Menu:
- Advantages of plastic pipes
- Choosing heating pipes or which pipes are better?
- Diameter selection
- Installation features
- Cost and where to buy
- Video on how to choose
Until recently, plastic structures were not used as the basis for a water heating system. But in our time, polymer channels have begun to be used very widely.
PVC pipes deserve special attention. They allow you to create a reliable and efficient heating circuit. In many technical characteristics they are superior to cast iron and metal counterparts.
In our article you can find out what this product is and read its review. You will also have the opportunity to compare it with analogues and analyze its pros and cons.
Is it possible to use plastic pipes for heating?
Most types of polymer products:
- They have a low thermal conductivity coefficient, which reduces heat loss during transportation of coolant to the batteries.
- Designed for maximum pressure up to 20 atmospheres.
- Able to withstand temperatures of at least +90 ºС.
In modern heating systems, the upper limit for heating the coolant is 70...80 °C, so plastic can easily withstand high temperatures of the circulating fluid and increased pressure levels.
Difference between plumbing and heating systems
Before the advent of plastic pipe products, plumbing and heating system wiring were installed from the same types of metal pipes, only their diameter differed. With the advent of polymer materials, pipes began to be selected depending on their heat resistance.
Any type of plastic pipe product is suitable for cold water supply. And since the operating temperature of heating systems is not less than 50...75 °C, it is recommended to install only such materials in them, the melting of which begins at higher values:
- Cross-linked polyethylene.
- Polypropylene.
- Metal-plastic.
PVC pipes are not the best choice for heating systems as they can melt.
The difference lies in the level of pressure of the working environment. In water supply networks, the pressure level is usually within 4–5 atmospheres. In heat supply systems of multi-storey buildings it already ranges from 2 to 12 atm. (depending on the number of floors), and for private houses - 1.8–2.5 atm.
Why is polypropylene good?
Various Internet resources have published many materials praising polypropylene (PP-R) and attributing mythical properties to it. To figure out which pipes are best to use for heating installation (including with your own hands), you need to identify the real pros and cons of PPR. If you study the advice of experts and reviews of homeowners on forums, the following picture emerges:
- The price of polypropylene pipes and fittings is the lowest among other plastic pipelines used for heating.
- PPR is harder and more durable than any polymer that is now used to install heating systems in private houses.
- High-quality heating made of polypropylene looks no worse, or even better, than steel or metal-plastic pipelines.

Note. We do not take into account the inherent advantages of all plastic pipes. For example, the absence of roughness on the inner surface, low hydraulic resistance, and not susceptible to corrosion.
The low price of polypropylene parts compared to metal plastic is the most attractive factor. The secret of the low cost lies in the design of the fittings, which are ordinary plastic castings that do not have a reinforcing layer. And the cost of PPR pipes with a reinforcing aluminum insert used for heating will not make you faint.

Perforated aluminum foil, basalt and fiberglass can act as a reinforcing layer of PPR pipes
The strength of propylene also plays an important role; it is quite difficult to break it. This favors the laying of highways in an open way in any place. The aesthetics of a beautifully assembled polypropylene system is also not the last factor, although this is not easy to achieve, as will be discussed below. This is where the positive aspects of the material end. But in order to understand what is better - metal-plastic or polypropylene, we need to consider the negative ones.
What requirements must be met when choosing heating pipes?
Plastic pipes for assembling heating systems must have the following advantages:
- Withstand long-term exposure to circulating liquid heated to a temperature of 70...75 °C.
- Be resistant to increased pressure in the working environment and possible negative processes associated with it (water hammer).
- Have a smooth inner surface so that scale does not deposit on it.
- Do not change the original shape and dimensions when heated (low expansion coefficient).
- Have a soundproofing effect. The movement of the carrier inside the heating system circuit may be accompanied by noise, and since plastic transmits sound less well, the noise level in the room will not increase.
- Do not corrode or oxidize when exposed to aggressive chemicals.
- Maintain tightness for the same period of time as other elements of the heating system.
- Be visually attractive to fit into the interior of the apartment.
Calculation of cross-country ability: what does it depend on?
When calculating permeability, the outer diameters of polypropylene pipes do not matter. How much water the pipe will pass in a certain unit of time is determined by the internal cross-section.
Patency depends on:
- - internal cross-section (with a small cross-section, the wall resistance increases and the flow slows down);
- — pressure in the system;
- — length of the pipeline (the longer it is, the stronger the friction that slows down the flow);
- — material (the speed of movement is higher with a smooth inner surface);
- — the age of the pipe, that is, the amount of deposits;
- — the number of transitions from one size to another and turns.
For home piping, you can use a simple formula. To determine the optimal diameters of polypropylene pipes, you need to know the water flow (Q) and flow rate:
D = square root of (4-Q-1000/n*v),
v= 0.7-1.2 m/sec (up to 32 mm) or 1.5-2 m/sec (32 mm or more).
A more accurate calculation is needed in an apartment building. When installing risers in this case, the internal diameter of polypropylene pipes is 32 mm.

