- Work acceptance procedure
- Specifics of drawing up a test report
During testing of external sewerage using the spill method, the same document is drawn up as during testing of the internal sewage system. The form of the act itself is not a form of strict reporting and can be drawn up by the customer, contractor or subcontractor.
Also, during experiments on an external water drainage system, one of the forms of SNiP 3.05.04-85 can be used, which is a general form of document for acceptance of work performed when installing or repairing a drainage system.
Forms of acts (forms) for maintaining executive documentation in construction
Heating, ventilation and air conditioning (HVAC)
Water supply and sewerage (VK)
External water supply and sewerage networks (NVK)
Gas supply. Internal devices
Certificate on carrying out commissioning works of the main gas propulsion plant download doc format
External gas pipelines
Certificate on carrying out commissioning works of the main gas propulsion plant download doc format
Thermomechanical solutions for boiler houses
Certificate of readiness of the foundation (supporting structures) for installation download doc format
Certificate of inspection of equipment installation on the foundation download doc format
Report of internal and external inspection of the boiler before installation download doc format
Hydraulic test report for hot water boilers download doc format
After all installation work on the arrangement of water supply communications has been completed, it is necessary to conduct a final test of the entire system in order to put it into operation in proper form. Tests are carried out to identify possible defects in the operation of communications and their subsequent elimination. The stages of inspection work and complete information on it are entered into the form of the act approved by SNiP. A sample or example of a document can be seen in our material below.
Find out how to correctly fill out the water supply system testing document form and what such work entails in our article.
Important: tests of finished internal water supply are in most cases carried out hydraulically using a large amount of water under pressure above the general average. If you have to test the external water supply, then at a temperature of +5 degrees you can still use the hydraulic method, and at lower temperatures the pneumatic method is used (pumping the communication with air under high pressure). Both methods are called pipe crimping in professional circles.
Purpose and order of testing
Hydraulic tests of water supply and wastewater systems are carried out to check the tightness, reliability of the water supply system and detect defective parts. Testing is prescribed before putting into operation a newly constructed network or after reconstruction (overhaul). All detected defects are immediately corrected, and tests are repeated until a satisfactory result is obtained. Tests are carried out twice: first preliminary
, after them
final
.
At the first stage, water is pumped into the water supply system under pressure; the pressure should be one and a half times higher than the working pressure. Preliminary hydraulic tests of water supply pipelines are prescribed with full access to the above-ground and underground parts of the pipeline, before the installation of plumbing fixtures.
Testing is scheduled before the final finishing of the premises. Hydraulic tests of drainage and water supply systems are carried out by specialists from the plumbing service.
Before the final stage of hydraulic testing of the water supply, the underground sections are closed, all installation work on the section is completed, but plumbing fixtures have not yet been installed. The exits are covered with plugs. During hydraulic tests of cold water supply, the pressure in the mains is increased by 1.3 times compared to the working one.
- Hydraulic tests of plastic water supply pipelines are allowed to be carried out a day after installation, at above-zero temperatures;
- To conduct hydraulic tests of drains in a house, the pipes are completely filled with water to the top of the risers. The condition of the pipes is first visually examined and noticeable defects are corrected. If a completely filled drainage system does not leak within 20 minutes, and the water remains at the marked level, the system has successfully passed the test.
Filling out the first part of the act
Before performing testing (pressure testing) of a finished water pipeline, you must stock up on a report form in which all important data will be entered. The act is an official document from Appendix 1 of SNiP 3.05.04-85. The title of the document sounds like “Act on conducting an acceptance hydraulic test of a pressure pipeline for strength and tightness.”
The very first information that needs to be entered into the document is the city in which the testing work is being carried out and the date of the event. Below is a list of commission members who will test the internal/external water supply system.
As a rule, the commission should include:
- A representative of the organization that installed all communications;
- Representative from the customer's technical supervision service;
- Person representing the operating organization.
Moreover, it is worth registering the organization that the commission member represents, his position in it, and his last name with initials.
