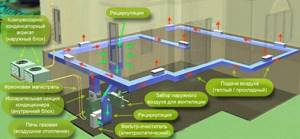
Equipment involved in air heating
- Heat generator
. It can be a gas air heater, a heat gun, a water heater or a solar collector. One of them to choose from will be the heat source. - Heat exchanger
. The purpose of this device is to heat the air; it is not allowed to mix the coolant with gas. It is also called a recuperator and economizer. Its installation is mandatory for large systems. - Air ducts
. Through them, heated air is supplied to individual rooms. There are square, rectangular and round sections, they are presented in certain standard sizes. Connecting them to each other is not difficult, so installation can be done independently. - The filter
, acting as a freshener and humidifier, is capable of keeping the air clean. - An automatic system for monitoring
room temperature, it controls the operation of the heat generator. - Air conditioner
. It is built into the system and used on hot summer days.
An interesting article on the topic: how to organize home heating without gas and electricity.
Solar collectors - cheap and economical
Solar collectors use heat from sunlight to heat water, which is then directed into the building. They consist of a panel of heat-absorbing material into which a mixture of water and antifreeze is pumped to collect heat. This mixture then heats the water in the hot water system, so solar collectors must be integrated into the existing heat distribution system.
Photo 3. Solar collectors installed on the roof of the house. Devices must be placed at a certain angle.
Such thermal systems can be useful not only in warm climates. Even a small increase in water temperature dramatically reduces the amount of energy required to heat it. Solar collectors create favorable conditions for the start of operation of any heating systems. This means less energy is used overall.
How to design and calculate air heating
Organizing air heating of a private house with your own hands involves preliminary development of the project.
During the calculation, the following parameters are taken into account:
- Heater power. It should be enough to fully heat all rooms in the house, given that some of the heat will go outside.
- Speed of circulation of air masses.
- The level of heat loss through the surfaces of walls, ceilings, ceilings, windows and doors.
- Cross section of air channels. In this case, the aerodynamic parameters of the contour are calculated, which makes it possible to determine the degree of reduction in air flow pressure.
Incorrect calculation can lead to the following consequences:
- The heater will overheat.
- The operation of the system will be accompanied by strong noise and vibration.
- Drafts will begin to appear in the home.
After considering all the preparatory issues, they decide on the location for installing the air heating heater with their own hands. There are no general rules on this matter. A supply ventilation circuit is usually used to supply heated air. The coolant is delivered through ventilation grilles to all corners of the home using special air channels. Sleeves are installed for these purposes. The optimal place for the air ducts to exit is the floor surface or the bottom of the walls. It is best to install air heating radiators away from places where people are.

Correct design requires taking into account the quality of ventilation through which fresh air enters the house (as a rule, this is almost ¼ of the total air flow). An innovative way to heat air for air heating is to use solar energy for this. In this case, you also have to take into account the average number of sunny days throughout the year, which will allow you to accurately determine how many solar collectors are needed. These elements are usually placed on the surface of the roofs and facade walls of the building, for which special fasteners are used. This approach allows you to save some money on energy consumption.
Why is ventilation needed?
The goals of ventilation systems are simple and understandable to everyone: the system serves to remove exhaust air from residential premises. After all, when food is prepared, bathrooms are used, in a word, vital activity is in full swing, the air acquires the following features: increased humidity, increased dust concentration, accumulation of unpleasant odors, decreased amount of oxygen. Meanwhile, if an unpleasant odor and dust are simply factors of discomfort, then an increase in humidity can lead to water that will appear on the walls in the form of condensation.
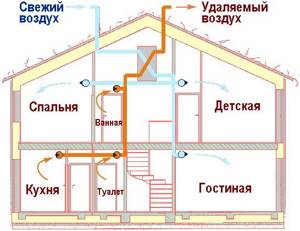
Ventilation of a private house
So, the ventilation system serves to replace dirty air with fresh air. Ventilation can be exhaust or supply and exhaust. In the latter case, air heating, like the ventilation system, is done taking into account the possibility of heat recovery: that is, the exhaust air flows next to the supply duct, while giving it some of the heat. The simplest recuperator can significantly reduce heat loss through ventilation.
How it works?
The operating principle of the air system is based on the use of a heat generator, in the heat exchanger of which the air is heated to optimal levels of 50-60C. Then the hot flows are distributed through the air duct and moved into the rooms, heating them evenly. The system also has in its design special openings in the form of gratings, built into the walls or floor. Through them, the cooled air flows back to the heat generator using air ducts. Thus, we can say that such a device acts simultaneously as a heating element, fan and heat exchanger.
Air systems often operate using a heat pump or gas burner, but sometimes the air is heated by hot water supplied from central communications. The rate of heating of rooms, as a rule, depends on their size. Therefore, the air flow can be from 1000 to 4000 m3 per hour, provided that the pressure in the system is not lower than 150 Pa. In order to minimize heat losses in large rooms, the device is supplemented with auxiliary thermal elements. In addition, it is recommended to install air ducts up to 30 m long; they shorten the path of air flow, maintaining its temperature.
The operational effect of the system is also increased by installing air conditioning units. Thanks to this scheme, the rooms will be well heated in the cold season, and cooled in the summer. This will allow you to maintain a constant microclimate favorable for living in the house.
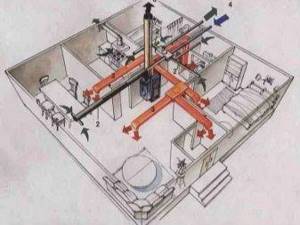
What does it mean to heat with air?
This kind of heating method has been known to ordinary people for a long time. Previously, ordinary houses were warmed by heated air, which from the stoves that were heated went through channels specially made for these purposes. And these days, many owners of country houses are thinking about how to make air heating for their homes with their own hands, since this heating method has many advantages over others.
To heat rooms, both internal and external air masses are used. If air is taken only from the street, then this kind of system will be called a supply air system. For this purpose, supply-type fans are used; they drive air directly to the heating unit.

