The heating system is one of the most important communications for an apartment and a private house. Thanks to its proper and high-quality work, the coziness and comfort in a residential building depends. The functionality, reliability, and practicality of the heating system depend on the quality of the elements. We bring to your attention a detailed overview of the types of heating pipes that exist today, with a description of their inherent advantages and disadvantages, as well as recommendations for choosing pipes for different rooms.
- 2 Metal-plastic pipes
- 3 Polyethylene pipes
- 4 Polypropylene pipes
- 5 Steel pipes
- 6 Selection of heating pipes
- 7 Pipe sizes for heating systems
Types of pipes for heating systems
Pipes most often used for heating systems are:
- steel;
- metal-plastic;
- polyethylene;
- propylene.
All pipes have their advantages and disadvantages . If you compare them with each other, it is best to consider the performance characteristics using a table.
| Material | Operating temperature °C | Roughness, mm | Pressure loss hPa/m | Coefficient of linear expansion mm/m*deg. |
| steel | 0,07 | 5 | 0,012 | |
| Metal-plastic | 95 | 0,004 | 1,5 | 0,025−0,03 |
| Polyethylene | 90 | 0,007 | 1,8 | 0,15−0,17 |
| Polypropylene | 70 | 0,01 | 2 | 0,15−0,17 |
Metal-plastic pipes have an aluminum layer , with the help of which they tolerate minimal linear expansion and high temperature loads while maintaining their shape. High elasticity allows pipes to be bent as needed.
Polyethylene pipes are heat-resistant , have high joint strength, and low hydraulic losses. It is necessary to choose polyethylene pipes for heating only with a reinforcing layer , which allows the pipe to maintain its shape.
Polypropylene pipes are used if the coolant temperature does not exceed 70 degrees. Due to expansion and high fluidity, this type of pipe requires additional fixation to avoid sagging and malfunctions.
If propylene pipes have a reinforced layer of aluminum, then they can be used not only for hidden, but also for conventional wiring.
Varieties for heating systems
Modern heating systems use rolled pipes and parts made of materials such as metal or plastic. The first category includes ordinary steel, alloy steel and copper pipes. The second includes polypropylene, metal-plastic and polyethylene cross-linked communication elements.
They all have certain positive qualities and manifest themselves effectively in different situations. The choice of a specific type of pipe is made individually, depending on the expected operating conditions and other important parameters.
Features of steel pipes
Until recently, steel pipes were used in the vast majority of heating systems and were the only material available. Today their positions have significantly weakened, and serious competitors have appeared nearby.
However, it was not possible to completely oust steel pipes from the market. Until now, they have been successfully used, but mainly in autonomous gravity-flow complexes, where the laying of large-diameter communications is required.
The laying of steel pipes is carried out by professional craftsmen before finishing activities begin, since welding work can damage wall or floor decor
Among the main advantages of steel pipes are a high tendency to thermal conductivity, low linear expansion during active heating, and resistance to intense pressure.
Justified advantages are considered to be unprecedented strength, both on straight and rounded sections, the ability to withstand aggressive temperature conditions and the affordable cost of elements.

To assemble a system of steel pipes, in addition to welding, there is an alternative method - installation on threaded connections using additional parts and fittings. To prevent joints from leaking, they are sealed with plumbing flax
Among the shortcomings, they point to problematic and labor-intensive installation, which is impossible without the presence of specialized expensive equipment, which can only be operated by professionally trained craftsmen with extensive experience in carrying out such activities.
The process of arranging a heating complex is also complicated by the impressive dimensions of the pipes. You won’t be able to do everything alone; it’s better to involve one of your friends or relatives who has the skills of welders and installers. It’s easier and faster to work with a team; everything can be organized clearly and accurately, ensuring the system has the necessary tightness.

