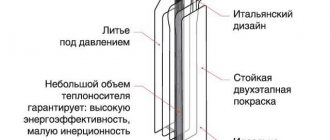
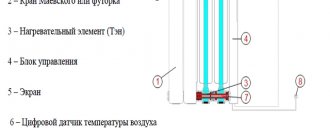
Choosing good building heating is always a difficult question. If the owners of private houses located outside the city have decided to change the heating system, the best option would be to install steel heating radiators.
This type of heating device has proven itself to be the best among property owners outside the city. This may be due to their cost. The price of steel batteries is relatively inexpensive, in contrast to aluminum radiators, and the degree of heat transfer is much higher.
Features and Pros
- The coolant temperature that the battery can withstand reaches 120 degrees.
- The heat output is increased, it varies from 1200 to 1800 W, and for some models this value is higher. This indicator is present in radiators operating by convection method.
- Thermal inertia is low, which means the radiator warms up and starts transferring heat faster.
- The center distance for radiators with side connection can be of different sizes.
- The length of the product reaches 3 meters, and if the structure is tubular, then even longer.
- Width of steel used. Typically it varies from 1.15 to 2 mm.
- The appearance of modern steel radiators is attractive. They do not require additional costs for decorative inserts to disguise imperfections.
- The weight is low, which simplifies assembly and installation.
- Long service life.
Advantages and disadvantages of panel-type radiators
Steel panel radiators have a lot of positive qualities, among which the following are worth noting:
- Easy to install . Since the steel panel heating radiator is a solid product, its installation is reduced to very simple operations - first you need to hang the device on the brackets, and then connect it to the heating pipeline. True, the inability to disassemble the radiator can also be considered a disadvantage - if the device is damaged, it will have to be replaced completely, while sectional batteries can be replaced in parts.
- High heat dissipation . The panels have a rather large area, due to which thermal energy is transferred to the room in full. The presence of convectors, which allows you to direct warm air in the desired direction, also greatly increases the efficiency of steel batteries.
- Economical . A relatively small volume of coolant passes through the internal cavities, so relatively little energy is required for heating. Compared to conventional cast iron batteries, panel devices produce about a third more heat.
- Low risk of injury . The design of steel panel radiators has no sharp corners that could cause injury. This point is especially relevant for families with small children - the smooth metal surface of the radiator reduces the likelihood of serious injury to a minimum.
- Good visual qualities . Panel heating radiators initially have a rather neat and pleasant appearance, so after installing them you will not have to think about various options for protective or decorative elements.

Panel devices also have disadvantages, of which the following stand out:
- Weak resistance to pressure changes . Panel batteries are made using welding - and the resulting welds do not withstand water hammer very well. However, this disadvantage can be mitigated with the help of gearboxes that absorb the effects of pressure drops.
- Dependence on the quality of the coolant . If there is a high concentration of impurities in the water poured into the heating system, then the radiators will very quickly become unusable. In centralized systems, the quality of the coolant is usually not very good, so the inner surface of the radiators becomes covered with a thick layer of scale and begins to rust.
- Low mechanical strength . The components of panel radiators are not very durable, so care must be taken when transporting and operating them - even a slight impact can lead to damage to the products.
How does a steel radiator work?

Water, heated to the required temperature, is supplied under operating pressure from the boiler to the room through the heating system. The radiator can withstand operating and pressure testing. The second is higher than the first.
After this, the water enters the radiator, which increases the temperature in the room.
Radiators have 2 types of connection - one-way and two-way. With one-sided installation, the device is connected to the heating system pipes on one side (hot water supply and cooled water discharge). A similar scheme is implemented in apartment buildings.
With a double-sided design, the battery is connected to the structure of the heating system, crosswise or with a bottom connection (supply on one side of the radiator, drainage of cooled water on the other). The diagonal (cross) option involves connecting the supply pipe at the top, and the outlet coolant at the bottom. This scheme is suitable for multi-section radiators.
The coolant is evenly distributed over the battery area, so heat transfer increases. With a bottom connection, both pipes, inlet and outlet, are connected to the two lower pipes. This provides an increase in heat transfer by 15-20%.
Manufacturing
For the production of panel-type radiators, special stamping machines are used to give steel blanks the required shape.
The manufacturing technology of panel products includes the following stages:
- First of all, steel sheets are processed on machines using the stamping method (the standard thickness of the workpieces is 1.25 mm);
- Two processed workpieces are adjusted in size and have a mirror configuration and are connected to each other by welding;
- Next, convectors with U-shaped ribs are made from sheet steel with a thickness of 0.3 to 0.5 mm by stamping;
- Ready-made convectors are attached to the finished panels by welding (of course, if their presence is provided for by the design of the radiator);
- When the main part of the panel radiators is assembled, pipes are welded to it, allowing the device to be integrated into the heating system;
- After completing the welding work, all remaining seams are cleaned, and the finished stamped steel radiators are painted.

