Cast iron heating radiator MS-140-500
Here you will learn:
- Features of the MS-140-500 radiator
- Technical characteristics of cast iron radiator
Despite the fact that steel, aluminum, copper and bimetallic radiators have appeared on the market, the cast iron batteries familiar to many people have not gone away. They are still sold in plumbing stores and are in some demand. In this article we will talk about the cast iron radiator MS-140-500 and its characteristics, and also tell about its features, advantages and disadvantages.
Total information
Batteries offered by manufacturers differ in the number of sections.
- in 10-section form;
- in 7-section design;
- in 4-section form.
Note! A different number of sections allows you to install cast iron radiators in rooms of different sizes. That is, you can choose a device that will be optimally suited for a particular room.
Types of MC batteries
MS-140-500 have a flat surface and are painted in different colors.
To compete with more modern types of devices, manufacturers of cast iron heating batteries had to expand this product line.
The following models are currently available on the Russian market.
- Cast iron heating radiators MS-140-500 are produced by the Republic of Belarus. This device has undergone several improvements. Now its surface, as a rule, has a flat appearance. In addition, the product comes already painted in different colors.
- Battery MS-140-500 with 7 heating elements. This is a frontal variation of the previous model.
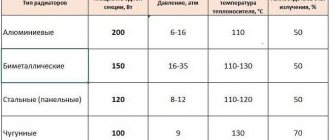
- Analogue MS-140-300. This device has a gap between nipples of 300 millimeters.
- The MS-140-108 model does not require significant care and does not require constant maintenance.
Difference between different device models.
- Cast iron heating radiators grade MS-140-180 and 98 have gaps between nipples of 108 and 98 millimeters. The devices, like the previous one, are produced in Russia and Ukraine.
Thanks to such a wide selection of products, property owners can optimally arrange heating in their home.
Indicators influencing the calculation of the number of sections
When choosing a radiator for a particular room, you need to take into account technical features. For example, the calculation will be different for a corner and non-corner room, for a room with different ceiling heights and different window sizes, etc. The most important parameters that are taken into account when determining the required radiator power are:
- the area of your premises;
- floor;
- ceiling height (above or below three meters);
- location (corner or non-corner room, room in a private house);.
- will the radiator be the main heating device;
- There is a fireplace and air conditioning in the room.
There are other important features that need to be taken into account. How many windows are there in the room? What size are they, and what kind of windows are they (wooden; double-glazed windows for 1, 2 or 3 glasses)? Was additional insulation of the walls done and what kind of insulation (internal, external)? In a private house, what matters is the presence of an attic and how insulated it is - and so on.

Cast iron radiators Conner (China)
According to SNIP, 41 W of thermal energy is required per 1 cubic meter of space. You can take into account not the volume, but the area of the room. For a 10 sq.m standard room with one door and one window, one door and an outer wall, the following heat output of the radiator will be required:
- 1 kW for a room with one window and an outer wall;
- 1.2 kW if it has one window and two external walls (corner room);
- 1.3 kW for corner rooms with two windows.
In reality, one kilowatt of thermal energy heats:
- In houses made of brick with a wall thickness of one and a half to two bricks, or made of timber and log houses (window and door area up to 15%; insulation of walls, roof and attic) - 20-25 sq. m
- In corner rooms with walls made of timber or brick of at least one brick (area of windows and doors up to 25%; insulation) - 14-18 sq. m
- In the premises of panel houses with internal cladding and a thermally insulated roof (as well as in the rooms of an insulated dacha) - 8-12 sq. m
- In a “living trailer” (wooden or panel house with minimal insulation) – 5-7 sq. m.
Technical characteristics of radiators MS-140 - 500
Radiators of the MC group belong to the category of sectional ones - they are assembled into a single whole from separate sections.
MS 140 cast iron radiator section.
The sections are connected into a radiator using intersection gaskets.

Intersectional gasket for cast iron radiator MS 140.