Steel pipes demonstrate a good level of resistance to water hammer and have an impressive melting point (up to 1500°C), unlike other materials
Steel pipes and steel fittings used to connect them are absolutely not suitable for organizing hidden heating systems. The metal has a low anti-corrosion threshold and in humid conditions quickly rusts, rots and leaks.
To fix the problem, complete dismantling of the decorative covering is required if the pipe runs indoors, or large-scale excavation work when the problem arises on the approach to the house.
What is the difference between alloy steel?
Alloy steel is a durable material that, in addition to traditional impurities, contains various additives that improve the physical properties of the metal.
An example of an alloyed material is stainless steel - this is a special steel alloy containing at least 12% chromium. This additive ensures pipe resistance to corrosion and easy processing with special tools.

When purchasing stainless steel pipes, it is important to take into account the carbon content of the metal. The more it is, the higher the strength, but the lower the flexibility. At low temperatures, such products become brittle and their scope of application is reduced.
For the production of pipes with a welded seam, cold- or hot-rolled steel sheets with a working thickness of 0.4 - 5 mm and 2 -50 mm, respectively, are used.
Finished products have less weight than conventional steel ones and have good resistance to structural destruction and mechanical damage. Due to the low coefficient of thermal expansion, they can easily withstand severe temperature loads during operation. They function perfectly at pressures up to 16 bar.

The cost of alloy pipes is slightly higher than that of analogues made of ferrous metals. However, the costs are justified, because simple steel communications last on average 15-20 years, while stainless steel works reliably at least 3 times longer
Another indisputable advantage of alloyed stainless steel pipes is the ability to transport not only coolant heated to high temperatures, but even heated steam.
Types of stainless steel pipes
Alloy stainless steel pipes are made in two ways: welded and seamless. In the first version, sheets of metal are connected to each other using electric welding, producing a longitudinal or spiral seam. To prevent heat-affected corrosion, the joint area is subjected to special treatment and grinding.

Welded pipes with a spiral or longitudinal seam are cheaper than their seamless counterparts, but their service life is shorter. In addition, they have restrictions on maximum operating pressure and are vulnerable to mechanical damage
Seamless products are made by cold or hot deformation of solid pipe blanks made of stainless alloy steel. The cold method produces thin-walled pipes, and the hot method produces thick-walled pipes. The finished product has a perfectly smooth surface and is characterized by unprecedented reliability.

Seamless steel pipes are ideal for arranging heating systems of any complexity. Despite their high physical characteristics, they are reasonably priced, and thin-walled models successfully compete with more expensive copper products
Pipes made using seamless technology are not afraid of corrosion, function perfectly in harsh and aggressive operating conditions and can easily withstand record temperatures and enormous pressure.
Copper pipes for heating
In the manufacture of pipes for heating systems, high-quality copper is used, and in rare cases, a copper-zinc alloy, where the volume of the zinc component does not exceed 5%. To reduce the level of heat loss and give the products a more attractive appearance, the outer surface is covered with a polyethylene or polyvinyl chloride layer.

Copper pipes for the heating system undergo additional phosphorus treatment. This significantly increases their physical characteristics, and in particular, resistance to water.
Among the main advantages of the material for copper pipelines, the unsurpassed strength is first noted, thanks to which the products last for 100 years during intensive use and are not subject to corrosion.
Their thermal conductivity is 389.6 W/mK, which significantly exceeds the actual performance indicators of cast iron, steel and metal-plastic.

Copper pipes, when heated even to high temperatures, do not emit any harmful fumes, therefore they are absolutely safe for humans
The operating temperature range of copper pipes is very wide. They perform well both at high (up to +250°C) and low (up to -100°C) temperature conditions, do not melt during intense heating, do not crack or deform during operation.

