Assembly
In general, there are few subtleties in installing heating with metal-plastic:
- It is best to wrap threaded connections with a steel pipe using plumbing linen with quick-drying paint
(for example, NC). In this case, the flax does not rot or fade; - You can cut metal-polymer pipes with a grinder with any cutting wheel or a hacksaw for metal. I already wrote above about the need for calibration, deburring and chamfering;
- A jumper
is required in front of ball valves or throttles that cut off the radiator . Otherwise, you will begin to regulate the permeability of the entire riser. In an apartment building, neighbors will not hesitate to pay you a visit and protest this technical solution in unparliamentary terms;
- When tightening the nut on the compression fitting, hold its body with a second wrench to prevent disruption of previously installed connections;
- Turns are made using corners, not bending the pipe. With a large bend radius, the liner will look sloppy; with a small radius, you are likely to break the aluminum core of the pipe;
- To connect the liner to the radiator, use American ones
. They will allow you to quickly disconnect the heating device if necessary.

In the photo there is an American woman on the radiator connection.
Working with metal-plastic
Metal-plastic is a fairly durable material. Therefore, work can be carried out without special restrictions and requirements. However, there are still some rules:
- pipe installation should be performed only at positive temperatures above 10 degrees;
- if metal-plastic was stored at least for some time at lower temperatures, then before starting work it should be allowed to adapt a little to the temperature;
- all such work must be carried out upon completion of finishing on the walls of the house;
- metal-plastic should be cut using a special tool - scissors;
- during the installation process, the metal-plastic should not be allowed to bend to the point of breaking; special frames should be used;
- All pipes must be attached to the walls using clamps or clips.
Related article: Gypsum stone and making it yourself
It’s worth saying a few words about cutting such pipes. It is best to cut metal-plastic, as already mentioned, with special scissors or a pipe cutter. You can, of course, use a hacksaw for metal. Only after cutting, the edge of the piece of pipe should be sanded with sandpaper to level it. You can also use a simple sharp knife for this purpose.
The use of metal-plastic pipes in autonomous and central heating systems
The use of metal-plastic pipes for the installation of heating networks allows you to save time, effort and money and equip a pipeline that has all the positive qualities of metal and plastic.
To obtain such a result, you must, first of all, understand the differences in the operation of central heating and individual heating:
- In a central heating system, a powerful heat-generating device heats a large volume of water. The heated coolant enters houses and apartments at a temperature of 40 to 95 degrees, but with preventive measures, the water supplied to the pipes can have a temperature of up to 150 degrees. The pressure is usually in the range of 4-5 atmospheres, but since an extensive and branched heating network is serviced, water hammers occur in the pipeline - pressure surges when it exceeds the norm by 2-3 times. For metal-plastic, 95 degrees is the operating temperature limit, and water hammer is a threat of instantaneous destruction of the walls, especially at corners and nodes. Therefore, the installation of metal-plastic pipes in rooms receiving coolant from a centralized system is undesirable. However, the above problems can be solved by equipping the pipeline with pressure stabilizers and temperature regulators.
- A small volume of coolant circulates in an autonomous system; temperature and pressure can be adjusted directly on the heat-generating device. Therefore, in houses, apartments, commercial and other buildings with individual heating, metal-plastic can be used without restrictions.
We recommend that you read: Sealing a chimney using heat-resistant sealant

