In the heating circuits of individual houses, the leading position is occupied by polymers, the leader among which is polypropylene (PP). When installing heating systems, it is important to know how to correctly connect a heating radiator to polypropylene pipes.
The solution to this problem is not unambiguous, taking into account various wiring diagrams and methods of connecting radiator outlets to the supply and return lines. The choice of the optimal option is complicated by the fact that it is necessary to take into account the aesthetic appearance of the batteries connected to the heating main.
Rice. 1 Designer batteries made of cast iron
Types of radiators
To organize heating of premises, several types of radiators are used; based on the materials used, they are divided into the following groups:
Cast iron. Old cast iron batteries, known since Soviet times, are currently not in demand, although some enterprises still produce them.
Radiators made of cast iron are dismountable products, the sectional fragments of which are connected to each other with nipples. Unlike classic batteries, devices with a relief pattern on cast iron sections are now in fashion. They are produced in different colors; exclusive models emphasize one of the room styles chosen by the designer (classic, Italian, retro, loft).
Solid cast iron has relatively low thermal conductivity; the thermal power of one section usually does not exceed 150 watts.
Radiators made of cast iron can withstand pressure up to 50 bar and are designed for operation in a working environment with a temperature of no more than 120 °C.

Rice. 2 Steel tubular heat exchangers and convection type devices
Steel. Metal batteries are presented on the market in several varieties: tubular, tubular convection and panel.
The first type includes a copper (steel) pipe made in the form of a coil, or horizontal, vertical tubular sections through which the coolant flows.
In convection tubular models, metal plates or other shaped elements (pipes) are installed on the pipeline, dissipating heat into the surrounding space.
Tubular and convection radiators can withstand pressures of up to 15 bar and heating fluid temperatures of up to 120 °C. The thermal capacity of each battery depends on its design and can be used by almost anyone.
In panel metal radiators, the heating fluid circulates through channels made in flat rectangular panels. A protective enamel coating, usually white, is applied on top of them, improving the aesthetic appearance of the products and protecting the panels from corrosion.
Panel radiators are not collapsible; they are made by spot welding from two stamped steel sheets. They are designed for a network pressure of no more than 10 bar and coolant temperature parameters of up to 110 °C.
Heat exchangers of this type differ from each other in the number of panels, the maximum number of which reaches 3. The power of the devices depends on the size of the panel heat exchangers and their number. With three panels 3 m long, it reaches 6500 W.
A distinctive feature of panel-type devices is the bottom connection unit, thanks to which the heat exchanger does not disturb the aesthetics of the appearance of the premises.
In addition to low pressure characteristics, the disadvantages of panel devices include the weak corrosion resistance of steel and its lower thermal conductivity compared to aluminum and copper.

