Water pipelines made from polypropylene pipes have long since become commonplace rather than a rare exotic item. In terms of the combination of cost, durability and reliability, polypropylene is the clear leader among modern materials. Can these pipes be used in heating systems?
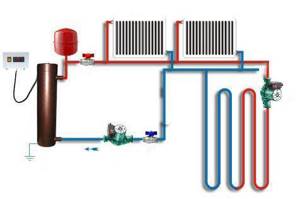
As you can see in the photo, polypropylene is successfully used in heating systems.
Diameter selection
Selecting the size of structures to create a heating circuit is the most important task.
To clearly cope with this task you need to consider:
- resistance coefficient value;
- calculated data for cooling water in batteries;
- indicators of the diameters of the boiler inlet and outlet;
- speed of media movement within the system;
- wiring diagram.
You need to pay special attention to the last point. If the wiring configuration is complex or the heating system contains not only radiators, but heated floors, the standard design scheme will not be the most successful
In such situations, it is advisable to seek the help of qualified specialists who will help you effectively solve this problem.
When installing a forced system, choose structures with a small cross-section. The lower it is, the less media consumption will be for heating. In addition, this will simplify installation and slow down the speed of movement of the media inside the circuit.
Below you will find out the characteristics of pipes of various diameters.
| Diameter (mm) | Wall thickness (mm) | Rod length (m) | Pressure |
| 16 | 1,2 | 5 | DN10-PN16 |
| 20 | 1,5 | 5 | DN15-PN16 |
| 25 | 1,9 | 5 | DN20-PN16 |
| 32 | 2,4 | 5 | DN25-PN16 |
| 40 | 3 | 5 | DN32-PN16 |
| 50 | 3,7 | 5 | DN40-PN16 |
| 63 | 4,7 | 5 | DN50-PN16 |
| 75 | 5,6 | 5 | DN65-PN16 |
| 90 | 6,7 | 5 | DN80-PN16 |
| 110 | 8,2 | 5 | DN100-PN16 |
| 160 | 7,7 | 5 | DN150-PN16 |
The most optimal cross-sectional size of structures for arranging a circuit in an apartment or private house is from 16 to 25 mm. In any case, before making a choice, you need to carry out the appropriate calculations. This is the only way you can select pipes of the appropriate diameter.
Types, labeling, scope of application
A wide range of polypropylene pipes arose due to the variety of types of this polymer. To make it easier for consumers to navigate, international marking of polypropylene pipes for heating has been introduced. From it you can determine the main technical characteristics of polypropylene pipes.
The main types of markings and technical data are presented in the table below.
| Marking | Pipe pressure designation (maximum) | Type of polymer | Purpose | Working temperature | Pressure parameters |
| PN (РРН) | Polypropylene pipes PN 10 | Homopolypropylene, thin-walled pipes | Cold water, ventilation systems, industrial pipelines (large diameter). | +20 °С…45 °С (depending on type) | 1 MPa (10.2 kg/cm²) – 10 atmospheres |
| PPB | PN 16 | Block copolymer, high deformation | Cold water, ventilation, heated floor. We produce fittings and connections for polypropylene pipes. | +60 °С | 1.6 MPa (16.32 kg/cm²) – 16 atmospheres |
| PPR | PN 20 (PPRC RS 20) | Random copolymer | Hot and cold water supply, heating with radiator system. | +80… +95 °С | 2 MPa (20.4 kg/cm²) – 20 atmospheres |
| PPs, (PPRS) | PN 25 | Random copolymer, reinforced with a layer of aluminum, fiberglass, nylon. | For all types of water supply, for central heating systems, heated floors. | +/–95 °C | 2.5 MPa (25.49 kg/cm²) - 25 atmospheres |
It is necessary to select polypropylene products for heating and water supply based on the parameters indicated above
.
Table: diameter, wall thickness, weight.
| Outer diameter (mm) | Wall thickness (mm) | Weight, mass (gram) | ||||||
| PN 10 | PN 20 | PN 25 | PN 10 | PN 20 | PN 25 | PN 10 | PN 20 | PN 25 |
| 20 | 20 | 20 | 1,9 | 3,4 | 3,0 | 110 | 167 | 172 |
| 25 | 25 | 25 | 2,3 | 4,2 | 3,3 | 159 | 261 | 242 |
| 32 | 32 | 32 | 2,9 | 5,4 | 4,0 | 253 | 424 | 381 |
| 40 | 40 | 40 | 3,7 | 6,7 | 5,0 | 398 | 653 | 587 |
| 50 | 50 | 50 | 4,6 | 8,3 | 6,5 | 625 | 1020 | 825 |
| 63 | 63 | 5,8 | 10,5 | 981 | 1620 | |||
| 75 | 75 | 6,8 | 12,5 | 1380 | 2300 | |||
| 90 | 8,2 | 1980 | ||||||
| 110 | 10,0 | 2950 | ||||||
Thus, pipes designated PPs (PPRS) have the highest performance.
All polypropylene is divided into types:
- Consisting of single-layer polymers of various types: PPH, PPB, PRR, PPs. Depending on the type of polymer, they have different technical parameters. Each of these types of pipes has its own class.
- Pipes consisting of several layers (reinforced) are mainly copolymers.
They are reinforced:
- aluminum foil: perforated and solid;
- polyethylene;
- fiberglass.
The second type is used for all types of communications. They have increased strength and are resistant to deformation. Polypropylene heating pipes of this type have a fairly long service life. They are not afraid of high temperatures up to +95 ° C, but at maximum loads the service life is reduced. To check the system after installation, it should be noted that setting a temperature close to +120 °C (steam temperature) is very risky.
The strength of the reinforced polymer itself has created the prerequisites for its use in the heating system of multi-storey buildings. It finds application not only in the pipeline of central heating systems. Due to the low linear expansion of PPs, polypropylene pipes for hot water have proven themselves well for laying routes, and therefore are in demand among consumers.
Reinforced pipes
Pipes reinforced with polyethylene and fiberglass are equated in class to metal-plastic. Their peculiarity is that the strength of the products is not inferior to pipes with an aluminum layer. The advantage is that there is no need to clean or chamfer before installation, so they form a tighter joint when soldered. Some experts doubt whether they can be used for hidden installation systems.
PPs (random copolymer) reinforced pipes are made from propylene with the addition of ethylene molecules, using high-temperature conditions, by pressing and mixing (extrusion). They can be used for hidden floor heating. Experts recommend polypropylene reinforced with polyethylene and fiberglass
.
Meanings of markings on pipes:
- the first word indicates the name of the manufacturer;
- the second means marking according to the type of polymer from which the pipe is made (PN, PPB, PPR, PPs);
- the third value will indicate the properties of the pipe according to the nominal pressure (designation: PN 10, PN 16, PN 20, PN 25);
- the next one is a series of numbers indicating the diameter and thickness of the walls;
- Next comes the class - this means the degree of reliability of operation;
- then follows a description of the permissible operating pressure in numbers (how much the pipe will withstand);
- At the end of the marking, TU and GOST are indicated, which depend on the grades of polypropylene pipe.
Of course, not all properties of the product are indicated in the labeling. But it's enough to get an idea of the general purpose.
PEX pipe cross-linked polyethylene