Specifications
Practice shows that metal-plastic pipes with an outer diameter of 16 and 20 mm are in greatest demand. The wall thicknesses of such pipes are, respectively, 2.0 and 2.25 mm. The thickness of the aluminum layer in them is 0.2 and 0.24 mm. The pressure created in the pipe will be determined by its diameter, wall thickness, and the temperature of the fluid passing through it.
Let's look at an example. If you raise the water temperature to 95 °C, the pipe can withstand pressure up to 10 atm, and if the water has a temperature of 25 °C, then the pressure can be raised to 25 atm (1 atm is equal to approximately 105 Pa). Metal-plastic pipes are also designed for higher temperatures (up to 110 °C), but for a short period of time.
Having learned to decipher the markings of metal-plastic pipes, the consumer will be able to independently find out the information necessary to put them into operation. Regardless of additional designations that may be included in the marking, manufacturers must indicate:
- what is the name of the company that produced this product;
— availability of a certificate of conformity;
— marking of the polyethylene used;
- letter designation of the method of cross-linking polyethylene (for example, a - by the pyroxide method, b - using silane);
— the diameter and wall thickness of the pipe must be indicated. They can be indicated in both mm and inches (1 inch = 25.4 mm);
— the nominal pressure calculated for a medium temperature of +20 °C must be indicated;
- followed by an icon indicating or prohibiting the use of a pipe for passing drinking water;
- then, the last inscription is usually associated with the product batch number and the date of its manufacture.
Simple process, but knowledge required
To understand the correctness of the process, let’s break it down into its components.
The entire instructions look like this:
- Available connection diagrams for heating radiators - select;
- Compatibility of various types of batteries and fittings - check;
- Connecting radiators with pipes - joining them together.
For information! Separately, the general rules for the spatial placement of the radiator will be considered, since neglecting them can significantly reduce the efficiency of the battery.
General concepts
Violation of simple rules for placing batteries can negate all subsequent stages of piping, reducing the efficiency of one link to 25%.
- The distance from the window sill should not be less than 10 cm;
- The distance from the floor to the bottom edge of the radiator should not be less than 12 cm;
- The radiator is not placed close to the wall; the minimum gap between them should be 20 mm;
For your information! The installation kit, along with plugs, includes holders for sectional batteries, and for panels, fastenings are included with the radiator. They were initially designed for the required gap.
But our person’s desire to save money and do everything his own way forces us to do this. Another trick that will remind you of the need for a gap is to glue insulation with a foil reflector to the wall under the radiator, and a gap is needed between it and the radiator.
- You need to be careful with battery niches. The desire to hide the heater can lead to loss of efficiency and heat loss. For lovers of aesthetics, the price may be 10% of heat transfer loss in semi-open niches and 20% in closed niches.
Selection principle
The set of advantages for both types is quite large. Therefore, when choosing, you should take into account the place where the pipe will pass, so that the characteristics of the material do not affect ease of use:
Polypropylene or metal-plastic pipes
- A metal-plastic pipe “sweats” almost the same as a steel pipe. Sweating structures are not suitable for all rooms.
- Polypropylene is lighter in weight.
- The level of heat resistance of metal-plastic is much higher (up to 110 0C). Therefore, it is good for installing heating, underfloor heating, and hot water supply.
- Metal-plastic is flexible. With pipes in a polymer sheath made of polyethylene, you can install water supply without using corner fittings, simply by bending them.
- Metal-plastic and polypropylene pipes have low resistance to thermal deformation compared to metals, but this indicator is much higher for metal-plastic.
- When installing polypropylene pipes for heating and hot water, compensation loops should be provided due to changes in the size of the pipeline when heated.
For urban pipelines, the response to water hammer during system checks and pressure drops is very important
Polypropylene ones burst in one place and form a leak, while metal-plastic ones delaminate over a fairly large period, although they can withstand much greater loads, this is especially important for supplying hot water and heating. Therefore, when eliminating a leak and replacing part of the water supply system in metal-plastic, you will have to change a larger piece
Types of plastic pipes
Related video: Which pipe is better - PPR, polyethylene or metal-plastic?
Publications on the topic

How and with what to solder plastic pipes

Features of insulation of sewer pipes

Simple and affordable methods for connecting pipes without welding
How to connect metal-plastic pipes with metal ones
Since polymer communications are very popular today for use in various systems, when performing repair and construction work it is often necessary to connect metal pipes with metal-plastic ones. As practice shows, such actions are not difficult, but require precision and accuracy.
The easiest way to do the joining yourself is to use a compression fitting. It is screwed using an open-end wrench onto a metal pipe, which must be free of rust.
Note! To ensure tightness, polymer sealing tape or tow is used.
A press washer with a nut is put on the end of the metal-plastic pipe. The product is calibrated and placed on a cone, which is attached to a metal product. At the final stage, the nut is tightened with an open-end wrench so that it tightly presses the second pipe. The resulting connection is strong and tight. It is important to select the fitting of the correct diameter.

You can connect the metal-plastic part of the heating with metal segments using special adapters
Installation
Connecting metal-plastic heating pipes can be done in 2 ways:
Using a compression fitting
The outer part of the pipe is clamped by a collet (O-ring) into which a fitting is inserted (the fitting and collet are equipped with special projections that make the connection reliable). A special nut is screwed onto the outside of the fitting, thereby ensuring a strong connection.
It is important not to overtighten the nut.
The advantages of such connections include the relatively low cost of the fittings, as well as the possibility of their dismantling and reuse (for example, for maintenance of this part of the heating system).
Crimp connection
The disadvantages include the fact that if such connections are installed in a private house, then after several months the nut may loosen. This is due to the cyclical operation of the boiler in a private house (the boiler turns on and off every 2-3 hours). Such cyclicality is absent in apartment buildings, where the heating is turned on once in the fall and turned off once in the spring.
Fittings for metal-plastic.
The fact is that the fitting and the metal-plastic pipe for heating have different thermal expansions, and with high cyclical operation of the boiler, this leads to wear of the sealing rubber, as a result of which the nut becomes loose. In this regard, in order to avoid leaks, the fittings must be periodically checked and, if necessary, tightened.
Important! During the circulation of coolant through the heating circuit, a metal-plastic pipe, like any other, expands. If the connection is not made well, there are cases when the pipe, expanding, may simply fly out of the fitting
At the height of the heating season, this situation will cause a lot of trouble for the home owners. Moreover, an emergency can occur at a time when no one is in the house.
To install the compression fitting, you will need the following:
- Pipe;
- Fitting;
- Scissors for cutting pipes (pipe cutter);
- Pipe bender is a special device for bending a pipe;
Valtec calibrator for metal-polymer and polymer pipes. 16-20-26, with chamfering knives.
- Chamfering device (calibrator). Once the correct size pipe is cut, it must be calibrated (before inserting it into the fitting). For this, a so-called tee is used, onto which a pipe is placed and turned several times in different directions. The protrusions on the tee will chamfer at an angle of 30°, after which the part can be freely put on the fitting. It is recommended to keep the pipe with the hole down to avoid cut parts getting inside the pipe;
- Wrench and gas wrench.
Important! If you do not remove the chamfer, the O-rings may break when putting the pipe on the fitting fitting.
Using a press fitting
Durable, maintenance-free connection. To create it, you need a special press, with which the sleeve is pressed into the surface of the pipe. The press has special nozzles with ring protrusions that make the connection reliable.
Crimping
Advice! Many people refuse crimping only because there are no press pliers. Today, almost every plumbing store provides tools for rental. The rental cost is about 300-400 rubles/day + a deposit is required.
Valtec VTm.293 manual radial press jaws. Weight without attachments – 4.76 kg. Cost – 9400 rub.
In addition to increased reliability and tightness, press fittings have a beautiful aesthetic appearance, so many people lay metal-plastic pipes for heating externally, without fear of spoiling the interior of the room.
The disadvantages of press fittings include their high cost compared to compression fittings. And also the fact that the connection obtained in this way is not detachable. It is no longer possible to twist such a fitting.
Tools for working with metal-plastic pipes
To install the fitting you will need:
- Pipe;
- Fitting;
- Scissors for cutting pipes (pipe cutter);
- Pipe bender;
- Manual or electric press pliers;
Important! When installing a metal-plastic pipeline on a wall, the distance between the fasteners should not exceed 0.5 m. If you ignore this recommendation and make the gap larger, this may lead to sagging of the pipe during operation, which in turn will disrupt the hydraulic characteristics of the heating system
Advantages and disadvantages of metal-plastic pipes
Let's start with the advantages :
- The inner surface is smooth, so there is no precipitation or silting. Over time, the lumen of the pipe does not decrease. Therefore, the service life of MP pipes is long - up to 50 years at an ambient temperature of up to 20°C and 25 years at a temperature of 95°C. These terms are valid only for certified quality products.
- Lower noise level than metal pipes. Factor of. The noise in the risers of apartment buildings is very noticeable. By replacing them with MP pipes, you will hear practically nothing.
- Compared to unreinforced polypropylene pipes, the coefficient of thermal expansion is low. If we take PPR-reinforced pipes, then the indicators are comparable: more than those of metal pipes, but quite acceptable (for heating distribution, compensators or compensation circuits are required).
- They do not conduct induced currents.
- Lungs.
- High-quality raw materials are chemically neutral and such pipelines can be used for any environment. Including for supplying drinking water.
- Elastic. You can bend it without the risk of breaking the foil layer (if the seam is welded).