They ideally hold their original shape, are not afraid of high pressure in the system, and even in the area of soldered joints they can easily withstand a load of 200-400 atmospheres, and this is tens of times greater than the ability of metal-plastic in the same area.
The thermal expansion rates of copper pipes are simply minimal. With regular exposure of metal to a coolant temperature of more than 90°C, each linear meter of communications lengthens by approximately 0.1%. All other materials here are significantly inferior to copper.
Due to the ability to maintain an aesthetic, attractive appearance over time, they are suitable for laying pipelines of not only internal, but also external heating systems and can serve not only for their intended purpose, but also serve as a decorative interior element.
Among the disadvantages, professionals note incompatibility with other metals. In order to reduce the cost, it is not recommended to use connecting parts made of cast iron or stainless steel for copper pipes. Such “savings” will subsequently backfire on the owner, since the chemical reaction between the elements will ultimately provoke corrosion of the entire heating system.
In the assembly of copper pipelines, only copper fittings are used. They are used to make connections by crimping, high-temperature and low-temperature soldering.
Among the disadvantages of copper pipes, their high cost is most often mentioned in comparison with other types of materials.
Distinctive features of polypropylene products
Polypropylene is a rigid, non-toxic synthetic polymer with high physical and mechanical characteristics. Pipes made from this modern material demonstrate exceptional impact resistance and multiple bending capabilities, low gas and vapor permeability, wear resistance and complete dielectricity.
Advantages of PP material
Thanks to these qualities, PP pipe material is actively used for arranging heating systems both on an industrial scale and in the private sector.

You can install a heating system made of polypropylene pipes yourself. But it is necessary to ensure that there are no sudden changes in pressure and temperature. Installing a boiler that limits the maximum possible water heating (no more than 70C°) will help create such conditions.
Polypropylene pipes are included in the category of budget communication parts and are lightweight, making them easy to transport and install alone.
Other advantages include the following:
- a perfectly smooth inner surface that does not contribute to the accumulation of lime deposits, which significantly complicate the free circulation of the coolant;
- quick and affordable installation that does not require the use of expensive professional equipment (all work can be done using a soldering iron, which is so easy to use that even a person very far from such work can easily “obey” it);
- long service life without loss of efficiency (on average about 25 years at full load);
- good resistance to negative temperatures;
- neat, aesthetic appearance that does not deteriorate over time.
The disadvantages of polypropylene pipes include the weak rigidity of the plastic, which in the future can cause sagging of the heating main and, as a result, lead to a crack in the joint or breakage.
To fix the problem, simply patching the fragment will not work. For subsequent correct operation and restoration of the integrity of the heating complex, it will be necessary to replace the section of pipe located between the two fittings.
The parts of a polypropylene pipeline are connected by welding, the specifics of which are described in the article we recommend.
You can also familiarize yourself with the features of choosing a welding machine for constructing a polypropylene pipeline and the recommended operating temperature limits for soldering on our website.
Types of polypropylene pipes for heating
In order for a home heating system to work longer and demonstrate the highest possible efficiency levels throughout the entire operational period, reinforced polypropylene pipes are used. They are classified according to the type of reinforcing material.
The PP pipes used in the heating device are reinforced with aluminum foil along the outer layer, in the middle or along the inner edge. In this case, sheets of metal can be discontinuous, solid or corrugated.

Polypropylene is highly plastic and can increase in size upon contact with a hot coolant. If communications are built into walls or floors, this may cause cracks in the coating. Reinforced pipes are subject to minimal expansion due to the presence of a protective frame
The foil reduces the actual thermal expansion of the material and creates a diffusion barrier, preventing oxygen from penetrating the walls. As a result, calcium sediment does not form and does not provoke oxidation processes on the walls of the radiators and boiler.
Fiberglass is also an effective reinforcing material for pipes. By coextrusion, it is placed in the middle layer of a polypropylene pipe. Due to the fact that both materials are similar in composition and basic properties, during welding with a fitting, a high-strength alloy is formed that is not subject to delamination even during long-term operation.
Polypropylene pipes with fiberglass reinforcement are simple and easy to install, unlike aluminum pipes, they do not require additional cleaning of the edges before soldering, and demonstrate excellent sound insulation properties.

