The functioning of a forced circulation heating system depends on each element of this complex structure. One of the most important components that provides home heating is the injection pump. Therefore, a bypass for the circulation pump is required. Installation of this part into the system is necessary for several compelling reasons that cannot simply be ignored.
Is an additional pump needed for a Navien double-circuit boiler?
After installing a double-circuit condensing boiler, many users consider installing an additional pump in the heating system of a country house.
The need to use an additional pumping device is explained by the uneven heating of the living spaces of a two-story house with sufficient power of the boiler equipment. Advice! If the temperature differences of the coolant in the supply and return pipelines exceed 20 degrees, it is necessary to switch the circulation pump to a higher speed or get rid of air pockets.
Installing another pump is necessary in the following cases:
- When installing heating in a private house with an additional circuit, or in cases where the length of the pipes is more than 80 meters.
- For uniform supply of coolant through the heating system.
There is no need to install an additional pump if the heating is balanced using special valves. Therefore, before purchasing pumping equipment, bleed the air from the heating radiators and add water, check the circuit for leaks using a manual pressure test pump. If after such procedures the autonomous heating of a private house works normally, then another pump will not be needed.
Why do you need a hydraulic arrow?
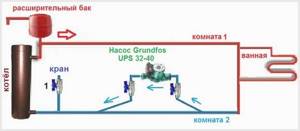
If several pumps are installed in the heating system of a summer house or cottage, a hydraulic separator or hydraulic arrow must be included in the circuit. This device can be used together with a single-circuit diesel boiler or solid fuel unit. In the latter case, the device regulates the supply of coolant in different phases (fuel ignition, combustion phase and attenuation). Installing a hydraulic arrow allows you to balance the operation of the heating system. The main tasks of the hydraulic separator are:
- Automatic removal of accumulated air;
- Catching dirt from coolant flows.
Important! The hydraulic arrow in heating allows you to balance the operation of the system, protects it from airing, and prevents the accumulation of dirt in the pipelines. Such a device must be installed without fail if there are several booster units
Installation nuances
When installing turnkey heating, a master plumber installs a circulation pump with a wet rotor. Such a device does not create much noise; its rotor rotates without lubrication. Coolant is used here as a coolant and lubricant. When installing pumping equipment, you need to take into account the following nuances:
- The shaft of the pressure-injecting device is positioned horizontally relative to the floor plane.
- Carry out installation in such a way that the direction of water coincides with the arrow on the device body.
- Install the device with the terminal box facing up, which will prevent water from entering the electronics.
Important! Experts recommend installing the pump on the return pipeline of the heating system of a single-story or multi-story residential building. Despite the fact that such equipment is designed to operate in hot water with temperatures up to 110 degrees, warmer liquid in the return pipeline will only extend its service life. Installation of the unit is carried out only after draining the water from the system
If there is a power outage, the pump will not be able to pump the coolant, so it is connected through a bypass, and a mesh filter is installed in front of the inlet pipe to prevent scale and debris from getting onto the impeller. In addition, shut-off valves are provided at the input and output of the device for possible replacement and repair of the device.
Installation of the unit is carried out only after draining the water from the system. If there is a power outage, the pump will not be able to pump the coolant, so it is connected through a bypass, and a mesh filter is installed in front of the inlet pipe to prevent scale and debris from getting onto the impeller. In addition, shut-off valves are provided at the input and output of the device for possible replacement and repair of the device.
As we can see, installing a circulation pump requires certain skills, so the installation of this equipment must be carried out by a professional. To order a service, you can leave a request on the website or call the number
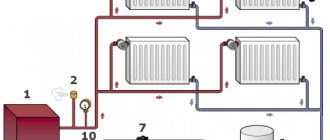
Basic heating schemes
Heating systems, where forced circulation of coolant is provided, can be organized according to a variety of schemes. The most common ones are discussed below. You should start with single-pipe water heating schemes:
Figure 2: Single-pipe horizontal system with end sections.
Flow (Fig. 1). For small houses, a single-pipe horizontal flow-through water heating system is perfect. It provides the following operating scheme: the coolant enters the main riser, and is then distributed among all horizontal risers and begins to flow sequentially through the batteries, cooling, it immediately returns through the return line. With closing sections (Fig. 2). There is another horizontal single-pipe system, which provides for the creation of sections that are subsequently closed. During its organization, a valve designed to remove air must be installed on each radiator. To regulate the temperature of the heating elements, shut-off valves are provided, which are installed at the beginning of the heating system with forced circulation on each floor of a country house. Single-pipe (Fig. 3). A water heating system that provides forced circulation can be vertical. In this case, the coolant immediately reaches the top floor of the house, then it flows through the risers into the installed radiators, then the liquid goes into the heating elements located on the previous floor, and so on until it drops to the very bottom. Such a water heating system can be organized both according to a flow-through circuit, and according to one where there are closing sections
It is important to take into account that it has one significant drawback: heating of the batteries in the house on the floors occurs unevenly.
