Electric heating is an easy and affordable way to heat any room. An electric radiator is the main device of the system; the only necessary condition for its operation is the presence of a power source of sufficient power. Its design includes 2 functional parts:
- heat-dissipating element (metal radiator battery);
- heating element (heater).
A tubular electric heater (TEH) is used as a heating element in electric radiators, which is not fundamentally different from those used in heating devices and household appliances.
With the help of a heat-transfer element, heat is transferred to the room through convective and radiant heat exchange. Developers mainly use sectional batteries to unify the production process and adjust the rated power of individual models by selecting the number of sections.
To buy electric heating radiators which are best suited for the conditions of a particular apartment, you need to choose the right type, number of sections and type of coolant. Also, when choosing, you should pay attention to the functionality of the control unit and the availability of a set of parts for installation.
You can purchase either a fully assembled product or a kit consisting of a control unit and a heating element, which you can independently install in a separately purchased radiator battery.
Classification of electric radiators
Depending on the type of radiator grille, devices are divided into 2 types:
- liquid;
- liquidless.
In liquid models, sections have special channels that are filled with coolant. As in water heating radiators, heat is transferred from the liquid to the metal, after which heat exchange occurs between the sections and the air (convective heat exchange) and objects inside the room (radiant heat exchange). The difference compared to water heating is that in electric radiators there is no circulation of liquid, and its heating is carried out by a heating element.
Diagram and principle of operation of a liquid electric radiator.
It should be noted that liquid electric radiators use sections that are structurally identical to those used in water heating batteries. The radiator of several sections has upper and lower collectors with through holes. A heating element is installed in the lower one, and a Mayevsky tap is mounted in the upper one.

Monolithic liquid electric heater.
Liquid devices can either be connected to a water heating system or operate as a separate heating device. For this purpose, the coolant supply and discharge pipes are equipped with ball valves, which are closed to allow the device to operate in autonomous mode.
Advantages of liquid models
The use of liquid electric radiators as heating elements connected to a centralized water heating system allows you to obtain an effective and economical source of heat. During the heating season, the device is heated by the coolant circulating through the general system, and in the fall and spring, a heating element can be used to heat the liquid.

Models by number of sections.
To keep warm during the several cold weeks before the start of the heating season (and at the end), residents of houses and apartments with central heating purchase additional electrical heating appliances - oil radiators, convectors, infrared heaters and fan heaters. Installing liquid-type electric radiators allows you to avoid purchasing additional heating devices. At the same time, you can save not only money, but also the space needed to store devices during the warm season.
Which coolant is better?
Two types of liquid are used as a coolant in electric radiators - distilled water and non-freezing liquid based on ethylene glycol. When connected to a circulation heating system, the coolant with which the system is filled is used.

Electric radiator with remote control.
Distilled water is used in homes intended for permanent residence. If the building is used as temporary housing, there is a risk that the liquid inside the appliance may freeze, which may cause the product to malfunction. Therefore, in such cases it is filled with non-freezing liquid that can withstand temperatures down to -20 °C.
Conclusions and useful video on the topic
The video will clearly show you how the electric radiator works:
Every year the range of electric radiators is updated. Not only their technical characteristics are changing for the better, but also their design.
In order to make the best choice, you need to analyze the available information and, based on this, decide which technical indicators are suitable for your specific case.
Please write your comments in the block form located below the text of the article. Tell us about how you chose an electric radiator for use in a country house, office or apartment. Share useful information, ask questions, post photos on the topic.
Liquidless radiators
Unlike liquid-type radiators, in liquid-free ones heat transfer from the heating element is carried out directly to the metal heat-transmitting element, without the use of a coolant. They cannot be connected to water heating systems and are installed exclusively as an independent heating device.

Liquid-free wall-mounted radiators with different numbers of sections.
As in liquid radiators, batteries made of several metal sections are used as a heat-transfer element. These sections are not unified with models used in water heating systems. The absence of an intermediate link in the form of a coolant reduces the inertia of the radiator. Liquid-free devices heat up faster, but also cool down faster. They also have less weight, so they are easier to transport from one room to another. In the case of a permanent installation, the lighter weight allows the use of less durable mounts.
Experts recommend installing liquid electric radiators in premises for permanent residence, while inertia-free liquid-free devices are optimal for use in country houses and guest houses, winter recreation centers, retail outlets and mini-hotels.
Mounting options
One of the questions that interests the buyer before purchasing an electric heating radiator is the method of mounting it. Regardless of the model, there are three installation options:
- stationary wall hanging using anchors;
- installation on stands;
- mobile unit on wheels.

