Why do you need to insulate external heating pipes?
It would seem, why do you need to insulate something that is already warm? In fact, the point is that the heating circuit is always at a high temperature due to the coolant circulating in it, but thanks to additional insulation, the coolant will maintain its temperature much longer.
Any kind of insulation has amazing heat-insulating qualities. And its use for pipes is very relevant, especially if the heating main is located underground or runs outdoors.
If there is no insulation on the pipe, this negatively affects the quality of heating. For example, a boiler heats water in the system and directs it to the supply point (usually residential buildings or non-residential areas). Under the influence of the walls of the coolant circuit, they heat up. At the same time, the walls come into contact with the environment, which provokes a decrease in temperature in the system. As a result, the temperature in the heated room also decreases.
From an economic point of view, this is very unprofitable. A lot of fuel was spent to heat the water, but due to the decrease in temperature at the time of movement through the system, the efficiency of the heater drops significantly. That is, it took a lot of fuel to heat the water, and the air temperature in the room is low.
To reduce fuel consumption and increase efficiency, heating pipes should be insulated. And for this purpose, various materials can be used.
Instructions on how to insulate pipes yourself
- it is necessary to make calculations and purchase thermal insulating materials;
- wrap the pipes with foil tape or foil. In this case, the foil plays the role of a heat reflector;
- installation of insulation around the pipe. The rigid sectional casing and soft insulation simply need to be placed on the pipe. Regarding other soft materials, they must be cut into pieces equal to the width of the pipe diameter. Then wrap it around the pipe and secure it with clamps, tape or wire. With rigid insulation the situation is more complicated. It is necessary to create a kind of box around the pipe from it (or use pipe shells of the required diameter);
- inspect the pipe for the presence of “cold bridges” and eliminate them;
- secure the thermal insulation to the pipe using metallized or plumbing tape;
- if necessary, cover the thermal insulation with protective material (film), and seal the joints with tape.
The money spent on the purchase and insulation of pipes quickly pays off thanks to savings on payments for heating the home.
Basic requirements for pipe insulation
Today, the choice of materials for thermal insulation is quite wide, so it is very easy to get confused when choosing. Be sure to focus on the basic requirements and characteristics of pipe insulation.
The selected material for thermal insulation work must meet the following parameters:
- low degree of thermal conductivity;
- hygroscopicity;
- material resistance to high temperatures;
- service life;
- ease of installation.
Today, for thermal insulation of outdoor heating systems, many insulation products are produced that meet all of the above criteria. Below we will consider in detail the most popular and suitable materials.
Electric heating
You can heat your home with electricity not only by installing a water system. Using electricity to directly heat rooms will be more correct and profitable. There are two options for electric heating:
- electric convectors;
- underfloor heating system;
- infrared long-wave heaters.
Heating with electric convectors
Electric convectors are less profitable compared to water heating, which uses gas as an energy carrier. However, compared to other options, their use will be cost-effective.

In addition, installing such devices is much faster than water radiators, and no pipes are required - only wires and an electrical network capable of withstanding the required power.
"Warm floor"
The use of heated floors will allow you not to use indoor shoes even in the coldest time of the year. Their advantage compared to convectors is more uniform heating of rooms.
However, “warm floors” cannot be used as the main source of heat – but there is no better option for additional heating.
Using infrared heaters
Almost the only disadvantages of using infrared radiation to heat a private home are the discomfort caused by the luminous panel and the low accuracy of power control. At the same time, among its advantages are:

- high heating rate;
- an increase in the temperature not of the air, but of the interior items;
- full automation of the equipment operation process.
Very often, especially in private homes, the heat source is located outside the house. The natural desire of the homeowner is to deliver heat to the house with minimal losses. Regardless of whether the heating main is laid underground or goes through the air, care must be taken to ensure proper thermal insulation of the pipes. Ignoring this measure is fraught with at least a loss of 25% of heat. The worst case scenario is defrosting of the heating system. Let's try to figure out what materials are best to use for thermal insulation of pipelines and how to properly insulate heating pipes on the street.
Types of heat insulators
Depending on the budget, your own needs, requirements and climate, you should select the most suitable heat insulator option.
Mineral wool
To insulate external heating pipes, special mineral wool is most often used. This is a very practical and comfortable material that has excellent durability.