Figure 3: Single-pipe vertical heating system.
There are also two-pipe water heating systems, where forced circulation of the coolant is provided (Fig. 4). They can be organized according to 3 schemes:
- Dead end. Here, each subsequent element of the heating system in the direction of movement of the coolant is located at the farthest distance from the heating element. This scheme leads to an increase in the circulation circuit, which makes it difficult to control the operation of the heating equipment. However, this system provides for a short pipeline length, which allows minimizing the costs associated with organizing heating for the home.
- Along the way. There is equality of circulation circuits here. This factor makes it easier to regulate the operation of the heating system, where forced circulation is provided. However, here the length of the pipeline increases significantly compared to a dead-end circuit, which leads to additional costs when installing heating.
- Collector. This provides for connecting each heating element individually to the heating system. Thanks to this, the coolant enters the radiators at the same temperature. However, this also implies a large consumption of pipes when installing the system.
Figure 4: Two-pipe horizontal system.
In addition, there is another scheme for the vertical organization of forced heating (Fig. 5). It implies the presence of a lower wiring. Here, the coolant enters the boiler using a pump, then it enters the pipeline and is distributed throughout the entire system, and then passes into the heating elements, giving up its heat, the liquid returns through the return pipeline through the pump and expansion tank to the heating element. A vertical heating system can also be organized with overhead wiring (Fig. 6). This means the location of the main pipelines above the heating elements (in the attic or under the ceiling of the upper floor). The water, which circulates using a pump, enters the boiler, then is distributed through the risers to the heating elements; the liquid, having given up its heat, goes into the return line, which is located in the basement or under the floor of the lower floor.
Where to put
It is recommended to install a circulation pump after the boiler, before the first branch, but on the supply or return pipeline it doesn’t matter. Modern units are made from materials that can withstand temperatures up to 100-115°C. There are few heating systems that work with a hotter coolant, so considerations of a more “comfortable” temperature are untenable, but if you feel safer, put it in the return line.
Can be installed in the return or direct pipeline after/before the boiler up to the first branch
There is no difference in hydraulics - the boiler, and the rest of the system; it makes absolutely no difference whether there is a pump in the supply or return branch. What matters is the correct installation, in terms of strapping, and the correct orientation of the rotor in space
Nothing else matters
There is one important point regarding the installation location. If the heating system has two separate branches - on the right and left wings of the house or on the first and second floor - it makes sense to install a separate unit on each, and not one common one - directly after the boiler. Moreover, the same rule remains on these branches: immediately after the boiler, before the first branch in this heating circuit. This will make it possible to set the required thermal conditions in each part of the house independently of the other, and also in two-story houses to save on heating. How? Due to the fact that the second floor is usually much warmer than the first floor and much less heat is required there. If there are two pumps in the branch that goes up, the speed of movement of the coolant is set much lower, and this allows you to burn less fuel, without compromising the comfort of living.
There are two types of heating systems - forced and natural circulation. Systems with forced circulation cannot work without a pump; systems with natural circulation work, but in this mode they have lower heat transfer. However, less heat is still much better than no heat at all, so in areas where electricity is often cut off, the system is designed as hydraulic (with natural circulation), and then a pump is installed into it. This gives high heating efficiency and reliability. It is clear that the installation of a circulation pump in these systems is different.
All heating systems with heated floors are forced - without a pump, the coolant will not pass through such large circuits
Forced circulation
Since a forced circulation heating system without a pump is inoperative, it is installed directly into the gap in the supply or return pipe (of your choice).
Most problems with the circulation pump arise due to the presence of mechanical impurities (sand, other abrasive particles) in the coolant. They can jam the impeller and stop the motor. Therefore, a mesh dirt filter must be placed in front of the unit.
Installing a circulation pump in a forced circulation system
It is also advisable to install ball valves on both sides. They will make it possible to replace or repair the device without draining the coolant from the system. Turn off the taps and remove the unit. Only that part of the water that was directly in this piece of the system is drained.
Natural circulation
The piping of the circulation pump in gravity systems has one significant difference - a bypass is required. This is a jumper that makes the system operational when the pump is not working. One ball shut-off valve is installed on the bypass, which is closed the entire time the pumping is running. In this mode, the system operates as forced.