Metal-plastic pipes can be bent - Low thermal conductivity. This is very good for heating and hot water systems: during transportation the temperature drops slightly, which means we will get hot water, which is good both in the shower and for radiators.
Now the disadvantages :
- Plastics are flammable, so they are not allowed for fire water supply installations.
- Limited area of use due to temperature restrictions (ambient temperature up to +110°C, fear of freezing).
- Metal-plastic pipes (unlike PP) are afraid of defrosting - they lose strength and can crumble.
- They do not tolerate ultraviolet radiation well and are therefore unsuitable for outdoor installation.
- The presence of thermal expansion requires the installation of expansion joints in long branches.
- The fittings have such a structure that they narrow the lumen of the pipe. So the presence of a large number of fittings significantly reduces the throughput of the pipeline. One good thing is that MP pipes are sold in coils and you can lay long sections by bending the pipe in the right places, rather than installing fittings, as in PP pipes. But even in this option, a more powerful circulation pump is required than when installing polypropylene pipes.

MP fittings narrow the clearance and this is one of the main disadvantages - During installation, crimp, threaded or press fittings are used. The specificity of using MP in heating is such that even high-quality and perfectly installed connections begin to “drip” after a few years and need to be tightened. Therefore, if you decide to wall up pipes in the wall (a popular solution), you will have to make inspection windows in the places where the fittings are installed. If they are not done, you will have to break the walls (to eliminate the leak).
- If we compare the prices for MP and PP fittings, then MP are much more expensive (of the same quality level). But fewer of them may be needed - due to the fact that pipes can be bent.
Most of the disadvantages can be attributed, rather, to the features and rules of operation: hide from ultraviolet radiation, do not use for high-temperature environments, make compensators and protect from fire (flammability). But the rest are not very pleasant. The need to tighten connections is especially disheartening: sooner or later a moment comes when there is no room to tighten. And then there is only one thing left: change. First, the fitting, and then, possibly, the entire system.
The use of metal-plastic pipes in autonomous and central heating systems
The use of metal-plastic pipes for the installation of heating networks allows you to save time, effort and money and equip a pipeline that has all the positive qualities of metal and plastic.
To obtain such a result, you must, first of all, understand the differences in the operation of central heating and individual heating:
- In a central heating system, a powerful heat-generating device heats a large volume of water. The heated coolant enters houses and apartments at a temperature of 40 to 95 degrees, but with preventive measures, the water supplied to the pipes can have a temperature of up to 150 degrees. The pressure is usually in the range of 4-5 atmospheres, but since an extensive and branched heating network is serviced, water hammers occur in the pipeline - pressure surges when it exceeds the norm by 2-3 times. For metal-plastic, 95 degrees is the operating temperature limit, and water hammer is a threat of instantaneous destruction of the walls, especially at corners and nodes. Therefore, the installation of metal-plastic pipes in rooms receiving coolant from a centralized system is undesirable. However, the above problems can be solved by equipping the pipeline with pressure stabilizers and temperature regulators.
- A small volume of coolant circulates in an autonomous system; temperature and pressure can be adjusted directly on the heat-generating device. Therefore, in houses, apartments, commercial and other buildings with individual heating, metal-plastic can be used without restrictions.
We recommend that you read: Welded air ducts made of black steel