During the stamping process, vertical channels are extruded on metal sheets, which, after welding two parts, form sealed cavities, inside which the coolant will pass. As a rule, sheet blanks are fixed using roller welding, which ensures the tightness of the internal channels.
When creating a radiator, a lot of attention should be paid to its coloring. The thing is that steel itself has poor resistance to corrosion, and the operating conditions of radiators are very closely related to this process. High-quality applied paint protects metal batteries from water and chemical impurities contained in it.
Types of steel radiators

There are 2 types of steel batteries, depending on their design - sectional and solid, which are divided into tubular and panel.
Sectional
Not popular with consumers. Low demand was generated by low resistance to internal pressure. These can only withstand 6 atmospheres.
Solid tubular
They are more expensive and are intended more for design decisions than for practical use. They consist of pipes and resemble old cast iron radiators. There are no ribs between the tubes, which makes cleaning easier, but impairs heat transfer.
The variety of colors in which batteries of this type are painted also speaks in favor of the designers. Due to their rounded shape, such radiators are used in children's institutions, as they are the least dangerous.
They can withstand high pressure, which reaches up to 22.5 atmospheres , so the resistance to pressure drops is higher than that of aluminum radiators. This is achieved due to the walls, the width of which is 2 mm. The laser seam of the batteries is unique - it provides insulation and is practically invisible.
They are assembled in the form of vertical tubes connected by upper and lower collectors. Coolant flows through them, which transfers heat to the radiator. It heats the surrounding air.
The cross-section allows you to increase the length to almost any size. Maximum depth – 22.5 mm.
Steel radiators practically do not become dirty, because dust rolls off the smooth pipes of the battery, unlike the old cast iron “accordions” - dust collectors. It is easier to clean devices, which is why tubular batteries are common in medical institutions.
Minuses:
- Low heat transfer is used only in small rooms or long sections are installed, which affects the price.
- Price.
Panel

Panel heating devices consist of one or more panels with channels for coolant. Some models have fins. They are sometimes fitted with a top grill to hide the ribs, adding to their appeal. Design:
- 2 sheets of steel with recesses made for coolant circulation.
- Several steel sheets with a U-shaped imprint inside, through which the coolant circulates.
- The back side contains ribs that increase heat transfer.
- The uniformity of heating of the room depends on the depth and location of the heating device during installation.
- If there is a tap on the device, you can bleed excess air from the heating system.
- Steel climate control units are more practical if equipped with a thermostat.
The batteries can withstand up to 12 atmospheres. Low resistance is created by the thickness of the panel walls, which on average reaches 1.25 mm.
The coolant temperature limit is 110 degrees. They range in height from 200 to 900 mm, and their length reaches 3 meters.
Connection methods for a panel heater: side, universal, bottom.
Devices of this type are divided into types depending on the number of panels and the number of fins or convectors (U-shaped elements welded to the radiator from the inside). Each of them differs in heat transfer parameters.
- Type 10.
The simplest in design. Does not have convectors. Easy to clean, little dust.
- Type 11.
Similar to type 10, however, on the reverse side there is fins, which increases heat transfer. But the presence of a convector makes cleaning difficult.
- Type 20.
Consists of 2 panels without convector. Has a grille for air outlet.
- Type 21.
As in 20, there are 2 panels. A convector is located between them. The design has an upper casing that covers the fins.
- Type 22.
It consists of 2 panels, with 2 convectors installed between them. Has a top casing. Due to their compactness and good heat dissipation, steel panel radiators are a common type.
- Type 3.
Contains 3 panels, but is not equipped with a convector, and is not equipped with a top casing, which simplifies cleaning.
- Type 33.
The most powerful, as it includes 3 plates and 3 convectors, is equipped with an upper casing. Power is countered by dustiness, since such a heating device is the most difficult to clean.
You can remember the types of radiators using the following rule:
The first digit of a two-digit number indicates the number of panels, and the second indicates the presence of ribs. Type 20, where “2” means two plates, and “0” means no convector.
Like tubular ones, panel-type heating devices look aesthetically pleasing and fit into any interior. This especially applies to the compact and energy-intensive type 22.
Pros:
The advantage is integrity. Batteries do not require preparation or preliminary connection of parts together. They just need to be hung. The advantages include increased heat transfer, because steel conducts heat well, and convectors installed between the plates increase this parameter significantly.
The efficiency of such climate control equipment reaches 40%. With less coolant in the structure, heating occurs faster.
Minuses:
- Low resistance to frequent water hammer, since the seams with which the panels are soldered do not always withstand them.
- Integrity. Despite the simple installation, such a device must be transported carefully, as it requires maximum care. During transportation, the slightest damage will cause the radiator to fail ahead of schedule.
Connection methods
Depending on the connection method, there are different types of steel radiators:
- with side;
- bottom;
- diagonally.
Steel radiators connected from below are equipped with an internal thermostatic valve. Thanks to it, it is possible to set the desired temperature in the room. Devices with side connections are considered the cheapest in terms of cost.