Correspondence of diameters of polypropylene pipes:
- — an external dimension of 16 mm corresponds to polypropylene pipes with a diameter of 10 mm (internal);
- — an external dimension of 20 mm corresponds to a polypropylene pipe 15 (internal diameter);
- — external size 63 mm — polypropylene pipes internal diameter 50 mm;
- — external size 125 mm — polypropylene pipes diameter 100 mm (internal).
Large polypropylene pipes are used for supplying cold water and external sewage systems (this type of material is never used for supplying hot water). For example, to supply water to a microdistrict, polypropylene materials of 500 mm or more are needed.
Plumbing and heating for a private house or apartment
To create a communications project for a small house or apartment, there is no need for exact calculations, since there are few water collection points, and the cost when purchasing a small batch depends little on the size. The diameters of polypropylene pipes should be slightly larger than the cross-section of the mixer.
Therefore, when installing household communications, simply purchase polypropylene pipes for heating, diameter 20 mm. And the diameter of polypropylene pipes for water supply can be even 16 mm. Large diameter polypropylene pipes (more than 500 mm) are not needed at all.
What materials are they made from?
For the manufacture of plastic pipes, inorganic material based on high-viscosity polymers of artificial or natural origin is used:
- Polypropylene.
- Polyethylene.
- Polybutylene.
- Polyvinyl chloride.
To increase strength, plastic is reinforced by connecting polymer layers with metal foil with a special glue or by adding fiberglass threads to the melt.

Types and characteristics
To assemble heating systems, you can use the following types of plastic pipes:
- Polypropylene.
- Made from cross-linked polyethylene.
- Metal-plastic products.
Polypropylene
For the installation of heating systems, polypropylene pipes are the most budget option. However, they have a high coefficient of linear expansion, which is why pipelines assembled from PP pipes can bend and sag during operation, which negatively affects the performance and aesthetics of the external appearance of the system. Therefore, this type requires a larger number of fasteners during installation.

There are three types of polypropylene pipe products according to the degree of heat resistance:
- Homopolypropylene (PP-N). PP-N pipes are characterized by high strength, chemical inertness, but are unstable to high temperatures. They are used when laying water pipes, ventilation ducts, drainage pipelines, etc.
- Polypropylene block copolymer (PP-2). Products made from PP-2 are intended for low-temperature heating systems, as they are resistant to temperature loads not exceeding +50 ºС. They are mainly used for installing heated floors and hot water supply pipelines.
- Random copolymer PP-3. The material is obtained by introducing ethylene units into the molecules of the main polymer. PP-3 pipes are characterized by increased flexibility, impact resistance, and high resistance to thermal loads. This is the most suitable option for arranging heating wiring from the boiler to the radiators.
The main technical characteristics for polypropylene pipes PP-3 are given in the table.
| Indicator name | Meaning |
| Limit temperature of the working environment during long-term operation | +70 ºС |
| Critical pressure level at maximum temperatures | no more than 10 atmospheres |
| Peak short-term permissible temperature | +90 ºС |
| Operating pressure at media temperature 25 ºС | up to 25 atmospheres |
| Linear expansion coefficient | 0.17 mm/m*ºС |
| Oxygen diffusion rate per day | 900 mg/m² |
Made from cross-linked polyethylene
PEX brand cross-linked polyethylene is a special type of polymer with a modified molecular bond structure. It is based on ethylene polymerized under high or low pressure. Cross-linking significantly improves polyethylene properties such as heat resistance, flexibility, wear resistance and the ability to self-heal after mechanical stress. Therefore, pipes made from cross-linked polyethylene are excellent for heating.