18. PEX pipe.
PEX pipe is a cross-linked polyethylene pipe that is highly durable and resistant to high temperatures.

19. Fittings for PEX pipe.
Such pipes are used in hot water supply systems and heating systems, in particular in underfloor heating systems.
And yet, PEX pipes are still little used due to the high price of the pipes themselves, fittings and installation equipment.
So, which pipes should you choose for heating?
If you intend to make a heating system yourself and do not have professional welding skills, then the best option for you is polypropylene pipes. And because these pipes are significantly cheaper than steel ones (if you mess up somewhere, it’s easy, quick, and inexpensive to fix). And because welding polypropylene pipes is very accessible to people who have never been involved in this type of activity. It is very easy and relatively quick to assemble a heating system from polypropylene pipes (in fact, the preparatory stages take more time: design, calculations, preparation of materials, but the actual soldering is quick and easy, especially after some practice).
In my opinion, the only drawback of installing a heating system made of polypropylene pipes is the need to acquire a special welding machine (soldering iron). But in many cities (and even villages - I know for sure, because I live in a village) such soldering irons can be rented for a daily fee, which is small (for example, for us it is fifty rubles per day).
Let me give you a couple of tips. For the heating system, use only glass fiber reinforced polypropylene pipes. And don’t skimp on faucets - install them right away from stainless steel, then you will be one hundred percent sure that there will be no reaction with the aluminum or copper elements of the system.
Why not choose metal-plastic pipes? Yes, it is easier to assemble a heating system from metal-plastic pipes, since the connections are detachable - just a wrench is enough. But the reliability of such connections, to put it mildly, is far from perfect. Unlike polypropylene pipes, where the connections are sealed and monolithic. That is, if you choose metal-plastic pipes for your water heating system, you will not be one hundred percent sure of the reliability of the hot water pipelines. But for a water floor system, a metal-plastic pipe is just right, because in this case, long-length pipes are used, and a minimum of connections is obtained.
Corrugated stainless steel is still exotic on the Russian market, although it has significant advantages
So, if finances are tight, if you have somewhere to buy, then you can pay attention to it
Good luck.
which pipes to choose for heating
Types of polypropylene pipes
Solid plastic pipes
Pipes made of solid plastic are the cheapest.
Monolithic products are made of solid PVC, the expansion coefficient is 0.15%. They can only be used when installing systems in which a substance with a low temperature moves, for example, for ventilation and cold supply.
At water temperatures above 10C°, the use of these pipes is simply impractical - they will not withstand and may crack or burst. This must definitely be taken into account.
Reinforced polypropylene pipes
Aluminum is used to reinforce plastic products. Layers additionally reinforced with aluminum can be located on the outside, in the form of thin foil, or on the inside, in the form of point perforations. Perforation is applied in the form of a mesh with holes. During the casting of a product, the viscous material, entering the holes, creates a tight adhesion of the polymer to the metal alloy.
Reinforced polypropylene pipes are the most reliable
Thanks to this type of strengthening, the system can withstand coolant heated to 90C°. It must be taken into account that installation and welding of aluminum-reinforced products can be complicated by the fact that they do not always correspond to the depth of insertion into the fittings and require additional stripping and removal of the top foil.
Fiberglass pipes
This product consists of two layers of plastic and a middle layer containing fiberglass. Plastic elements reinforced with glass do not require cleaning or calibration during installation. Soldering is quick and easy, which significantly reduces time and financial costs.
Glass increases rigidity, element density and service life. The disadvantage of such pipes is considered to be thermal elongation indicators, which are significantly higher than the same indicators for products reinforced with aluminum.