Rice. 3 Structural design of a panel battery
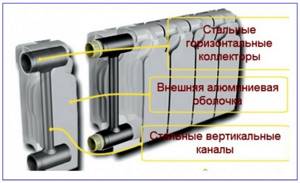
Aluminum. Aluminum batteries have long occupied a leading position in their use in domestic heating systems. Radiators are characterized by high heat transfer, capable of withstanding network pressure up to 50 bar at temperature parameters of the transported medium up to 115 ° C.
Aluminum radiators are assembled from separate sections, which are connected using nipples - in this way the power of the entire battery is regulated. The maximum heat transfer of one aluminum section is 180 W - this is the highest figure in comparison with other similar heat exchangers.
The disadvantages of aluminum devices include high requirements for the pH value of the coolant. If it goes beyond the narrow range of 7 - 8 units, the destruction of the protective oxide layer begins and the section quickly becomes unusable.
Bimetallic. To combat the destruction of aluminum by environments with a pH value outside its operating range, a bimetallic design was developed. In it, the medium is separated from contact with aluminum by a steel manifold. In production, during the manufacture of each section, the aluminum mass is pressed under pressure onto a steel tubular backfill.
As a result, the battery ceased to be sensitive to the hydrogen index of the heating fluid in the range of up to 10 units and acquired increased strength. Bimetallic radiators can withstand pressures up to 200 bar and can be operated at temperatures of the flowing medium up to 140 °C.
Their disadvantages include loss of power in sections due to the lower thermal conductivity of steel and heat loss in the contact zone of the filling with the aluminum shell.
Depending on the design of bimetallic devices (in the retail network, in addition to full bimetal, single-tubular and double-tubular semi-bimetal are sold), the heat transfer of one section is 160 - 170 W.
Article on the topic:
Connecting bimetallic heating radiators - instructions from “A” to “Z” . On our website there is a separate article about bimetallic radiators and their connection to the heating system of a house or apartment; it may be interesting to read it before connecting a heating radiator to polypropylene pipes.
Rice. 4 Bimetallic battery - internal structure
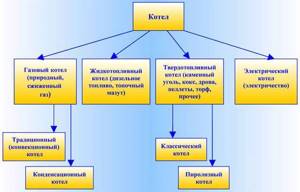
Heating boilers
The choice of heat source is a key factor on which the further selection of heating elements and the operating efficiency of the assembled system will depend. The cheapest fuel today is gas, therefore, if a gas main is connected to the site, a gas-fired boiler will be the best solution.
Condensing gas boilers with electric ignition, which have a couple of features, have proven to be the most economical:
- When the coolant is heated to too high a temperature, gas is simply not consumed, which reduces its costs by about 25%;
- The heat given off to water vapor is also used for heating, which saves another 10-12% of energy resources.
If we arrange heating equipment operating on other types of fuel in order of decreasing efficiency, we will get a list of the following type:
- Wood boilers;
- Pellet boilers;
- Coal boilers;
- Diesel boilers;
- Electric heating devices.
When choosing a heat source before heating a private home, you need to pay attention to a number of nuances:
- For gas boilers, you can use not only main gas, but also bottled gas. True, the cost of heating in this case increases several times.
- Before purchasing a heating device that runs on a certain type of fuel, it is worth at least approximately studying the dynamics of rising prices for different types of fuel, and when studying, you need to tie fuel prices to geography.
- Coal boilers use firewood for heating. This must be taken into account - firstly, kindling and warming up the system will take longer, and secondly, purchasing firewood will require additional costs.
- Gas, diesel and electric boilers operate uninterruptedly if fuel is available. Pellet boilers with an automatic feeding system can operate for a week. Solid fuel boilers must be heated and cleaned at least (and often more often) once a day. A long-burning boiler can operate on one burner for several hours longer, and the most expensive and modern devices operate without problems throughout the day.
- The waste can be used as fuel for diesel boilers - this will reduce heating costs several times. The disadvantage of such savings is the shortage of used oil, which is very difficult to purchase in sufficient quantities and on an ongoing basis.

Electricity in such devices is required only for the operation of the compressor. Such schemes turn out to be quite profitable - the cost of heating can ultimately compete on equal terms with the savings when using solid fuel boilers and gas.
Of course, you have to pay for the savings somewhere - the cost of heat pumps is very high, and the installation of such equipment costs a tidy sum. It is enough to give a simple example: to install a geothermal pump, you need to drill a well several tens of meters deep, or dig a pit, the area of which will be three times larger than the area of the heated building.
There is a solution to this problem - you can use a type of heat pump in which the coolant is air outside the house. Thermal energy is pumped out of it, which is subsequently used to heat the building. In essence, this scheme represents the operation of a conventional air conditioner set to heating mode.
Operational features of polypropylene pipes
Polypropylene pipes are widely popular among consumers when installing heating systems due to the following technical and operational characteristics:
- To transport coolant to radiator heat exchangers, two types of polypropylene pipes are used - fiberglass and aluminum reinforced.
- Glass fiber reinforced pipes are designed for a PN network pressure of no more than 20 bar and can be used for a long time (at least 25 years) at coolant temperatures of 70 - 90 °C. The disadvantages of fiberglass pipes include a relatively high coefficient of linear thermal expansion of up to 2 mm per linear meter at a temperature delta of 70 ° C, as well as their high oxygen permeability.
- The maximum pressure ratings for PP pipes with aluminum reinforcement are 25 bar with a service life of 25 years when transporting a working medium with temperatures up to 90 °C. Aluminum-reinforced PP pipes have a negligibly low linear elongation coefficient and do not allow oxygen to pass through.

Rice. 5 PP pipes with fiberglass and aluminum reinforcement
- Polypropylene pipes are connected by soldering using a special soldering iron for polypropylene pipes at a temperature of 260 °C.
- During installation, a wide range of shaped products are used, including adapters from polypropylene to metal with threads, produced along with pipe products by each manufacturer.
- PP pipes are divided into classes according to areas of application (sometimes they are indicated on the markings with numbers from 1 to 5 and XB symbols) and wall thickness. The latter indicator is indicated on the marking, and is also set by the dimensional ratio of the outer diameter to the wall thickness of the SDR.
- The thermal conductivity coefficient of products reinforced with glass fiber is about 0.3 W/m °C, with an aluminum shell - 0.45 W/m °C.
- Polypropylene pipes are afraid of exposure to direct ultraviolet radiation, which, however, does not prevent anyone from laying them openly, leading them to heat exchange devices under the windows.