No. 8. Metal-plastic pipes for heating
In centralized heating systems, the pressure can rise to 4 atm, in autonomous ones it rarely exceeds 1-1.5 atm. The coolant temperature is about +70 0 C, sometimes it rises to +90 0 C (if you use, then this parameter can easily be adjusted). This once again convinces us that metal-plastic pipes can be used to organize a heating system.
The only limitation
, which is present in this case, is the need to maintain positive temperatures in the house. The linear expansion of such pipes is minimal, so if the water in them freezes, the metal-plastic will tear. That is why it is used to organize heating in constantly heated rooms.
If used where overheating of the coolant is possible, it is better to install a heat accumulator, otherwise with frequent temperature increases above +100 0 C the pipes may leak.

Can you trust metal-plastic?
Today, debates are still ongoing about which pipes are more reliable for heating systems - polypropylene or metal-plastic. Although their mechanical and thermal resistance is approximately the same, the question most often lies in the joining method used.
Plastic systems use welded joints. They are more airtight than push-out fittings. But if you install compression fittings, then metal plastic has significant advantages. The fact is that in the process of welding polyethylene it is necessary to very accurately maintain the temperature regime. When underheating or overheating, the quality of the connection is impaired. In addition, if the connection is incorrect, melted plastic can narrow the passage. The use of fittings also narrows the cross-section of the pipe, but not as much as soldering errors.
The resulting cost of a system assembled using metal-plastic elements will be slightly higher, not so much because of the price of the pipes, but because of the costs of fittings and adapters. But if all installation rules are followed, this system turns out to be more stable. It maintains the strength and tightness of the connections, and the expansion coefficient of such pipes is lower. In addition, you can always improve the system by adding new equipment.
Read other articles on this topic
| Heating your home is the most economical way | Heating diagram for a two-story house |
| Combined heating system for a private house | How to save on heating a country house |
| Heating a private house with convectors | Heating distribution for a two-story house |
| Installation of a heating system: rules and description | Heating system for a private house with natural circulation |
| Do-it-yourself heating of a private house made of polypropylene | Water heating in a private house |
| Thermal trace - purpose, classification, use cases | How to heat a private house |
| Heating the house with liquefied gas | Gas consumption for heating a private house - consumption calculation |
| Heating options for a frame house | Infrared heating of houses |
| Heating a private house with forced circulation | Heating a private house with electricity |
| How to heat your home without gas | How is pressure testing of a heating system performed? |
| Heating wiring diagrams from a boiler in a private house | About heating schemes for a private house with a gas boiler |
| Collector heating system for a private house | Heating project for a private house |
| Installation of a heating system in a private house | Basic rules for the location of radiators when heating a private house |
| Heating system for a private house using a warm baseboard | Heating a private house with underfloor heating |
| Autonomous heating of a private house | Country house heating system |
| Heating a private house with a heat pump - pros and cons | Features of heating a country house with electricity |
| The best heating for a private home | Heating and water supply of a country house: description of installation technology |
Services on this topic
| Heating design | Turnkey solid fuel heating |
| Turnkey gas heating | Turnkey heating |
| Heating in a turnkey wooden house | Turnkey water heated floor |
| Installation of water heated floor | Heating a two-story house |
| Heating installation in a cottage | Heating a country house: options and prices |
| Heating installation | Heating installation in a private house |
| Installation of plumbing and heating engineering systems | Diesel heating of a country house |
| Autonomous heating on a turnkey basis | Air heating of a country house |
| Prices for heating installation in a private house | Design and installation of heating systems |
| Water heating in a private house | Electric heating of a country house: options and prices |
| Heating in a townhouse | Gas heating design |
| Heating design cost | Heating calculator for a private house |
| Installation of water heated floors in a private house | Price for installing a water heated floor |
| Installation of water heated floors on a wooden floor |
Fittings for installation of heating systems based on polypropylene pipes