There are several types of mineral wool:
- Basalt. It is made from a special rock containing a large percentage of basalt. The main feature of this type is a high level of resistance to heat, since the operating temperature can reach 650 degrees. Unlike many heat insulators, basalt mineral wool does not enter into a chemical reaction and does not produce any toxic elements or substances when heated.
- Fiberglass. Its base consists of quartz sand. This component is used to make glass, which is also included in this type of mineral wool. This material can only be used for finishing external pipes, since the permissible operating temperature should not exceed more than 200 degrees.
The big disadvantage of mineral wool is the high percentage of moisture absorption, which reduces its thermal insulation properties to almost zero. But why then is mineral wool the most commonly used material for finishing external pipes?
The fact is that this type of heat insulator is always used in combination with hydrolysis. This way any contact with moisture is absolutely excluded.

The easiest way for these purposes is to use roofing felt, which should be used to wrap the line insulated with mineral wool. The roofing material should be secured with thick wire. This method is the most practical, effective, easy to install and proven over many years. For waterproofing, you can use any other material. The main thing is that it has a low percentage of moisture absorption and is resistant to mechanical damage.
Water heating of a private house
Water heating in a private house is carried out using a closed circuit filled with hot water circulating through it. In this case, the heating device is a boiler, from which it is necessary to run pipes throughout the house to each radiator. The water passes through the radiators, gives off heat to the rooms and returns to the boiler. There it heats up again and enters the system. Antifreeze can also be used as a coolant.

Most often, the heating system consists of copper pipes, the most reliable, however, also the most expensive.
Steel is used less often, and water heating is almost never made from polymer materials that do not tolerate temperature changes well.
In addition to pipes, the circuits must be equipped with additional elements:
- an expansion tank that collects excess liquid;
- thermostats that control the temperature in front of the radiators;
- a circulation pump that ensures forced movement of liquid through pipelines;
- shut-off and safety valves.
Subspecies
A system of this type can be:
- single-circuit, providing only air heating;
- double-circuit, which also allows you to get hot water.
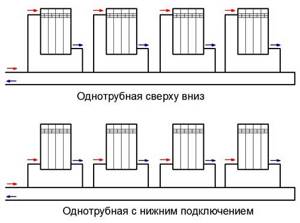
Based on the principle of fluid movement in pipes, one-pipe, two-pipe and manifold systems are distinguished. The first involves a sequential transfer of coolant from one battery to another. Its advantages include ease of wiring, while its disadvantages include low efficiency, impossibility of regulation and difficulty in replacing individual elements.
Two-pipe
A two-pipe system is better, as it is more maintainable and ensures minimal heat loss.
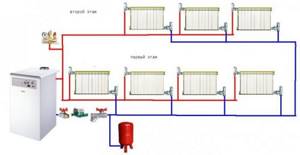
But the most convenient and effective way to set up a water heating circuit is achieved if you carry out a manifold wiring, which ensures quick replacement of a worn-out element and simple temperature control, but also costs more.
Pros and cons
The main advantage of all water heating systems in a private home is the efficient transfer of heat throughout all serviced rooms. Among the disadvantages are:

- complexity and labor intensity of installation;
- the need for regular maintenance of pipes and the boiler, which can be carried out either by yourself or using the services of specialists.
Advantages and disadvantages of various insulation materials
Before giving preference to any particular material, you should study all its advantages and disadvantages.
So, mineral wool has many advantages, and in general this heat insulator, perhaps, occupies a leading position in popularity and frequency of use. The main advantages of mineral wool include:
- excellent thermal insulation;
- resistance to aggressive environments;
- does not rot;
- durable;
- not affected by rodents;
- can be used for pipes with high temperatures;
- budget cost.
Along with so many advantages, there is a huge drawback - hygroscopicity. But this minus can easily be corrected by waterproofing.
As for seamless foam insulation, it has excellent thermal insulation, does not require an additional layer of waterproofing and is a biologically stable material. The main disadvantage is the need for special equipment for coating. Therefore, this method is far from budget-friendly.
Foam insulation is a very worthy option, characterized by the same advantages and relatively low cost. Thanks to the fastening grooves, the polystyrene foam shell is carefully fixed to the pipes and allows for good tightness of the structure. Again, the downside is hygroscopicity and the need for additional waterproofing, as is the case with mineral wool. In fact, both of these materials are almost identical in effectiveness.
Polyethylene foam is a new generation material that has such advantages as low thermal conductivity, moisture resistance, and ease of installation. The downside is the presence of seams when covering pipes, which requires additional costs for the purchase of a special adhesive. In its absence, moisture and cold will enter the heating system.
And the last material, heat-insulating paint . Advantages: effect even with one layer of application, ease of installation, possibility of use in hard-to-reach places. The disadvantage is the high cost.
Expanded polystyrene
Also a polymer material that has become traditional, called “shell” because of its rigidity. The insulation consists of two hemispheres with recesses to suit the size of the insulated pipeline elements.