Installation diagram of a circulation pump in a system with natural circulation
When the electricity goes out or the unit fails, the valve on the jumper is opened, the valve leading to the pump is closed, and the system operates as a gravity system.
Installation features
There is one important point, without which the installation of the circulation pump will require rework: it is necessary to rotate the rotor so that it is directed horizontally. The second point is the direction of flow. There is an arrow on the body indicating which direction the coolant should flow. This is how you turn the unit so that the direction of movement of the coolant is “in the direction of the arrow”.
The pump itself can be installed both horizontally and vertically, just when selecting a model, make sure that it can work in both positions. And one more thing: with a vertical arrangement, the power (pressure created) drops by about 30%. This must be taken into account when choosing a model.
Analysis of installation technology
The installation process itself is quick; to secure the housing, you need to secure two union nuts. This is very convenient for further maintenance and repair work. But before installation, it is necessary to choose the right installation location, otherwise the pump will either work intermittently or will soon fail.
Schemes for inserting a pump into the network
When choosing one of the schemes, it is necessary to take into account the type of heating system, boiler model and ease of maintenance.
Option 1. This is the most common solution: the pump is mounted on the “return”, through which the cooled coolant returns to the boiler. Warm water does not have such an aggressive effect on the parts of the device, so it lasts longer.
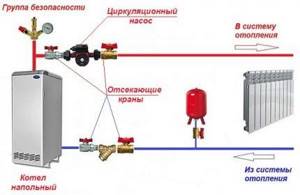
Option 2 . This solution is relevant if for some reason it is not possible to install a pump on the return line. Then it is fixed at the beginning of the circuit, at the supply, but not near the boiler, but after the safety group.
Modern devices can easily withstand high temperatures, but there are still experts who reject such a scheme.
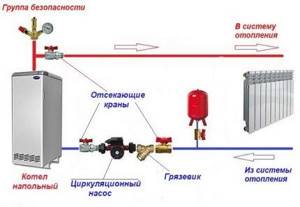
There is such a heating network option as an open system with an expansion tank installed at the highest point of the circuit.
If you install a circulation pump, you will be able to operate it in two modes: natural and forced. Natural circulation will come in handy if there are power outages.

The last scheme applies only to networks with a solid fuel boiler. The supply pump is not installed due to the risk of explosion. The fact is that with solid fuel boilers it is impossible to quickly stop the heating process, as a result of which the water boils.
Boiling water with steam gets inside the pump, it reduces productivity, the cooled water in the circuit does not have time to flow back into the boiler in the required quantity - and it heats up even more. The result of overheating is an explosion.
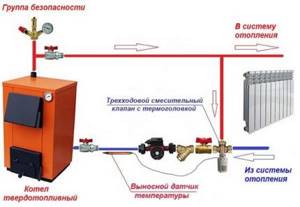
If you run cooled water from the circuit into a heating boiler, condensation will form. To prevent this from happening, the water is first heated in the small circuit to +55°C, and then the thermostatic valve smoothly switches to the large circuit.
As a result, cold water is mixed with already heated water and “temperature shock” does not occur for the boiler.
How piping is done
The circulation pump piping is the equipment necessary for its proper functioning, as well as for the smooth operation of the entire heating system.
First you need to finally decide how many pumps there will be. For one simple circuit, one device is enough, but with complex wiring it is possible to install two or more.
If you plan to use a “warm floor” system in your house or install an indirect heating boiler, then it is better to increase the number of appliances to two. If two boilers are installed - solid fuel and electric - you will also need a separate pump for each unit.

As mentioned above, ball valves are mandatory elements. They are mounted together with the pump, and in the event of an emergency, they will have to be used.
A check valve made of brass or cast iron is also required so that the coolant moves in one given direction. It is mounted on the pipe immediately after the pump, in the direction of water movement.
A “dirt filter” will be required to prevent solid particles from entering the device housing. Fine filters are not installed in heating circuits. If clean water is needed, it is pre-purified before being poured into the system.
There is a risk of air getting into the network, so there is a need to install an air valve. It can turn on automatically, but there are also manual models.

After installing all the devices, the pump is connected to power. A big mistake is to use an ordinary outlet without grounding. This is a safety violation and can cost lives in the event of an accident.
There are smarter ways to power power:
- via uninterruptible power supply (UPS);
- through a differential circuit breaker;
- by connecting to the boiler automation.
The easiest way is to use a circuit breaker: you will need an 8 A switch itself, contacts, and wires. But for practical use, a solution with a thermostat is very convenient.