Polypropylene pipes reinforced with fiberglass are considered the most suitable option for arranging home heating systems and last much longer than their counterparts.
Another modern reinforcing element is composite. It is a mixture of polypropylene and fiberglass. Added to the pipe, it increases the adhesive properties of the reinforcing layer and enhances performance characteristics such as strength and resistance to mechanical damage.
Rules for assembling pipelines for heating systems made of polypropylene pipes are given in the following article, the contents of which we advise you to familiarize yourself with.
XLPE pipes
Cross-linked polyethylene is a progressive material made using modern technologies. It is a polymer of ethylene with molecules connected cross-linked by chemical or physical cross-linking. It has a homogeneous structure, flexibility and a high level of tensile strength.
The list of main advantages of cross-linked polyethylene pipes includes:
- excellent shrinkage properties;
- the ability to clearly hold its shape along the stitching line even when heated to 200 C°;
- excellent wear resistance during intensive use;
- absence of halogens and heavy metals;
- immunity to corrosion and high pressure;
- low vulnerability to chemically active aggressive substances;
- normal impact strength at low temperatures (down to – 50 C°);
- minimum percentage of expansion under the influence of heat;
- suitable for hidden installation;
- minimal need for preventative maintenance.
Due to its plasticity, the material can be easily processed and does not require special tools, special professional abilities or serious experience. Even an amateur can handle installing a heating system if he has step-by-step instructions on hand to describe the necessary work.

Another distinctive feature of cross-linked polyethylene pipes is the “memory effect”, when a fragment “remembers” its position in the system and does not change it even over time
The most significant disadvantage of cross-linked polyethylene is its high vulnerability to ultraviolet radiation and the objective technological impossibility of producing large-diameter pipe material.
Methods and technology for welding polyethylene pipes are described in an article entirely devoted to this interesting issue.
Metal-plastic for pipeline construction
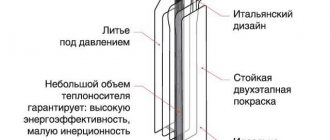
Metal-plastic products are the most common and practical material for arranging home heating systems. They harmoniously combine the advantages of plastic and metal, only absorbing the disadvantages of both materials to a minimum.