Below, it is mandatory to provide detailed information about the tested object. That is, enter its full name (can be taken from the project documentation), indicate the numbers of pickets located at the boundaries of the object, the total length of the water pipeline and its diameter, as well as the material from which the communication is installed and the pipe joints are made.
At this point, the “header” of the official document is considered completely filled out.
Paper rules
Based on the general requirements of the current regulations, each paragraph of the act must be completed. As soon as the final list of responsible persons is formed and filled out, you can begin to draw up the remaining points of the document.

Act
In order to avoid mistakes and omissions in the act, it is worth remembering all the details in each paragraph:
- First point. This part of the paper contains information about the name of the company that developed and approved the house project. The document compliance code is also written down here, and the serial numbers of the revision of all components of the drainage system based on the working design are listed. In addition, it is necessary to list the working numbers of the drawings used for the drainage system in a specific type of building.
- Second point. This part of the document contains exact values for the number of all simultaneously open visible sanitary points. The time periods during which the checks were carried out are listed. Sanitary points can be all plumbing fixtures that a person uses in everyday activities (toilet, sink, shower, bidet, and so on). It is important to remember that filling out the second paragraph implies hydraulic testing of the sewer system when working at least three quarters of the total number of sanitary points.
- Third point. The violations and inconsistencies identified during the inspection stage are listed. Here it is important to indicate all the comments that the commission had during the testing process with a detailed description of the problem. If there are no deficiencies, “not identified” is written in the column.
- Conclusion. This part of the act contains the final decision of the commission and the recommendatory part to eliminate the identified shortcomings. The last sentence must indicate whether the system is permitted for operation.
You may also like: All about hydrodynamic drain cleaning
Carrying out system testing

To check the tightness of an internal or external water pipeline (pressure test), you must adhere to certain rules.
- So, during the check, the water flow from each plumbing point is taken into account. It should be at least 0.2 liters per second.
- It is worth considering the water supply pressure. This is especially important for the highest water intake points. In this case, the pressure should be at least 2-3 meters.
- It is also worth checking the compliance of the parameters of the entire system according to the design documentation. Here they check the length, diameter of the pipeline, as well as the materials from which it is made.
- Visual initial inspection of external and internal communications also allows you to avoid strong gusts of the system as a result of testing.
- Pressure testing of a water supply system involves supplying water under high pressure to the system. Testing time is at least 10 minutes. The pressure when supplying water to the system should be one and a half times higher than the maximum permissible for a particular communication.
Example: household water supply can withstand a maximum gauge pressure of 0.45 MPa or just 45 meters of water column. Therefore, to test such sewerage and water supply systems, it is necessary to apply a gauge pressure equal to 0.675 MPa or simply 67.5 meters of water column.
Testing is considered successful if no leaks or ruptures in the water supply (sewer) pipeline are detected under the influence of water.
Work acceptance procedure
When accepting such work, the tests themselves are carried out first, which can be:
- Hydraulic - only non-pressure drainage systems are exposed to them, be it wastewater pipelines or storm sewers. testing is carried out in areas between wells by filling the system with process water. The tests are carried out in two stages - checking pipes and connections before filling the soil and checking the performance of the entire sewer system after filling the soil. Tests are carried out by pumping water into wells or receiving grids for 30 minutes; during the tests, the performance of the system is measured and the tightness of seams and joints is monitored. Tests may also be performed to determine the ability of pipes and connections to withstand the maximum allowable pressure throughout the entire drain.
- Pneumatic - during such tests, the ability of the waste system to withstand the design pressure is checked, according to GOST standards or design documentation. For such a series of studies, specialized organizations with the necessary equipment and licenses are involved; the process itself includes checking the pressure in the system or in its individual sections when supplying air under pressure.
If during the experiments the entire system met the standard indicators of SNIP 3.05.04-85, then an acceptance certificate for the work performed is drawn up, otherwise a defective statement and a drainage troubleshooting report are drawn up.
During periodic monitoring at enterprises with drinking water pipelines, external drainage systems are also tested during disinfection or treatment with special reagents.
