the water has not yet been let into the house. Of course, by the time I arrived, the whole house was frozen. I start heating - for example, after a few hours the house is already warm, + 20. That is. You can now give water. I supply water from a well (there is a submersible pump), the hydraulic accumulator is filled, everything is fine.
I stayed at the dacha for several days - and here the problem arises of how to drain the water from the entire system, because when I leave, the house will completely cool down. It is clear that the pipes are buried at freezing depth - and the water will not freeze there. But what to do with the water that is in the pipes inside the house? When the house cools down, all the water will freeze and the pipes will burst.
What solution do I see? The hydraulic accumulator should not be located in the house, but somewhere on the street and buried at freezing depth. Its control should be somehow displayed in some kind of panel, to which I will have easy access. Also, next to the hydraulic accumulator there should be some kind of device (I don’t know if there are any in nature), which, when turned on, pushes all the water out of the pipes in the system (of course, with the taps open) under air pressure. Those. This is not just a compressor, but some kind of device through which water passes. I understand that if you have access, you can connect a compressor to the tee and just blow everything out, but it will all be buried at 1.5 m - I wouldn’t want to constantly climb there. Those. in fact, it turns out that in the winter, before leaving, I turn off the hydraulic accumulator, open all the taps, turn on this device that blows all the water out of the pipes, then turn everything off and calmly leave, not thinking that there is water left in the house. It all comes down to simply pressing buttons.
Is it even possible to do this in my situation? Or am I approaching the solution to my problem incorrectly and there are already ready-made solutions?
Preparation of siphons for washbasins, sinks, sinks.
If you have a plastic sewer system and, accordingly, plastic siphons, then theoretically you can not prepare them for winter. The water plug in plastic siphons is small in volume, plastic has higher thermal insulation properties than metal or ceramics, in addition, plastic can be slightly deformed, so usually the water that does not have time to evaporate from the siphon before frost freezes a little slower than in ceramic the toilet bowl or cast iron elbow and turning into ice, the siphons do not break.
We invite you to familiarize yourself with Soil for tomato seedlings
If you have cast iron siphons, then it is necessary to remove water from them for the winter. This can be done in several ways, for example, using a kvak (plunger) to push water from the siphon further along the pipe. If you don’t have a plunger, you can try blowing it out with a bicycle or car pump, or carefully insert a cloth between the drain grate and gradually soak up all the water.
I have been using these technologies for 15 years now and so far everything is reliable. And yes, do not forget to drain the water from the tank. One of my friends did everything correctly, but did not drain the water from the tank. When the frost came, the seal of the gasket in the tank was broken, the water flowed into the bowl and froze there. As a result, the toilet had to be replaced.
I hope, dear reader, the information presented in this article has helped you at least a little understand the problem you have. I also hope that you will help me get out of the difficult situation I recently found myself in. Even 10 rubles of help will be of great help to me now.
I don’t want to burden you with the details of my problems, especially since they are enough for a whole novel (at least it seems so to me, and I even started writing it under the working title “Tee”, there is a link on the main page), but if I’m not mistaken in your conclusions, then there will be a novel and you may well become one of its sponsors, and possibly heroes.
For terminals, Yandex Wallet number 410012390761783
For Ukraine - hryvnia card number (Privatbank) 5168 7422 0121 5641

Webmoney wallet: R158114101090
User rating:No
The role of the hydraulic accumulator in the water supply system
The hydraulic accumulator reduces the frequency of switching on an important component of the water supply system - the hydraulic pump. The electric motor is subject to minimal wear, thereby increasing its service life.
Another important property is the volume of the hydraulic tank.
It has a reserve of liquid in case of a pump or power outage or in case of breakdowns of the water supply system. This function is convenient for its use in suburban areas where there are problems with power supply. The hydraulic accumulator protects the water supply system from water hammer that occurs when the pump is turned on and maintains the required level of pressure in the pipes.
Draining the remaining water from the accumulator
Before carrying out repair work on this device, it is necessary to arrange for the remaining liquid to be drained from the tank. This process is carried out in different ways depending on the design features of the hydraulic tank. Some device models are equipped with a drainage mechanism. When it is opened, the accumulated liquid is quickly drained.
If the hydraulic tank does not have such a function, use the threaded method to connect the device to the pipes. Using an “American” fitting is the most convenient way. The presence of such a unit in the water supply system allows you to remove the hydraulic tank to drain the remaining water and subsequent repairs. Before draining the water from the accumulator, the electric pump is de-energized.
The next action is to open any water tap of the system and disconnect the water supply pipe to the hydraulic tank.
After this, the drain itself is carried out. This sequence of actions will ensure the safety of stopping the water supply system. The accumulated water is drained in the following cases:
Water is drained from the hydraulic tank in various cases
- Before repair work. They can be caused by a violation of the integrity of the storage tank, loss of tightness of rubber gaskets.
- After a long period of system stagnation. Draining is carried out before fresh water is supplied.
- Preservation of the system for the winter. A necessary operation to protect the integrity of the tank.
- Failure to organize water drainage in winter leads to freezing of water inside the hydraulic accumulator and increases the risk of its breakdown.
The tightness of the safety membrane plays an important role. It separates the air and water chambers. The integrity of the membrane is difficult to determine. The operation of the system does not change if it is damaged. But when frost sets in, the membrane that has lost its integrity is completely destroyed.
After draining the accumulated fluid, the accumulator is pumped. The air cavity becomes accessible after removing the membrane. After removing it, make sure that there is no water in the air compartment. Inspect the tank walls for corrosion. Its presence is a sign of a violation of the membrane tightness. The tank is dried and the damaged area is cleaned. There is no need to inspect the water tank. It is made of a thick layer of rubber.