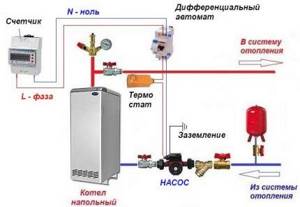
If you plan to install a UPS, you can connect an uninterruptible power supply to both the pump and the boiler at the same time.
Principles for selecting pumping equipment
Having decided on the type of heating pump unit, you need to correctly calculate its optimal power. There is no point in installing a circulation pump with a large power reserve - it is more expensive and makes more noise during operation.
The circulation pump unit performs the following tasks
:
- creates a liquid pressure capable of overcoming the hydraulic resistance of the heating circuit components;
- pumps through the pipeline the volume of coolant necessary for high-quality heating of all rooms.
To correctly calculate the power of the unit, you need to know
:
- pump performance (flow rate, measured in m3/h) - the volume of coolant that is pumped by the device in one hour;
- pressure (measured in meters) is an indicator that determines the hydraulic resistance overcome by the pump.
For a cottage with several floors, with complex architecture, the calculation of the power of the pumping unit should be carried out by specialists. But for small houses, calculations are carried out using simple formulas and tables.
Determining power
Standard calculation formula: Q=0.86R/TF-TR, where
- Q – pump flow (m3/h);
- R – thermal power (kW);
- TF – coolant temperature (°C) in the supply pipe;
- TR – coolant temperature (°C) in the return at the entrance to the boiler.
It is difficult to determine the thermal power yourself, so it is more convenient to use ready-made solutions
:
Method 1. According to European standards, the thermal power indicator (R) for a small private house is 100 W/m2, for a multi-storey building - 70 W/m2, for buildings with good insulation - 30-50 W/m2. These standards are suitable for Russian regions with a mild climate.
Method 2. Russian SNiP standards are designed for climates with frosts down to -30° C. The thermal power indicator for one- and two-story houses of a small area is 173-177 W/m2, for houses with a height of 3-4 floors—97-101 W/ m2.
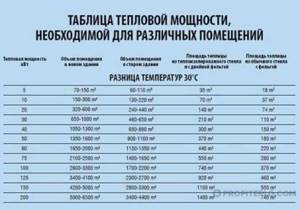
Method 3. The value for calculation is selected according to the table presented, based on the characteristics of the building:
There is another method for determining coolant flow (pump performance). The flow rate (Q) is equal to the boiler power (P). For example, 20 liters of coolant pass through a boiler with a power of 20 kW per minute. And each 10 kW radiator passes 10 liters of liquid per minute. To calculate the coolant flow in each heating circuit, you need to sum up the indicators of all radiators and add the indicators of the pipeline. The coolant flow in the pipeline depends on its length and diameter. The smaller the diameter, the higher the hydraulic resistance. A table compiled for a standard coolant speed of 1.5 m/sec will help you calculate the pipeline performance.
| Water consumption | Diameter in inches | Water consumption | Diameter in inches |
| 5,7 | 1/2 | 53 | 11/4 |
| 15 | 3/4 | 83 | 11/2 |
| 30 | 1 | 170320 | 221/2 |
For every 10 meters of pipeline, 0.6 m of pressure is required, which is provided by a circulation pump. For example, if the length of the heating circuit is 100 m, the pump must provide a head of 6 m.
Bypass functions in the heating system
Let us clarify that a bypass is a pipeline designed to allow water to flow bypassing a certain section of the main line where some equipment is installed. In heating circuits it can be found in two places:
- in single-pipe systems as a jumper on radiators;
- on the distribution manifold of water heated floors.

As you know, in a one-pipe heating system, the heat transfer of the first battery affects the operation of the next one, and so on. This applies to both vertical and horizontal layouts. If a bypass is not installed in the heating system, the radiators will be switched on in series. As a result, the first of them will take the maximum amount of heat, the second will take all that is left, and the third will receive only the cooled coolant.
To prevent this from happening, the supply and return near each battery are connected by a jumper, whose task is to direct part of the coolant bypassing the radiator. In this case, the principle of operation of the bypass is to transfer the same part of the heat to near and far heating devices and reduce their dependence on each other. How this is implemented can be seen in the figure:
In a heating system, a bypass is needed to distribute heat evenly across the radiators, as well as to perform their repair or maintenance. If for some reason you need to disconnect and remove the heating device, then simply turn off the 2 taps installed at the coolant inlet and outlet. Then the water will follow a bypass path through the jumper.
But the heating bypass on the water heated floor manifold plays a different role. Here the bypass line is part of a mixing unit with a three-way valve. The task of the unit is to prepare the coolant at the required temperature for supply to the heating circuits of underfloor heating. Indeed, in these circuits the water temperature does not exceed 45 ºС, while in the supply line it can be 80 ºС.