Operation of plastic pipes with fiberglass in different coolant temperatures
Metal-plastic pipes
Metal-plastic products are equipped with a top layer of PVC and an inner layer of aluminum. Such samples are able to withstand very high temperatures and can be used for heating and water supply of a private home. The disadvantage of elements made of metal-plastic is that the metal layer, being in contact with the transported substance, may be susceptible to corrosion.
Choosing heating pipes or which pipes are better
There are several types of material. The most common type is called Green Line Type One.
Product type “Flow Guard Gold Type Two”
It can be used in systems with media temperatures up to eighty degrees. More often this type is used in the installation of air conditioning systems and refrigeration units.
The type of material in question begins to undergo deformation already at a temperature of ninety-five degrees
Therefore, it must be used with extreme caution
In the heating circuit from it, the temperature of the medium should not exceed the above limit.
Flow Guard Gold Type Two is a universal grade of chlorinated PVC. Withstands temperatures up to one hundred degrees. It is used for arranging both the internal and external parts of the circuit. You can even install risers from this type of plastic. The table below shows the technical characteristics of CPVC and PVC.
| Properties | Chlorinated PVC | Regular PVC |
| Linear expansion coefficient | 0,62 | 1,2 – 1,4 |
| Density (g/cm2) | 1,57 | 0,95 |
| Thermal conductivity (W/Mk) | 0,14 | 0,22 |
| Tensile Yield Strength (MPa) | From 50 to 55 | From 18 to 26 |
| Design strength (MPa) | 10 | 6,3 |
| Oxygen permeability (upon reaching +70 in the system) | Less than 1 | 13 |
| Modulus of elasticity (MPa) | 2400 | From 550 to 800 |
Based on the information above, we can conclude that the chlorinated version of the material is characterized by a lower thermal conductivity. This property allows you to significantly reduce heat losses in the system. The structures will not get very hot. The likelihood of condensation will be minimal. These properties make it possible to construct a heating circuit without installing an additional thermal insulation layer.
Pipes made from the material in question are suitable for arranging a central water circuit and floor heating. They can be used in systems based on gas and solid fuel boilers.
Products made from other types of plastic are also suitable for solving this problem. But they also have their pros and cons. For example, polypropylene (PP) structures are less rigid, which reduces the number of fittings required when installing the system. However, they do not have sufficient resistance to high temperatures.
There is no clear answer to the question of which pipes are best for arranging a heating circuit. When designing a system, the smallest details must be taken into account. This is the only way to most effectively select the most suitable material for solving the problem.
Which pipes to choose
As mentioned above, we use polypropylene only in autonomous heating systems. Moreover, for a strengthening effect, we take pipes only with reinforcement. And this is due not only to the fact that such a material is more tensile (25 kgf/cm2). Few people know that polypropylene also gives the highest elongation coefficient when heated. So, every meter of your pipe, when heated to 70 degrees, lengthens by six and a half millimeters.
Which reinforcement to choose? Nowadays aluminum and fiberglass are used for these purposes. The foil is simply glued between two layers of polymer. But the fiberglass is welded to the inner and outer shell.
How does such reinforcement help? It significantly reduces pipe elongation at elevated temperatures.
Do you need to overpay for a brand? When buying Valtec or Rehau, you, of course, overpay, but you get really high quality products. And if these are reinforced pipes, then they are made using the highest quality glue and in compliance with all technology requirements.

What diameter should I choose? Let's say right away that for steel pipes they usually talk about the internal diameter, while for polypropylene it is the external diameter. This means that the throughput of such a pipe will be less than the steel one that stood in its place before. Therefore, with such a replacement, the size of polypropylene pipes is taken with an increase of 1-2 steps. That is, 25 mm instead of DN 20, for example.
In addition, experts advise adhering to the following dimensions when designing an autonomous heating system using polypropylene pipes:
- filling with forced circulation – from 25 to 32 mm;
- filling with natural circulation – from 40 to 50 mm;
- connections to radiators – 20 mm.
We recommend: What is included in heating system maintenance?
DIY heating installation
You can install the heating system yourself. The main thing is to choose the right materials, compare them correctly and seal them tightly. The design itself is quite simple to assemble and operate.
What connectors to use
In order to attach one pipe to another, pipes to risers and radiators, pressure gauges and other devices, special connectors are needed. The following types are distinguished:
- Straight (regular couplings). They are necessary in those places where one pipe connects to another of the same diameter, but not at an angle;
- Curved. Used in places where the system bends and rotates;
- Triples. They are needed if you need to make two from one pipe or one from two. For example, in the places where branches extend from the main pipe to the radiator;
- Blind (stubs). They are installed in “dead-end” areas, for example, on the outer radiators;
- With a change in the internal section. They are used when moving from a larger diameter pipe to a smaller diameter pipe. For example, when connecting pipes with risers;
- With plastic and metal. Such connectors are necessary in places where there is a transition from plastic products (pipes) to metal ones (radiators, pressure gauges, tanks).
Before starting installation work, it is necessary to recreate on paper the exact diagram of the proposed system and calculate the number of connectors of each type
In addition, it is important to select connectors whose internal diameters will coincide with the diameters of the pipes
Installation work algorithm
After drawing up a heating scheme and purchasing all the necessary elements, you can begin installation work.
To do this, you will need a special kit consisting of a soldering iron with attachments (couplings and drones) and shaders.