Further filling out the act
Important: the document should include all stages of communication research that were applied to a specific communication (did the pressure decrease periodically when water was supplied, was the water pressure changed, etc.).
- If there were no violations in the tightness of the water supply/sewage system, then in the “Check Results” column it is written down that at the time of the check no leaks or ruptures were found.
- Below is the item “Decision of the Commission”. If the tests are successful, the commission issues permission to put the water supply system into operation.
- Below, all members of the commission must put their signatures indicating their last name and initials, as well as their positions.

Document year: 2019
Type of document: Act
Download formats: DOC, PDF
Test reports are drawn up in the form of document forms in which the results of testing the performance of mechanisms and equipment are recorded.
In today's article, we will consider in detail the testing of pipeline systems, sewerage systems, stairs and stepladders, roof fencing and fire tests.
Examples of drafting acts can be downloaded for free at the end of the article.
The procedure for flushing the heating system and its design
The sequence of work performed by organizations that specialize in flushing heating structures is as follows:
- The equipment is being inspected. An assessment of its technical condition is made. Primary pressure testing is carried out, and the pressure must exceed the operating indicators by 1.25 times (minimum value - 2 atmospheres). This is necessary so that during operation, leaks do not cause a conflict with the customer of the work. Any deficiencies found should be corrected before flushing begins.
- An act is drawn up to perform hidden operations in the process of cleaning system elements. This could be, for example, dismantling heating radiators.
- Make a choice of heating system cleaning technology. As practice has shown, hydropneumatic washing is most often used using a pulp formed by water and compressed air using a special one. Chemical cleaning is used much less frequently.
- They calculate and prepare an estimate for flushing the heating system. The cost of work includes payment for equipment rental, consumption of reagents and fuel. The calculation takes into account the cost of the work, including hidden ones.
- After drawing up an estimate, a contract for flushing the heating system is drawn up, which stipulates a number of aspects, including the cost of the work, the obligations of the parties, including the deadline for completing all activities.
Often the document provides for penalties for missed deadlines or the quality of services not meeting obligations. An important point is the clause that stipulates the responsibilities of the parties, since it helps to avoid conflict situations. The document also specifies the procedure for making changes to it and the conditions for its termination. - When the contract is signed, the washing work itself begins.
- After completion, a secondary pressure test of the heating structure is performed in order to check its functionality.
- When the work is completed, fill out the heating system flushing report; a sample can be seen in the photo. The customer of the services either accepts them or reports that the terms of the contract have not been fulfilled. Controversial issues are resolved in courts in accordance with the established procedure.

Hydraulic testing report for the heating and water supply pipeline system
Checks of heating and plumbing systems are carried out:
- when introducing new engineering communications;
- when reconstructing an existing one;
- during a routine check of the functioning of the system.
The step-by-step inspection and its results are recorded in the test report. The system is tested for tightness and strength in two ways, one of which is the hydraulic method: testing by using water with increased load. This method is suitable for indoor and outdoor systems (at temperatures not lower than +5C). The second method is pneumatic.
Both methods of acceptance testing are called pipe testing.
The results of the inspections are recorded in a report, the form of which is established by the Code of Rules for building codes and regulations. The template is presented in Appendix 1 to SANPin “External networks and structures of water supply and sewerage.” The presented form of the act is mandatory.
Procedure for drawing up the act:
1. Indication of general organizational information: city of compilation and date.
2. Representation of the members of the commission that carried out the pressure testing and acceptance of the pressure pipeline. Three parties become members:
| The company that installed the pipeline |
| Technical supervision representative from the customer |
| Operating company representative |
3. Below is information about the inspected object and a description of the pipeline (length, diameter, material of pipes and joints), information specified in the working documentation is given, and information about the pressure gauge used is given.
Hydraulic testing of pipelines and commissioning
Testing of water supply, sanitation
The installed pipeline is subject to testing for strength and density (tightness) using a hydraulic method. The maximum length for testing a pipeline made of cast iron pipes in one step should be no more than 1 km, with longer lengths in sections of no more than 1 km.