Electric radiator hung on the wall.
The methods of permanent installation do not differ from the suspension of traditional radiators of water heating systems. An electric radiator can be installed on any wall that can support its weight in working condition.

Option on wheeled supports.
Mobile installation allows you to easily carry (transport) it from place to place. Not all models are equipped with stands or wheels, so this issue needs to be clarified with the seller before making a purchase. If fasteners are not included in the kit, they can be purchased at an additional cost.

Stable wheel supports.
To provide the air circulation necessary for effective convective heat exchange, it must be installed with the following minimum distances to nearby surfaces:
- from the back wall to the wall – 30 mm;
- to the floor – 50 mm;
- to the window sill - 50 mm.
Wall-mounted oil batteries: the worst?
We have included oil batteries in this list only to protect you from these heaters. We believe that such electrical appliances cannot even stand on a par with those listed above for some reasons that we know from practice:
- Fire hazardous
- Not reliable
- Can't stand intense work

You may think that we are wrong. After all, many of you have such heaters, and many of you have never failed, and some of you will say: “Yes, I have had such a battery in my dacha for 10 years and it still works!” And everything you say will be true, but only from a subjective point of view.
From an objective point of view, the majority of fires caused by electric heaters are oil heaters.
Their housing is often subject to depressurization and oil leakage. As soon as the oil level drops below the heating element and exposes it, it begins to reach a fire-hazardous temperature, and there is a danger of the oil catching fire.
Therefore, such heaters cannot be left unattended, much less used as the main heating. But in defense of these models, we can say that they really heat well, since they have numerous sections and heat primarily by convection.

If you decide to buy an oil heater, we recommend using it as additional heat for your room and only under human supervision.
Pros:
- Low price
- Heats the room quickly
- Mobility (usually used with wheels on legs)
Minuses:
- Fire hazardous
- Unreliable
- Human supervision required
- Consumes a lot
- Not suitable as main heating
What is the best way to choose a radiator for a specific room?
On average, the rated power of one section is 0.13 kW. The required number of sections is selected depending on the area of the room according to Table 1. The data presented in the table is relevant for city apartments located in an insulated apartment building. If the room is located on the corner of the building, or the house is poorly insulated, the recommended number of sections should be looked at 1-2 lines below the specified area of the room.
Table 1 - Selection of an electric radiator depending on the area of the room
| Room area, m2 | Recommended number of sections | Rated power, kW | Electricity consumption, kW/hour |
| less than 4 | 3 | 0,39 | 0,10 |
| from 4 to 6 | 4 | 0,52 | 0,15 |
| from 6 to 8 | 5 | 0,65 | 0,20 |
| from 8 to 10 | 6 | 0,78 | 0,25 |
| from 10 to 12 | 7 | 0,91 | 0,30 |
| from 12 to 14 | 8 | 1,04 | 0,35 |
| from 14 to 16 | 9 | 1,17 | 0,40 |
| from 16 to 18 | 10 | 1,30 | 0,45 |
| from 18 to 20 | 11 | 1,43 | 0,50 |
| from 20 to 22 | 12 | 1,56 | 0,55 |
If the area of the room exceeds 22 meters, heating it requires the installation of two or three radiators. It is also recommended to increase the number of radiators if there is more than one window in the room. In this case, heating devices installed under each window create a thermal curtain, reducing the outflow of heat outside the room.
Efficiency mark
A heating element for a radiator is not a heating device that can be constantly used to heat a large area. One kilowatt of electrical appliance power is converted into one kilowatt of thermal energy, which is completely used to heat the room.
When using cast iron batteries, a heating element equipped with a thermostat with a heating power of 100 Watt/m² can heat no more than 25 m² of space. Electrical energy consumption for twenty-four hours will be 36 kW/h, which approximately corresponds to 167 rubles. This takes into account the average power consumption of 1.5 kW. If the heating system is well organized, installing a tubular type electric heater does not make sense.
A heating element for a radiator is most effectively used as an emergency device. If the heating system is unstable, such a device will allow you to maintain the required level of heat in the room even in severe frosts. Installing a tubular heater makes sense if its power is correctly selected and all safety rules are observed.
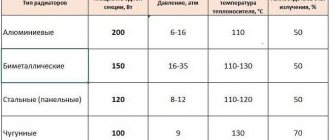
What material should I choose for radiator sections?
The vast majority of models are available with aluminum sections. This material has good thermal conductivity, and sections made from it are lightweight, affordable and attractive in appearance. When using an aluminum radiator as part of a circulation heating system, its internal surfaces are oxidized due to impurities contained in the coolant. Autonomous electric heaters use impurity-free distilled water or an ethylene glycol-based solution as a coolant, which do not react chemically with aluminum.