The complete recirculation scheme looks like this: the internal air is in motion all the time, moving from a hot state to a cold state, after which it goes to the heating device, where it heats up again and moves into the room to release heat and a new cooling stage.
Air heating is a type of heating that you need to pay attention to if the choice is made first in order to save money. The most economical method is designed for the air to be heated in a heater or heat exchanger and distributed throughout the rooms through special channels
In each room, several holes can be placed near the floor, through which the air will fill the room with heat.
The most economical method is designed for the air to be heated in a heater or heat exchanger and distributed to rooms through special channels. In each room, several holes can be placed near the floor, through which the air will fill the room with heat.
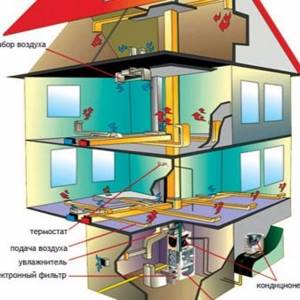
Description of heating type
First, you need to stock up on three main ingredients.
- Heat generator. For this purpose, a heating boiler or furnace is most often chosen. The boiler will operate on any known type of fuel or be powered from the home electrical network.
- A network of air ducts that are usually made of galvanized steel. They may look unsightly, but are often decorated with all sorts of finishing materials to match the design of the room.
- Supply fan.
This heating design, equipped with your own hands, will heat any room well and fairly quickly. Climate control devices can be built into such a system, which in the summer will serve as air conditioning and air purification. The location of air conditioning devices is carried out both at the top of the room and at the bottom - this depends on the selected air heating scheme.
The supply fan forces warm air into the ducts. It is installed immediately under the combustion chamber of the boiler and, using a filter, cleans the air from all kinds of impurities and dust in order to supply it to the heating site - the heat exchanger. After it passes through the duct network, the cooled air is returned to the heat exchanger.
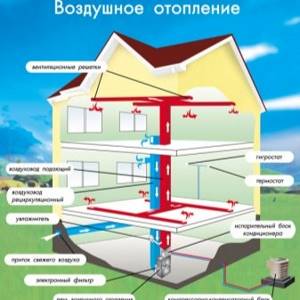
Types of air heating
The operating principle of the air heating system is based on direct heating of the air of the heated room. In addition to the heating function, the complex can perform a number of other functions - air conditioning, ventilation, air purification and humidification.
Air heating has various configurations and is classified according to several criteria. According to the method of laying the air distribution network, the system is divided into 2 types:
- Hanging;
- Floor-standing.
Suspended (ceiling) installation of air ducts is carried out along the ceiling of the premises, air is supplied from top to bottom. The flooring system is installed around the perimeter of the room in the baseboard area or directly in the floor structure.
The floor configuration is more advantageous because the volume of warm air enters directly into the human occupancy area. The advantage of the ceiling system is that it saves space in the room - the network is laid in the upper part of the room.
According to the type of air circulation, the system also has two subtypes:
- Natural circulation;
- Forced (pressure) circulation.
Natural circulation is based on the principle of convective air movement. Heated air tends to the upper part of the room, and heavier cold air takes its place. The only advantage of convective circulation is its complete energy independence. Disadvantages of this type of circulation - instability, low temperature in the zone of human presence - have practically excluded it from implementation.
The main type of circulation of the air heating system is forced. This is achieved through the use of a fan. Depending on the size of the system, the air injection pressure of the fan ranges from 100 to 2000 Pa. The advantage of pressure circulation is high-speed heating, stable operation, and maneuverability of the complex. Heating in this case depends entirely on the constant availability of a stable supply of electricity.
According to the qualitative criterion - the method of heat exchange - air heating has 3 configurations:
- Straight-through;
- Recirculation;
- Combined (mixed).
The direct-flow system combines the functions of heating and ventilation. Air is taken from outside the room, and after heating it enters the heated zone. In this case, high microclimate indicators in the heated room are achieved, but fuel consumption is the maximum among all system configurations.
The recirculation system operates in a closed cycle - air is taken from the room, heated and supplied again. This type of air heating is not the best in terms of air quality, but it consumes a minimal amount of air.
The mixed system includes the operating principles of two main types - direct-flow and recirculation complexes. A certain amount of fresh heated air is constantly mixed into the recirculated volume in a certain proportion.
According to their purpose, air heating systems are divided into autonomous (individual) and centralized. Individual systems are designed for heating private houses, centralized systems are intended for heating large objects.
Air heating control and regulation systems have varying degrees of complexity, ranging from manual control to fully automated operation.
What components does the system consist of?
Heat generator – furnace or boiler
In a furnace for water heating of a house, the heat exchanger container is placed above the firebox, from where the heated liquid enters the pipeline.
- on solid fuel (coal, pellets, firewood, peat);
- diesel (liquid fuel);
- gas (main gas or liquefied in cylinders);
- on electricity (heating elements, electrolysis, induction);
- combined (diesel + gas, gas + firewood, etc.);
- universal - several fireboxes for different types of fuel.
The wiring is almost independent of the type of heating element; there are features only in the wiring of the boilers themselves. Any stoves for a house with water heating are suitable - brick (Russian, Swedish, Dutch), steel and cast iron (potbelly stoves).
- Steel. Connected mechanically or welded. Minus: when water freezes, pipes may burst;
- Metal-plastic. They are connected only with fittings. Installation of the pipeline is done in an open way, otherwise it will be difficult to get to the leak in case of repair;
- Polypropylene. Mostly welded, hidden installation possible. Easily tolerate freezing and thawing. Disadvantage: not used in all parts of the chain. In the boiler piping, for supplying gas to the gas firebox, only metal pipes are suitable for the chimney, because they have higher maximum permissible temperatures;
- Copper. Absolutely reliable, almost eternal, but incredibly expensive.
Expansion tank
Serves to compensate pressure in the pipeline.
Depending on the design of the tank, the entire system is called closed or open:
- In the open model, the outlet pipe is connected to the atmosphere, the container is not sealed. This tank is not suitable for forced circulation pipelines;
- In a closed model, the container is divided into two compartments by a flexible membrane. In the lower part there is a hot coolant, in the upper part there is gas compressed under pressure. The container is completely sealed, suitable for any method of coolant circulation.