Methods for connecting radiators
The very principle of connecting a radiator to the heating system is not as noticeable as from below. Higher heat transfer is achieved by devices made from two to three panel slabs. The surface that gives off heat is increased by a U-shaped plate welded to the inside of the device; this system makes it possible to transfer warm air flows to planes located outside.
Heating radiator devices made from three panel sheets also have disadvantages. Firstly, weight. In terms of weight, they are not inferior to cast iron radiators, they are just as heavy. Secondly, a large volume of water is required, therefore, the heat regulation effect will be lower. Thirdly, their thickness reaches one hundred and sixty millimeters, which is significantly larger than all other devices. And finally, fourthly, cleaning the inside of such a device is much more difficult than others.
Flaws

Material
Steel is susceptible to corrosion, especially when water comes into contact with air. Manufacturers fight this disease by covering radiators with an anti-corrosion layer on the inside and special powder paint on the outside. However, even the slightest defect in the coatings leads to early failure of the device.
Considering the water that flows through the pipes, this is a problem. If it is possible to do without water and fill it with another coolant, it is better to do this, then the likelihood of an early breakdown will be minimized.
Painting
It should protect the device from corrosion. Manufacturers do not always use the right materials to paint steel radiators. Some types of paint coating may not withstand elevated temperatures, and the paint will peel off over time.
Manufacturers sometimes save on painting materials so that the overall cost of the heating device is lower and sales increase. If the inner layer comes off, then over time corrosion begins to “gnaw” at the battery.
This manifests itself during the non-heating season, when there is no water pressure and air bubbles form in the structure. The installation of such heating devices does not require compliance with special parameters.
Types and characteristic features of bimetallic heating batteries
The name of the product is associated with the use of two manufacturing materials - steel and aluminum. The inner side of the radiator is made mainly of steel, and sometimes of copper, since both materials withstand the effects of heated coolant. On the outside of the device there is a ribbed casing made of aluminum, which has high thermal conductivity. Using stainless steel nipples and temperature-resistant rubber gaskets, the radiator sections are interlocked.

When choosing bimetal radiators, you need to know what they are and what technical characteristics they have
Radiators according to their structure are divided into two groups:
A distinctive feature of semi-bimetallic models is the minimal amount of steel used for the cores, and in bimetallic products all frame pipes are made from steel.
Semi-bimetallic products are not always suitable for central heating systems, which most often contain low-quality coolant with a high alkaline content.
Therefore, there is a high chance of corrosion and damage. These models are primarily suitable for autonomous heating systems.
Precautionary measures