- low cost;
- low heat transfer value;
- moisture resistance – polystyrene foam does not absorb liquid;
- ease;
- ease of installation;
- Possibility of combination with metals and polymeric materials.
The main disadvantage is the inadmissibility of use on excessively hot pipes.
Indoor insulation
Do-it-yourself insulation of heating pipes indoors will only be necessary in the case of unheated buildings. This refers to various basements, attics, and so on.
Be sure to pay attention to the fact that in such rooms there may be an increased level of moisture, and there are often rodents that can damage the finishing material.
To thermally insulate pipes in unheated rooms, you can use any of the above materials; in some situations, you may not even need an additional layer of waterproofing (if the room is closed).
The most convenient way to use finishing in such cases is with covers made of expanded polystyrene foam. But this is quite an expensive pleasure, so most people still prefer mineral wool.

As for insulating pipes in the attic, when choosing a material, be sure to pay attention to the thermal insulation characteristics. It must be resistant to heat.
Classification of heating systems for a private home
First of all, heating systems differ in the type of coolant and are:
- water, the most common and practical;
- air, a type of which is an open fire system (i.e. a classic fireplace);
- electric, the most convenient to use.

In turn, water heating systems in a private house are classified according to the type of wiring and are single-pipe, collector and two-pipe. In addition, there is also a classification for them according to the energy carrier required to operate the heating device (gas, solid or liquid fuel, electricity), and according to the number of circuits (1 or 2). These systems are also divided by pipe material (copper, steel, polymers).
Insulation underground
When laying heating pipes underground, it is important to take into account the following nuances:
- communications should be buried below the soil freezing level, and this indicator is absolutely individual, depending on the region;
- The ingress of moisture onto the insulation must be prevented;
- There should be no deformation of the insulation under the influence of the weight and pressure of the earth.
Laying heating pipes underground is quite an expensive pleasure, since in this process it is important not only to use high-quality materials, but also to be especially careful.

The most effective and common option for thermal insulation is the use of finishing material in combination with rigid casings. There are only two options here:
- pipes wrapped in insulation and placed in plastic sewer pipes (any heat insulator can be used, preferably mineral wool, polystyrene foam or foam materials;
- factory multilayer pipes.
Both of these options are united by a plastic or metal pipe covering the insulation layer and the frame itself.
Heating using liquid fuel
Liquid fuel equipment should be installed correctly in buildings where the use of both gas and electricity is impossible or simply impractical (for example, the electrical network will not support such a powerful boiler). Its advantage can also be called independence from electricity and gas supplies. Although the disadvantages of such boilers usually outweigh the advantages:

- for fuel it is necessary to install a special fireproof tank;
- the energy carrier is very expensive, and this option turns out to be the most unprofitable;
- large volumes of fuel combustion products are released.
Electric boilers
Using electric boilers in water heating systems is convenient and quite profitable. And at the same time, high automation of the process is ensured.
Insulation of pipes on the street
If you are faced with the task of insulating outdoor heating pipes on the street, then you should take into account contact with moisture. Therefore, waterproofing is mandatory in any case. Otherwise, the whole point of thermal insulation is nullified.
Algorithm for a standard insulation scheme:
- a layer of mineral wool;
- winding with silk threads;
- a layer of roofing material to limit contact with moisture;
- winding using corrosion-resistant wire (aluminum or galvanized).
Insulating heating pipes is a serious and responsible task. And if you want to significantly save your heating budget, then this procedure should be mandatory.
If you decide to do everything yourself, then pay attention to the choice of material, its resistance to various external factors, including moisture resistance. Remember that if moisture gets on the insulation structure, all work will be useless, since under the influence of water the thermal insulation becomes wet and loses all its properties.
Materials for thermal insulation
Today, a variety of materials can be used to reduce heat loss and insulate heating pipes. The choice of one or another heat insulator for basement pipes will depend, first of all, on the specific requirements of the owner of the house, operating conditions and pipe sizes.
There are a huge number of thermal insulation materials on the modern market, but not all of them are suitable for heating pipes.
This point must be taken into account before purchasing this or that thermal insulation material.
Of course, the most common and traditional thermal insulators, which are used everywhere, include fibrous insulation, including mineral wool. It can be used in a variety of conditions, and almost always the thermal insulation will be quite effective. Materials based on mineral wool can potentially withstand extremely high temperatures, so they can be used in basements and boiler rooms.
What can be identified from the main advantages of this heat insulator?
- high level of resistance to chemicals;
- safety for humans and the environment;
- minimal water absorption (but with serious exposure to water, the insulation will lose its properties);
- small price.
Mineral wool, according to experts, is excellent for thermal insulation of external pipelines, as well as heating systems in the basement of a private house.
In recent years, derivative materials have been increasingly used: basalt wool and glass wool, which also have good performance and performance characteristics. Materials of this type are suitable for most country homeowners.
Heat Loss Mechanism
Cooling of the working environment and heat loss occur as follows: protective slabs of pipeline insulation and heating main insulation are laid using a certain technology on top of the pipe surface. Accordingly, excess thermal insulation material is formed from below.
All material in excess of the required footage is cut off, and the pipe is sewn into a special metal casing. What happens next when the pipe is connected to the heating main system?
Algorithm for loss of protective properties by insulation:
- On the working surface of the pipe, the insulation material is compressed under the influence of the environment.

Poor-quality outdated insulation and ineffective thermal insulation technology for heating mains ultimately hit the consumer’s pocket.
- The heat coming from the heat pipe tends upward, through the layer of thermal insulation coating.
- The volume of insulation on top of the pipe is significantly reduced, but the amount of non-functional insulation at the bottom of the pipe is rapidly growing.
- Heat loss approaches 50%.
- There is ineffective heating of the adjacent space.
- The cost of heat increases.
- Consumer expenses increase in proportion to the cost of heat.
Disadvantages of outdated insulation. Conclusions:
Poor-quality outdated insulation and ineffective thermal insulation technology for heating mains ultimately hit the consumer’s pocket. What the pipeline loses as a result of ineffective outdated thermal insulation leads to an increase in the cost of a unit of heat for the end consumer.
Methodology for forming a pipeline system