For the installation of a heating system based on polypropylene pipes, the following products are used:
- Couplings. Couplings are available: straight, transitional, with steel threads (both internal and external). They are designed both for connecting pipes by soldering, and for connecting steel or metal-plastic pipes to polypropylene pipes. They are also suitable for connecting shut-off valves and heating devices.
- Transition couplings.
- Taps and valves. They also come with or without metal threads. They are installed on heating devices, as well as main circuits, so that they can be turned off for repairs and preventive maintenance.
- Crosses and tees. Similarly, like couplings, they can have soldered or combined connection threads. Required for connecting multiple pipes.
- Corners. Used to connect pipes at right angles.
- Plugs. Used to close temporarily unused connections.
Before you start purchasing fittings, you need to make a drawing of the entire system indicating all its elements, their sizes, diameters. Only in this case can you accurately determine how many and what connections you need to buy.
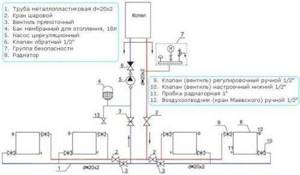
Types of installation of heating systems in a private home are:
- Single circuit system. In this arrangement, all radiators are connected in series. In this case, the total length of the pipes and the number of connecting elements required is minimal. There is one big drawback in such a system - the further “along the pipe” the radiator is installed, the less it will heat up. Therefore, the heating of rooms in the house will be uneven.
- Double circuit. This system is the most popular. Each radiator is connected to two circuits: “supply” and “return”. Thanks to parallel connection, each radiator has the same heating temperature.
- Multi-circuit. With this system, the room has several heating circuits, which are connected using a heating manifold. With such a system, it is possible to regulate the supply of coolant to each circuit, thanks to which energy resources can be used more optimally. This system requires a large number of pipes and connections.
- The design of heating systems for a private home should be carried out by specialists. Otherwise, there is a high probability of building a system that will not meet the requirements of the heated room.
How to choose pipes for use in a central heating system
Nowadays there are many brands of metal-plastic pipes intended for space heating systems on sale.
However, choosing to advise a specific brand is not always correct; you should always pay attention to the technical characteristics of the product, that is, to the declared operating parameters of pressure and temperature in the system. It goes without saying that the higher the latter, the better.
The next question is what diameter of pipes to choose. Let's say right away that it should be larger than that of the same steel pipe that could be installed in this place. So, for risers, pipes with a diameter of 32 or 26 millimeters are taken, but 26 mm products can also be used for connections to radiators. The thing is that the marking of a steel pipe (DU) is a conditional diameter, which usually corresponds to the internal diameter. While for metal-plastic pipes the outer diameter is taken into account. This means that the useful cross-section of the latter is reduced taking into account the wall thickness.
Selecting the type and diameter of heating pipes
The most common diameter of metal-plastic pipes for heating is from 16 to 32 mm. However, this applies exclusively to centralized heating, and if a “warm floor” system is being installed, an even smaller diameter is needed - 8 or 10 mm.
When buying metal-plastic pipes for heating, you should pay special attention to versatility in relation to fittings. After all, some manufacturers produce products designed exclusively for shaped products from the same series. This can be an unpleasant surprise and seriously complicate installation.

Metal-plastic pipes for heating with fittings
Depending on the composition of the plastic that was used to produce the pipeline, metal-plastic heating pipes may have an outer layer:
- Polyethylene;
- Heat-resistant polyethylene;
- Cross-linked polyethylene;
- Polypropylene.
The composition of the material is indicated by special markings printed on the outside of the product.
Do-it-yourself heating in a private house from polypropylene pipes
The main components of heating are a heat generator, pipes and heating devices. The rest of the equipment ensures the system operates under various loads. Equipping the system with additional elements depends on the size of the house and the modification of the selected boiler. The specified operating parameters of the unit are ensured by a safety group, an expansion tank with an overflow pipe, a supercharger and a pressure control device.
If the circulation pump is not built into the boiler circuit, then the blower is installed on the return line of the pipeline, in the immediate vicinity of the heat generator. The installation location of the closed type expansion tank for heating is in front of the circulation pump. The safety group is mounted on the supply line near the boiler.
Advantages over others
Metal-plastic pipes are especially durable and efficient. When wondering where to buy metal-plastic pipes for heating, you must remember that you need to pay attention to the main positive qualities of the product provided by each manufacturer:
- Metal-plastic pipes are not subject to corrosion, deposits and blockages do not form on them. The smooth inner surface is not subject to oxidative processes. The material does not change its state, and the composition of the transferred liquid does not change throughout its entire service life.
- Resistance to aggressive environments on the outer layer.
- The formation of silt and growth in the inner part of the pipe are excluded even after 10 years of operation.
- Easy to use. Installation of metal-plastic pipes is considered one of the simplest, since they are quickly attached without causing difficulties, bend easily, and are highly resistant to damage during installation. Their light weight is noted, which helps speed up the work on fixing pipes.
- Wear resistance. The inner surface is very durable and therefore does not deform even at high speeds of movement of the working medium.
- Efficiency. Polymer materials used in the production of metal-plastic pipes have a much lower thermal conductivity coefficient than metals, so heat loss is minimized.
- Small number of connections. The elasticity and flexibility of the pipes is characterized by the highest rates, therefore, to avoid corners and irregularities on the surface, the use of additional fittings will not be required, which significantly increases the reliability of the entire system.
- During the installation of metal-plastic pipes, a minimal amount of waste is generated.
- Heating pipes are sold in coils, so the consumer can measure the necessary parameters of the material in advance, and the seller will cut the footage specified by the buyer.
- A standard set of tools is required. Without additional processing or restrictions, the pipes can be placed under the screed, that is, after installation, they can be filled with concrete.
- Repairs can be carried out without the use of professional pipe bending and welding equipment, so the owner, having the necessary knowledge, will be able to carry out repair work independently.
- Low price. The purchase of equipment and labor costs for workers cost a small amount, since the cost of the raw material and the time spent on installation are small.
Disadvantages and positive aspects of products
Before deciding whether a (metal-plastic) pipe can be used for a heating system in a house, it is important to better study their disadvantages and positive qualities. Among the latter are:
- environmental cleanliness;
- good compatibility, allowing the connection of metal-plastic pipes with metal ones;
- resistance to the formation of various deposits in the form of stones and rust;
- the ability to retain any shape that is given to them when bent;
- the ability to organize heating with your own hands from metal-plastic pipes without using many tools;
- minimum amount of waste;
- flexibility, allowing you to organize the wiring of metal-plastic pipes with your own hands with fewer connection elements;
- good sound insulation, antistatic and maintainability.
The undeniable advantage of using such pipes in a private home is their throughput, which is 30% higher than that of steel analogues.