It is not necessary to purchase it to install one heating system; it can be rented.
The installation algorithm looks like this:
Cutting pipes and laying out connectors
This is a preparatory stage that is important to perform strictly according to the instructions. The pipe is cut using special scissors. Cleaning pipes with a shaver
This step is only necessary when installing pipes with aluminum reinforcement. To do this, take a shaver and put it on the pipe, and rotate it manually or with a screwdriver. Soldering iron assembly. Couplings and mandrels of the appropriate diameter are put on the apparatus, after which it is turned on and heated to 260 ͒ C. At this time, a depth mark is made on the pipe corresponding to the connecting element. Compound. A pipe is inserted into the coupling of a heated soldering iron to a certain depth, and a connecting element is inserted into the mandrel on the other side, after which the elements are soldered to each other over a certain period of time. The time is calculated as follows: with a pipe diameter of 1.6 cm - 5 seconds, 2.0 cm - 7 seconds, 3.2 cm - 8 seconds. All other sections of the pipe are assembled in a similar way, after which the structure is connected to the heating system.
Features of installation in an apartment and private house
It is easier to install a heating system in an apartment. As a rule, one radiator is installed in each room, which extends from a common riser. The pipes are connected according to the proposed scheme, and then connected to the riser and radiator.

If you install several radiators, you can choose two-pipe and single-pipe heating systems. In the first case, the coolant flows from each previous radiator to the next one. Accordingly, in all subsequent radiators the temperature will be lower than in the previous ones. In the second case, there are two pipes: one for liquid input, the other for output.
Before carrying out work in the apartment, it is necessary to coordinate heating repairs with the housing office and the closest neighbors. Replacement of risers is usually carried out centrally.
When installing a heating system in a private house, there will be more work. It is necessary to select the type of coolant, the type of boiler and the system for removing the coolant from the boiler and in the reverse order.
Installing the boiler itself can also cause difficulties if you lack experience. The heating pipe is usually installed in the basement of the house. The boiler is then connected by pipes to radiators in each room. Such systems are quite complex, but they also have advantages - the temperature and pressure in the pipes can be adjusted independently.
The use of propylene pipes in the heating system
The range of propylene pipes on the modern construction market is very large. You can find not only domestic pipes, but also those made in Turkey, the Czech Republic, and Italy . Pipes are used in different heating systems:
- centralized;
- boiler installations;
- underfloor heating system;
- hot and cold water supply system;
- organization of risers.
It is best that the temperature of the coolant in the pipe does not exceed 70 degrees to prevent deformation.
Pipes with a diameter of 20 mm are used in the hot water supply system . Pipes with a diameter of 25 mm are used for central heating systems and risers.
For autonomous heating, the pipe diameter is selected individually.
Warm floors are created using polypropylene pipes, the diameter of which does not exceed 16 mm.
Pipe connection and processing
Propylene pipes are very easy to process and prepare for installation. Using special scissors, pipes are easily cut to size and there is no need to use a saw. Propylene pipes are connected by soldering the joints , and the sealed joints are very reliable and durable, which is necessary if the pipes are embedded in walls.
In order to solder propylene pipes together, you do not need to process or prepare them in advance; the joints are simply sealed, which guarantees the reliability of the heating system.
Advice . Propylene pipes should be connected to each other very carefully and carefully to avoid defects and unpleasant situations.
What are the advantages of using polypropylene
It is important to remember that a heating system made from propylene pipes has a number of undeniable advantages over heating created using a pipeline made from other types of pipes:
You can focus on the low cost of this material; the big advantage is the low thermal conductivity coefficient, which reduces all heat losses to a minimum; the service life of the heating system is significantly increased due to stronger and more reliable welding joints when compared with collet ones.
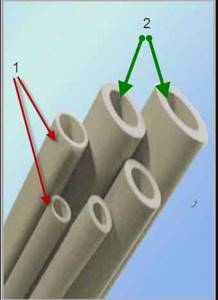
Polypropylene pipes. 1 - thin-walled; 2 - thick-walled