One pipeline system is for transferring heat to the consumer from the source of its generation, and the other pipeline system is for removing the used material.
In order to correctly select the material for pipeline insulation, you need to know the following basic methods of forming a pipeline system:
- Laying a route using the functionality of reinforced channels
- Pipe system inside a special pipe tray made of reinforced concrete structure
- Formation of a pipeline system above the surface of the earth, actually under the feet of consumers
- Placing pipelines in the ground without channels and trenches using a special technique
All of the above options for constructing a pipeline system require various methods of insulation and insulation.
Why isolate
When laying a pipe outside a building, it (and the environment flowing inside) can be adversely affected by moisture and low temperatures. In addition, some materials (polymers) deteriorate faster and lose their quality when directly exposed to sunlight.
The pipeline can also be damaged by human actions (intentional or unintentional).
It is preferable to lay pipes in the ground for the following reasons:
- To prevent the negative factors mentioned above.
- In order not to create a network of communications (which will take up space and interfere with passage/travel) on the surface.
When laying a line underground, the following dangerous factors remain relevant:
- Possibility of freezing of the liquid flowing inside.
- The possibility of corrosion of the pipe itself is due to exposure to moisture.
The first factor is relevant in winter: the depth of soil freezing in most Russian regions reaches (or exceeds) 1 meter. That is, in order to prevent the flowing medium from freezing in cold weather, the pipes should be laid in the ground deeper than this indicator.
This is often inconvenient: it complicates further maintenance of the line (if inspection or repair is necessary, you will have to dig a deep trench), and increases the cost and time of excavation work during installation.
About the danger of lack of insulation
Water supply and sewerage pipes are laid in the ground - both municipal (going from and to multi-apartment residential buildings), and for private houses and various industrial buildings. Insulation must be used in both cases - since water flows inside these lines.
Moreover, it freezes very quickly - in less than an hour an ice plug will form inside.
Since the pipeline is laid in the ground, to remove it you will have to dig a trench, look for a frozen place and warm it up. And all this - in the cold. Moreover, the sewerage or water supply will not work in the house (depending on which line “runs down”).
In addition to the troubles that the sewer or water supply in the house stops working, when an ice jam occurs, there is also the possibility that the pipe will burst. This happens because when moisture freezes, it expands, meaning ice will take up more space than water. As a result, the pipe walls may not withstand it.
Fixing this problem is an even more difficult and less pleasant task than steaming a frozen area. In winter, in the cold, you will have to not only dig a trench (and not a small one, but along the entire line of the pipe - in order to find the damaged part) - but also repair the pipe itself. Often this can only be done by completely replacing the cracked segment.
Heating pipes with electric cable
Obviously, it is possible to insulate sewer pipes by burying them to a sufficient depth only in external areas. However, there are other areas, located both on the street and in rather poorly heated rooms. For such areas, you can use a special heating electric cable laid along the most important components and connections. The result of the work performed will be constant heating, protecting the sewer system regardless of the weather.
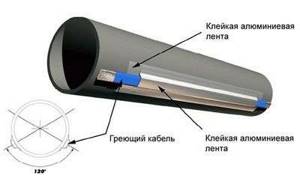
True, this method has a couple of disadvantages. First of all, electricity consumption increases, especially in the case of heating rather long pipelines. There is also a dependence on the operation of electrical networks. Of course, if there is a power outage, the generator will start working, however, this also costs a lot of money.
Fiberglass
Glass wool has an average thickness of up to 3-4 microns and 1550-200 mm. Thermal insulation materials made from glass staple fiber have a low density and application temperature (up to 180°C). Such materials are recommended for use in overhead pipelines, for example, heating networks. Therefore, fiberglass is used in a more limited area. High-quality fiberglass is characterized by high vibration resistance, biological and chemical resistance, as well as a long service life. (See also: Polypropylene pipes for heating)
Egor Guest
It is more convenient to use ready-made insulation. We found polyethylene foam for 13mm pipes (this is the norm for hot water supply).
Next, we selected the finished pipe insulation so that it fits over the first thermal insulation. There can be any number of such layers.
If there is an air gap between the first and second insulation, this is good.
It is important to seal the seams of the last layer of insulation with reinforced tape
You can wrap it with roll insulation, but it’s easier to wrap it not in two layers of 5 mm, but in one layer of 1 cm.
The foil inside will not work because... she needs a gap, in my opinion, 20mm. It can be oriented outward or simply wrap the last layer with foil tape (this is done when installing air conditioners).
Insulation of heating pipes is a mandatory stage of work during the installation of the entire system. This is especially true for pipe sections located outside a residential area (for example, on the street) and most exposed to adverse weather conditions.
The insulation material serves as a protective layer that maintains a given temperature regime, prevents the formation of condensation and slows down the process of metal corrosion.