Metal-plastic pipes are destroyed by ultraviolet radiation, so it is better to use them in closed systems, for example, heated floors
At the same time, we must not forget about the shortcomings. A metal-plastic pipe for heating needs high-quality insulation. Although it is suitable for outdoor installation, if it freezes with water inside, the product will burst. Also, metal-plastic cannot be placed in places where there is direct exposure to ultraviolet rays.
Note! If it is necessary to use hidden communications in the house, it is prohibited to make connections with threaded fittings.
It must be taken into account that fittings for metal-plastic pipes have a slightly narrowed cross-section. This leads to a slight decrease in the permeability of the pipeline.
Rules for installation of metal-polymer structures
When laying metal-plastic systems, it is important to be guided by the following provisions:
When laying hidden pipelines from this material, it is important to provide removable shields (hatches) that are free of sharp protrusions. They provide access to compression fittings. It is important to lay systems through building structures using sleeves whose internal diameter is 0.5-1 cm larger than that of the pipe. The gap that forms between the elements must be filled with soft, non-flammable material that allows the pipe to move in the longitudinal direction. When laying metal-plastic plumbing or heating systems, it is important to avoid damage to the surface of the elements, including scratches or cuts
To unpack the bay, it is better to avoid sharp objects and mark the structure with a pencil or marker. Installation of the structure can be carried out using a support or suspension, which are usually present in the range of manufacturers of metal-polymer pipes. They help to attach products to the wall, while metal parts are installed with spacers made of soft material.
The gap that forms between the elements must be filled with soft, non-flammable material that allows the pipe to move in the longitudinal direction. When laying metal-plastic plumbing or heating systems, it is important to avoid damage to the surface of the elements, including scratches or cuts. To unpack the bay, it is better to avoid sharp objects and mark the structure with a pencil or marker. Installation of the structure can be carried out using a support or suspension, which are usually present in the range of manufacturers of metal-polymer pipes
They help to attach products to the wall, while metal parts are installed with spacers made of soft material.
All stages of operations must be carried out carefully and carefully, since metal-plastic elements are sensitive to ultraviolet radiation and mechanical damage. External installation of such structures is appropriate only in places where there are no such factors.
Useful tips for soldering polypropylene heating pipes

Important tips and tricks to follow:
- When the pipeline passes through a wall, it is necessary to provide for the presence of steel sleeves. They will protect polypropylene from mechanical damage.
- On straight sections of pipelines longer than 5 meters, it is necessary to provide expansion joints.
- When soldering stopcocks and valves, it is necessary to think through their position in advance so that they have free and full movement. This is a very common mistake for beginners.
- Don't forget about the clip brackets that will support the welded pipes. They should be installed in advance.
- If you are not sure of the quality of the welded seam, it is better to cut it off and redo it. Carrying out work on a finished system in the event of a leak will be problematic.
- When joining heated elements, it is necessary to take into account the joining marks on the parts. After connection, their position can be adjusted by 1-2 mm.

Installation of heating from PP pipes

Heating installation
Installation of a heating system that uses polypropylene heating pipes does not require serious physical effort or time.
In this case, the following requirements for tools and parts must be observed:
- Installation work must be carried out at a temperature of at least 5°;
- Before work, ensure that the material is free of contamination and damage;
- Do not expose elements made of polypropylene to open fire;
- Threading is not allowed on polypropylene elements;
- Polyfusion welding is performed using an electric welding machine with nozzles;

Scissors for cutting PP pipes
Special scissors are used to cut pipes.
Compensator
You should also talk about a rather important detail that is part of the heating system made of polypropylene pipes - the compensator. The main function of the compensator is to compensate for the thermal expansion of the PP pipe
It should be remembered that using a compensator can be dangerous for the entire heating system.
Installing the compensator in the position shown in the figure above leads to the accumulation of air in its upper part, which will lead to the cessation of water circulation in the system and its irreparable breakdown.
Therefore, the compensator should only be installed with the hinge facing downwards to avoid air trapping.
Before starting installation, the welding machine should be heated to a temperature of 270° in order to obtain a homogeneous, high-quality seam.
The main stages of installation of a heating system made of polypropylene pipes
- First of all, measure and cut the required length of the pipe. In the case of welding a foil pipe, the middle and top layers are removed (the size of the removed layer is equal to the insertion depth of the fitting);
- The end of the pipe is cleaned of burrs;
- A marker marks the depth of complete insertion of the fitting. To prevent narrowing of the passage, leave a 1-mm gap between the end and the protrusion of the fitting;
- Using a marker, mark on the surfaces of the pipe and fitting the place where they are connected to each other;
- The pipe and fitting are placed on the welding machine and both parts are heated simultaneously;
- After sufficient heating of the elements, they are connected to each other in accordance with pre-made marks. In this case, it is necessary to control distortions in the radial and axial directions;
- Cooling of the seam lasts from 10 to 30 seconds, which makes it possible, if necessary, to make minor corrections to the connection;
- The connection of the remaining pipe components is carried out similarly. It is advisable to determine the order of their connection in advance, which can significantly speed up the work.
Knowing how polypropylene heating pipes are installed, you don’t have to worry about the efficiency and reliability of the heating system. In addition, you can be sure that the use of a heating system made of polypropylene pipes will provide a cozy and warm atmosphere in the house for many years.
Input connection
If the heating system inlet is located on the right, screw it into the upper right corner and similarly to the left side. We use a metal-plastic pipe. To connect it to a standard hole in the radiator, you will need an appropriate metal adapter. Since the input pipe is located at the bottom, and the place where it needs to be screwed is at the top, the adapter must be angled.
It is screwed in in a special way, but first it is better to screw the adapter in the usual way and count the number of turns until it is clamped and fixed in a position in which the hole will “look” down. Remember the number, it will come in handy a little later. Having unscrewed the adapter, we repeat the action in the reverse order, but according to all the rules of plumbing. The threaded connection must be sealed.