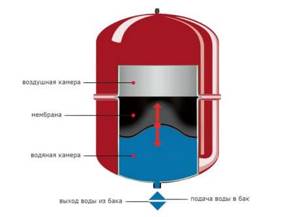
Membrane tank design
Batteries differ in the number of sections (the surface area that gives off heat depends on their number) and the material of manufacture:
- steel;
- aluminum;
- bimetallic radiators (steel core, aluminum surface);
- cast iron.
In addition to radiators, heated floors (water) can be used in all schemes.
Glue for non-woven wallpaper
The non-woven base, in comparison with paper, does not require additional impregnation. The interaction of the adhesive solution with the working surface occurs instantly. But, after some time, mechanical defects appear on the finish, which are typical in the case of:
- Incompatibility of glue with finishing;
- Improper treatment of walls before applying the solution.
When choosing glue for non-woven fabric, you should give preference to products marked “non-woven glue”. They have a base made of special modified starch and PVA, which ensures quick adhesion of the non-woven fabric to the surface. The prepared solution is used immediately, without additional infusions.
When choosing glue for non-woven fabric, you should give preference to products marked “non-woven glue”.
What requirements must it meet?
Non-woven adhesive should not have pigment that appears after drying. It spoils the appearance of the finish and the quality of the materials used. The consistency of the finished mass at the exit is thick, mixes well without forming lumps. This is necessary for uniform application from the initial surface treatment.
You should carefully select the adhesive for non-woven wallpaper, which is intended for gluing to painted walls. Many formulations are vulnerable to concentrations of third-party pigments, which can lead to fading or the appearance of other shades after drying.
Differences in product composition:
- Which non-woven wallpaper adhesive is better - one with a predominance of PVA and starch in the product;
- Components for moisture resistance, better adhesion, protection against fungus, temperature changes, etc.
You also need to think about the expected costs of the solution. The packages contain information calculating the waste of a given dry mass after dilution in a certain ratio.
The consistency of the finished mass at the exit is thick, mixes well without forming lumps.
The bourgeoisie has it better, or we can too
Everyone has always thought about high-quality and inexpensive home heating. For certain reasons, water heating was suitable for mass implementation, but its feasibility for private housing construction was reconsidered quite quickly. Already in the second half of the twentieth century, during the construction boom and especially since the energy crisis of the mid-seventies in the USA and Canada, homeowners and designers began to give preference to air heating systems. Calculations have shown that its use will be 1.5 times more economical than if water heating, air conditioning and air purification systems were installed separately.
For the post-Soviet space, air heating was and still remains exotic, but even in such conditions, domestic engineers made their contribution to the development of technology. If American specialists used classic asynchronous motors and standard “scroll” fans for their climate systems, then the designers of the first domestic air heater “ATM Climate” were the first in the world to use a fan with a valve motor and an impeller with reverse-curved blades.
American snail with asynchronous and valve motor Source www.antarcom-m.ru
See also: Catalog of companies that specialize in engineering systems: heating, water supply and sewerage
This significantly simplified the control system, and therefore made it more reliable. In addition, unlike an asynchronous motor, a valve motor has the ability to smoothly adjust the speed from 0 to maximum and has lower energy consumption with higher performance.
In addition, the domestic air heater “ATM Climate” provides modes of background ventilation and “accelerated heating” of the house - these solutions were also used for the first time in world practice and have proven themselves to be excellent.
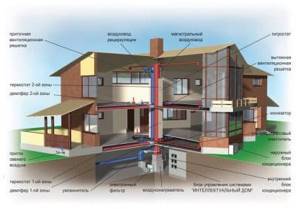
Do-it-yourself air heating of a private house
Air heating has many advantages over water heating. Such systems are characterized by high efficiency. When using them, there is no risk of defrosting or bursting pipes, and the rooms warm up almost instantly. Further in the article we will look at how to arrange air heating of a private house correctly and with your own hands. Below you will be presented with detailed installation instructions.
Air heating system diagram
Systems whose operation is based on direct heating of indoor air include the following equipment:
- Heat generator.
- Air ducts.
- Sleeves designed for air intake from the street.
- Decorative grilles.
- Fan.
Air heating installation stages
Since the design of such a system is quite simple, it is not difficult to install air heating with your own hands. The installation instructions for such equipment usually provide the following procedure:
- Installation of a boiler with a heat exchanger.
- Fan installation.
- Layout and insulation of supply and return air ducts.
- Making a hole in the wall for air intake from outside the building and installing an additional hose into it.
Heat generator installation
The boiler is usually installed in the basement. To connect it to the gas main, you should invite a specialist. Doing this on your own is very dangerous. The chimney can be made of tin. The supply air duct is connected to the top of the boiler heat exchanger. A fan is mounted below the combustion chamber. A return air duct is connected to it from the outside.
Air duct installation
The routing of air ducts is an important stage in such an event as the installation of air heating at home. Let's see how to mount them with your own hands efficiently. First of all, the main supply air duct is connected to the heat exchanger. Next, distribution flexible air ducts with a round cross-section are connected to it. In this case, aluminum reinforced tape is used. Flexible pipes are attached to walls or ceilings with clamps.
It is better to carry out the wiring in such a way that the supply air ducts enter the rooms as close to the floor as possible. In this case, the warm air coming from the pipes, rising to the ceiling, will evenly warm the rooms.
The next step is to install the return air duct. Cold air is also taken from the floor of the premises. Air entering one room can be taken from another. Return pipes always have fewer outlets and are larger in diameter than supply pipes.
The next step is to install an air duct designed to take in air from outside. It must be insulated. Otherwise, condensation will form on it. A throttle valve is installed on this pipe. It allows you to regulate the amount of outside air coming in. If the house has an air conditioner, the supply pipes should also be insulated. This will also prevent moisture vapor from settling on them. Air heating of a private house is assembled using elements that are not particularly aesthetically pleasing. When installing it yourself, the easiest way is to hide the pipes behind plasterboard structures.