Polypropylene pipes are distinguished by pressure and also by temperature. The simplest and cheapest are designed for operation in a system where the pressure does not exceed 10 atmospheres. They are designated PN-10. These pipes, as a rule, are used only for supplying cold water, since they are thin-walled, and the wall thickness varies between 2.5 - 2.8 mm.
Before proceeding with the installation of the heating system, it is necessary to create a diagram indicating the dimensions of the polypropylene heating pipes.
So, in addition to PN-10, there are also PN-16 pipes, designed for a pressure of 16 atmospheres and an operating temperature of 80 degrees, and the wall thickness reaches 3 mm. PN-20 pipes function normally at temperatures up to 85 degrees and a pressure of no more than 20 atmospheres. Such pipes are considered thick-walled (4mm wall thickness).
When installing a heating system, preference should be given to reinforced polypropylene pipes. Their price, of course, is almost 40% higher, but their appearance is more attractive. When installing reinforced pipes, much fewer expansion loops will be required, which reduces the number of welding seams and increases the strength of the entire system as a whole.
Which polypropylene pipes for heating should I choose?
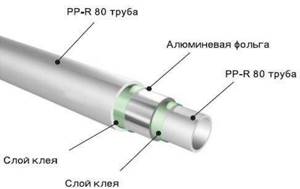
To select reinforced polypropylene pipes, you need to know reinforcement methods:
- When reinforcing a pipe with a solid sheet of aluminum, a solid sheet of metal is applied to the outer surface of the pipe, which is cut off by 1 mm during welding. Reinforcement with perforated aluminum sheet occurs in a similar way. When reinforcing a pipe with aluminum sheet, the wall of the product is strengthened either in the middle or closer to the inside of the pipe. Manufacturers claim that there is no need to pre-clean before welding.
- The glass fiber reinforcement is made exactly in the middle part of the pipe, so the outer and inner parts are made of polypropylene.
- When reinforced with a composite, a composite material consisting of a mixture of polypropylene and fiberglass significantly increases the strength of the product. In such pipes, the composite material is located in the middle of the product, and the upper and inner parts consist of polypropylene.
Polypropylene heating pipes, reinforced with a solid sheet of aluminum, have one, but significant drawback - they need to be cleaned before welding. Many companies have included in the production of products reinforced with perforated aluminum, however, perforation contributes to significant penetration of oxygen into the heating system, which can damage the heating boiler.
Many manufacturers have solved the problem of pipe stripping by launching the production of glass fiber reinforced products.
Can polypropylene withstand all this?
The physical and chemical properties of the material are as follows.
Polypropylene has the lowest density, but has sufficient strength. Thanks to this, it will be able to withstand the effects of abrasive substances that are invariably contained in the coolant. Therefore, neither sand nor slag present in hot water can damage the integrity of the internal walls.
Polypropylene pipes can only be melted by prolonged heating. The softening temperature of polypropylene is + 140 degrees, and the melting point of the material is +170. This means that the material corresponds to the operating characteristics of central and autonomous systems. Moreover, if you consider that water in central systems is heated to +105 degrees only during very severe frosts. During the rest of the time, the coolant heats up to no more than +95 degrees.
This is precisely the temperature that manufacturers claim as the maximum possible limiter. But in this situation, it is necessary to take into account that hot water flows under high pressure in the supply heat pipe. Often water enters the risers of houses directly, bypassing the nozzle in the elevator, which allows you to regulate its temperature. And this can lead to dangerous accidents if polypropylene is used.
Destruction of the internal and external surfaces of pipes can be caused by exposure to concentrated acid and other additives that are often used in hot water to reduce corrosion.
But it is necessary to take into account the fact that polypropylene has a very high coefficient of linear expansion. Therefore, when the coolant temperature increases to 92 degrees, the vertical risers will definitely begin to sag.
Major manufacturers of polypropylene products for water supply
On the Russian PP pipe market you can most often find domestic manufacturers, as well as products from China, Turkey and the EU. European manufacturers have the highest prices, while Russian manufacturers are considered the most budget-friendly.

Jakko-products from Turkey of good quality
Good quality and the best price can be offered by such well-known brands as:
- Blue Ocean (China);
- FIRAT (Türkiye);
- Kalde (Türkiye);
- Jakko (Türkiye);
- PROAQUA (Russia);
- PBK (Russia);
- Aquatherm (Germany).
The same companies also produce connecting elements.