One section is pressed against another using a nipple.

Cast iron radiator nipple ms 140.
The ends of the radiator are closed with plugs, which can be shut-off or pass-through.

Radiator shut-off plug ms 140.

Radiator passage plug ms 140.
Sections are cast from gray cast iron with graphite additives. Individual parameters of MC 140 radiators may vary slightly in models from different manufacturers.
Main characteristics of the cast iron radiator model MC 140:
| Radiator type | sectional |
| Number of coolant channels, pcs. | 2 |
| Number of sections, pcs | from 2 to 10 |
| Nominal heat flow of one section, W | 160 |
| External casing coating | primer GF-021/0119 |
| Section material | gray cast iron in accordance with GOST 1412-85 |
| Intersectional gasket material | rubber according to GOST 1412, capable of withstanding temperatures up to +150ºC |
| Nipple material | cast iron or steel. GOST 1412 or 1050 |
| Heating area of one section, m2 | 0.195 |
| Center distance, mm | 500 |
| Nipple hole thread size | G11/4 |
| Type of coolant | water |
| Maximum coolant temperature, 0 C | + 130 0 C |
| Operating excess coolant pressure, MPa (kgf/cm 2) | 0.9 |
Other technical data:
| Number of sections, pcs. | Weight, kg | Length, mm | Nominal heat flow, kW | Capacity, dm 3 (l) |
| 2 | 12.8 | 227 | 0.32 | 2.50 |
| 3 | 18.8 | 331 | 0.48 | 3.75 |
| 4 | 24.8 | 435 | 0.64 | 5.00 |
| 5 | 30.8 | 539 | 0.80 | 6.25 |
| 6 | 36.8 | 643 | 0.96 | 7.50 |
| 7 | 42.8 | 747 | 1.12 | 8.75 |
The basic characteristics of the radiator can be determined by the model name and markings.
For example , model MC-140-500-0.9-7 designates a radiator with the name MC, depth 140 mm, center distance 500 mm, maximum pressure in the system 0.9 MPa, with the number of individual blocks in the radiator equal to 7.
- Types of heating radiators, their advantages and disadvantages
Section counting
The number of sections entirely depends on the configuration of the room. The main parameter is the area, but there are also such important aspects as zoning, floor, niche dimensions, ceiling height, the presence of double-glazed windows, and the number of windows.
If there is more than one window in the room, then experts recommend placing heating radiators under each one. This installation will significantly reduce heat loss. Below is a formula for calculating the required number of heating radiator sections.
Important! The comfort of corner apartment owners may be affected by additional heat losses. Therefore, such rooms need more powerful cast iron radiators. One or two sections are added to them.
There are many different methods for technical calculation of a radiator, but for standard rooms a simplified but fairly accurate formula is used to calculate the required number of sections.
So, to make the calculation, you need to multiply 100 W by the area of the room and divide by the thermal output of one battery section.
Important! If you end up with a fractional number , then the best solution is to round it up. This will create a small power reserve.
After the calculation is completed, you can proceed directly to installing the cast iron battery.
Technical characteristics of MS 140 batteries
For the manufacture of this type of radiators, an entire GOST 8690–94 was developed at one time, regulating all parameters of the product. In accordance with it, 5 standard sizes of batteries were produced with center distances of 300, 400, 500, 600 and 800 mm. The table below shows cast iron heating radiators with technical characteristics of dimensions in accordance with GOST 8690.
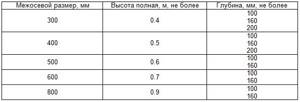
Previously, all standard sizes of these devices could be seen not only in apartments, but also in industrial or administrative buildings. It is advisable to review the characteristics of the two most popular standard sizes: 300 and 500 mm, which are still in demand. Other modifications are now very rare, and they are made only to order.
The main technical characteristics of the cast iron radiator MS 140 with center distances of 300 and 500 mm are reflected in the following table.