If the supply hoses are of unequal length and have a different number of elbows, the rooms will be heated unevenly. In order to correct the situation, dampers should be used.
Filters and additional equipment
Air heating of a private house is often complemented by various useful structures, which you can also install with your own hands. Installation instructions for third-party equipment are usually supplied by the manufacturer. For example, cleaning filters can be built into the supply air ducts. Some air heating systems are even used to cool the air in the house in the summer. To do this, an air conditioner evaporative unit is installed in the main line.
When deciding to assemble an air heating system yourself, you should keep in mind that if the design is incorrect, various kinds of problems will certainly arise. Therefore, before purchasing a kit, you should contact a specialist who will make all the necessary calculations.
Air heating options
So, our task is to heat the air masses and supply them to the premises of a country cottage or apartment. How to organize air heating:
- From the fireplace, wood stove.
- Use VRF systems using freon. Simply put, inverter air conditioners, air source heat pumps.
- Install a combined boiler + chiller + fan coil air conditioning system.
- Organize centralized air heating (abbreviated as VO), combined with ventilation of a private house. Use an electric heater or a gas air-heating furnace as a heat source.

A veranda with a large glass area can be conveniently heated with hot air supplied from the floor
Reference. The latter option is often implemented in American and Canadian cottages built using frame technology. The heater is a gas oven.
For heating/cooling large production workshops, a slightly different scheme is implemented. There are 2 networks of air ducts built in the premises - supply and exhaust. Both converge to a ventilation unit - a central air conditioner, consisting of the following blocks:
- 2-3-stage filters purify air masses before being supplied inside the building and emitted outside;
- heat exchanger-heater No. 1 heats the flow using hot water from the boiler room;
- heat exchanger No. 2 serves to cool the air and works in conjunction with a chiller;
- a plate cross (or rotary) recuperator removes heat from the exhaust flow and transfers it to the supply flow, saving 50...80% of energy;
- humidification unit;
- Centrifugal fans force flows through sections of the central air conditioner and further along the air ducts.
Why did we describe the design of an industrial climate control system? So that you immediately understand: installing full-fledged air heating + ventilation + cooling is not an easy and expensive task. But, as the owner of a country house, you can consider all heating methods, choose the simplest and cheapest, or return to the water scheme - heated floors, radiators.

Industrial series heating system running on natural gas
Direct air heaters
Direct air heaters are based on the principle of heating a room with red-hot porous ceramic tiles emitting infrared radiation, in the depths of which natural gas is burned. These are nothing more than gas fireplaces, near which it is pleasant to spend time, basking in the flow of radiant energy. Usually these are relatively inexpensive devices with a power of 3-4 kW, the production of which has been mastered by some manufacturers of heating devices (about the selection and placement of heating devices).
The biggest disadvantage of heating devices of this type is that oxygen “burns out” in heated rooms, and gas combustion products remain in the room. Therefore, such devices serve more for decorative purposes and cannot be recommended as the main source of heat.
Indirect air heaters
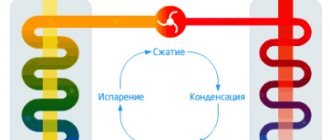
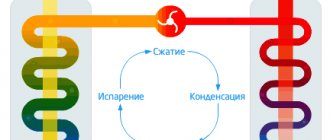
The above disadvantages can be partially or completely avoided by using indirect air heaters. This equipment is a convective-radial heat exchanger and heat exchangers with a built-in combustion chamber. When heated, the air becomes lighter and rises, and in its place comes cold air, which heats up, etc. (picture 1). Thus, the idea of a convector that warms a room without using forced air circulation devices arose.
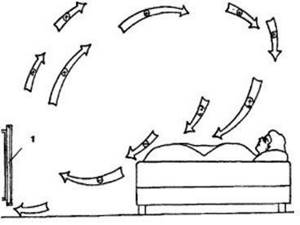
Figure 1. Convector air exchange in the room: 1 - convector; (+) - warm air; (+/-) — cooling air; (-) - cold air.
Gas convectors and heaters
Gas convectors are independent heating equipment that represents a real alternative to traditional heating devices. They provide not only the ability to maintain a set temperature in the range from 8 to 33°C in a heated room, but also allow you to set different temperatures in different rooms.
We recommend: Electric heat guns - operating principle, how to choose, best models, prices and reviews, where to buy
Convectors operate on the principle of burning natural gas in a metal heat exchanger, which ensures highly efficient heat transfer to the room. At the same time, combustion products are removed outside and combustion air is taken in. This ensures the environmental cleanliness of the room and its effective ventilation. Compared to a traditional heating system, which requires boilers, radiators, room piping, fittings, pumps and other components, when using convectors, all this equipment is not required, since there is no water circuit. It is this feature of gas convectors that allows them to be used for efficient heating of country houses, cottages, garages, greenhouses, etc. The gas-air mixture in these devices is ignited either by a spark from the electronic unit or by the wick of the pilot burner, which, in turn, ignites when the button of the built-in “piezo lighter” is pressed. In the latter case, no electrical energy supply is required.
Duct air heating
In the practice of cottage construction in regions with cold and temperate climates, ducted air heating systems have been widely used (Figure 2). This system allows you to heat the premises of the house with warm air supplied through special channels without traditional pipelines and radiators. The advantages of this method over traditional ones are the low inversion of the system, which allows you to raise the temperature in the house from -10 to +22°C in 35 - 40 minutes.
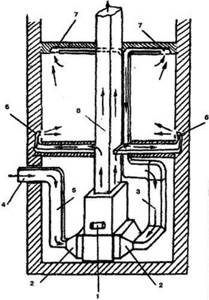
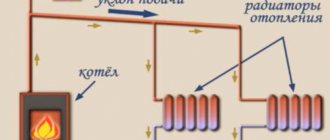
Figure 2. Scheme of air heating of a house: 1 - stove; 2 - filters; 3 - air intake pipe from the premises; 4 — fresh air intake; 5 — fresh air supply pipe; 6 — supply of warm air to the premises; 7 - air intake from premises; 8 - chimney.
