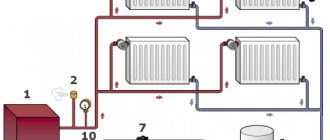
What speed should I set on the heating pump at low boiler power?
Adjusting the power of the circulation pump is usually carried out in order to increase or, conversely, reduce its performance . The higher its speed, the faster the hot water passes through the pipes and the more heat it gives off. In turn, the lower it is, the slower the liquid passes through the system, the faster it cools and, accordingly, the heat transfer will be less.
The minimum power of heating equipment is set mainly in the spring . At this time, it is already quite warm outside, but the house itself does not warm up enough and there is a need for a little heating of the room.
Pump speed modes may vary depending on the model and configuration. On average, the minimum is 30-35 l/min , the maximum is 80-90 l/min .
Why do you need to check the settings?
To ensure maximum performance of the device, before using it . This is done, as a rule, according to two parameters.
Noise insulation. There are several reasons why a heater may make a lot of noise:
- incorrect installation;
- air in pipes;
- voltage fluctuations;
- device malfunction.
To avoid these problems, it is better to entrust the installation to a specialist who will carry out comprehensive diagnostics and ensure the correct installation and functionality of the device.
Uniform heating. The main reason for uneven heating of radiators is insufficient power. Low speed contributes to the rapid cooling of the water, as a result of which the heat simply does not reach the end of the system.
Airiness or an incorrectly selected thermostat mode also leads to a similar problem . May affect the performance of the device and improper installation . This is especially true for aluminum and bimetallic batteries, which must be installed as level as possible.
controlled pumps for heating systems
controlled pumps for heating systems
Post by svr007 » 20 Nov 2021, 12:57
Good afternoon. I decided to create a topic here parallel to this one viewtopic.php?f=33&t=5708, since it is not entirely correct to ask questions about hydraulics in that topic. And so, at the beginning of the system design, it was planned to install UPS pumps; in the process, pumps of the new ALPHA 1L line were purchased, at a price almost UPS. ALPHA 1L pumps can be controlled (change power and performance) using an external PWM signal. The hydraulic circuit is standard: a priority boiler, a 4-point manifold with a hydraulic arrow, zonal manifolds for a radial circuit with electric valves (radiators and TP) so far 2 on the first floor. External automation on an industrial PLC.
Due to the installation of pumps of a new series, the proposed automation algorithm changes radically. I ask for criticism on plans for adjusting CO, including through hydraulics. And so here we go: 1. Adjustment of supply T through the boiler street sensor 2. Control of the boiler pump arrows with a PID controller using the Tpod and Tobr delta, so we will try to optimize the operation of the boiler with variable flow in the circuits. 3. Control of the pumps of the radial collectors is also a PID controller based on the delta Tpod and Tobr, so we will achieve control of the power of the heating devices by supplying the amount of coolant. Delta T will be variable, depending on the required heating rate. 4. Turn off radiators when the required room temperature is reached.
controlled pumps for heating systems
Post by Erik » 20 Nov 2021, 14:14
Of course, you didn’t ask anything, but if the topic is “for discussion,” then
1. Using the external temperature sensor, let the circuit mixers operate. Each on their own curve, if necessary. And the boiler must be able to produce the maximum output at the command of the automation system, regardless of the weather outside. If, for example, you switched the mode from “away” to “comfort” an hour before returning from work, and you want the house to heat up in an hour.
2. In my opinion, it is more correct to control the boiler pump not by temperature, but by the power of the consumer pumps. To equalize the flow rates in the boiler circuit and the consumer circuit. Plus. Turn on whenever there is a heat request. Turn off after a specified time after turning off the burner.
3. You have 3 controls for each heater. The fluid temperature set by the mixer, the loop solenoid valve, and the pump speed. A large difference between the set and actual temperatures is processed at maximum speed and adjusted by the mixer until it reaches the deviation limit of 1 degree. After this, the pump control is activated. When there is one pump for several loops, then two options are possible - either speed control is proportional to the number of open loops on the collector, or by temperature. Based on temperature, the speed is usually adjusted from 0 to 100% in the range of 1 degree to the set value. Less by a degree - 100%. The closer to the desired temperature, the slower. If there is only one loop, you can dispense with the valve. If there are several, they operate at the minimum temperature. But solenoid valves cause confusion. When, for example, 3 out of 4 loops on the manifold are closed, the entire flow velocity will rush into one open loop. But the confusion is more purely mathematical, because from the point of view of comfort, it is impossible to notice the difference due to the large inertia.