Having studied all the characteristics, we can draw conclusions about the advantages and disadvantages of the heating devices in question. Their advantages are as follows:
- Durability. It is at least 30 years old.
- Heat dissipation. Despite its outdated design, the cast iron radiator MC 140 shows good thermal power values.
- Unpretentiousness. The gray cast iron from which the devices are made is not subject to corrosion and easily tolerates poor coolant with a high oxygen content.
- Low maintenance. It is not superfluous to flush the channels of the product once every 2 years, but if this is not done, then the MS 140 will continue to work safely. Only the heat transfer rate will begin to decrease.
- Inertia. It is both a plus and a minus of batteries. The advantage is that after the heating is turned off, the device continues to radiate heat into the room for a long time.
- Affordable price.
Now about the shortcomings, of which there are also many. The same inertia of the devices causes them to heat up for a long time and excludes the possibility of regulation using thermal heads. There are others:
- Large coolant capacity. This affects the rate of heating and cooling of the system, and also forces a lot of thermal energy to be spent on heating a large volume of water.
- The considerable weight of the products affects the installation of radiators. They are very difficult to mount on walls made of porous lightweight materials, which are very popular nowadays.
- Low operating pressure threshold. This makes it impossible to install it in high-rise building systems.
- Fragility. The wall-mounted cast iron radiator MC 140 500 is shock-resistant because it has thin walls. It cracks at the slightest freezing of water from frost.
- Unpresentable appearance compared to more modern analogues of cast iron batteries.
Characteristics and Features
The secret of their popularity is simple: in our country, the coolant in centralized heating networks is such that it even dissolves or erases metals. In addition to a huge amount of dissolved chemical elements, it contains sand, particles of rust that have fallen off pipes and radiators, “tears” from welding, bolts forgotten during repairs and a lot of other things that are unknown how they got inside. The only alloy that doesn’t care about all this is cast iron. Stainless steel also does this well, but one can only guess how much such a battery will cost.

MS-140 - an undying classic
And another secret of the MS-140’s popularity is its low price. It has significant differences between different manufacturers, but the approximate cost of one section is about $5 (retail).
Advantages and disadvantages of cast iron radiators
It is clear that a product that has not left the market for many decades has some unique properties. The advantages of cast iron batteries include:
- Low chemical activity, which ensures long service life in our networks. Officially, the warranty period is from 10 to 30 years, and the service life is 50 years or more.
- Low hydraulic resistance. Only radiators of this type can be installed in systems with natural circulation (some also use aluminum and steel tubular ones).
- High temperature of the working environment. No other radiator can withstand temperatures above +130oC. Most of them have a maximum limit of +110oC.
- Low price.
- High heat dissipation. For all other cast iron radiators, this characteristic is in the “disadvantages” section. Only MS-140 and MS-90 have a thermal power of one section comparable to aluminum and bimetallic ones. For MS-140, heat transfer is 160-185 W (depending on the manufacturer), for MS 90 - 130 W.
- They do not corrode when the coolant is drained.

MS-140 and MS-90 - difference in section depth
Some properties are a plus under some circumstances, and a minus under others:
- Large thermal inertia. It may take an hour or more until the MS-140 section warms up. And all this time the room does not heat up. But on the other hand, this is good if the heating is turned off, or a conventional solid fuel boiler is used in the system: the heat accumulated by the walls and water maintains the temperature in the room for a long time.
- Large cross-section of channels and collectors. On the one hand, even a bad and dirty coolant will not be able to clog them in just a few years. Therefore, cleaning and washing can be carried out periodically. But due to the large cross-section, more than a liter of coolant “fits” in one section. And it needs to be “driven” through the system and heated, which means extra costs for equipment (a more powerful pump and boiler) and fuel.
“Pure” disadvantages are also present:
- Heavy weight. The weight of one section with an axial distance of 500 mm is from 6 kg to 7.12 kg. And since you usually need from 6 to 14 pieces per room, you can calculate what the mass will be. And you will have to wear it, and also hang it on the wall. This is another drawback: difficult installation. And all because of the same weight.