Aluminum electric radiator.
If desired, heating elements with an electronic control unit can be installed on radiators of any type - if you plan to use previously purchased heating batteries, or the use of an alternative material to aluminum is dictated by the interior design of the room. Thus, electric heating of the coolant can be implemented inside steel, bimetallic, cast iron sections, as well as design radiators made of glass or stone.
Energy saving
Energy savings in electric heaters occur by controlling the required room heating temperature using a thermostat. The device reaches the set temperature, the power turns off, and when the heater cools down, it turns on again. The choice of housing material and type of coolant are also aimed at energy saving.

temperature sensor
Modern electric radiators automatically adjust the heating intensity depending on the air temperature in the heated room. This parameter is measured using a temperature sensor, which can have two designs:
- built into the control unit housing;
- remote
If the radiator is intended to be installed permanently as the main source of heating, it is better to choose a model with a remote air temperature sensor. This option provides a more reliable temperature measurement, since the sensor is located at some distance from the radiator, in the immediate vicinity of which the air is always warmer than at a distance.
Where is the best place to mount the remote sensor?
If the device is equipped with a remote temperature sensor, it is mounted on the surface of the wall closest to the radiator. The distance from the sensor to the floor surface must be at least 1 meter, and to the radiator - at least 0.5 meters.
It is prohibited to place the sensor in a draft or in a place where there is direct sunlight, as this may affect the accuracy of the measurement. It is also not recommended to mount the sensor on the floor or windowsill.
About power calculation and safety requirements
The main parameter when choosing an electric battery is power. And if you know about this indicator, you will be able to determine the required number of heating devices for each individual room or for the house as a whole. Moreover, thanks to the total power, you can find out what your heating costs will be.
Video - How to choose a heater for your home
https://youtube.com/watch?v=olLrgRIRSRs
Below is one of the most primitive examples of determining power. Let's say the room area is 20 square meters - in this case, we need battery power from 1.5 to 2 kilowatts. This means that for a house with a total area of, say, 100 square meters, five heaters will be required, the total power of which will be ten kilowatts. But this, of course, is only an approximate calculation, and in order to obtain more accurate data, you need to take into account a number of important factors, including:
- electrical network parameters;
- thermal conductivity of the materials that were used in the construction of the building;
- type of radiator, thermoregulation technology with which it is equipped;
- possible places of thermal energy leakage (ventilation, doors or windows);
- what temperature should be maintained in the house.
We will also consider general recommendations that relate to the choice of a heating device.
- If you plan to purchase a convector with an electric thermostat, then it is better to purchase models from well-known manufacturers - this will serve as a kind of guarantee that the device will last a long time and reliably.
- You cannot place any things on the top cover of the device - they will not dry there anyway, because if it overheats, the system will automatically stop functioning.
- Do not forget about fulfilling the manufacturer’s requirements regarding installation - the socket, for example, should be located at least 10 centimeters from the battery, and not from above, but exclusively from below or to the side.
- Contact of the supply electrical wire with the radiator body is prohibited; the distance between the latter and the wall surface (in the case of a stationary location) must be at least 5 centimeters.
Operating modes
When choosing a radiator that is best suited for specific operating conditions, the buyer needs to pay attention to the number of modes of its operation, as well as a description of each mode. Modern radiators assume the following operating modes:
- Basic mode. The radiator heats up to the set temperature and then turns off. When the air temperature decreases by a certain amount (usually 0.5 - 1.0°C), the heating element comes back into operation.
- Economy mode. Tuned a few degrees lower than the main one. It turns on if the room is empty for some time. The difference between main and economy mode is configurable.
- Programmable mode. The radiator switches from mode to mode depending on the specified time of day. The program can be set for a specific time (day, week). The control unit allows you to configure several operating modes, and then easily switch between them.

Six-section radiator with programmable timer.
Electrical safety measures
To ensure safe operation of the device, the following safety precautions must be observed:
- When connecting to the power supply, grounding must be used.
- It is not recommended to connect the device to the same outlet as other electrical appliances, as this may cause overloading of the wiring.
- The actual parameters of the electrical network should not exceed the limits specified in the operating instructions.
- Air humidity in the room should not exceed 80%.
- The radiator should be regularly wiped from dust and moisture should not be allowed to get into its electrical part.