4. Yes. Turns off three times. First, the mixer is set to 0, turning off the supply of hot liquid to the circuit. Then the valve, then the pump. This is if there is no thermostatic valve installed on the radiator itself. It could be the fourth time he switches off.
If the room has both radiators and heated floors, you can adjust the difference so that the radiators turn off 2 degrees before the set temperature, and then the floor extends. Then, if the floor suddenly stops working (for example, in cold weather, due to the limitation of the maximum floor temperature), the radiators turn on and help. And when switching modes for quick heating to a comfortable temperature.
How electronically controlled circulation pumps should work
Models with electronic heating type have two types of speed control: manual and automatic. Manual regulation involves setting the power of the device at the desired level. In this case, pressure drops are not corrected.
Photo 1. Control circuit for the DAB EVOSTA circulation pump with electronic control. Selecting the operating mode is done with one button.
In the case of automatic control, the reduction or increase in speed is carried out by the system itself and directly depends on the temperature in the pipeline. The autopilot itself determines the optimal level of performance and, if necessary, reduces energy consumption without reducing productivity.
Important! Automatic reduction of pump speed is only possible after hydraulic balancing of the system.
Recommendations for installing pumps
When installing pumps in the heating main, the following rules must be observed:
- The unit is installed in such a way that its shaft is in a horizontal position; the direction of movement of the coolant must correspond to the arrow on the device body.
- The selected device is fastened with an adjustable plumbing wrench using threaded fasteners (socket nuts from American fittings) with gaskets.
- Connection to the power supply system is made according to the electrical connection diagram, using three wires with a cross-section of at least 0.75 mm. sq. and an outer diameter designed for the sealing coupling in the box.
Before turning on for the first time, check the pipeline for the absence of foreign objects, the tightness of threaded connections, the correct connection of wires and the parameters of the power supply network, and make sure that the shut-off valves are open.
When turned on, remove air from the pump by unscrewing the screw plug, check the current strength in the electric motor winding with an ammeter (it must correspond to the data given on the housing marking), and make sure that there is no increased vibration and noise during operation of the unit.
Rice. 16 Connection and installation of a Grundfos circular distributor with a bypass branch
A change in temperature outside is a reason to turn on a different speed
The presence of several modes in the heating pump will allow you to adjust the heating level in a particular room . This function is important when there is a sharp change in temperature outside. In this case, the device can be manually switched to the required power or the autopilot can be turned on, and the system itself will adjust to the desired temperature.
Actually, according to the subject, the question is. At what speed of the central heating system will gas consumption be minimal and heat transfer to the radiators will be maximum? AOGV boiler 23 kW, radiators - M140 cast iron, 7 pieces of 10-12 fins each, system - Leningrad, no regulators on the radiators. The power consumption of the boiler is about 6-8 kilowatts according to the gas meter (constant low flame). The chimney is not very hot, the hand holds it.
alexposter wrote: is the heat transfer to the radiators maximum?
at maximum speed
300 liters per hour.
But at maximum speed, gas and electricity consumption will be maximum. And in Lviv the temperature usually does not drop below -5 degrees. So, to save gas, you need to debug the automation on the boiler.
Yann: - I understand. The higher the speed of movement of the coolant in the system, the more uniform the temperature distribution in the system, and therefore the more uniform the heat transfer. How will pump speed affect gas savings? So I don't have any pump at all. There are no miracles. You need to spend 1 m3 of gas to produce 10 kW of heat. This is how you spend it. You need to spend 8 kW of heat on your area, and you will spend it. And in order to use less gas, you need to reduce the heat loss of your home. And in order to reduce heat loss from your home, you need to insulate it. Or resort to alternative heat sources.
viktor48 wrote: But at maximum speed, gas and electricity consumption will be maximum. And in Lviv the temperature usually does not drop below -5 degrees. So, to save gas, you need to debug the automation on the boiler.
We have a limit - a maximum of 90 km / h, I think in Lviv (by the way, how is your bus plant there? What does it produce?) the same rules
Yann wrote: The higher the speed of movement of the coolant in the system, the more uniform the temperature distribution in the system, and therefore the more uniform the heat transfer. How will pump speed affect gas savings? So I don't have any pump at all. There are no miracles
since with a low natural velocity of the coolant, the heating of the heating system will be weak and, accordingly, not uniform, it will be cooler for the final points, for uniform heating and an increase in temperature in the heating system in general, good circulation is needed due to the constant heating of the coolant, and so the pump equalizes the required temperature in the system and holes in the hydraulics, forced circulation does not require large pipe diameters in relation to natural circulation, hence the ratio of coolant in the system
orinbasar wrote: and so the pump equalizes the required temperature in the system and holes in the hydraulics
Yann: - That's right, if there were errors in the system with natural circulation, then it simply won’t work, with a pump everything is simpler.
orinbasar wrote: forced circulation does not require large pipe diameters in relation to natural circulation
But you need electricity.
orinbasar wrote: hence the ratio of coolant in the system
The more coolant, the greater the thermal inertia of the system, and this is more of a plus than a minus.