Compression fittings are used to assemble a heating system from metal-plastic pipes. They provide a reliable connection of all elements, but require subsequent additional maintenance
Metal-plastic pipes have a complex design and multi-level structure. The outer plastic layer acts as a fuse and protects the product from aggressive environmental influences. Next are aluminum foil and a polymer of increased smoothness, which prevent sediment and deposits from accumulating inside.
The connection of metal-plastic pipes is made using specialized fittings designed for crimping and clamping. In the first case, theoretically detachable connections are created, which are still not recommended to be disassembled unless absolutely necessary. In the second - one-piece.
No expensive tools are required to form connections with press fittings. The article we recommend for reading will familiarize you with his choice. The system can be assembled by a completely inexperienced performer.
Of the distinctive features of metal-plastic pipes, the most important are:
- minimal linear expansion under the influence of the coolant, which does not lead to deformation and sagging of the pipeline system or its individual fragments;
- pronounced smoothness of the inner surface, due to which the passage does not become clogged and the coolant circulates as expected; good temperature resistance (lower than metal parts, but higher than other plastic products);
- bending and tensile strength, ductility within acceptable radii (if the threshold is exceeded, “breaking” is possible);
- light weight, greatly facilitating the installation process;
- corrosion resistance;
- possibility of processing without the use of special equipment.
The disadvantages include the not very long service life of pipe products (up to 15 years according to manufacturers) and the significant cost of connecting fittings.
Metal-plastic pipes
Metal-plastic pipes have a structure of 5 layers: plastic, aluminum glue, glue, plastic. Thanks to their multi-layer structure, pipes easily withstand temperature changes, are resistant to corrosion and chemical attack, do not oxidize, and do not deposit salts.
Metal-plastic pipes are used for cold and hot water supply and heating.
Technical characteristics of metal-plastic pipes:
- maximum temperature - 95 degrees;
- maximum pressure at the highest temperature - 10 bar;
- maximum pressure at a temperature of 0−25 degrees - 25 bar;
- the maximum permissible short-term temperature is 130 degrees.
If all operating conditions are met, the pipes will last at least 50 years.
In order to connect metal-plastic pipes to each other, brass fittings are used, which ensure the reliability and strength of the structure. The disadvantage of this connection is the reduction in the diameter of the fitting's flow area.
Advice . It is best to use metal-plastic pipes if the coolant has a high temperature.
Polyethylene pipes
Polyethylene pipes for heating systems are made from durable and reliable polyethylene with the PEX modification. Such pipes are used not only for autonomous, but also for central heating.
Polyethylene pipes have the following advantages :
- strength;
- environmental friendliness;
- heat resistance;
- resistance to chemicals;
- do not corrode;
- have a smooth surface, due to which salts are not deposited and biological fouling does not occur.
To connect polyethylene pipes to each other, fittings made of bronze, polymers and brass are used. The fittings do not have seals in the form of rubber rings, because the pipe material serves as a seal and this increases the durability and reliability of the connection.
Advice . It is best to choose polyethylene pipes for heating systems with a reinforcing profile.
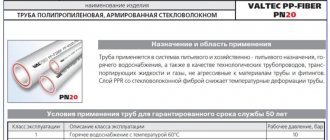
Polypropylene pipes
Polypropylene pipes are made from a special type of polypropylene. This type of pipe is heat-resistant and durable, but has some disadvantages that other materials do not have - high fluidity and the ability to change shape under the influence of high temperatures.
Metal-plastic and plastic pipes, unlike polypropylene, bend much easier, which makes installation much faster and more convenient, and when installing polypropylene, you will need a huge number of rotary fittings.
Polypropylene pipes have the following characteristics:
- maximum temperature 70 degrees;
- maximum pressure at 70 degrees - 10 bar;
- pressure at temperature 0 = 25 degrees - 25 bar;
- permissible short-term temperature is 90 degrees.
Fittings made of polypropylene are used to connect pipes.
The structures are connected to each other using diffuse welding of polypropylene and a temperature of 270 degrees. The strength of this type of connection allows you to extend the service life of pipes. You can use soldering of pipes to each other on straight sections, and with the help of fittings, turns are provided where necessary. Propylene pipes are most often used with a reinforced profile, which gives the structure strength and reliability. To prevent the pipes from changing shape, it is necessary to use additional fasteners that will support the structures and prevent them from sagging. Supporting structures are installed every 50 -60 cm.
Advice . Polypropylene pipes should be chosen for heating systems only if the coolant temperature does not exceed 60 degrees.
Calculation of diameter for a two-pipe heating system
We will calculate using the example of a simple two-story house. On each floor we have two wings. The house itself will have a two-pipe heating system with the following parameters:
- total heat loss – 36 kW;
- loss on the 1st floor – 20 kW;
- loss on the 2nd – 16 kW;
- polypropylene pipes were installed;
- system operation in 80/60 mode;
- temperature – 20 C.
Below is table (a) based on the data from which we will determine the required pipe diameter. In the table, cells with the best (optimal) fluid velocity are marked in green.
Let's count. Through the section of pipe that connects the first fork and the boiler, the entire volume of liquid passes through, therefore, all the heat, and this is 38 kW. Let's determine which pipe we need to take here.
We take our table, look for the corresponding line in it, then go through the green cells and look up. What do we see? And we see that with such parameters two options suit us: 50 and 40 mm. Naturally (this was written about above), we choose a smaller diameter of the pipe for heating the house, 40 mm.