The technical characteristics of polyethylene pipes are as follows:
- Density - 940 kg/m3.
- Low coefficient of linear expansion.
- The maximum operating temperature is 95 ºС.
- Melting point - 200 ºС.
- Peak temperature load (short-term) - 130 ºС.
- Operating pressure parameters at:
- 20 ºС - 2.3 MPa.
- 95 ºС - 0.8 MPa.
Metal-plastic
The wall of metal-plastic products consists of five layers:
- Internal plastic smooth surface, which during operation is in direct contact with the coolant.
- Adhesive layer.
- A barrier layer made of aluminum foil, which increases the strength and durability of pipelines, and also reduces the degree of thermal expansion of products.
- Another layer of special glue.
- Polymer protective layer.

Due to the multilayer wall structure, high mechanical strength of the pipes is ensured, the sound insulation effect is enhanced, and thermal conductivity is reduced. This type of plastic pipe has the following performance characteristics:
- The maximum operating temperature is 95 ºС.
- The maximum temperature (for short-term exposure) is 130 ºС.
- The maximum pressure level at 95 ºС should be 10 bar; at a media temperature of 0 to 25 °С, it should not exceed 25 bar.
- Service life is at least 15–20 years.
Cross-linked polyethylene is a type of plastic
The production technology of such plastic pipes involves cross-linking polyethylene using a molecular bond method. If we consider the advantages of such a material, then first of all I would like to highlight the following characteristics:
- polyethylene has a fairly high density;
- high thermal stability parameters - the performance indicators of polyethylene are 90° C;
- memory of the material - if such a pipe was bent under temperature, then after the material cools down it retains its shape;
- long service life of 50 years;
- light weight, which does not create additional load on the walls and facilitates the installation process;
- simplicity and convenience during the installation process - when assembling heating, you can use connecting elements, both threaded type and fittings;
- resistance to deposits - limescale does not settle on the inner walls of the pipes throughout the entire service life.
Plastic pipes made of cross-linked polyethylene can be installed both outside and inside walls, since they do not have high linear expansion .
Which ones are better for heating?
Plastic pipelines perfectly cope with the assigned tasks in heating systems. Each type of polymer pipe may be more preferable under certain conditions. For example, for a hidden gasket it is better to take reinforced propylene, the parts of which are reliably welded together. Metal-plastic pipelines assembled using threaded compression fittings cannot be walled into the wall or filled with screeds. To inspect union nuts, free access is required.
Possibility to hide pipes
The reliability and quality of the heating circuit largely depend on its installation pattern. Polypropylene lines, soldered at the joints, form an integral system, so they can be safely mounted in cavities, filled with screeds, laid and sealed in grooves.
A metal-plastic pipeline connected by means of compression threaded fittings cannot be hidden, since access to the nuts is required. Over time, under the influence of temperature changes and water hammer, the fixation of connections may weaken. Every few years you need to tighten the fittings, and if necessary, change the gaskets.
Diameters and reinforcement
To assemble heating systems for residential buildings and industrial facilities, plastic pipes with a diameter of 16, 20, 25, 32 mm are used. The following diameters are suitable for laying heating mains: 40, 50, 63, 75, 90, 110. Wall thickness is 1.9–110.5 mm.