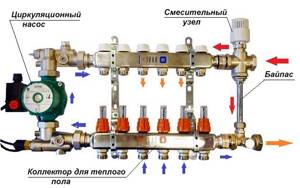
In normal mode, the three-way valve allows hot water from the system to reach the heated floor in a limited amount. The rest of the coolant passes through this automatic bypass, mixes with cold water from the collector and returns back to the boiler. Since the temperature difference in the main and collector is significant, the bypass line is used constantly. It turns out that without it, normal functioning of underfloor heating is impossible.
For systems with a solid fuel boiler
When used in combination with solid fuel heating equipment, a circular pump allows you to create a small circulation circuit.
To do this, the bypass pipe is placed in the supply, where there is a coolant heated to the limit, and is connected to a three-way valve located on the other side of the structure. Thanks to the valve, hot water from the circulation pump and cold water coming from the return circuit are mixed. As a result, a coolant whose temperature exceeds 50 degrees is returned to the boiler for the future heating cycle.
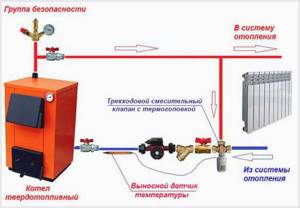
The need to return warm liquid to the boiler is due to the fact that otherwise condensation will form on the iron walls of the combustion chamber, which will encourage corrosion and cause damage to the unit. If you supplement the system with a circular pump, then such problems can be very easily avoided.
Price and recommendations

If we analyze the prices for bypass and components, we can summarize that they are not that high and completely depend on the region of your residence. So, in Moscow you can buy it for 5,000 rubles, and in Yekaterinburg for only 3,000 rubles. These amounts are simply meager compared to those that you will save on heating when using this pipe and taps.
How to choose a suitable bypass?
Just follow our advice and you definitely won’t go wrong:
- Buy only certified products.
- Demand to show the seller a hygiene certificate.
- Upon visual inspection, the bypass you choose should be smooth, without any dents, chips or signs of corrosion.
- If the product has threaded connections, check that they are easy to screw on and off.
- Welding seams must be solid, without pores.
- After purchasing a product, always keep the receipt and warranty card until the period indicated on it expires.
Pump selection
The heating system is connected to water. The pump is usually powered by electricity and should not come into contact with liquid. For this reason, all heating circuit pumps are divided into dry and wet.
Dry type
In the dry scheme there is a division into two sealed compartments. In the first pumping part there is direct contact with water, and in the second electrical part there is power from the network. It is completely isolated from liquids.
The advantages of dry appliances include:
- high power;
- high throughput;
- ensuring optimal pressure in the network.
Dry type products are justified in large industrial buildings. It is better not to install them in apartments due to the following disadvantages:
- big sizes;
- complexity of installation;
- the presence of a shaft that wears out over time and requires repair;
- noisy work.
Wet type
This type of equipment is suitable for apartments, one- and two-story private houses. Wet type pump design: a housing with a closed electrical part, which is connected to the pump chamber. It pumps coolant. Sealing is achieved by using a gasket. At the inlet and outlet there are pipes and flanges for connecting pipes.
The electrical part is also divided into two parts. In the center there is a glass that contains all the electrical mechanisms except the starter power circuit. It is hermetically located outside the glass and does not come into contact with water. The glass contains a rotor, on the shaft of which the impeller is attached. To place the glass in the coolant, a valve is used to release air.
The disadvantages of the system include a decrease in efficiency. Pros - low power consumption, simple installation and the ability to install on any section of the pipe
It is important that the glass is in a horizontal position, otherwise when installed vertically the mechanism will overheat and quickly fail
How to assemble
A circular pump for a circulation pump is best represented as a continuation of the return pipe running from the heating devices to the boiler. A pump is installed parallel to the selected section of the pipe, for which pipe sections are cut. To prevent direct current through the circular pump, a shut-off type fitting or valve is required.
The following are installed along the pump switching line:
- ball valve;
- reusable filter;
- pump with American connections;
- ball valve.
Along the edges of this assembly, elbows and pipe sections are mounted for insertion into the main pipe. The order of the components is indicated according to the direction of fluid flow, so the filter must be strictly in front of the pump. The pipe diameter is chosen equal to the outlet cross-section of the pump, while for the circulation pump the same pipe is used as for the return itself.
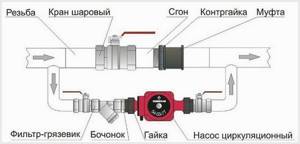
Assembly diagram of the circulation pump
In the area of the circulation pump itself, only shut-off or control valves are installed: a ball check valve, a ball or needle valve.