Rice. 6 Classes of PP pipes
Do-it-yourself heating system installation
Before heating a private home, you need to stock up on the following tools for soldering polypropylene pipes:
- A shaver that allows you to remove reinforcement from the soldering area and chamfer the pipe;
- Pipe cutter;
- Soldering iron for polypropylene pipes with a set of nozzles of the required diameter.
The pipe connection technology is as follows:
- First you need to put the shaver on the pipe and turn it several times to remove the aluminum layer. If this is not done, the metal will gradually become damaged upon contact with the liquid, thereby having a negative impact on the entire heating system.
- The soldering iron nozzle is heated to the required temperature, then a pipe is inserted into the socket, and a fitting is put on the opposite side of the nozzle.
- When the parts melt a little, they need to be combined with some force and held in this position for a few seconds. After the plastic has hardened, you can begin soldering the next section.

A safety group is installed near the boiler outlet pipe. The installation location is determined by the fact that it is in this section of the system that the pressure rises when the system malfunctions. The expansion tank can be mounted anywhere, but there is one caveat: when installing the tank in front of the pump, the distance between them should be more than two filling diameters, and if the tank is attached behind the pump, then the distance increases to ten filling diameters. Failure to comply with this rule leads to premature failure of the membrane - and it is unlikely that it will be possible to determine the problem immediately, so you will also have to think about how to check the heating in a private house.
Sometimes the question arises whether a gravity system can be converted into heating with forced circulation. The answer to this question is affirmative - if necessary, the pump can be installed in any circuit, which allows you to completely remake the heating in a private house.
- The diameters and wiring configuration are selected so that the system can operate with natural circulation;
- Parallel to the wiring, two connections are installed in front of the boiler, to which the circulation pump is connected;
- The taps are separated from each other by a check ball valve.
When the pump is running, the valve closes and completely closes the passage in the bypass, thereby ensuring forced circulation of the coolant. When the pump is turned off, the heating automatically switches to natural circulation - the valve opens and the coolant continues to move. Of course, the check valve can be replaced with a gate or ball valve - but in this case, you will have to switch the operating mode of the system manually.
This article gives a superficial idea of how to install heating in a private house with your own hands. Each design element can be examined in more detail, so if there is such a need, you can look for the relevant article for a deeper understanding of a specific issue. In general, it can be noted that the heating system has a fairly simple design, and with due attention it is quite possible to assemble it yourself.
Fittings for connecting heating radiators
When connecting radiator heat exchangers to the heating main, as well as in them themselves, the following types of connecting elements and fittings are used:
Ball Valves. Shut-off valves of this type are designed to completely shut off the coolant supply to radiators. Thanks to this, any battery can be either connected or unscrewed from the pipeline for repair, cleaning or replacement with a new device. Ball valves operate in the closed and open position; it is not recommended to use them to regulate the flow of the working medium.
Valve taps. Valve fittings are used to regulate the volume of coolant supply and shut it off. It is used in cases where there are no thermostats on the radiators and the temperature on each device has to be set manually.
During the setup process, the temperature parameters of the radiators are measured with a non-contact electronic thermometer, and based on its readings, the valve tap is rotated, controlling the flow.
Sgons and Americans
What it is
Let's start with a short excursion into history.
Quite recently, by historical standards - some twenty to twenty-five years ago - only three types of heating devices were massively sold and used in our country:
- Convectors, which were a coil made of a steel pipe with steel plates pressed onto it to increase heat transfer.

Domestic design, meaningless and merciless.
Let us clarify: optionally, their design could include a decorative screen and blinds to regulate heat transfer.
- Plate radiators are two stamped steel plates welded around the perimeter. The coolant moved through a labyrinth of grooves between them.
- Cast iron sectional radiators. They, it seems, do not need any introduction, since they are now installed in most apartments.
There were only two methods of fastening:
- Welding . They were welded to the convector connections exclusively: their mechanical strength and service life, at least not inferior to the service life of the risers and connections, did not require dismantling for repair or replacement.
- Sgony . The coupling (in the case of a convector or plate-type device) or the radiator plug (in the case of a sectional radiator) was driven along the long thread on the connection, simultaneously screwing onto the thread of the device or screwing into it. The connection was then sealed with a wound locknut.
The first aluminum radiators were mounted the old fashioned way - on saddles. However, after a few years, simple fittings - American ones, which included detachable connections with a union nut and a rubber seal - became widespread. Their main advantage was the simple and quick dismantling of the device: an operation that previously took up to half an hour now took no more than a minute and did not require much effort.