Reinforcement of plastic pipes is carried out for the purpose of:
- Increasing strength characteristics.
- Protection against oxygen penetration into the coolant.
- Reducing thermal expansion of products.
- Increased heat resistance.
The barrier layer can be made of fiberglass, solid or perforated aluminum tape. Some models are stabilized with basalt fiber, which is fused into the plastic during the production process. This method of reinforcement reduces the coefficient of thermal expansion of a plastic pipe by 3 times.
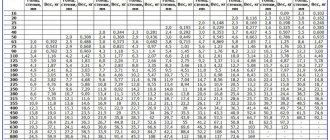
Selection of pipe diameter according to a given coolant speed.
| Selection of pipe diameter based on coolant speed. (80/60 mode) |
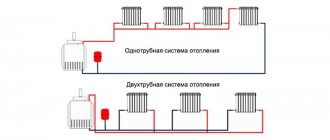
The above description is very similar to what happens in a two-pipe dead-end heating system.
The heating system has its own plant that produces heat - this is the boiler. Pipelines play the role of roads. The coolant, often water, “carries” the heat to the radiators, where it is consumed, replenishing the heat losses of the room. The “unloaded” cooled water returns to the boiler again to be filled with heat. The process happens constantly.
The diameter of the pipes for the heating system is selected according to the same principle as the width of the roads in our example. The more heat carried by water needs to be transferred, the larger the diameter of the pipe must be. As the heat demand decreases in each individual area, the diameter of the pipes decreases.
How much heat can a particular pipe pass through?
Omitting detailed explanations and calculations using well-known formulas, we will only say that one of the common ways to determine pipe diameters is to determine the speed at which the coolant will move inside the pipe.
On the one hand, the coolant speed should not be less than 0.25 m/sec. At lower speeds, air pockets form, preventing coolant circulation.
| Selection of pipe diameter based on coolant speed. (75/60 mode) |
On the other hand, it should be no higher than 1.5 m/sec. At high speeds, noise occurs from the coolant moving inside the pipes.
Practice and calculations have established that the coolant speed, which lies in the range of 0.3 - 0.7 m/sec, is the most optimal in terms of energy efficiency and material costs.
The tables show the speed of water movement through the pipeline depending on the thermal load and pipe diameter.
In the left column you see the thermal load. Above are the outer diameters of polypropylene pipes. The table itself shows the speed of water moving through the pipes.
Recommended speeds for a specific pipe diameter for a given thermal load are indicated in red.
Let's look at using data from a table using an example.
An example of pipe diameter selection.
Let's assume we have a private two-story house with a total area of 380 m2 with heat losses of 38,000 W.
Also, calculations have established that on the first floor the heat loss is 20,000 W, and on the second - 18,000 W.
The thermal regime is set to 80/60. (80 o C - supply; 60 o C - return)
As a scheme, we chose a two-pipe floor-by-floor dead-end heating system, divided on each floor into two equally loaded branches (direction in two wings).
Left branch of the first and second floors
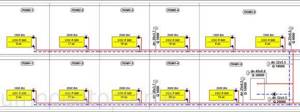
Right branch of the first and second floor

What is the required diameter of the main supply and return pipes connected to the boiler?
The entire flow of water intended to heat the entire house passes through it. And this is 38000 W.
We find 38000 W in the table and move horizontally to the red field. Then we go up vertically and find the required pipe diameter.
As you can see, three pipe diameters are suitable for our case: 40, 50, 63. Which one should I choose? In this case, it is logical that 40, because it is cheaper. Why do we need to build an eight-lane road for six cars?
We have reached the first fork. Part of the heat, 20,000 W, should go through the pipeline to heat the 1st floor, and the other, 18,000 W, will rise through the risers to the second floor. What pipes will we need now?
We look at the table for the coolant speed and the corresponding pipe diameters.
As you can see, you need to use 32 pipes for both the first and second floors.
In accordance with the data from the example, on each floor the pipes are divided into two branches of equal thermal load.
For the first floor, each of the branches carries heat equal to 20,000 / 2 = 10,000 W.
For the second floor - 18000 / 2 = 9000 W.
What pipes will we use for each branch? Look at the table again.
So, pipes with a diameter of 25 mm were selected.
What's next? Finally, along the path of each branch, radiators began to be encountered, which gradually began to remove the heat load from the branches.
Looking at the table, we see that as soon as the thermal load drops to 5000 W, it will be possible to switch to pipes with a diameter of 20 mm and then the remaining wiring can be done with these pipes.
In practice, we switch to pipes with a diameter of 20 mm at a thermal load of 3000 W.
Advantages and disadvantages
The use of plastic pipes for heating is due to their advantages:
- Ecological cleanliness. When heated, plastic does not release toxic substances.
- Low thermal conductivity.
- High throughput.
- Light weight, so they are easy to transport and install without using anchors.
- Does not need painting.
- They retain a pleasant appearance for a long time.
- They cut easily.
- They are simply connected to the pipeline using fittings using the soldering method.
- Suitable for both open and hidden installations.
- They have anti-corrosion properties.
The disadvantages include:
- The uniqueness of the installation technology of each type of plastic pipe.
- Temperature restrictions.
- Inability to use in fire extinguishing systems.
Advantages of polypropylene pipes
- light weight (compared to “traditional” steel);
- resistance to the formation of salt deposits, biological fouling, absence of growths and rust inside the pipes;
- low cost;
- guaranteed service life up to 50 years;
- the walls of the pipes are thicker than those of metal-plastic ones, and therefore the pipe is less susceptible to mechanical damage;
- low hydraulic losses in the pipeline due to low roughness;
- resistance to hydraulic shocks;
- low electrical conductivity, electrical impermeability;
- polypropylene pipe can withstand repeated freezing;
- in a water supply system made of polypropylene pipes, water does not change its taste, smell and color;
- the ability to install taps and valves between pipes by soldering, without threaded connections, and, as a result...;
- ...the ability to seal the entire structure (pipeline) under plaster or drywall;
- there are clips for attaching to walls, and they (clips) are cheap and available (they are sold almost “every step” - in many (and perhaps in all stores selling goods for construction and repair);
- simplicity and speed of installation, and you can master the installation of polypropylene pipes in just a few minutes;
- welding polypropylene pipes does not require the use of harmful materials (glue, flux, solder, electrodes), so work can be carried out even in an unventilated room;
- installation labor costs are less than for steel pipes.
How to choose
Criteria for choosing plastic pipes for a future heating system:
- Design diameter and wall thickness size.
- Acceptable operating parameters.
- The degree of flexibility of pipe products.
- Features of installation (open and hidden type of installation).
It is advisable to select plastic fittings from the same manufacturer.