A ball check valve is better for organizing a circulation pump into a circulation pump. It works on the spool principle. If the pump is turned on, the ball in the middle of the valve, under the influence of pressure, closes the flow through the circular pump. If the pump is turned off, then the direct flow of liquid from the boiler, bypassing the pump, dominates, and the valve does not interfere with this.
The ball valve has two positions closed/open. It is prohibited to place it in intermediate positions, because the surface of the shut-off ball quickly wears out and becomes covered with sediment, which leads to damage to the Teflon insert. If you need to fine-tune the flow capacity of a circulation pump, then preference is given to a needle valve, only if you take into account that its flow area is much smaller than that of a ball valve of the same size.
It is better to use ready-made solutions. We produce prepared circular pumps for circular pumps. They already have ball valves or valves installed in a common section of the pipe and all the piping for the pump, including a filter and fasteners. A ready-made circular pump may turn out to be much better in assembly and more durable in operation. The installation location of the pump is unified and is suitable for any model of suitable power and throughput. You have to select according to the diameter of the key pipe and productivity.
Before installation, the coolant must be completely drained from the system. A circular pump with a circular pump is installed on the cold return pipe specifically near the heating boiler. This reduces the effect of high temperatures on equipment.
You must first determine the ideal inclusion option:
- For a plastic pipe, it is better to use collapsible American-style connections and connect a pre-assembled pump unit with a circular pump. Connect the branch with the pump using tees soldered into the main pipe.
- For steel pipes, first the pipe sections for the branch with the pump are welded, and then the valve on the bypass.
It is necessary to take into account when working with welding that the valves do not tolerate overheating. Especially spherical ones, in which the Teflon insert can change its shape. The connection point of the key pipe should be distanced from the valve using extended pipes or fittings by at least 20 cm on both sides. Shut-off type valves are connected to fittings using fastening connections in the form of threads.
Therefore, it is necessary to orient the entire structure so that the pump outlets are located strictly vertically or horizontally, and the working shaft is only horizontal. This will increase the survivability of equipment and reduce the production of parts. All valves must be freely accessible and nothing should prevent them from being closed. It is necessary to take into account the amount of space for ease of dismantling the pump and other elements.
Quick installation tips
Among the common options is when the heating circulation pump is installed on a bypass. It is easier to dismantle such a system when the need arises, when the device is temporarily disconnected from the network. The work will require the purchase of the following tools:
- Sealant.
- Tow or linen thread.
- Pliers.
- Assembly is carried out using open-end and adjustable-type wrenches.
Adapters with bends and taps are prepared separately, “American nuts” become part of the original kits
The diameter of the product and reliable material are the most important characteristics that are worth paying attention to
Actions are performed in the following order:
- Assembling the crane assembly. One is assigned to a straight pipe, the other two are located at the edges of the pump. Precise welding of a fragment with a tap requires preliminary measurement of the “return” section.
- Assemble the pump loop. For now, the nuts are only screwed on, and their tightening is postponed to one of the finishing stages of the work.
- Try on the bypass loop. Separate markings are for places where welding to the pipe takes place.
- Welding. It is better to trust it only to specialists with sufficient qualifications.
- Assemble the lower assembly on the return line.
- Connection of the pump to the power supply.
An arrow is always drawn on the body. It is needed to indicate where the coolant is moving. Preservation of the specified side is ensured when turning the units.
The pump is powered from conventional 220-volt networks. It is advised to opt for a conventional connection with a separate power supply line. A phase with zero and protection is required. A three-pin socket with a plug helps organize the connection of elements with each other. If there is a connected power wire, the relevance of the solution increases. Correct installation of the heating pump with your own hands is completed.
Carrying out work
Correct installation of the pump in the heating system of a private home requires performing work following certain installation rules. One of them is an insert on both sides of the circulation unit of ball valves. They may be needed later when dismantling the pump and servicing the system.
It is necessary to install a filter for additional protection of the device.
Typically, the water quality leaves much to be desired, and particles that come across can damage the components of the unit.
Mount a valve on top of the bypass - it doesn’t matter whether it is manual or automatic. It is needed to bleed air pockets that periodically form in the system. The terminals should be directed straight up
The device itself, if it is a wet type, must be mounted horizontally. If this is not done, only part of it will be washed with water, and as a result, the working surface will be damaged. In this case, the presence of a pump in the heating circuit is useless
The terminals should be directed straight up. The device itself, if it is a wet type, must be mounted horizontally. If this is not done, only part of it will be washed with water, and as a result, the working surface will be damaged. In this case, the presence of a pump in the heating circuit is useless.