The aluminum heating device is connected with modern fittings.
Help: a cast iron radiator cap from a new radiator can be unscrewed with a gas wrench number 2. To deal with an old stuck cap, you have to lengthen it with a lever or use a wrench number 4. In this case, the cap often does not unscrew, but is literally torn in half, losing the thread .
Does the American woman have any disadvantages? In essence, there is only one drawback: the strength of the connection is limited by the quality of the rubber seal and the tightness of its pressure. With high pressure in the circuit (for example, during water hammer), it is the seal and the relatively thin American union nut that turn out to be the weak link.
Recommendations
The conclusions that the author made for himself will certainly be challenged by many other experts; however, they are quite unambiguous.
- In central heating systems with a high probability of exceeding the standard pressure, it is better to use the usual threaded fittings.

The cast-iron radiator in the central heating system is connected via leads.
- It is advisable to use American ones in autonomous systems.
Piping diagrams
When installing a heating system, use the following diagrams for laying pipes to radiator heat exchangers:
Single-pipe sequential. It is used in apartment buildings, when all radiators from the first to the last floor are connected in series to one pipe (Fig. 10).
To ensure a continuous supply of coolant in the event of emergency situations in any of the apartments that require removal or repair of the radiator, a parallel bypass jumper must be installed in its piping. The use of ball valves in the bypass in this case is strictly prohibited.
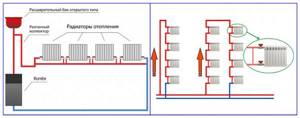
Rice. 10 Options for single-pipe distributions: Leningradka and side with bypass for apartment buildings
Single-pipe parallel. It is used in gravity (gravity) heating systems and wiring of the Leningradka type.
In gravity-type heating systems, the coolant from the upper storage tank is supplied to the radiator heat exchangers through one common pipe with side branches to each device. The media is supplied through the upper battery pipe and flows out through the lower one, located under or diagonally to the inlet (Fig. 11).
The pipelines from the lower pipes of all batteries connect to one common return pipe of a larger diameter, which is connected to the boiler at an angle.
In the popular single-pipe system Leningradka, the main pipe of large diameter makes a closed loop returning to the boiler, and radiator heat exchangers are connected to it using pipe sections of smaller diameter in parallel through the lower bends.
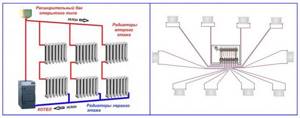
Rice. 11 Schemes of gravity system and radial (collector) wiring
Double-pipe dead-end. A simple piping diagram in which two supply and return pipes depart from the boiler. A radiator pipe is connected to each of them.
For supply use the upper or lower outlet, for return only the lower one.
With this connection scheme, the coolant is supplied to the furthest radiator and the return flow occurs along the longest path. As a result, the last main battery heats up less than the others and can be completely cold.
A dead-end system requires the mandatory use of thermostatic valves or, in the absence of them, balancing with valve taps.
Its advantages include lower pipe consumption and the associated more aesthetic appearance of the premises.
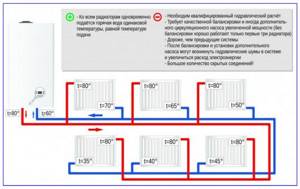
Rice. 12 Two-pipe dead-end circuit and its features
Along the way Tichelman. In the associated Tichelman scheme, the coolant is supplied to the upper or lower radiator pipe through one pipe extending from the boiler. The return is connected to the bottom point of the radiators, but is directed to the boiler not from the first battery connected to it, as in a dead-end circuit, but from the last one in the circuit.
As a result, the total length of the supply and return lines to each heat exchange device is the same, and accordingly the heating temperature of all batteries will not differ from each other. Thanks to this, there is no need for balancing with valve taps and installation of expensive thermostats.
Despite such obvious advantages, Tichelman’s scheme has not found wide application. This is primarily due to the high consumption of pipes - parallel to the two pipelines, you will have to lay a third return pipe of the same length, or stretch it along the perimeter of the walls to close the loop. Also, due to the third pipe, the associated gasket has an unaesthetic appearance.
On the wall under the battery, with the open method of placing the pipeline, there will be three pipes in a row: supply, return and return lines to the boiler.
Collector (radial). With this wiring diagram, several heat exchangers are connected to one collector unit. Each battery has its own supply and return pipes.
If the collector unit is placed in the middle of the house, then a pipeline of approximately the same length approaches each radiator. This helps to equalize temperatures in heat exchange devices. To accurately set the required temperature parameters, each radiator with radial connection is equipped with its own thermostat.
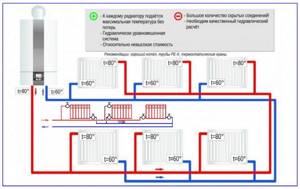
Rice. 13 Two-pipe associated scheme and its features
What to consider when choosing
When purchasing a regular installation package, you should decide on the diameter of the heater’s connecting hole. Some boiler equipment manufacturers may give specific installation recommendations, which will include the type of faucet connection kit. You should pay attention to such recommendations in order to avoid damage to thermal convectors. Fittings produced by well-known manufacturers are more reliable.
If the choice falls on a universal set, which also contains fasteners, it is worth considering that for heavy cast-iron radiators you should take special long steel pins to be able to bury them into the thickness of the wall; for light models of heaters, brackets screwed with screws are sufficient.
It does not matter which unit is installed in the thermal circuit - aluminum or bimetallic - they are not adapted for conventional plumbing fittings due to the fact that on the right side, if you look at the front panel, they have holes with a right-hand thread, and on the left side, accordingly , there is a left cut. Left-sided fittings solve the issue, allowing valves, valves and plugs to be connected to them.
When buying a set, you need to carefully check the direction of the turns of the holes on the fittings; it should be different in pairs.
Options for connecting radiators to pipes
When installing radiators, use the following options for connecting them to the pipeline:
Lower. It is used in single-pipe distribution of the Leningradka type and when connecting metal panel heat exchangers. Although the bottom connection is considered not very efficient in terms of heat transfer, many people prefer it for aesthetic reasons.
Diagonal. It is considered the most effective in terms of heat transfer; it is widely used in all types of two-pipe distributions and in gravity flow systems.
Lateral. The main type of battery connection in apartment buildings has slightly less heat transfer than a diagonal connection.
When connecting laterally, in many cases an additional bypass jumper is used.
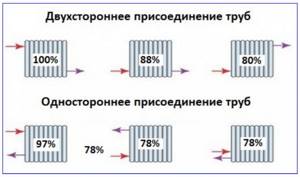
Rice. 14 Options for connecting radiators to pipes and their effectiveness
Battery tying
Before heating the house yourself, you also need to think about the amount of fittings that will be used in the system. In the event that you only plan to turn off the radiators, then two ball valves installed on the connections on each side of the heating devices will be sufficient. Such cranes are quite reliable and durable, so there will be no problems with them.