The products of the German companies Rehau, Banninger and Wefatherm have proven themselves well. Products from these companies can be used for assembling heat supply routes and heating systems with the following coolant performance characteristics:
- Temperature conditions up to 130 ºС.
- Pressure up to 25 bar.
Materials from Czech companies Ekoplastik, FV-Plast and Wavin are to some extent inferior in quality to German products, but Russian builders willingly purchase them. The lower price segment is occupied by plastic products from Turkey and China. However, their operating temperature limit is +95 ºС.
The cost of domestic plastic products is significantly lower than that of foreign analogues. At the same time, in terms of strength and heat resistance, they are not inferior to them, and even superior.
Installation features
Unlike metal elements of heating systems, plastic parts can significantly increase in length when heated. Because of this, during open installation, horizontal pipelines may sag or risers may deviate from the vertical. Recessed sections of wiring, deformed due to linear thermal expansion, can cause considerable damage to the material of the building’s structural elements.
To reduce or eliminate the negative consequences of this property of plastic materials, the following rules must be observed when installing heating systems:
- On long straight sections, round or U-shaped compensation loops should be provided.
- To fix plastic heating pipelines, you need to use not only blind fastening elements, but also sliding clamps. They will allow the elements to move freely.
- If part of the pipeline network of the heating system is filled with concrete, then a protective sleeve made of corrugated or foamed polyethylene must be used.
- To join metal-plastic blanks in hidden heating systems, it is advisable to use compression fittings. They form a stronger and more reliable connection.
The process of assembling heating from plastic pipes with your own hands:
- Develop a general diagram of the pipeline network, determine the location of radiators, shut-off and control valves. Then, according to the drawing, calculate the amount of material required, buy it and deliver it to the installation site.
- Cut into pieces of the required length.
- Heat the soldering iron.
- Insert the nozzle from the soldering iron into the cavity of the pipe workpiece.
- Install a fitting and a piece of pipe with a nozzle onto the heating element of the soldering iron.
- Remove the parts from the soldering tool and join them together.
- Allow time for the connection elements to cool and the weld to harden.
Connecting pipes to each other
socket welding
There are 2 methods of connecting plastic pipes to each other:
- Socket welding.
- Welding using connecting elements.
Socket welding technology involves the use of a manual machine. The essence of its application is that when the material is heated, the process of diffusion of molecules occurs (the molecules of one component combine with the molecules of another, resulting in the formation of a seamless shell).
With this welding method, one end of the product is placed into the pre-expanded end of the other.
To carry out soldering using fittings, the end of the pipe and the coupling are inserted into a soldering iron nozzle of the appropriate size and heated at a temperature of 260 degrees.
The temperature can be set on the iron's thermostat. After the required time has passed for heating the material, the components are removed from the nozzle and then combined.
Products with a diameter of more than 63 mm are connected by butt welding.