Yann wrote: The more coolant, the greater the thermal inertia of the system, and this is more of a plus than a minus.
on gas consumption, the question is under what conditions gas consumption will be minimal
Pump operating principle
Circulation devices for heating houses are needed to ensure the movement of heat in the water circuit. After installing the device, the natural process of fluid circulation in the system no longer occurs; in this case, the pumps begin to operate in constant mode. That is why many specialists take a closer look at circulation devices and set many requirements for them . These include:
- high reliability indicator;
- isolation from unnecessary sounds;
- high performance;
- long service life of the equipment.
An air circulation pump should be used for water boilers, as well as single-pipe or two-pipe indoor systems. In larger houses, domestic hot water is used for systems.
As many users note, if you place the station in any system with natural coolant operation, the heating rate of the house will increase and ensure uniform heat distribution along the entire perimeter of the water circuit.
The main disadvantage of such a device will be a certain dependence of the functioning of the pumping device on electricity, but the difficulty is most often solved by connecting a special uninterruptible power supply. Experts recommend installing a pump in the heating of a house both when creating a new structure and for pumping an existing one.
Why do you need a circulation pump?

Owners of private households often face a similar situation - in the most remote part of the heating structure, the radiators are much colder than at the starting point. Experts consider the optimal solution in this case to be the installation of a circulation pump, as it looks like in the photo. The fact is that in small houses, heating systems with natural circulation of coolants are quite effective, but even here it would not hurt to think about purchasing a pump, since if you properly configure the operation of this device, heating costs will be reduced.
What is a circulation pump? This is a device consisting of a motor with a rotor immersed in a coolant. The principle of its operation is as follows: by rotating, the rotor forces a liquid heated to a certain temperature to move through the heating system at a given speed, resulting in the creation of the required pressure.
Pumps can operate in different modes. If you set the circulation pump in the heating system to maximum operation, a house that has cooled down in the absence of the owners can be warmed up very quickly. Then consumers, having restored the settings, receive the required amount of heat at minimal cost.

Selecting a heating pump.
Heating systems in which water moves through pipes due to its temperature and density (by gravity) are becoming a thing of the past.
There are many reasons for this, but the most important is the emergence of modern composite materials and pipes based on them. And the second important detail is the low efficiency of the heating system with natural circulation. Heating pump UPS in flanged design
Our private households, dachas and country houses are increasing in size. It is simply impossible to build heating systems other than multi-circuit ones. Naturally, a well-balanced heating system that works due to natural circulation is difficult to calculate and build. But is it worth building such a monster with fairly large pipe diameters, if it is enough to install a circulation pump in the heating system ?
At the same time, the pipes supplying heat to the heating devices become small in diameter and can be easily hidden in the wall or behind a plasterboard partition. Cast iron heating radiators, which have spoiled the appearance of our apartments all our lives, are being replaced with elegant bimetallic or aluminum ones. The volume of water in the heating system decreases, which means that the heating system warms up faster, and if there is a circulation pump in the heating system, the speed of water movement increases, the temperature difference between heating devices decreases, and as a result, the temperature in all rooms will be the same, which does not cause discomfort.
And, probably, most importantly, due to the circulation pump, the efficiency of the heating system as a whole increases, which means that fuel consumption, which is becoming more expensive from year to year, is reduced. And you can’t even dream of devices such as heated towel rails, thermostats, temperature controllers in each room, humidifiers and dehumidifiers in the absence of a circulation pump in the system.
Procedure for calculating pump parameters
The circulation pump must solve two main problems:
- create in the heating system such a coolant pressure that will be able to overcome the hydraulic resistance that arises in individual structural elements;
- provide the required performance and thereby facilitate the movement of heat through the system, sufficient to heat the house.
Based on the assigned tasks, calculation of the circulation pump for heating is required to determine the thermal energy needs of the house and the hydraulic resistance of the entire system. Without knowing these parameters, it is impossible to select a device for forced movement of coolant.