It's another matter if the system needs to be configured. To regulate the coolant flow, you will need radiator valves. Structurally, they are ordinary valves in which a metal valve is installed. To automatically adjust the permeability of the connections, it is better to take valves with thermal heads that regulate the heat transfer of the batteries when the air temperature in the room changes.
Connecting a heating radiator to polypropylene pipes
When installing PP pipes, they can be laid in wall grooves. At the same time, the aesthetics of the appearance of the premises increases, the pipes do not interfere with cleaning.
However, in practice, hidden installation of polypropylene in walls, in contrast to hot and cold water supply, is used quite rarely.
This is primarily due to high labor costs during installation work associated with gating walls and the inconvenience of soldering the heating main in the grooves and connecting radiators to it.
In addition, the best alternative to hidden installation of polypropylene in walls is the use of flexible pipelines made of cross-linked polyethylene, which are usually laid under a screed.
For installation, polyethylene pipes are connected to a compression fitting with a threaded outlet, which is fixed in the wall. Radiators are connected to it through adapters.
Taking into account the above, it should be said that in the vast majority of situations, open line laying technology is used for radiator heating with polypropylene. Also, when wiring, a dead-end circuit is used more often than others, with temperature settings of the batteries set by thermostats.

Rice. 15 Tool for installing PP pipes
Fittings: division by type of installation
Welded fittings are versatile connecting elements that allow you to secure parts of a pipeline. In this case, the joints are sealed with a strong, hermetically sealed seam, which eliminates leaks. Made from stainless steel.
Solder fittings. They are fixed with a torch. These connecting parts are made of copper or bronze. They are excellent for soft and hard soldering. These fittings are only used for metal piping.
Crimp fittings differ from the previous type in that such a connection does not require a welding or soldering machine. In this case, a crimp ring is required, which is secured with an open-end wrench.
Compression - used to connect pipes made of any material. This type of fitting is very popular because it provides a reliable connection with minimal installation time.
Press fittings are fittings for heating radiators, designed to connect pipes that require a special expensive tool - a press machine. Such elements provide high tightness, since there is an O-ring inside the ridge.
Self-fixing is a copper fitting that is perfect for fastening pipelines made of any material and of various cross-sections. This is a reliable type of connection that allows for repeated use. Removing it is as easy as installing it. To do this, you just need to press on the element with a special key.