After quickly warming up the premises, the automation switches on, allowing you to maintain the temperature at a given level. The advantages of air heating systems include:
- uniform heating of the room throughout the entire volume with a slight “pressure” of air, which completely eliminates drafts and the possibility of penetration of street dust;
- the ability to ventilate rooms, filter heated air to eliminate odors, germs and other foreign matter;
- low operating costs, allowing to increase efficiency up to 93%;
- ability to work in economical mode.
Gas or liquid heaters with safety automatics are used as heat generators. If the house is well thermally insulated, the heater is turned on 3-4 times a day to maintain the set temperature, which saves fuel and, consequently, money for heating residential premises. For example, to heat a small country house, one cylinder of liquefied gas is enough for about 8 - 12 days.
In almost all heating systems, the heat generated by the heat generator is transferred to the consumer by air. Even in a water heating system, water acts only as an intermediate coolant, and the final distribution of heat from the radiators still remains with the air. The only exceptions are heating devices from which heat is transferred by radiation - open fireplaces, infrared emitters, etc. But they play a limited role in heating residential buildings in our country.
The air is heated on heat-releasing surfaces (the surfaces of water heating radiators, convective-type electric heaters, “mirrors” of stoves, etc.) and enters the heated room, where it cools, giving off heat to walls, ceilings, and pieces of furniture. After this, the air should heat up again. This air circulation can occur under the influence of natural forces (warm air is lighter and therefore rises) or forcefully - due to a fan. In the future, we will use the term convection heating (by the way, here is general information about heating) for systems with natural air circulation and air heating (AH) for systems with forced air circulation.
This definition of VO is not generally accepted. A heating system is often called air-based if there is a system of air ducts for distributing heated air from a heat generator (without a fan). Wood-burning stoves such as “Buleryan” and “Professor Butakov” also fall under this definition, since they have the ability to connect air ducts and distribute warm air to other rooms due to convection.
Based on our definitions, these ovens should be classified as convection-type systems.
VO systems can be divided into two types - channel and local. Ducted systems require a system of air ducts, both supply and return. For local systems, air ducts are usually not needed. The simplest local heating systems are fan heaters and heat guns.
Figure 3. Direct heating heat exchanger: 1-hot air; 2- heat exchanger; 3-fan; 4-cold air; 5-burner; 6-chimney.
Figure 4. Indirect heating heat exchanger: 1 - hot air; 2 - heat exchanger; 3 - fan; 4 - cold air; 5 - burner; 6 - intermediate coolant circuit; 7-chimney.
How to organize stove heating
An important advantage of any stove: it simultaneously heats the air and surrounding surfaces with intense infrared radiation. No batteries or coolant pipes are needed.
Clarification. Stoves or fireplace inserts with a water circuit can be used to heat 2-3 small rooms. The coil is connected to a gravity or closed system with a pump.
How to use a stove for pure air heating:
- For 1 room it is enough to install a cast iron or steel potbelly stove.
- To heat 2–3 rooms with a total area of up to 40 m², place a brick stove of a suitable design in the wall between the rooms.
- It is not easy to build a stove in a lived-in house. If there are no high aesthetic requirements, we install a potbelly stove, attach convection casings to the firebox and connect air ducts.

Option No. 3 involves laying air ducts into adjacent rooms and installing duct fans that can withstand the temperature of the moving medium 100–150 °C. Air can move through the pipes on its own, but too slowly, and the ventilation duct must slope upward. How such an air heating system works, see the video below.
The first two options are well known, but not always applicable:
- It is generally unrealistic to install a stove in an apartment;
- even a large Russian stove is not able to cover an area of more than 50 square meters (on one floor), so it is suitable for heating a dacha or a small house;
- the foundation plus a brick stove-fireplace is erected during the construction or major renovation of the building;
- a metal potbelly stove takes up space and is dangerous for small children (in terms of burns).
You can install an iron stove with your own hands - this is a tangible plus. But you will also have to heat it, which results in a lot of inconveniences: frequent loading, the smell of firewood and smoke in living rooms, dust. The author of the video acted wisely by placing the potbelly stove in a separate furnace room. We do not recommend repeating one thing after the home craftsman - installing air ducts made of aluminum corrugations. Such pipes create high aerodynamic resistance and greatly slow down the flow. It is better to use galvanized boxes.
We recommend: Features of exhaust pipes for heating boilers
Preliminary conclusion. Solid fuel stoves are a budget option for air heating with their own advantages and disadvantages. Suitable for small buildings - country houses, garages, greenhouses.
Application of air conditioners and heat pumps
As you know, modern split systems are able to operate in heating mode, consuming three times less electricity than a conventional electric boiler of the same power. Hence, a completely workable solution is to buy and install an inverter air conditioner in each room.
Reference. Why an inverter? The compressor in such “splits” does not stop, and therefore does not freeze in the cold. The air conditioner successfully heats the air down to -5 °C outside, after which the efficiency noticeably decreases.
The advantages of this scheme are obvious:
- lack of batteries, pipes, boilers and other heating equipment;
- relative ease of installation;
- aesthetic appearance of the indoor unit;
- cooling mode in summer;
- Possibility of installation in apartments.

The air-conditioned heating method is viable in the southern regions, where the temperature rarely drops below -15 °C. To the north, “splits” are used only during the transition period – in spring and autumn.
Other disadvantages of heating with a split system:
- Air conditioners will have to be installed in all rooms, which is unacceptable for cottages of 2–3 floors. A multi-split VRF system will cost more than the same number of single coolers/heaters.
- The device “can” clean, dry and change the temperature of the air flow. Rare models are designed to mix in outside air. This means that you will have to do separate ventilation.
- When the external unit of the air conditioner is operating, the distinct noise of the fan and the hum of the compressor can be heard from behind the wall.
The problem of efficiency at low temperatures is solved by an “air vent” heat pump, whose performance remains intact down to -30 degrees below zero. The design and operating principle are identical to the split system, the differences being the larger size and price. If the external unit is installed on the ground and carried 2-3 m from the building, the noise of the unit will become inaudible.