- Fragility and low working pressure. Not the most pleasant characteristics. Despite their massive size, cast iron products must be handled with care: they may burst upon impact. The same fragility leads to not the highest operating pressure: 9 atm. Pressure testing - 15-16 atm.
- The need for regular coloring. All sections come only primed. They will need to be painted often: once every year or two.

Thermal inertia is not always a bad thing...
Application area
As you can see, there are more than serious advantages, but there are also disadvantages. If we summarize everything, we can determine the scope of their use:
- Networks with very low coolant quality (Ph above 9) and a large number of abrasive particles (without mud traps and filters).
- In individual heating when using solid fuel boilers without automation.
- In networks with natural circulation.
Why cast iron?
Cast iron radiators have a number of advantages, let’s look at the main ones:
- High resistance to corrosion. This property is due to the fact that during operation the surface of the radiator is covered with “dry rust”, which prevents corrosion from developing. Cast iron is also very wear-resistant; stones and various debris from heating pipes do not cause much harm to it;
- Good thermal inertia. The cast iron heating radiator MC 140 retains 30% of the radiated heat even an hour after the boiler is turned off, while for steel radiators this figure is only 15%;
- Long service life. So for high-quality cast iron radiators it can reach 100 years, although manufacturers talk about 10-30 years of reliable operation;
- Large internal cross-section of radiators. It is for this reason that cast iron heating radiators MC 140 500 rarely require cleaning;
- Cast iron, due to its composition, under no circumstances can cause electrochemical corrosion. In other words, no conflicts can arise with plastic (steel) pipes.
Cast iron radiators MS 140 technical specifications
Attention!
Heating radiators are sold ONLY in bulk upon request to complete an object. There is no retail sale.
We offer you to buy traditional cast iron heating radiators in Novosibirsk with delivery by our vehicles (pickup or delivery to a transport company for shipment to the regions is possible).
| Cast iron radiators MS-140M. Cast iron radiators are manufactured in accordance with GOST 8690-94 standards |
Technical characteristics of Radiators MS-140M 500 4 sections, Minsk
Cast iron radiators are manufactured in accordance with GOST 8690-94 standards
| Radiator type | Sectional, two-channel, medium height | |||||||||
| Nipple hole thread | G 1¼–B | |||||||||
| Maximum coolant temperature | 130°C | |||||||||
| Gasket material | heat-resistant rubber ITS and ITP TU 38 105376-82 | |||||||||
| Material of sections and plugs | SCH 10 GOST 1412-85 | |||||||||
| Nipple material | KCH 30-6-f GOST 1215-79 | |||||||||
Cast iron radiators are an inexpensive solution to space heating issues, but such a radiator does not have an aesthetic, not modern appearance. If you are interested in cast iron radiators, then pay attention to modern cast iron radiators. Their prices are higher, but they look like modern aluminum radiators.
Main characteristics
| 140 | 500 | gray cast iron | 4 sections |
| Section depth, mm | Center distance | Housing material | Number of sections |
| Amount in a package | 1 |
| Weight | 28,7 |
| Volume | 0,03717 |
| Section height, mm | 588.0000 |
| Section width, mm | 108.0000 |
| Coolant operating pressure, MPa | 0.9 |
| Heat transfer of one section, W | 160 W. |
| Maximum coolant temperature, C | 130 |
| Capacity of one section, l | 1.45 |
| Weight of one section, kg | 7.1 |
| Manufacturer's warranty period, years | 3 |
| Nipple hole thread (DN) | G 1¼" |
Technical characteristics of Radiators MS-140M 500 7 sections, Minsk
| 140 | 500 | gray cast iron | 7 sections |
| Section depth, mm | Center distance | Housing material | Number of sections |
| Amount in a package | 9 |
| Weight | 51 |
| Volume | 0,00716 |
| Section height, mm | 588.0000 |
| Section width, mm | 108.0000 |
| Coolant operating pressure, MPa | 0.9 |
| Heat transfer of one section, W | 160 W. |
| Maximum coolant temperature, C | 130 |
| Capacity of one section, l | 1.45 |
| Weight of one section, kg | 7.1 |
| Manufacturer's warranty period, years | 3 |
| Nipple hole thread (DN) | G 1¼" |
Available assembly options:
What do the numbers in the name of MS-140M radiators mean?