- When installing a steel battery yourself, the tap opens gradually to prevent water hammer.
- It is advisable to install the air valve in the top hole.
- In summer and spring-autumn, a small amount of coolant is present in the heating pipes. A heating device without water should not be idle for more than 15 days a year.
- Transport, install, and store carefully to avoid mechanical damage or chipping of the paintwork. Protect from damp environments and exposure to alkaline and acidic environments.
- Consider the coolant recommended by the radiator manufacturer.
Advertising from sponsors: // // //
Installation
The most advantageous place to install a radiator is under a window, under a windowsill. This allows you to create a “thermal curtain” in the path of cold air emanating from the window.
The installation process of steel panel radiators consists of the following steps:
- Depending on the model of the device, it is necessary to mark the places for drilling holes for fastenings so that there remains 110 mm from the floor to the bottom of the device (the distance from the top to the window sill should be 100-150 mm). This distance is sufficient for the convection process to occur. In addition, with this distance it is easier to clean the space under the device. The battery should not be mounted too high (no more than 200 mm from the floor), because in this case, the temperature spread between the upper and lower parts of the room will increase;
- Using a drill or hammer drill (depending on the wall material), drill holes with a diameter of 10 mm. For devices with a length of 1800 mm, 3 mounting holes are required;
- Hammer the dowels into the holes and screw the screws into them. In this case, the screws are not screwed in all the way, but in such a way that there is a distance of 4-5 mm between the wall and the screw;
- Next, you should put on the fasteners and screw the screws in completely;
- Hang the device on the mounting bracket. The upper mounting bracket has a lock against “accidental dismantling,” therefore, before installing the radiator, it is necessary to pull up the upper mounting clamp and lock it in this position. After this, hang the device on the lower mounting clamp, while the upper clamp will automatically snap into place and the radiator will be tightly fixed to the brackets;
- Place spacers on the lower brackets of the device and adjust the distance from the battery to the wall;
- Connect the battery to the heating system pipes;
- Install the air vent, which is supplied in the kit, into the upper plug. The air vent is equipped with an O-ring, so there is no need to use other sealing materials such as Tangit, fluoroplastic sealing material, linen, etc.
After the end of the heating season, it is recommended to disconnect steel panel radiators (by closing the ball valve in front of the device) from the rest of the heating system. In this case, it is imperative to open the air vent, this will avoid rupture of the device.
Operating principle: convection vs. radiation
The operating principle of a heating radiator is extremely simple. Water, which has already been heated to the required temperature, flows from the boiler into the room through pipes. Then it enters the heating devices, which heat the air in the rooms of your home.
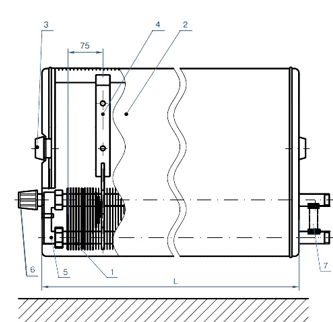
It is worth noting that if heat is transferred by convection - this is accelerated heating of air that flows through the heating surface, then such a heating device will be called a convector. If heat is transferred by radiation, that is, heating of the surrounding air is produced by a surface that has an increased temperature and heat capacity, then this will be a radiator.
The operating principle of a heating battery can also have a combined form - panel radiators-convectors.
Considering how a heating battery works, it is worth noting that in order to quickly warm up a room, a convector is more suitable. However, such a cross-sectional heating battery has one drawback - due to the passage of active convection, a lot of dust is released into the air, which will not have the best effect on the health of those present. That is why convector batteries are used only where there are problem areas of the heating system. For example, to create an air curtain in a room with a large glass area, where conventional devices cannot fit in size.
Regardless of the temperature in the heating radiators, they will give off approximately 60 percent of the heat by radiating thermal energy, while the rest will be given off by convection. Thus, a minimum of hot air convection is achieved and those objects located in the room are well heated. In this regard, it can be noted that the way a radiator works is similar to a heated floor system.

Design features
When you choose radiators, there are several important points to consider. If you choose sections of radiators, you can increase the heating area if necessary. If the design of the heating radiator is panel, or it is a convector, then you will not change it structurally. When calculations are first made, it is very difficult to take into account all the nuances that will affect the amount of heat required for each individual room. And if the heating battery device is sectional, then this will make it possible to reduce and increase the number of sections, and replace those elements that have failed.