Construction of the caisson
If you want and have the opportunity to install a water supply system according to all canons, then you need to build a caisson. It will allow you to deepen the well to the freezing point.
Manufactured in different forms. Round ones are suitable for constructing wells. Caissons are made from concrete, metal or polypropylene. A unit made of polypropylene is the easiest to install; you can install it yourself, with your own hands. In terms of price, plastic caissons are cheaper than metal ones, but the most durable ones can cost tens of thousands of rubles. The cheapest ones are made of concrete rings. Installation includes preparing a pit, installing a container, installing the appropriate equipment in it, and setting it up. A hatch is installed on top. The caisson also serves to protect the well from the penetration of groundwater and rainwater.
Preserving a well for the winter will make it possible for it to remain clean during the winter and ready for use by the beginning of the spring season.
Video

Sometimes land owners try to find out whether it is possible to leave the pump in the well for the winter. There is no exact plan of action, because... it all depends on the type of pumping equipment, its installation method and the nuances of operation.
If the well pump is planned to be used in winter, the well should be insulated.
Installing a new accumulator membrane
If water is detected in the air compartment, urgent measures are taken to replace the membrane. It serves as a fuse between the two main components of the device, the storage and air chamber. To get to the membrane, unscrew the flange with the water supply fitting. The membrane is removed. The tank is dried and a new part is installed.
During installation, sealants are used. They coat the area of contact between the flange and the membrane. This allows you to organize the correct operation of the water supply system, protecting the tank from loss of air pressure through an unprotected joint. After all the work has been completed, the hydraulic accumulator is connected to the water supply and drainage pipes. If the membrane is replaced not before the winter period, the device begins operation.
Myth 1. The hydraulic accumulator is designed to maintain constant pressure in the water supply system.
This phrase can be found quite often in descriptions of hydraulic accumulators. Variations - the hydraulic accumulator creates constant pressure, etc.
Let's start with the fact that a membrane (rubber bulb) in a metal casing is simply not able to create any pressure, either constant or “variable”. The pressure is created only by the pump. Whatever pressure the pump provides, the same pressure will be in the accumulator. The only thing that can be said is that the hydraulic accumulator, in the absence of water flow, maintains the pressure created in it and contributes to its smooth decrease with the start of water collection and a smooth increase after closing all the taps. Those. without it, the pressure would change instantly, but with it it changes smoothly, due to a change in the hydraulic volume by stretching and compressing the membrane. This is the main point of using it. For the correct functioning of the system with the ubiquitous pressure switch, a smooth change in pressure is required, which is ensured using a hydraulic accumulator.
There is no need to talk about constant The whole point of the functioning of such a system comes down to the fact that the pressure is constantly changing, due to which the operation of the pump is automated using a pressure switch. There can be constant pressure only with a constant flow rate, but as soon as the water flow rate changes (an additional tap is opened or closed), the pressure instantly changes. All that a hydraulic accumulator can do is to give the system inertia, which is what is actually required of it. Constant pressure in systems with variable flow can only be achieved by using a frequency converter, when the pump rotation speed changes depending on the water flow.
Myth 2. The larger the volume of the accumulator, the better.
So much the better for what? For the accumulator itself, for system reliability, for the pump? A large-volume hydraulic tank is more expensive, takes up more space, and the cost of replacing the membrane is higher. Only disadvantages.
But there is a certain logic in the statement and it lies in the following: the larger the volume of the hydraulic tank, the less often the pump will turn on. And the less often the pump is turned on, the longer it will work, since the service life will be preserved (the electric motor starting mode is the most intense - a jump in the starting current, high starting torque, increased load on the pump parts).
However, on the other hand, it is logical to assume that there is a certain limit on the volume of the accumulator at which it is necessary to stop. After all, it never occurs to anyone to buy a hydraulic accumulator with a capacity of thousands of liters for a private home. Although with such a tank the pump may turn on only once or twice a day or not turn on at all. Do not forget that the useful volume of the hydraulic accumulator is about 30%.
The misconception is that even if we reduce the number of pump starts per hour by half (increasing the volume of the accumulator), the pump will not last twice as long. Even knowing the number of starts per hour, we cannot estimate the total operating time in each cycle, which is much more important for the resource. Likewise, if you only use the pump for six months, for example, during the summer season, you do not need to expect that the pump will last twice as long as that of your neighbor who uses the pump all year round.
Prepare your lawn for winter
One of the weak points of a dacha that is unheated in winter, or more precisely, a dacha where no one lives in winter, is the sewer system, of course, if there is one.
The fact is that even if no one uses the sewer system in winter and the sewer pipes are laid with the correct slope, then there is still water in the siphons and elbows, the so-called water plug.
The purpose of the water plug is to keep odors and gases from the sewer out of the house. This very necessary and useful quality in summer can turn into harmful in winter. Because water, due to its physical properties, expands when it freezes and can damage siphons and elbows.
The first step is to clear the lawn of debris. A layer of fallen leaves or branches will inhibit photosynthesis and can also provide an excellent home for pathogens and pests. The lawn also needs to be mulched to preserve the sown grass and reduce moisture evaporation. Don't forget about cutting the grass - this procedure in the middle zone can be carried out until the end of October.
In the first half of October, do not forget to feed the lawn with phosphorus-potassium or special autumn lawn fertilizer (according to the instructions). If holes and bald spots have formed on the cover, they need to be “patched” by adding soil and sowing seeds.