Range of polypropylene products
Related article:
Installation and wiring, what are the nuances?
The structures of polypropylene pipes are one-piece. They are mounted using diffusion welding. Special fittings are used to install internal outlets. When connecting plastic and metal parts (faucets, mixers), corner joints with pressed-in brass segments are used.
Polymer pipelines are suitable for all types of installation:
- in separate channels and shafts;
- exposed wiring on the surface of the walls;
- closed laying in a layer of cement-sand screed or plaster.
Work order:
- Plastic pipes are cut with special scissors included in the equipment assembly kit.
- Measure the distance with a tape measure and use a pencil or marker to transfer this value to the surface of the product.
- The junction area is thoroughly degreased. Pipe markings that fall within the installation area must also be removed.
- Nozzles are installed on the unit and plugged into the network. The heating temperature regulator is set to 260°C. The heating time of the material is controlled by a burning light bulb. When the operating temperature is reached, the indicator goes out.
- The prepared parts are put on welding attachments. Wait 7 seconds and remove the blanks.
- Quickly, without rotation, the pipe is joined to the fitting and pushed to the specified level.
- Before installation, the finished connection must cool and gain strength (2 minutes).
- It is better to pre-assemble complex components, such as a manifold, branches, and then install the entire set in place.
- When installing water pipelines on walls and ceilings, it is not recommended to use fixed supports.
What plastic pipes can be used for heating
Despite the variety of polymer products, not all of them are suitable for installation in systems with hot coolant. For example, HDPE (low-density polyethylene) pipes are not suitable for this, since they can withstand heating of no more than 70 ⁰C. For this purpose, 3 types of materials are used:
- metal-plastic;
- PEX (cross-linked polyethylene);
- polypropylene.
Pipes made from them can withstand prolonged heating up to 95 ⁰C and a pressure of 25 atm, so they can be used for the installation of individual and centralized heating systems.
Metal-plastic pipes
The main material is polyethylene, from which the inner and outer layers are made. Aluminum foil is inserted between them. It increases the strength of the structure and prevents the outer layer from heating, eliminating condensation problems. The shells are fastened together with glue.
Metal-plastic pipes are manufactured with diameters of 16-64 mm. In individual construction, the most popular sizes are 16 and 20 mm. Products with these parameters have the following characteristics:
- wall thickness – 2.5 mm;
- possible pressure surges – up to 15 atm;
- weight 1 m – 170 g;
- thermal conductivity coefficient – 0.44 W/(m K);
- tensile strength – 2900 N;
- maximum permissible temperature – 95 ⁰C;
- standard pressure - 10 atm.
Metal-plastic pipes are connected using compression and press fittings. The advantages include light weight, low cost, and antistatic properties. However, when heated, layers of different materials expand unevenly, which leads to leaks at the joints. They are usually eliminated by periodically tightening the fittings. But an increase in crimping force often leads to damage to the walls.

PEX
These pipes are also made from polyethylene, but using a different technology. Depending on the stitching method, they are divided into modifications:
- PEX-a – peroxide catalyst (% cross-linking – 85);
- PEX-b – silicone polymer (70%);
- PEX-c – radiation (60%);
- PEX-d – nitrogen (70%).
The percentage value determines the degree of rigidity and strength. PEX pipes cannot be bent, so changing the direction of installation is done using corner fittings. The remaining varieties have sufficient elasticity for practical purposes.
The range of PEX pipes consists of products with a diameter from 10 to 110 mm. Popular 16-mm varieties among the population have the following characteristics:
- wall thickness – 2 mm;
- weight 1 m – 110 g;
- thermal conductivity coefficient – 0.32 W/(m K);
- operating temperature – 90 ⁰C with peaks up to 100 ⁰C lasting no more than 1 hour.
PEX pipes are connected by welding with a special soldering iron. Their ends are heated until melting and joined. After holding for a minute, a monolithic connection is obtained, the strength of which is equal to that of a solid material.

Polypropylene pipes
The designation PN is used for their marking. Depending on the characteristics, they are divided into 4 types:
- PN10 – with a maximum permissible pressure of 10 atm and a temperature of up to 45 ⁰C, not used in heating systems;
- PN16 – 16 atm, 60 ⁰C, can be used for installation of heated floors;
- PN20 – 20 atm, 95 ⁰C, installed in heating systems of private houses;
- PN25 – pipes with reinforcement, can withstand 25 atm and 95 ⁰C, can be used in centralized systems.
Unlike the first three, the last variety is non-plastic. Aluminum foil or fiberglass is used for reinforcement. The coefficient of thermal expansion is respectively 0.03 and 0.035 W/(m K).

Specifications
The production of polypropylene pipes (PP) is regulated by GOST 21553 and GOST 15139 standards.
Pressure resistance
In heating systems, it is not always possible to maintain constant pressure; its indicators may vary depending on the temperature regime and the throughput of the collector. Therefore, when using PP in the heating circuit, it is necessary to take into account the reserve of the internal diameter of the pipe, which will have a positive effect when pressure changes and will protect the system from ruptures.
Paying attention to the markings, you can easily select the required bore diameter, taking into account the margin. So, with a design diameter of 20 mm, a manifold with a bore diameter of 25 mm is selected, which takes into account the expansion margin when the pressure in the system changes. The letters PN and two numbers on the marking indicate the pressure for which the materials used are designed.

Features of the use of polypropylene pipes in the heating system
When determining which brand of pipe can be used for heating, it is necessary to take into account the supply temperature, which depends on the characteristics of the installed heating devices, their technical capabilities, the type of expansion tank and the method of recharging the system.