We use sanitary flax for this.

We wind it with an even thread along the thread of the adapter.
But that's not all!

We spread fireclay clay (or silicone sealant) on top of the thread and the wound flax.
You can buy it at plumbing stores. Clay is supplied in tubes.

We screw the prepared adapter into the hole.

Wipe off excess clay with a rag.
We attach a pipe to the adapter.

We bend the metal sheet as needed and bring it to the required place.

We outline the required length and cut off the excess using special scissors for this type of pipe.
We put a metal connection element onto the pipe with an adapter that was already screwed into the radiator earlier. For a high-quality connection of a metal-plastic pipe, it needs to be slightly flared.

A special hand-held device will help you do this. You just insert it into the pipe and rotate it.

After this, you can put the connecting element on the pipe.
Then the metal connection and adapter just need to be twisted together. To fasten the heating pipe, special clips of the required size are used, pre-fixed in the right places on the wall.

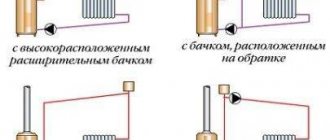
Heating system diagrams
Select the optimal pipe layout for self-installation of polypropylene heating. In the future, you will receive recommendations for connecting individual elements and place them in accordance with the chosen plan.
Single-pipe scheme
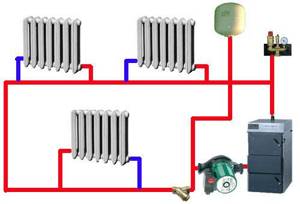
Single-pipe scheme
The simplest method of arranging a heating system. In accordance with this wiring method, each battery installed further from the heating unit will heat up to a lower temperature compared to the previously installed battery.
This method makes it possible to reduce the consumption of materials for the arrangement of the heating system. However, the heating efficiency will be low, because The temperature distribution with such pipe routing is uneven.
In view of this, you should try to refrain from a single-pipe pipe routing scheme.
Collector circuit
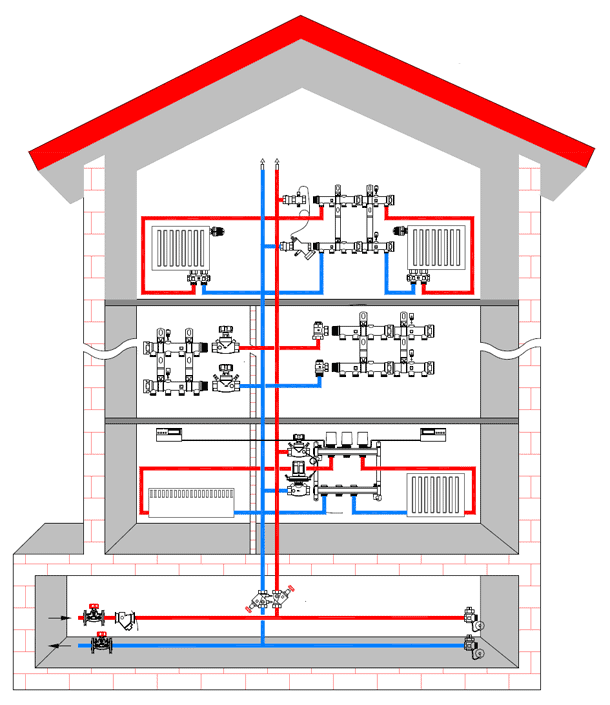
Collector circuit
To equip a heating system according to this scheme, you will have to spend more materials, however, the basic operational properties of such heating will be much higher.
Heat distribution throughout the rooms will be fairly uniform and high quality.
Two-pipe system
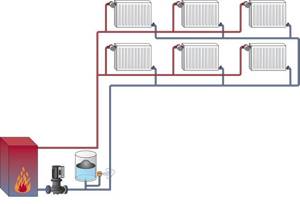
Two-pipe system
The most optimal method of arranging a heating system. The pipes are laid into the floor or into the walls of the house around the perimeter. Two-pipe heating is best suited for heating a home. Therefore, experts recommend giving preference to this particular pipe routing option.
Selecting a heating scheme
It is worth immediately noting that the heating scheme in which metal-plastic is used is drawn up based on various factors, for example, the location of the heating boiler, the location of the rooms and other similar ones.
One way or another, we can identify general principles for constructing heating schemes, according to which they can be classified:
- collector circuits;
- single-pipe or two-pipe circuits;
- diagrams with upper and lower pipe junctions.
There are other types of schemes.
It is worth noting that the heating scheme largely depends on the location of the gas boiler, if we are talking about a private house that has just such a heating element.
The thing is that a gas boiler can only be installed under certain conditions, that is, in compliance with all requirements and maintaining all specified distances to certain objects in accordance with the technical documentation of the boiler.
In addition, the type of heating system layout is largely determined by the entry point of the water supply pipes into the house. There are other factors too.
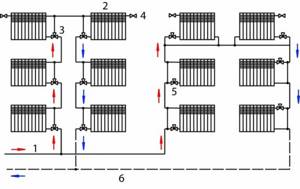
Diagram of a one-pipe heating system: 1 - supply line, 2 - heating device, 3 - three-way valve, 4 - air outlet, 5 - control valve, 6 - return line.
So, with regard to a specific type of system, for each of them it is possible to highlight both positive and negative aspects. For example, a single-pipe heating system made of metal-plastic is good, rather, for a small house used as a summer house, in which the number of radiators does not exceed 5 units.
This is due to the fact that with a single-pipe design, each subsequent radiator will have a lower temperature than the previous one. If their number is small, the temperature will be approximately the same; if there is a large number, the last radiator may never warm up at all.
Related article: We repair it ourselves: options for sealing holes and cracks in the walls
The positive aspect of this scheme is that the amount of material spent is much less than for other schemes.
As for the collector circuit, it requires the largest amount of material of all existing circuits. However, adjusting the heating temperature of each individual element is so simple that it easily compensates for all costs. In addition, the heat distribution between all elements is almost ideal.
Something in between the two schemes described above is a two-pipe heating scheme. It requires slightly more costs compared to a single-pipe, but less compared to a collector one.
Heating according to this scheme can be with lower and upper pipe routing. Installation of radiators, gas boiler and other elements of the heating system Installation of a heating system where metal-plastic is used begins with the installation of the boiler, radiators and other individual elements of the heating system.
It is worth noting that the installation of gas equipment should only be carried out by qualified workers from the relevant service. Installing a gas boiler yourself can lead to serious liability.