Types and characteristics
A circulation pump is a centrifugal-type device, the impeller of which takes in and discharges liquid in a given direction. Like all similar devices, it works on suction and discharge with equal efficiency. Considering the specifics of use, these qualities are the main ones for it.
There are two main types of circulation pumps:
With wet rotor
The impeller of these pumps is mounted directly on the motor shaft. The pump housing is sealed, and a seal is placed on the shaft to protect against leaks. For household systems, such designs are considered the most suitable, since they do not create noise during operation. In addition, pumps with a wet rotor are capable of independently removing air pockets, and the liquid provides lubrication and cooling of the electric motor;
With dry rotor
The pump and motor are two separate units connected by a coupling or flange. Such designs are designed to work in large heating systems, as they can pump large volumes of liquids. The main disadvantage of dry pumps is the high noise level during operation, which is unacceptable at home.

Pumps: 1-With a wet rotor 2-With a dry rotor
Main technical characteristics of circulation pumps:
- Productivity . This is a value indicating the amount of coolant pumped by the pump per unit time. Determines the ability of the installation to provide a given speed of fluid movement for the available volume of the system;
- Napor . They are often confused, but this is a wrong approach. The pressure shows how high a given pump is capable of lifting a column of liquid. For heating systems of houses with several floors, this indicator is very important, since the hydraulic resistance in the circuits is high and must be overcome;
- Engine power . This indicator is important because insufficient power will not allow the pump to perform its tasks, and excess power will make the pipes make a lot of noise;
- Maximum temperature . Since we are talking about a heating system, the coolant is hot. If the pump is unable to operate under these conditions, it will seize, leak and other problems will occur. It must be taken into account that when rotating, the parts of the device heat up, and an additional rise in temperature sometimes becomes an excessive load for them.
- Connecting dimensions . Installing the pump is simple, but it requires the appropriate elements. They should be selected immediately after purchasing the pump, so as not to find yourself in a difficult position during installation;
- Manufacturer . This factor does not significantly affect the operation of the system, but products from well-known and reliable companies are much more durable and do not create such problems as products from little-known companies.
Calculation of pump performance
The performance of this device is usually denoted in formulas by the letter Q. This value reflects the amount of heat transferred per unit of time.
For calculation use the formula:
R is the thermal power required to heat the room (kW); TF is the temperature of the coolant in the supply pipe of the system (°C); TR is the temperature in the pipeline at the outlet of the system (°C).
In European countries, the R indicator depends on operating conditions; it is usually calculated in accordance with the standards:
- in houses with no more than two apartments, the power of the circulation pump for heating is taken equal to 100 W/m²;
- in multi-apartment buildings - 70 W/m².
When pump calculations are performed for buildings with poor thermal insulation, the value of the above indicators must be increased. If the building is well insulated, the R value is used, which ranges from 30 to 50 W/m².

Manufacturers and prices
Despite the wide range of pumps in stores, it is not easy to choose a truly high-quality product. The market is flooded with Chinese goods and counterfeits of famous brands. First, let's list the popular manufacturers in the CIS:
- The highest price category is Grundfos (Denmark), Wilo (Germany). Prices for original “Germans” start from 75 euros, “Grundfos” UPS series – 65 euros.
- Middle category – DAB, Aquario (Italy), Sprut (quality China). The cost of units of various models ranges from 40-100 euros.
- Other cheap pumps (Oasis, Neoclima, “Whirlwind”, “Caliber” and so on ad infinitum). Price – from 20 euros per piece.

The latest development is the Grundfos Alpfa-3 “smart” pump, which transmits information to a smartphone and helps balance the system
Comment. It is likely that we did not include some very worthy products in the highest or middle price category. The most common brands are listed here.
What is the difference between inexpensive and counterfeit pumps and high-quality superchargers:
- service life – 1…3 heating seasons;
- The product number is only on the sticker, the unit body is clean;
- pumping devices from the same batch often come with the same numbers;
- the weight of the fake is noticeably different from the original (it is lighter);
- A low-quality unit begins to make noise and squeak after working for 1 season in a closed heating system, and the housing gets very hot.
Sometimes counterfeit heating pumps are indistinguishable from the original, only the price is half the price. The secret is in the aluminum winding, which reduces the cost of the product. How to check: find a lot of the original model on the company’s official website and compare it with a market copy. Most likely, an informed seller will refuse to weigh a counterfeit device or will immediately recognize the unknown origin of the product.