Brief conclusion. VRF systems are good for apartments and small houses located in the southern regions. Heat pumps can also be installed in northern latitudes, but the cost of the equipment plays a role here. If desired, you can install the air conditioner yourself.
Combined multi-zone systems
In this case, the coolant is still used, which is why the system is called combined. How this equipment works:
- Each room has an air heating/cooling unit - a four-pipe fan coil unit that looks like an indoor air conditioner unit.
- One pair of pipes supplies the units with coolant from the boiler. Hot water passes through a heat exchanger blown by a fan, causing the room air to heat up.
- When it is necessary to switch to cooling, the automation switches the fan coil to the second pair of pipes supplying cold water from the chiller.
- Users in rooms can set different air temperatures, but they cannot turn on cooling and heating at the same time. Hence the second name of the air conditioning system – multi-zone.
Note. Chiller is a type of refrigeration machine designed to cool liquid. Usually located on the street under a canopy or in an open place (depending on the design).
Various fan coil units are used inside the building - wall-mounted, duct-mounted, floor-mounted, ceiling-mounted. It all depends on the wishes of the homeowner and aesthetic requirements. Duct-type units can be built inside ventilation ducts to heat/cool the supply air.

Connection diagram of a cassette, duct and floor fan coil to a chiller and boiler
Advantages of multi-zone air systems:
- applicable in large buildings with 20 or more rooms - administrative and residential buildings, warehouses, and so on;
- can work in conjunction with forced ventilation of the cottage;
- any heat generator is used for air heating - a boiler using solid fuel, gas, electricity, diesel fuel;
- pipes with coolant (coolant) take up little space, air units are easily built into the ceiling, hung on the wall or hidden behind the cladding;
- closed terraces with stained-glass windows covering the entire wall are heated by in-floor convectors or wall-mounted fan coil units;
- possibility of adjusting the temperature in individual rooms, remote control.
We believe that the boiler + fan coil + chiller scheme is the most universal and successful from the point of view of aesthetics and operation. Of course, you can’t do this type of air heating yourself; this is a minus. It is necessary to make calculations, select equipment, install, adjust... without knowing the basics, it is extremely difficult to carry out these works.
Let's list other negative points:
- high price of air conditioning units;
- the boiler and chiller are quite large devices, occupying 2–3 m² of area;
- the operation of the system depends entirely on electricity; when the lights are turned off, the heat supply will stop.
Conclusion. A multi-zone combined scheme is the best way to air-heat a home. But implementation will require significant investments.
Heating combined with ventilation
This is a classic method of heating buildings with air, used in enterprises since the last century. Subsequently, manufacturers began to produce small-sized analogues of industrial ventilation units installed in private homes. Thanks to less stringent requirements for air purity, the treatment scheme has also been simplified.
Let us explain the principle of operation of the “ventilation + heating” system step by step:
- The heat source is a stove, usually a gas one. A burner, an air heat exchanger, a fan and an electronic control unit are installed inside.
- The first network of ducts radiates from the furnace, distributing heated air throughout the rooms. With the help of diffusers, grilles and other supply devices, jets are supplied to the premises (usually to the upper zone).
- The second network of channels collects polluted/cooled air from the lower zone of the rooms into a common collector connected to the stove from below.
- Having passed through the collector, the exhaust air masses are cleaned in a mesh or cell filter, then sent to a heat exchanger, where they are heated by a burner.
- Electronics monitor the safe operation of the gas air heater, maintain the outlet temperature, and signal when the filters are dirty.
Typical air heating circuit with recirculation. The heater is a furnace and an air conditioner with a ducted indoor unit
Addition. Since the heater dries the air, an automatic humidifier with an electronic hygrometer is usually installed on the supply duct. The latter is located on the return air duct to measure the humidity of the flow.
The air heating stove is a rather noisy unit, so it is installed in a separate room. Combustion products are removed through a conventional or coaxial chimney (depending on the design of the heater). Air ducts made of galvanized steel are laid in several ways:
- in the basement or ground floor;
- hide in floors and wooden ceilings;
- in the attic;
- vertical channels run along the walls and are covered with facing materials.

Large ventilation ducts are laid under plasterboard finishing
The supply air temperature reaches 40...45 °C, the speed of movement through the ventilation ducts is 4-5 m/s. You can't go any faster; there will be additional noise. In this situation, the diameter of the main collector reaches 300 mm, we took a typical flow rate of 1000 m³/h, although it can be more.
Recommend: Heat Resistant Oven Sealant, High Temperature Chimney Sealant
A logical question: why heat air masses to 40 °C if 22 degrees is sufficient in the house? We answer: the heating system must compensate for 2 types of heat loss - through building structures and energy consumption for heating the inflow, since ventilation is needed in any case. Accordingly, we bring the air to a temperature of 20–24 °C (compensating for losses at home), then overheat it to 40…45 °C.
Conclusion. The “ventilation + heating” scheme is the most cumbersome and expensive. The building must be prepared in advance - even at the design stage, otherwise the air ducts will go directly through the rooms. Operating efficiency is highly dependent on the way the building is ventilated, which we will discuss next.
Feasibility of application
It is advisable to use an air heating system in the following cases:
- If necessary, arrange heating as soon as possible
- For heating large rooms with complex configurations
- If necessary, organize zones with different temperatures
- The air heating system can be used as temporary heating during construction, reconstruction or finishing work. This system can, if necessary, be upgraded to a permanently functioning level. And in the future use it as the main or backup
- If the budget is limited, the heat source for air heating is comparable in cost to water heating boilers of equal power, and air ducts are much cheaper than pipes, fittings, radiators used in heating systems with liquid coolant
Simple heating of a country house: without gas or electricity
Heating your home with electricity is expensive and unreliable. Using gas is cheaper, but it is not always possible to connect it. Then you have to look for other options.
There are several modern alternative sources: energy from the sun, underground resources or an ice-free reservoir. But their installation is quite expensive and complicated. Therefore, a traditional option such as stove heating is often chosen for a dacha.
Pechnoe
It has been known for quite a long time, but remains relevant to this day. There are many variations of stoves. They can heat the entire house or a single room. Sometimes they are connected to a water heating system. Ovens not only heat, but also cook food.