The circulation unit and mountings must be positioned in the heating circuit naturally, in the correct sequence.
Before starting work, drain the coolant from the system. If you haven’t cleaned it for a long time, clean it by rinsing it several times.
On the side of the main pipe, in accordance with the diagram, install a bypass - a U-shaped piece of pipe with a pump built into its middle and ball valves on the sides. In this case, it is necessary to take into account the direction of water movement (it is marked with an arrow on the body of the circulation device).
Each fastener and connection must be treated with sealant to prevent leakage and make the entire structure more efficient.
After securing the bypass, fill the heating circuit with water and check its ability to function normally. If errors or malfunctions are discovered, they must be corrected immediately.
Bypass assembly
The bypass is a section of the main pipeline between the heating boiler and the working circuit. In this section of the direct current, a ball valve is installed, which, when the supercharger is turned on, blocks the movement of the coolant. A less practical solution is a shut-off valve, the normal position of which is closed when the system is running.
The pump is installed in parallel, by means of two branches, embedded in the main pipe and directed towards each other. For fastening, you should use quick-release fittings of the “American” type, which will allow you to quickly dismantle it if necessary. As the fluid moves, a coarse filter is installed in front of the supercharger, and on both sides this design is limited by shut-off valves. The diameter of the pipes must correspond to the inlet and outlet openings of the pump.
Often the best solution is to buy a ready-made bypass assembly. Manufactured for pumps of various diameters, they are already equipped with all the necessary shut-off valves and filter. All you need to do is install it in the desired area of the heating system and install the pump. The key parameter is the distance between the fittings. For the most common type of circulation pumps, it is 110 mm.
Mechanism design
One of the most popular schemes for the heating system of an individual house is a scheme where the central water supply line is preserved, and the circulation pump is installed in a parallel pipe.
Before making a bypass into the heating system, you should consider: the design of this device depends on its area of application:
- a product consisting of a jumper and 2 ball valves are installed near the radiator;
- such a device includes several parts: a circulation pump, a filter, two taps, as well as an additional tap for the main circuit;
- You can also install a pump to automatically regulate the room temperature, replace the ball valves with thermostats that, if necessary, shut off the flow of coolant into the pump if a certain temperature is reached in the room.
The shut-off valves are a ball valve, as well as a check valve, the need for which in the heat supply system is justified. A check valve can be used to replace a faucet. When the circulation pump is turned on, the valve is closed. If the power goes out, the check valve will open automatically, allowing the system to switch to natural circulation.
Therefore, it is important to choose the right bypass design and shut-off valves. When there is no valve, the pump is turned on through a small system circuit formed by a pipeline and a bypass. The check valve device requires a ball to block the lumen of the pipe and a plate with a spring
Installing such a valve in a heating system is due to its advantages, because it operates without human presence. When the circulation pump is turned on, the water pressure closes the valve
The check valve device requires a ball to block the lumen of the pipe and a plate with a spring. Installing such a valve in a heating system is due to its advantages, because it operates without human presence. When the circulation pump is turned on, the water pressure closes the valve.
However, the valve is still inferior to the valve in terms of operational reliability, since the coolant contains abrasive impurities.
Experts recommend using only high-quality valves from trusted manufacturers, since if the ball valve leaks, repairs will not help.
Device installation
Installing a bypass in the heating system does not cause any particular difficulties; it can be done with your own hands
It is only important to adhere to a few requirements:
- select a bypass cross-section that will be smaller by a size than the diameter of the supply and return, so that, if necessary, the water flow will bypass the battery;
- the device should be mounted closest to the heating device and furthest from the riser;
- it is necessary to place the control valve between the radiator and bypass inlets;
- instead of ball valves, you can use thermostats, thanks to which the process of removing the coolant can be automated;
- when using a home-made product, before installing a bypass in the heating system, you need to carry out welding work;
- When installing the device, it must be mounted near the boiler so as to prevent the pump from overheating.
Bypass - such a seemingly simple detail, is important to ensure that the heating operation in an individual home is as useful as possible. It allows you not only to simplify radiator repair when necessary, but also to save heating costs by 10%. If the selection and installation of the device is carried out correctly and all requirements are taken into account, then the operation of the heating equipment will not cause unnecessary trouble for the owners
If the selection and installation of the device is carried out correctly and all requirements are taken into account, then the operation of the heating equipment will not cause unnecessary trouble for the owners.
Bypasses with manual adjustment
Bypasses that are adjusted manually (manual bypasses) are equipped with ball valves. The use of ball valves is determined by the fact that they do not change the pipeline capacity at all when switching, since the hydraulic resistance in the system does not change. This quality makes the ball valve an optimal option for bypass.