Calculation of hydraulic resistance
Another important indicator when choosing a circulation pump is hydraulic resistance, which is what the device will need to overcome.
First of all, you need to find out the suction height H of the pump using the following formula:
R1, R2 - the value of pressure loss on the supply and return pipes (Pa/m); L1,L2 - length of the supply and return parts of the pipeline (m); Z1,…..ZN – data on the resistance that individual elements of the heating structure have (Pa).
To determine the values of R1 and R2, use tabular data given in special reference books.
When calculating a circulation pump for heating, the hydraulic resistance for the units and elements of the heating supply structure is usually indicated by the manufacturer in the technical documentation attached to the device.
You can use example data:
- heating boiler - 1000-2000 (Pa);
- thermostatic valve - 5000-10000 (Pa);
- mixer - 2000-4000 (Pa);
- heat measuring device -1000-15000 (Pa).
Other pump calculation options
The above calculation method is one of the options for calculating the necessary parameters. A number of manufacturers use a different technique. You can also entrust the calculation of the circulation pump to a qualified specialist. Knowing the details of the design of a particular system and its operating conditions, he will professionally make all the calculations.
Usually the maximum load for the operation of the heating system is determined. In reality, it will be lower, so it would be wise to purchase a device whose parameters are slightly lower than the calculated data. Calculating the power of the heating circulation pump reflects the optimal result. Purchasing a more powerful device is not advisable and the system’s performance will not improve, and costs will increase.
After receiving the calculation results, it is necessary to pay attention to the pressure and flow data on pump models, taking into account its operating speeds. The characteristics can be reflected on a graph with two coordinates - pressure and productivity, and then the point of intersection of these values can be determined. Based on the graphic image, the desired heating pump model is selected for a particular home.
Point A in the figure corresponds to the required parameters based on the calculation results, and point B indicates the actual characteristics of a certain device model specified by the manufacturer. The circulation pump is more suitable for the operating conditions in a particular heating system, the smaller the distance between these two points.
A few important points
Since circulation pumps are available for sale, equipped with a “dry” or “wet” rotor, with manual or automatic speed control, experts advise purchasing a device whose rotor is completely immersed in the coolant. You should choose it not only because of the reduced noise, but also because it will cope with the load more successfully. The pump should be mounted so that the rotor shaft is in a horizontal position.
To produce a high-quality product, durable steel and a ceramic shaft are used. The service life of such a circulation pump is at least 20 years. You should not choose a device with a cast iron body for hot water supply - it is destroyed very quickly when used in such conditions.
It is preferable to buy a product made of stainless steel, bronze or brass.
Types of circulation devices
For domestic purposes, manufacturers produce two types of central heating units: with a wet and dry rotor. They have significant design differences, but work equally effectively in heating systems of residential buildings.
With wet rotor
The main difference between this central unit is the absence of seals between the volute and the engine housing. The rotor is located in an aqueous environment, which provides effective noise suppression and bearing lubrication during operation of the device. Electronic components and the stator winding are separated from the coolant by a sealed glass.
Water is 800 times denser than air, so it creates increased resistance to rotor rotation, which significantly reduces the efficiency of the pump. This drawback is more than compensated for by the simplicity and reliability of the device. The silent operation of the central heating unit allows it to be installed in residential premises.
Wet rotor pumps have the following technical characteristics:
- do not require maintenance;
- service life is 5–10 years;
- The efficiency of most models is 50–60%;
- There is virtually no noise or vibration during operation.
Important advantages of this type of central heating unit are its affordable price and simplicity of the device. The electric motor can be removed for repairs without dismantling the pump housing.
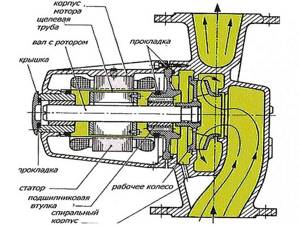
With dry rotor
The design of this type of central heating unit contains a sealed partition with o-rings between the “volatile” and the engine housing. Only the impeller is in contact with the coolant, and the electric motor rotor is located in the dry compartment. When rotating, there is no additional resistance to movement, so such pumps consume less energy.
These blowers have the following properties:
- Efficiency reaches 70-80%;
- operation time between repairs - 3 years;
- high noise level;
- require regular maintenance (MOT).
Due to their noisy operation, central pumps with a dry rotor are used mainly in industrial premises. If heat generating equipment is installed in a utility room of a residential building, then the use of such a pump will bring significant energy savings. But you will need to carefully monitor the sealing gaskets and change them in time during the next maintenance.