Fuel burns in the combustion chamber. It heats the walls of the stove, which release heat into the house. The following materials are used:
- brick;
- cast iron;
- stainless steel.
The brick takes a long time to heat up, but it also takes longer to release heat. To maintain a comfortable temperature at the dacha, 1-2 heatings per day are required. Steel furnaces heat up quickly and cool down just as quickly. Cast iron ones also heat up quickly, and in terms of heat transfer they occupy an intermediate place between other varieties.
The following is used as fuel:
- firewood;
- coal;
- pallets;
- fuel briquettes.
Advantages and disadvantages
The advantages of heating a dacha with a stove include:
- Autonomy. There is no dependence on gas and electricity.
- Suitable for houses where people do not live permanently.
- You can also cook in the oven.
There are the following disadvantages:
- Requires space to store fuel.
- Brick stoves are quite massive, and it is advisable to lay them together with the house.
- Less heating efficiency.
- If the water circuit is not connected, the rooms far from the stove will be cooler.
- It is necessary to make a chimney.
Calculation of the home heating system
| Calculating the heating systems of a private house is the very first thing where the design of such a system begins. We will talk to you about the air heating system - these are the systems our company designs and installs both in private homes and in commercial buildings and industrial premises. Air heating has many advantages over traditional water heating systems - you can read more about this here. |
System calculation – online calculator
Why is a preliminary calculation of heating in a private house necessary? This is required to select the correct power of the required heating equipment, allowing you to implement a heating system that provides heat in a balanced manner to the corresponding rooms of a private house. A competent choice of equipment and correct calculation of the power of the heating system of a private house will make it possible to rationally compensate for heat loss from the building envelope and the influx of street air for ventilation needs. The formulas themselves for such a calculation are quite complex - therefore, we suggest you use the online calculation (above), or by filling out the form (below) - in this case, our chief engineer will make the calculation, and this service is completely free.
How to calculate the heating of a private house?
Where does this calculation begin? Firstly, it is necessary to determine the maximum heat loss of an object (in our case, a private country house) under the worst weather conditions (this calculation is carried out taking into account the coldest five-day period for a given region). It will not be possible to calculate the heating system of a private house on your own - for this purpose, specialized calculation formulas and programs are used that allow you to build a calculation based on the initial data on the structure of the house (walls, windows, roofing, etc.). As a result of the data obtained, equipment is selected whose useful power should be greater than or equal to the calculated value. When calculating the heating system, the required model of duct air heater is selected (usually a gas air heater, although we can use other types of heaters - water, electric). Then the maximum air performance of the heater is calculated - in other words, how much air the fan of this equipment pumps per unit time. It should be remembered that the performance of equipment differs depending on the intended mode of use: for example, with air conditioning the performance is greater than with heating. Therefore, if you plan to use an air conditioner in the future, then the air flow rate in this mode must be taken as the initial value of the required performance; if not, then only the value in the heating mode is sufficient.
At the next stage, the calculation of air heating systems for a private house comes down to correctly determining the configuration of the air distribution system and calculating the cross-sections of the air ducts. For our systems, we use wafer-shaped rectangular air ducts of rectangular cross-section - they are easy to assemble, reliable and conveniently located in the space between the structural elements of the house. Since air heating is a low-pressure system, when constructing it it is necessary to take into account certain requirements, for example, to minimize the number of turns of the air duct - both the main one and the terminal branches going to the grilles. The static resistance of the route should not exceed 100 Pa. Based on the performance of the equipment and the configuration of the air distribution system, the required cross-section of the main air duct is calculated. The number of terminal branches is determined based on the number of supply grids required for each specific room of the house. In a home air heating system, standard supply grids measuring 250x100 mm with a fixed capacity are usually used - it is calculated taking into account the minimum air velocity at the outlet. Thanks to this speed, there is no air movement in the rooms of the house, there are no drafts or extraneous noise.
| The final cost of heating a private house is calculated after the design stage is completed, based on a specification with a list of installed equipment and elements of the air distribution system, as well as additional control and automation devices. To make an initial calculation of the cost of heating, you can use the questionnaire for calculating the cost of a heating system below: |
online calculator
How to warm up a house with air?
Air is a very effective coolant, much more convenient than water. The simplest option for such heating is a conventional fan heater. This device, consisting of a fan and a heating coil, can warm up a small room in literally a matter of minutes. Of course, for a private home you will need more serious equipment.
A gas or solid fuel boiler can be used as a heat source. An electric heater is also suitable, but this option is not considered very profitable, since electricity costs increase significantly.
Image gallery Photo from In air coolant systems, the air itself is a secondary coolant, which is processed by heating units before supply. Air for air heating systems is heated with water or steam, the preparation of which is carried out by all known types of heating equipment. Fire furnaces are used as heating equipment, processing solid, liquid and gaseous options Fuel Until now, Russian stoves are used in heating schemes for country houses. Their disadvantage is that they can normally heat no more than three adjacent rooms. A common heating option for private cottages is based on the use of a fireplace with heat sinks connected to it. The decoupling of heat pipes of an air heating system is usually arranged within the attic or located behind suspended ceiling structures. A very economical way to obtain energy for heating the air. involves the use of an air-to-air heat pump. In the scheme of operation of an air-to-air heat pump, the internal block externally resembles a similar part of climate control equipment. The principle of heating the coolant. Installation with a gas heater. A fire stove outside the premises. A stove in the heating of a country house. A fireplace in the formation of the heating of a private house. The installation of heat sinks within the attic. air-to-air heating systems
An interesting and environmentally friendly heating option is the use of solar panels or a solar collector. Such systems are placed on the roof. They either directly transfer thermal energy from the sun to a heat exchanger or convert it into inexpensive electrical energy. In the latter case, the fan can also be powered from the battery.
The air is heated in a heat exchanger and supplied to individual rooms through air ducts. These are rather bulky structures made of durable metal. The cross-section of the air ducts is significantly larger than the diameter of the water heating pipe.