Timely insulation of heating pipes can significantly reduce the percentage of heat loss and protect the pipes from deformation in conditions of sudden changes in weather conditions.
Heat loss on the way from the boiler to the radiators can vary between 5-15%. Accordingly, in order to achieve the optimal temperature in the house, the owners have to significantly increase the boiler power and pay the costs out of their own pockets.
Insulated heating pipes allow you to forget about this problem for a long time.
In this case, the coolant circulating through the pipes cools much more slowly, does not change its temperature and does not crystallize at the lowest temperatures.
Which pipes are suitable for heated floors?
Polymer pipes for laying under screed
Naturally, modern heated floors are installed from plastic, but it can be different and has different characteristics. Laying heating pipes in a private house under a screed replaces traditional radiator systems. To select a material, you need to determine the selection criteria:
The laying of heating pipes in a private house under a screed is carried out only in whole sections, without connections. Based on this, it turns out that the material must bend and the direction of coolant flow must change without the use of fittings. This characteristic does not include products made from single-layer polypropylene and polyvinyl chloride;
resistance to heat.
All polymer pipes for heating, external and hidden, can withstand heating up to 95 degrees, while the temperature of the coolant rarely exceeds 80 degrees. In a heated floor, the water heats up to a maximum of 40 degrees;
For laying heating pipes in the floor screed, only reinforced products are used, they are also called metal-plastic. Although the reinforcement layer is not only metal. Each material has a certain thermal elongation. This coefficient indicates how much the circuit lengthens when it is heated by one degree. The value is determined for a section of one meter. Reinforcement is needed in order to reduce this value;
Once the heating pipes are laid in the floor screed, there will no longer be access to them. If a leak occurs, you will have to dismantle the floor - this is a sawing and labor-intensive process. Manufacturers of polymer pipes provide a 50-year guarantee on their products.
Reinforced polymer pipes consist of five layers:
- two layers of plastic (inner and outer);
- reinforcement layer (located between the polymers);
- two layers of glue.
Thermal linear expansion is the property of a material to increase in length when heated. The coefficient is indicated in mm/m. It shows how much the contour will increase when it is heated by one degree. The coefficient value shows the amount of elongation per meter.
PEX pipe reinforced with aluminum
Immediately we should mention the types of reinforcement. It could be:
- aluminum foil (AL), thickness 0.2–0.25 mm. The layer can be solid or perforated. Perforation is the presence of holes, like in a colander;
- fiberglass fiber is thin fibers of plastic, steel, glass or basalt. The markings indicate FG, GF, FB;
- ethylene vinyl alcohol is a chemical element that changes the composition of plastic. Labeled Evon.
Before laying heating pipes in a private house, you should make sure that they have a layer of reinforcement with aluminum foil or ethylene vinyl alcohol. Since one of the requirements when choosing a material is the elasticity of the contour. Products reinforced with fiberglass fiber cannot be bent; fittings and couplings are used to change the direction of coolant flow, which is unacceptable in our case.
Let's look at the types of materials used for the production of metal-plastic pipes:
polypropylene. Such products are marked PRR/AL/PPR. Thermal linear expansion is 0.03 mm/m;
cross-linked polyethylene. It differs from conventional low-density and high-density polyethylene in that it undergoes an additional production step called cross-linking. On it, the number of bonds between molecules increases, thereby giving the product the necessary characteristics. It is marked PEX/AL/PEX and has a coefficient of thermal linear elongation of 0.024 mm/m, which is less than that of propylene.
We will separately consider products made of cross-linked polyethylene reinforced with ethylene vinyl alcohol, since it is best to lay such heating pipes in the floor. They are labeled PEX /Evon/PEX. This reinforcement method allows you to kill two birds with one stone. Firstly, it reduces the linear expansion of the material to 0.021 mm/m, and secondly, it creates a protective layer that reduces the air permeability of the pipe walls. This figure is 900 mg per 1 m2 per day.
Installation of shells made of basalt or expanded polystyrene
Insulation for water pipes made of basalt or expanded polystyrene is installed using the following technology:
- shell halves of the corresponding internal diameter are placed on the pipe, with an overlap of 10-20 cm relative to each other required;
- preliminary fastening can be done with tape;
- in places of pipe outlets, specially selected segments or segments cut from straight sections of the shell are used;
- for thermal insulation of street areas, roofing felt or foil insulation can be used as a protective material;
- final fastening to the pipe is carried out using the tightening method;
- If dismantling is necessary, it is carried out in the reverse order.
Price
What is the price of insulation for pipes in the ground?
Since many thermal insulation materials are of foreign origin, it will be more clear to compare their cost in euros. Let’s take 1 cubic meter of insulation per unit of production.
So, cube. m will cost:
- mineral wool – from 30 to 50 euros;
- polyurethane foam – 220-350 euros;
- extruded polystyrene foam – 75-90 euros.