For example: MS-140M 500 4sec. Minsk
Radiator MC - Name 140 - radiator depth 500
— Center-to-center distance (distance between connection points)
4 sec. — 4 sections (Number of sections in the assembled radiator)
Attention!
Heating radiators are sold ONLY in bulk upon request to complete an object. There is no retail sale.
Our specialists will help you decide on the choice of radiator based on your needs. To get advice, find out the current price based on your volume (and/or) order radiators, you need to contact our managers by phone:
+7 +7
What is an equivalent square meter or ECM?
The equivalent square meter (ESM) is usually called the heating surface that is heated by the heating device. This surface gives off 435 kcal/h of heat with a difference in average temperatures of the coolant and air of 64.5°. 17.4 kg/h of water passes through the device, while the coolant is supplied to the device according to the “top-down” scheme.
Cast iron heating radiators GOST 8690.
Classification by radiator type:
— high (distance between nipple holes 1000 mm, total height 1100 mm);
— medium (distance between nipple holes 500 mm, total height 600 mm);
— low (distance between nipple holes 300 mm, total height 400 mm);
Dimensions and technical characteristics of cast iron radiators.
Fig.1. Cast iron radiator section GOST 8690.
Weight of a section of cast iron heating radiators of models M-140, M-140 AO, RD-90, RD-26.
Table 1. Main technical characteristics and dimensions of cast iron radiators according to GOST 8690.
| Radiator model | Section heating surface | Internal volume, l | Dimensions, mm | Average weight, kg (with nipples and plugs) | ||||||
| m 2 | ekm | sections | per 1 ecm | H | HP | A | IN | sections | per 1 ecm | |
| M-140 | 0,254 | 0,31 | 1,42 | 4,6 | 500 | 582 | 140 | 96 | 7,6 | 24,4 |
| M-140 AO | 0,287 | 0,35 | 1,42 | 4,6 | 500 | 582 | 140 | 96 | 7,6 | 22,45 |
| RD-90 | 0,2 | 0,275 | 1,43 | 5,22 | 500 | 582 | 90 | 96 | 6,95 | 25,3 |
| RD-26 | 0,293 | 0,275 | 1,36 | 4,95 | 500 | 593 | 90 | 88 | 6,95 | 25,3 |
Note: These radiators are designed for operating pressure up to 6 kgf/cm 2.
Complete set of cast iron radiators for heating.
Each radiator must be equipped with four plugs, two of them will be blind with left-hand threads, and the other two with holes and right-hand threads. The plugs are cut with internal pipe thread ¾ or ½ ʺ at the customer's choice.
Radiators are supplied to the customer with a disposable primer coating for painting.
Radiator plugs and nipples are shown in Fig. 2.
Cast iron radiator plug size.
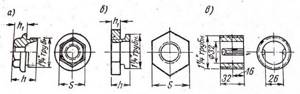
Fig.2. Radiator plugs and nipple.
a – turnkey plug S=36 mm; b – turnkey plug S=55 mm; c – nipple.
Table 2. Dimensions of cast iron radiator plugs.
| Key plug S | h | h1 |
| 36 | 36 | 20 |
| 55 | 25 | 9 |
Did you find the article useful?! Share with your friends on social networks.
Installation
The number of sections has been calculated, the radiators have been purchased, all that remains is installation. There are two options here - turn to specialists and spend money, or do everything yourself. Let's consider the second option.