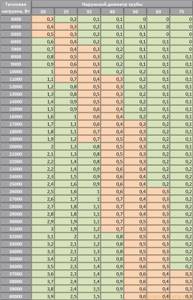
Next we look at the fork, which divides the coolant movement into the second and first floors (16 and 20 kW). Again we look at the values from the table and find that in both directions a pipe diameter of 32 mm is needed.
We have two wings on each floor. The circuit is also divided into two branches. We count the first floor:
20 kW / 2 = 10 kW per wing
Second floor by analogy:
16 kW / 2 = 8 kW per wing
Again, we take our table and determine that in these areas we need a pipe with a cross-section of 25 mm. It is also clearly seen from the table that we will use this diameter until the load drops to 5 kW, then we will use 20 mm pipes.
Important! From personal experience I can say that it is better to switch to a pipe diameter of 20 mm when the heat load is not 5 kW, but 3 kW.
In this simple way, we calculated all the pipe diameters for heating the house of the polypropylene pipes we needed for a two-pipe heating system.
For the reverse supply of water, you do not need to calculate anything, everything is much simpler: you do all the wiring with pipes of the same diameter as for the direct supply. As you can see, there is nothing complicated. All you need is a good table suitable for a specific case.
Some nuances of calculating the diameter for metal pipes
If you decide that you will use metal pipes for the heating system, then you need to take into account that they lose heat. In small areas, it is practically unnoticeable.
But on extended systems, it may happen that the very last heating elements in the chain will be cold or slightly warm. This is also a consequence of incorrect choice of pipe diameter. Fortunately, heat loss can be easily calculated:
q = k * 3.14 * (tv-tp) q - heat loss per 1 meter (W/s); k – heat transfer coefficient (W * m/s); tв - temperature of hot supplied water (C); tп — ambient temperature (C).
Let's take a pipe with a diameter of 40 mm. Let's say the wall is 1.4 mm thick. Material – steel. Let's calculate:
q = 0.272 * 3.15 * ( 80 – 22 ) = 49 W/s
Here is another proof of why you need to take a pipe diameter for heating a house with a smaller diameter. After all, it is clear that the thicker the pipe, the much more heat we will lose.
And in this example, we received losses of almost 50 W per 1 meter of distance. And if the system is quite extended, then all the heat can be lost.
But don't be upset! Such accurate calculations are needed only for multi-storey residential buildings. For individual heating systems, everything is simpler: calculations are rounded up and this gives a certain margin.
Steel pipes
Steel is a material that is being used less and less for heating systems. The fact is that although steel pipes are strong and of high quality, they are subject to corrosion . Installation of heating systems made of steel pipes is a rather complex and labor-intensive process that only a professional can handle with the necessary equipment.
Due to high pressure losses and roughness, the use of steel pipes will lead to the formation of salt and biological formations inside them, which will reduce the flow of the pipes.
Steel pipes can easily withstand temperature changes and do not deteriorate or deform under the influence of hot water.
Advice . Steel pipes must be used where it is difficult to control the heating of the coolant and if a high temperature of the coolant is noticed.
Selection of heating pipes
The process of selecting pipes is quite complex. When choosing pipes, you should decide:
- with pipe diameter;
- material;
- quantity.
The choice of pipes is made depending on what heating system will be used.
Steel pipes are very strong and reliable, but care must be taken to ensure that two different materials are not used in the design and galvanic couples do not occur, which can lead to corrosion of the steel. Working with this type of pipe is quite difficult, because it is necessary to use welding .
To install steel pipes, you must have knowledge and skills. Propylene pipes are very economical and profitable. They heat the room and prevent heat loss. The use of this type of pipe is possible only when the coolant temperature does not exceed 60 -70 degrees.
Metal-plastic is another modern material that is very convenient to use for heating systems. The disadvantage of installing this type of pipe is the need for additional equipment. Metal-plastic is afraid of sunlight, high temperatures, and shocks.
For private houses it is best to choose polypropylene pipes , and for apartments - metal-plastic . For a summer house or a compact private house, it is best to choose steel pipes.
Rules for design and installation of heating
One of the parameters that allows you to decide which pipes to choose for heating a private house is the heat source. If there is a gas main connected to the house, the optimal and obvious option for such equipment would be a gas boiler equipped with protective elements, automation and a forced circulation system. An alternative to gas equipment are boilers that run on electricity or solid fuel.
In any case, when designing and installing a heating system, the following rules must be taken into account:
- Heating systems allow you to use several types of pipes at the same time, but in this case you need to figure out in advance which pipes to use for heating the house so that they do not conflict with each other.
- The best option for two-pipe systems, regardless of the method of circulation of the coolant, are metal-plastic heating pipes.
- If the house area is 100 m2, the length of the pipeline between the boiler and radiators should not exceed 25 m.
- To connect a large number of radiators to heating, only two-pipe wiring, equipped with a main pipe of increased diameter, is suitable.
- Gas heat sources (and some other types of boilers) must be equipped with a system for exhausting combustion products into the atmosphere.
- There should not be a single element of shut-off valves in the section of the system located between the safety group and the heat source.
- When installing elements of the heating system, you need to ensure that a certain gap is maintained between the communication lines.

In systems with forced circulation of coolant, it is recommended to install a filter in the area in front of the pump. The heating pipes themselves can be laid hidden, but in this case you need to take into account the rules for such an installation and think in advance which pipe is used for hidden heating.