The higher the water temperature, the shorter the service life of propylene pipes for water supply and heating.
In an apartment, the cross-section of polypropylene water pipes should be equal to the internal diameter of the supply pipelines (risers). It should be taken into account that the wall thickness of polymer pipes is greater than that of steel reinforcement. In a private house, central wiring is carried out with a Ø 32 mm profile, connection to radiators is carried out using pipes with a cross-section of 20-25 mm.
For individual heating, multilayer reinforced products are used, but it must be remembered that for products with aluminum foil, the linear expansion is much greater than for products with a fiberglass layer.
When using a floor heating system in a private house, the pipes are calculated based on the design temperature of the structure, the type of room and the area of the heated area. The heat exchange limit is within the range of +35…+45°C.
Advantages of propylene pipes
Propylene products are increasingly displacing metal heating pipes from the market every day. They have many advantages over others:
- high pressure resistant ;
- do not corrode ;
- thanks to the smooth surface do not accumulate and do not wear out ;
- resistant to chemicals;
- can operate at sub-zero temperatures down to -10 degrees;
- maximum temperature is +90 degrees, but for a short time it can withstand +100;
- are light in weight;
- hygienic;
- can operate in the heating system for 25 years;
- do not deteriorate and are not destroyed if water freezes;
- do not conduct electricity, which is especially important when using induction heating boilers;
- easy, simple and convenient installation that does not require the use of expensive equipment.
Due to the absence of corrosion and resistance to the effects and deposition of salts, propylene pipes have a long service life, which makes it possible to use them in hidden wiring, under plaster and screed without additional treatments, unlike steel ones.
Polypropylene pipes are most often used for internal wiring due to the fact that under the influence of high temperatures the pipes expand and can be deformed. To avoid this, it is necessary to fasten pipes every 60 cm, or even better, choose reinforced ones.
Advice.
To extend the service life of propylene pipes, it is best to ensure that the coolant temperature does not exceed 60 degrees.
Metal-plastic pipes
Pipes for water supply
In fact, metal-plastic, or more precisely, a pipe made from it, is a reinforced product where aluminum is used as a frame. This is a multilayer structure in which you can count 5 layers - three of plastic and aluminum, and two of the adhesive composition. It turns out that the first and last layers are plastic, and between them is aluminum, which is attached to the plastic planes using a special glue.
We took reinforced polypropylene pipes as an example so that you can understand the design. But they cannot be classified as metal-plastic products. After all, high-strength polyethylene and elastic aluminum with a layer thickness of 0.2–0.3 mm are used as the plastic component.
These products are manufactured using the latest technologies using high-quality materials. You can give just one technical characteristic that will show how high the quality of these pipes is. They can withstand coolant pressure up to 70 atm.
Of course, these pipes do not work under such conditions, so manufacturers indicate the following characteristics:
- Operating temperature +95C.
- Maximum temperature +130C.
- Working pressure at a temperature of 95C is 10 atm.
- The maximum pressure at a temperature of 25C is 25 atm.
- Under such operating conditions, metal-plastic pipes will last more than 50 years.
Everything that was said above about polypropylene products is fully consistent with metal-plastic pipes. That is, it is the same durable and reliable pipe material that can be used in the heating system of a private home.
Compound
Pipe installation
But the installation process is significantly different, because the joints of metal-plastic pipes can be made using different technologies.
What types of connections are there?
- Detachable - collet or threaded. In this case, two pipes are connected to each other with special fittings. If necessary, they can be easily separated, and the system can be dismantled, moved to another location and re-installed. Pipes can be used repeatedly. This also reduces the complexity of repair work.
- Conditionally detachable. Here, special fittings are used that crimp the joint parts using a special crimp ring. To redo the heating route, you simply need to dismantle the ring and replace it during the new connection.
- One-piece. This type of connection uses special press fittings that permanently join the two ends. Essentially, this is the same soldering, sealed and durable. This crimping is done using special equipment. It is not cheap, so home craftsmen use this heating assembly option very rarely.
Flaws
If the advantages of two types of products are almost the same, then the disadvantages are different. After all, polyethylene is more susceptible to the negative effects of natural and aggressive environments:
Metal-plastic is afraid of direct sunlight. Under their influence, it changes color and structure. In addition, it cannot withstand heavy mechanical loads and high temperatures. Typically, threaded connections use fittings whose diameter is much smaller than the diameter of the pipe. This, firstly, reduces the passage for the coolant, which negatively affects its circulation
And, secondly, it creates the likelihood that it is in this place that the hole will become overgrown if the quality of the coolant is not up to par. It is very important not to overtighten the union nut when docking. The consequences can be very unpleasant
For example, a cut will remain, and then a crack and rupture will appear.
Criterias of choice
And now, in fact, we have come close to the problem of choosing heating pipes. What should you pay attention to when purchasing? We will need as detailed instructions as possible.
Pressure
The PN** type marking is directly related to the working pressure of the pipe. After the letters, two numbers indicate the maximum operating pressure for which the pipes are designed, in atmospheres.
Note: the operating pressure is indicated for a temperature of 20C. At 80-90 it can be safely divided into three, so it is better to choose PN25 pipes. However, this is more of a reinsurance: PN20 pipes are widely used for heating and do not create problems for owners.
Temperature
The maximum operating temperature is also usually present in the pipe markings. Most manufacturers indicate either 90 or 95C for reinforced pipes. From the consumer's point of view, these values are equivalent: one of the manufacturers simply protects itself to a greater extent from possible lawsuits.
Diameter
To accurately calculate the required diameter, builders use rather complex formulas that take into account the thermal load, the temperature difference between supply and return (which in the case of centralized heating depends on the thermal power plant), the roughness coefficient of the pipe material, the color of the rising Venus and the phase of the Moon.
However, from a practical point of view, it is enough to remember two simple rules:
- When distributing heating throughout the apartment, the polypropylene pipes used should not reduce the clearance relative to the risers. Most new houses use risers made of DN20 (3/4 inch) pipe; accordingly, you will need a polypropylene pipe with an outer diameter of 26 millimeters). In steel risers with inch risers, it would be reasonable to use pipes with an outer diameter of 32 mm.
- For a private house with an area of up to 250 square meters, the most efficient and problem-free heating system is the Leningradka (a ring of pipes around the perimeter of the house on each floor, parallel to which, without breaking it, heating devices are embedded). For the ring, a pipe with a diameter of 32-40 is taken, for inserting radiators - 20 - 26 millimeters.