Metal-plastic radiators are strong and durable. They are distinguished by high heat transfer and environmental friendliness.
As for heating radiators made of metal-plastic, you can mount them yourself. First, the mounting locations for the radiators are selected. They are attached to the walls using special brackets. The brackets, in turn, are attached directly to the walls using anchor bolts. Holes are drilled in the walls for them, and then the bolt itself is screwed into the outer part, securely securing the bracket.
If we are talking about cast iron radiators, then one bracket is required for every 3 sections, but there should not be less than two brackets for the entire radiator.
After installing all kinds of equipment, for example, a pressure gauge, if the gas boiler is not equipped with one, or any shut-off valves, you can begin to directly work with the pipes.
Installation of a heating system with metal-plastic pipes
Metal-plastic products are connected using three types of fittings:
- - detachable (threaded or collet) - the connection can be disassembled and then reassembled;
- - conditionally detachable (compression - can be disassembled, but during assembly it is necessary to replace the crimp ring);
- - one-piece (press) - requires an expensive press, can be embedded in walls or floors.
Required tools for installation
- — scissors (pipe cutter);
- — calibrator;
- — pipe bender (internal or external spring);
- - adjustable wrenches;
- - Teflon or fum tape (for sealing threaded connections).
When assembling, you must follow some rules
- — open laying is carried out after finishing work;
- — the ambient temperature should not be less than +5°C;
- — it is better to cut the material with a special tool;
- — when bending, fracture of the internal aluminum layer is not allowed;
- — the pipeline is attached to the surfaces using clips;
- — during installation it is necessary to leave a reserve for thermal expansion;
- — when using threaded connections, care must be taken not to pinch the material when tightening the nut.
Before installation, you need to cut the sections in accordance with the diagram. If you don't have a pipe cutter, you can use a hacksaw, but the edge may end up uneven. Then, using a calibrator, the ends are returned to a round shape.
To bend the elements, use a pipe bender or a spring. The spring can be external or internal. The use of a tool prevents the aluminum from breaking at the bend. If the bending radius is less than 7 diameters, it is better to use a fitting.
Heating system made of metal-plastic pipes with compression fittings. To create compression connections, no special tools are required. You can purchase a variety of fittings - adapters, angles, tees, crosses. All of them are equipped with a fitting with an O-ring, a union nut and a clamping ring. The pipe must be put on the fitting, the clamping ring must be installed and the union nut must be screwed on.
Methods of connecting pipeline elements: compression and press
Metal-plastic pipes for heating can be easily installed with your own hands, because they do not need to be soldered or welded. Installation is carried out using brass fittings, which are pre-selected to the diameter of the pipeline. Depending on the type of shaped elements used, there are two main methods of connecting metal-plastic:
- Compression;
- Pressed.

Metal-plastic pipe with fittings
Compression fittings make installation as easy as possible. The heating system is installed with your own hands and without the use of expensive tools. However, this type of connection cannot be performed under a concrete screed, because it requires constant monitoring. If the tightness weakens, the fitting nut will have to be tightened, which means there must be constant access to the components.
Compression joints are not suitable for underfloor heating systems due to the impossibility of constant access to the joining points of the elements.
Press connections are more reliable and airtight. However, installation requires a special tool that crimps fittings with a pipeline. Such a device was press pliers, which are sold with a set of interchangeable attachments of different diameters.
Also, the disadvantages of press connections sometimes include their inseparability, i.e. impossibility of reuse when dismantled.