The heating radiator diagram is also characterized by an important aspect - the center distance, which displays the vertical distance between the centers of the inlet and outlet pipes. This point should be especially taken into account when an existing radiator or pipework is being replaced. If you buy a radiator with a different center distance, you will either have to change it or change the placement of the pipes.
The design of a heating radiator also means that it is important to consider the diameter of the pipes. If it is too small, it will cause the heating devices to clog faster.
After all, the quality of the coolant usually leaves much to be desired: the water contains sand, scale and rust. All these unpleasant moments when settling first cause the heating system to operate ineffectively, and then can even lead to its complete breakdown.
The correct choice of heating radiators is the most important nuance. A suitable sectional heating radiator is the key to good operation of the heating system.
Characteristics of aluminum radiators
Aluminum heating radiator cross-section
Heating devices made of aluminum are considered one of the most popular types of radiators. Aluminum is a light and ductile metal, therefore, batteries made from it weigh a little and have increased heat transfer.
The devices consist of sections, each of which is a set of interconnected plates. Thanks to this, heat saving here is also at a fairly high level.
Section of aluminum radiator, manufactured by casting method. Radiator, manufactured by extrusion method.
The advantages of such units are as follows:
- fast heating;
- high heat capacity;
- light weight;
- affordable cost (especially when compared with bimetallic units);
- wide model range.
At the same time, after turning off the heating, such radiators cool down quite quickly. Other disadvantages include:
- instability to chemical influences (the problem can be solved by polymer coating on the inner surface);
- low strength;
- poor quality of the threaded connection in the top valve for releasing air from the system.
In view of this, before purchasing it is necessary to inquire about the operating pressure of the heating system. The maximum pressure of a particular product must be looked at in the data sheet, since it is different for different models.
But still, according to its characteristics, aluminum is excellent for the manufacture of radiators, and its fusibility has made it possible to significantly expand the model range. Today you can choose exactly the battery that fits perfectly into the interior of your home.
Aluminum radiator assembly
Table 1. Comparison of aluminum batteries from well-known brands
| Manufacturer | Model | Weight, kg | power, kWt | Volume, l | Pressure, bar. | Dimensions, cm | Distance between axles, cm |
| 1. Rifar, Russian Federation | Alum 500 | 1,45 | 0,183 | 0,27 | 20 | 9x8x56.5 | 50 |
| 2. Fondital, Italy | Calidor Super-500 | 1,32 | 0,193 | 0,3 | 16 | 9.7x8x55.7 | 50 |
| 2. Rovall, (Italy) | Alux-500 | 1,31 | 0,179 | 0,23 | 20 | 10x8x54.5 | 50 |
| 3. Radiatori 20000 SpA | 500R | 1,6 | 0,199 | 0,58 | 16 | 9.5x8x57.7 | 50 |
| 4. Faral | Green HP-350 | 1,12 | 0,136 | 0,26 | 16 | 8x8x43 | 35 |
| 5. Faral | TrioHP-500 | 1,58 | 0,212 | 0,5 | 16 | 9.5x8x58 | 50 |
Aluminum radiators from STOUT Bravo are ideal for installation in apartments and houses with individual heating. These heating devices are manufactured at facilities in Italy. Each stage of production is controlled by European specialists. Each section is manufactured by injection molding and is a monolith of two collectors and fins connecting the sections. Available center distance is 350 or 500 mm. Manufacturer's warranty – 10 years.
Aluminum radiators from STOUT Bravo Aluminum radiators from STOUT are covered by a ten-year manufacturer's warranty
Summarizing
Panel heaters are very different from the usual sectional heating radiator. Such heating devices look stylish and look good in any interior, and the possibility of bottom connection is worth a lot.
As for which panel heating radiators are better, we can advise you to choose models with internal fins, in which thermal energy will be transferred in 2 ways.
The video in this article shows the design of a steel panel radiator.
Did you like the article? Subscribe to our Yandex.Zen channel
Bottom radiator connection unit - advantages of use
Radiator fittings, which are used to connect from below, are intended for use in steel panel heat exchangers and are not suitable for aluminum radiator sections - due to this, steel types are highly competitive with them. Bottom inclusion compared to other types has the following advantages of using fittings:
- Saving pipe materials and outlets - in the floor structure or on the wall there are only two short outlets for connecting the radiator; the pipes do not go to its upper inlet.
- The connection at the bottom is aesthetically pleasing, and if the pipeline comes out of the wall, it is practically invisible under the body and does not interfere with cleaning the floor covering.
- Shut-off control valves (ball valves or valves) in the “binoculars” allow you to control the intensity of the liquid entering the heat exchanger, and when it is completely shut off, remove the batteries for maintenance or repair.
- The bottom connection unit with a vertical bypass evenly distributes water throughout the radiator with heating of its coldest upper corners, which is observed with the bottom connection. Also, with single-pipe wiring, the bypass helps to equalize the temperatures of the incoming and return flows, which in turn leads to uniform heating of the devices built into the line.

Rice. 2 Straight and elbow 3/4" bottom fittings installed