Installation process
Selecting fastenings
The first installation step is choosing a mount for the radiator. In the photo you can see different types of fastenings.
For example, for sectional radiators, pin and corner brackets are used. The first ones are used to fix the battery on a wall made of brick or plaster, and the corner ones are used if the wall is wooden. You should also remember that for corner fastening you need to stock up on screws and dowels.

Types of fasteners. As you may have guessed, fastenings No. 3 and No. 4 are applicable for our case.
Direct installation
At this stage you need to select places to install the brackets. Remember that one radiator requires at least three brackets. Afterwards, using dowels and a drill, you need to secure the brackets.
The next step is to attach the radiator to the brackets.
Advice. There is no need to immediately tear off the protective film from the radiator; first install it on the brackets, and then, without fear of scratching the radiator, remove the film.
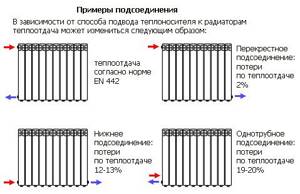
Connection examples
Carefully connect the supplied pipes to the radiator. Fasten carefully and carefully, but do not damage the threads, otherwise you will experience water leakage from the system. Before watching, check out the installation video in our gallery.
During installation, it is important to maintain certain distances. For example, the installation height above the floor should be approximately 10 centimeters. The distance between the wall and the battery should be from 2 to 5 cm.
Find out also about the features of electric double-circuit heating boilers.
Weight of imported cast iron radiators
Today, many models of domestic imported production have been put into operation, all of them are classified differently. Many modern cast iron batteries are designer, imitation in retro style. They can repeat classic designs in functionality and dimensions, but are significantly superior in aesthetics, adding weight due to artistic soldering or molding of patterns. Many initially have legs for floor mounting, such as Viadrus Termo (Czech Republic).
Installation of radiator MS 140 500
Installation is carried out in one of two options. Either we trust the process to specialists, or we do everything ourselves. The second option is more convenient.
- The first step before installing the MC 140 radiator is selecting a mount . For sectional radiators, pin and corner brackets are used. The first type is used to fix the radiator on a brick or plaster wall, the second - on a wooden wall. It should be remembered that in order to carry out the corner fastening you need to purchase screws and dowels.
- The second step is direct installation . The first stage begins with choosing locations for mounting the brackets. One MC 140 radiator requires at least three of them. Then, using a drill and dowels, the brackets are attached.
- The second stage is mounting to the radiator brackets.
Important! Remove the protective film only after installing the cast iron radiator, as its surface can be scratched.
Carefully connect the supplied pipes to the battery. Fastening must be done carefully but carefully, making sure not to damage the threads, otherwise you risk water leakage.
When installing, pay attention to the distance of the structure from the floor and wall. The MC 140 radiator should rise approximately 10 centimeters above the floor. The interval between it and the wall should be within 2-5 centimeters .
So, the cast iron radiator MC 140 500 can be safely installed in your homes. They are slightly inferior in technical characteristics to new devices, but the price is their advantage. In addition, they have a long trail from the past, proving their suitability throughout the 20th century both in our country and abroad. The main indicator was long service life.
solutions and problems
What troubles can the owner of a cast iron battery expect?
Intersectional leaks
The reason for their appearance is cooling and multiple heating cycles (see compression and expansion) during normal operation of the heating system. As a result, paronite gaskets lose their elasticity, and when the battery is cooled again, moisture appears at the joints of the sections.
If there is a small leak through one or two gaskets, instructions for eliminating the leak look like this:
- When the coolant is discarded, the blind plugs are opened.
- The distance to the problem nipple is measured on the radiator key.
- The key is inserted into the manifold until it engages with the nipple and tightened using any lever or gas wrench No. 2 - No. 3.
If the leaks become widespread, the radiator is rebuilt and all gaskets are replaced. In the role of the latter, it is possible to use both standard paronite products and rubber ones cut out with your own hands from a car inner tube.