This is what the sidebar will look like.
Manufacturers
Studying forums with customer reviews will help here.
If we omit all the verbose delights and outpourings, the bottom line will be approximately the following rating (in order of decreasing popularity):
- Valtec;
- Firat;
- FV-Plast;
- Banninger;
- Ekoplastik;
- Tebo.
There are probably other manufacturers that are not included in the list, but offer quality products at reasonable prices. A simple Internet search using the name of the manufacturer will help you.

The listed properties apply, in general, to all polypropylene pipes.
Installation of a heating system made of polypropylene pipes
If the choice of pipes is made in favor of polypropylene products, then before starting work you need to know the intricacies of installing the system and how welding is carried out.
So, from the above it follows that it is imperative to use reinforced polypropylene pipes for heating. These pipes can withstand pressure up to 25 atmospheres, and the operating temperature reaches 90 degrees.
It is more advisable to pay attention to reinforcement made of aluminum foil, since here the expansion coefficient is slightly lower than using fiberglass. But the latest products are often used, especially where the pipe is closed from the observer
Using polypropylene heating pipes (fiberglass), you can be one hundred percent sure that it will never break, even despite significant curvature, which can only spoil the design.

You should spend a little time connecting the pipe to the tee. The main advantage of such a connection is that, due to the absence of metal in such a connection, the appearance of hardness salts is completely eliminated, which means that the connection becomes practically monolithic.
As you know, in order to completely get rid of traces of linear expansion, polypropylene expansion joints are used, and they are installed in places where they are not visible. When working with polypropylene, you should consider absolutely all actions in advance in order to protect yourself from possible troubles. To do this, you just need a heating diagram made of polypropylene, which is not difficult to draw with a pencil yourself, starting from the boiler, where all the steps and adjustments will be made.
If there is a sufficiently long section of pipe, and there is simply nowhere to install the compensator (nowhere to hide), a gap of 5 - 10 millimeters should be provided in advance between the turn of the pipe and the wall (for linear expansion).
Heating system in an apartment: instructions for its creation
Sometimes situations arise when it may be necessary to replace heating pipes in an apartment. Despite the complexity of such events, provided that the rules are followed and the strict installation algorithm is followed, it is quite possible to carry out this work independently, without resorting to the help of specialists.
Initially, you need to think about the type of system that should ultimately be installed. Not only the final cost, which is determined by the number of radiators, pipes and mounting hardware, but also the quality of the heating depends on whether it is single-pipe or double-pipe. So, when installing a two-pipe system, a large number of radiators may be required, and if you plan to install more than 8 of them, pipes with a cross-section of 32 mm will be optimal in this case.
Installing a single-pipe system will be cheaper, but with this wiring configuration there is a high probability that the coolant temperature in each radiator will be lower than in the previous one. To minimize this effect, it will be necessary to install thermostats to regulate the power of each radiator.

Regardless of the type of system chosen, it is extremely important to provide for the installation of Mayevsky valves in the upper part of the radiator to bleed air. The lower holes should be sealed with plugs, having previously cleared the inlet hole of possible contamination and paint deposits. This point applies to new radiators too.
You should select fastening accessories (fittings, clamps, plug couplings, tees, adapters) in accordance with the selected heating scheme.
Having previously cleaned the foil of aluminum-reinforced polypropylene pipes, you can begin to connect them using a special welding machine. In this case, it is important to observe the required time interval, which is usually different for each type of pp heating pipes. So, to melt pipes with a cross-section of 25–32 mm, 7–8 seconds will be enough.
To achieve efficient and high-quality operation of the system, it is necessary to strictly adhere to the following action plan:
- Coordinate restoration measures with the relevant utility services in order to be able to shut off the water and discharge it.
- If possible, notify residents whose apartments are located on the floor below and above. However, if due to circumstances it is not possible to completely replace the riser, you can use special adapters from cast iron to plastic pipes.
- Dismantle old communications of the heating system, using extreme caution and accuracy. It is advisable not to neglect safety precautions and wear safety glasses and a respirator. The fact is that with prolonged use, cast iron becomes very fragile, and with careless or sudden movement, its fragments can get into the pipe and disrupt the movement of the coolant.
- Proceed with the installation of the new system, installing new heating radiators along the specified perimeter.
- Assemble polypropylene pipes and connect radiators to them (more details: “How to connect a heating radiator to polypropylene pipes - methods, fittings used”).
- Check the system for integrity and tightness. In this case, you should pay attention to the fact that if the newly installed system is a two-pipe system, then when checking, the coolant should move in the opposite direction. And the pressure, if checked, should be approximately 1.5 times higher than the usual initial one.