Gas boilers and other types of heating equipment are also suitable for air heating. The efficiency of such systems reaches 90%; they are used not only in residential premises, but also in workshops and warehouses
But radiators for air heating are not needed. Warm air simply fills the rooms through special grilles. As you know, hot gas tends to rise. Cold air will be forced downwards.
From here, cold air flows move back to the heat exchanger, heat up, enter the rooms, etc.
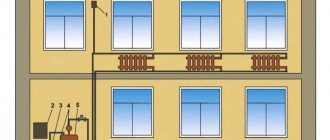
This diagram clearly demonstrates a recirculation-type air heating device with partial intake of outside air, as well as an air conditioner, ionizer and ultraviolet purifier
Design and types of air heating in private homes
Most often, an air heating system for a private home has the following components:
- heat generator - usually its role is played by a water heater, which is responsible for heating the air;
- air ducts to ensure the supply of warm air to the room;
- fan to set the direction of air flow indoors.
VO systems are formed according to gravitational or forced schemes.
Gravity diagrams
The natural or gravitational scheme implies that warm air circulates due to its density changing as its temperature changes. The main advantage of this type is that the system operates almost autonomously from the electrical network. However, due to disadvantages, the range of use of this approach is limited.
Work can be disrupted by a draft or an influx of cool air from the street, which will result in excessive heating of the air near the ceiling and strong cooling of the main part of the room.
Forced schemes
The main difference between the forced system is the presence of a fan that regulates the direction of air flow. The heat generator heats the air, the fan creates pressure and directs the mass through the pipes. Such ventilation systems are installed under a heater, into which air purified from dust and foreign odors is supplied. After the heat exchanger, the air is directed into the air ducts, and its return is provided by return air ducts or ventilation grilles.
System Design Principles
When designing air heating systems, many important factors are taken into account. First of all, this is the heat demand of each individual room, as well as the heat loss for each room. Doors, windows, vents and other objects allow precious kilojoules of heat energy to escape.

The Buleryan stove is an economical heater option that can be used to organize air heating. A long-burning wood stove can also be an excellent solution.
The most important point is the presence of high-quality insulation of the building. If the house has plastic windows, good doors, and its facade is reliably insulated, there will be less heat loss, and heating costs can be significantly reduced. If we are talking about the reconstruction of a building, we should start with the design of insulation.
After the need for thermal energy and its costs are correlated, the power of the heating equipment is calculated and its type is selected. Then the hot air flow parameters are calculated. Special aerodynamic calculations are performed to calculate the required dimensions of the air ducts.

A diffuser grille is installed at the outlet of the air duct. Its size and configuration may affect the speed of air flow
You can preliminarily calculate the power of the equipment based on the following figures: for heating every 10 sq. meters of room you will need about 0.7-0.8 kW of heat. This is provided that the house is well insulated, otherwise more powerful equipment will be needed. But it is better to entrust complete design and detailed calculations to an experienced engineer.
Incorrect calculations can have a very bad effect on the state of the finished system. An unprofessionally designed air heating system is characterized by such problems as frequent equipment breakdowns, overheating of indoor air, overheating of equipment, drafts, and increased noise levels.
Simultaneously with designing an air heating system, it makes sense to think about the placement of stationary pieces of furniture in the house. Supply and exhaust grilles should be located in places away from the constant presence of people.
They also should not be hidden under cabinets, cabinets or other objects that impede the free movement of air masses.
In a multi-storey private house, it is recommended to place exhaust grilles in such a way that on the upper floors the cooled air is taken into the system from above, and on the lower floors - from below. This will ensure a more even distribution of heat throughout all rooms. Read more about how to correctly calculate air heating in this material.
Image gallery Photo from In air heating systems, two air flow supply patterns are used: inclined and horizontal. The inclined method of supplying warm air is usually preferred because it is delivered to the consumer area. The horizontally directed flow of warm air is less effective, but if it is close to the heating unit, it is better to use them due to the high temperature of the flow. In thermal curtains that combine the principles of water or electric heating with an air circuit, the air flow is directed upwards. Oblique direction of the air flow. Scheme of operation of the inclined supply of warm air. Horizontal direction of heat supply. Vertical supply of warm air flow.
Installation standards
The installation conditions for VK are simple, but for specialists, there are many nuances that need to be known so that the user is not disappointed in choosing an air-heating boiler.
The boiler looks great in the interior. Photo source: ogodom.ru
Features of VK installation:
- The boiler is installed indoors during the construction of the building.
- Specialists must first complete an installation project, taking into account the actual heating and structural characteristics of the building, in accordance with which the main and auxiliary equipment will be selected.
- The system must be equipped with a backup power source.
- To increase efficiency, the boiler should be installed in a room with well-insulated walls.
- The combustion room must have a good ventilation system for ventilation.
- Air ducts make sense if you are installing them in multi-level houses with an area of more than 100 m2.
To select a VC you will need the following data:
- AC power taking into account heat losses in the building;
- the rate at which heated air enters the room;
- technical data of the air duct system;
- VK installation location.
If installing a boiler seems to be a difficult and impossible task for consumers, it is better to entrust it to a company that will perform the entire set of installation and adjustment work for the home heating system; in this case, inconsistencies can be avoided and reliable and safe operation of the equipment can be ensured for many years.
Commissioning works
After completion of the installation work, the most difficult stage to perform independently begins - commissioning of the system. This refers to the need to regulate the volume of air entering the room.
To calculate this, you need to know the speed of air flows (ideally, it should correspond to the calculated one). We measure speed using an anemometer. Knowing the speed, we can easily find the air flow rate (remember the formula: Q=V•S, that is, multiplying the speed by the cross-sectional area we get the flow rate).
Stages of adjustment work
Let's look at the setup step by step:
- Using an anemometer, the speed in the supply air duct is measured and the average value is found
- Among the rooms, the rooms with the maximum speed are selected
- Using dampers, we regulate the flow rate in these rooms so that it becomes equal to the calculated average value, or differs from it by no more than 3%.
Despite the simplicity of the description of the adjustment process, it is not so simple and takes on average from 2 to 6 hours.