Despite the difference in prices from different manufacturers, their approximate ratio remains the same.
The figures presented in this and the previous sections allow us to conclude that the most profitable material for private construction is extruded polystyrene foam: it costs approximately twice as much as mineral wool, and can last several times longer.
Metal-plastic pipes are flexible and have anti-corrosion properties. You can find out more about them in the article: metal-plastic pipes - application and technical characteristics.
Read about how to build a water supply system in a dacha from a well on this page. Useful recommendations for installation work.
Vertical pipeline laying
Schemes with a vertical arrangement of highways are very popular among residents of multi-storey cottages.
This is due to the peculiarities of the functioning of such schemes:
- The coolant is heated in the boiler and rises up the line. After this, it descends along all existing risers to the radiators;
- From these radiators, the coolant returns back to the boiler, while, in the case of two lines, the return movement is carried out along horizontally located elements.
It must be said that the supply branch is also located horizontally. The scheme got its name - vertical or top - for the simple reason that the coolant comes from above, which can be seen in the image below:
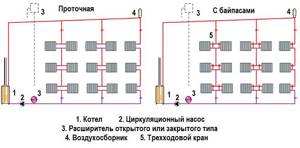
Consists of the following elements:
- Heating boiler;
- Circulation pump (as a rule, it is present, but it may not be);
- Expansion tank of an open or closed type (if there is a pump, then a closed-type membrane tank is used, but if there is no pump, that is, natural circulation, then the tank is used of an open type);
- Vertical and horizontal branches;
- Batteries;
- Shaped elements.
Principle of operation
The operating principle of all vertical structures is quite simple. From the heating element, the coolant flows into the expansion tank. The movement occurs along the riser.
The expansion tank should be located at the highest point. This container serves to normalize and create pressure.
Further from the tank there is a branch, which is called the supply branch, or in this case, the branch branch. This line goes to each battery. Thus, from the expansion tank, the heated coolant through this line enters the batteries.
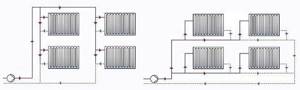
Here it gives off its heat to the environment. At this time, the denser cold water pushes the heated water out of the boiler. This creates coolant movement. Thus, slightly cooled water from the batteries enters the return line, which leads directly back to the boiler.
Today, almost all such schemes are equipped with a circulation pump, which forces water to move through the mains. This leads to faster heat transfer, and therefore increases the efficiency of the entire structure.
The great advantage of the upper location of the branches is that their arrangement allows heating multi-story buildings.
In addition, no one forbids, as in the previous case, putting its own shut-off valve on each individual radiator. In this case, there is no need to cut in separate lines, since the design already provides for a parallel supply of coolant to all batteries.
Trenchless methods of pipeline laying
There are technologies for laying a pipeline in the ground without making trenches.
Such methods are aimed at:
- reduce the volume of excavation work - saving time and costs;
- minimize damage to infrastructure - less costs for restoration of decorative and road surfaces, unexpected damage to highways;
- lay pipes in a straight line, without going around obstacles of low complexity;
- minimize damage from excavation work to the environment.
Today, the following trenchless methods are used in industry:
Sanitation
- This is the replacement of old pipes with new ones, which, in turn, is done in two ways: relining and the renovation method.
Relining
is based on drawing a new polymer pipe of smaller diameter inside the working pipeline while preserving the old one as a protective shell.
Renovation
– installation of a new pipe to replace the old one, worn out and destroyed, the fragments of which will also protect the new main from external damage.
Piercing (pushing)
- this is the connection of two pits dug to the required depth by a puncture made at a certain height of the wall.
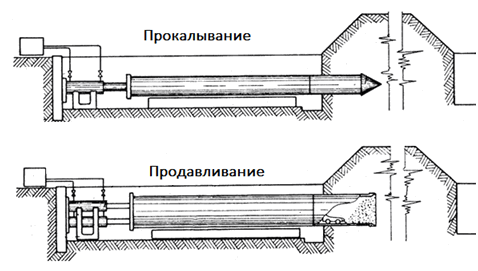
Of the listed methods, we will perform only the relining method in everyday life. A cable is inserted into one end of the old pipe and pushed until it comes out of the other end. Then a new lash is attached to the cable and pulled back. The possibility of using this method depends on a number of factors:
- the condition of the lumen of the old pipeline;
- diameter of the new pipe;
- flexibility of the new whip;
- length of the repaired area;
- ratio of the diameters of the old and new pipeline.
With a favorable combination of the listed factors, the technical execution of installing a new pipe is not difficult. However, all this applies to drawing a new line without thermal insulation, and the condition of the insulation of the old pipe is unlikely to be satisfactory. Since it is not possible to insulate heating pipes inside an old line, the method loses its attractiveness when applied to heating.
Therefore, when installing heating pipelines buried in the ground in private housing, digging a trench or, at a minimum, alternatively laying the pipe on the ground with backfill is indispensable.
Today, according to their design, all heating systems can be divided into many types and types - the classification is very diverse and has many parameters. Among others, the type of wiring is also distinguished.
The layout can be horizontal or vertical. Depending on the chosen type of installation, the composition of the heating circuit may change, but more about everything below.