Shut-off valves of this type allow you to regulate the volume of liquid that passes through the bypass section. When the tap is closed, the coolant moves in full along the main line. The operation of ball valves has one important nuance - they need to be turned regularly, even if there is no need to adjust the system. This is due to the fact that if left stagnant for a long time, the taps may become tightly stuck and will have to be replaced. Sometimes a heating system feed valve is also installed, which plays a significant role.
Manual bypasses in heating systems can be used in several ways. Most often they are used to connect batteries to a single-pipe main, as well as for piping circulation pumps.
How to choose a water pump for heating your home
A heating pump for a private home is selected according to several basic parameters:
- Productivity and pressure;
- Rotor type;
- Power consumption;
- Control type;
- Coolant temperature.
Let's look at how to choose water pumps for heating a private home.
Performance and pressure
Correctly made calculations will help you choose the unit that best suits your needs, which means it will help you save your family budget.
The performance of an electric water pump refers to its ability to move a certain amount of water per minute. The following formula is used for calculation – G=W/(∆t*C). Here C is the thermal capacity of the coolant, expressed in Wh/(kg*°C), ∆t is the temperature difference in the return and supply pipes, W is the required heating power for your home.
The recommended temperature difference when using radiators is 20 degrees. Since water is usually used as a coolant, its heat capacity is 1.16 W*h/(kg*°C). Thermal power is calculated for each household individually and expressed in kilowatts. Plug these values into the formula and get the results.
The pressure is calculated in accordance with the pressure loss in the system and is expressed in meters. Losses are calculated as follows - losses in pipes are considered (150 Pa/m), as well as in other elements (boiler, water purification filters, radiators). All this is added up and multiplied by a factor of 1.3 (provides a small margin of 30% for losses in fittings, bends, etc.). There is 9807 Pa in one meter, therefore, we divide the value obtained by summation by 9807 and obtain the required pressure.
Rotor type
Home heating uses wet rotor water pumps. They are characterized by a simple design, minimal noise levels and no need for maintenance. They are also characterized by small dimensions. Lubrication and cooling in them is carried out using a coolant.
As for dry-type water pumps, they are not used in home heating. They are bulky, have a high noise level, and require cooling and periodic lubrication. They also require periodic replacement of seals. But they have a large throughput capacity - for this reason they are used in heating systems of multi-storey buildings and large industrial, administrative and utility buildings.
Power consumption
The most modern water pumps with energy consumption class “A” have the lowest power consumption. Their disadvantage is their high cost, but it is better to invest once to get reasonable energy savings. In addition, expensive electric pumps have lower noise levels and a longer service life.
Control type
Through a special application you can get information about the operation of the device wherever you are.
Typically, the rotation speed, productivity and pressure are adjusted using a three-position switch. More advanced pumps are equipped with electronic control systems. They control the parameters of heating systems and allow you to save energy. The most advanced models are controlled wirelessly, directly from a smartphone.
Coolant temperature
Water pumps for heating a private home differ in their operating temperature range. Some models can withstand heating up to +130-140 degrees, these are the ones that should be preferred - they can cope with any thermal loads.
As practice shows, operation at the maximum temperature is possible only for a very short time, so having a solid reserve will be a plus.
Other characteristics
When choosing a water pump for heating, you need to pay attention to the maximum operating pressure for the selected model, installation length (130 or 180 mm), type of connection (flange or coupling), and the presence of an automatic air vent. Also pay attention to the brand - under no circumstances buy cheap models from little-known developers. The water pump is not a part you should skimp on
The water pump is not a part you should skimp on.
How to properly install a circulation pump for heating
Many people are faced with the need to independently install a circulation pump. There are usually two reasons - either the boiler does not initially have a pump (and it is irrational to change pipes to products with a larger cross-section), or its power is not enough to uniformly heat all the rooms through which the heating circuit is laid.
For example, if a heated extension (garage or other) was erected after the residential building was built and inhabited. How to properly install a pump that circulates the coolant through the heating system, what to consider - many questions arise during the installation process. This article will give detailed answers to the most common ones.
Bypass purpose
return of excess coolant
If there were no bypass, it would be impossible to repair the batteries when the heating system is in working order. The bypass also simplifies the process of emptying and filling the system.
Among other things, the bypass ensures the operation of heating systems when power is lost. At that moment, as soon as the electricity is lost, the taps that supply coolants to the pump are simply closed and the tap on the central pipe is opened.
If you use a bypass with a valve, then you will not need to turn off the taps manually, because everything will happen automatically.