The length of test sections of pipelines during hydraulic testing is allowed to exceed 1 km, provided that the permissible flow rate of pumped water should be determined as for a section 1 km long.
Pipeline testing should be carried out in 2 stages:
— preliminary testing for strength and tightness, performed after partial backfilling of the pipeline;
— final (acceptance) test for strength and tightness, performed after the pipeline is completely backfilled.
Both stages of the test must be performed before installing hydrants, plungers, and safety valves, in place of which flange plugs should be installed during the test.
The values of the internal design pressure Рр and test pressure Risp for carrying out preliminary and acceptance tests of the pressure pipeline for strength must be determined by the project and indicated in the working documentation.
Before starting the hydrotest, you should check and make sure that the air has been completely removed from the pipeline presented for testing. It is recommended to fill the pipeline with water from the lower side of the site. When testing a pipeline for strength, the following operations are performed:
— gradual increase in pressure in the pipeline (3-5 kgf/cm2) with holding the pressure at each stage for at least 5 minutes and inspecting the pipes and butt joints;
— if a leak is detected during an increase in pressure, it is necessary to establish the cause of the leakage and take measures to eliminate it; Elimination of detected defects in the pipeline can be carried out after reducing the pressure in it to atmospheric pressure;
— it is strictly prohibited to walk along the pipeline being tested, tapping, tightening bolted joints, or having workers in the trench;
— when the pipeline reaches test pressure Rsp for at least 10 minutes, do not allow the pressure to drop by more than 1 kgf/cm2, performing additional pumping of water to Rsp.
The pipeline is considered to have passed the strength test if, when the test pressure is reached, no pipe rupture occurs in it, butt joints are not broken, and no water leaks are detected during inspection of the pipeline.
Certificate of pneumatic testing of pipelines
Pneumatic method: diagnosis by pumping the system with high pressure air. Often the method is used for external systems if the temperature on the thermometer is less than +5 Celsius.
The procedure for crimping pipes by pneumatic testing is given in the same SanPiN; the test report is drawn up in the required form, which is given in Appendix No. 3.
Requirements for drawing up test documentation:
- Filling in the name of the city and the date of compilation.
- Indication of the members of the commission (as in the hydraulic test, three parties are involved).
- Description of the pipeline: length, diameter, material of pipes and joints.
- Information about the pressure value: calculated value, to what value the pressure in the pipes was increased, final pressure, amount of reduction. The crimping time is indicated.
- In the “Decision of the Commission” section, each of its members signs with a transcript if the pipeline has passed pneumatic diagnostics and is sealed and durable.
Testing basic principles
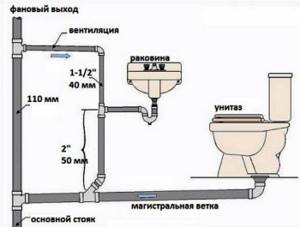
The internal system includes the following objects:
- All plumbing points and household appliances that drain water;
- The entire pipeline connected to the central manifold;
- Central sewer riser.
The external test system includes:
- A pipeline placed outside a building to transport wastewater to a point of accumulation or disposal;
- All inspection and rotary wells;
- Storm drainage channels.
In order for the testing to pass efficiently and fully reflect the condition and performance of the sewer communication, it is necessary to adhere to the basic rules:
Thus, all plumbing points must be cleared of possible construction and natural debris before carrying out work; It is worth checking all points for cracks, chips and other damage; It is important to monitor the evenness of all straight sections of the network. There should be no deflections or bends; All vertical risers must be checked using a plumb line; To check the pipeline, you can use either a hydraulic method (spill method) or a pneumatic method (pumping the system with air); Important: drainage of sewer lines can only be carried out if the air temperature around does not fall below +5 degrees
If the outside temperature is below the specified parameter, then a pneumatic testing method is used. It is worth conducting a separate communication check for each floor of the building. To do this, audit plugs are installed on all other floors.
After installing the sewer system, before moving on to finishing work inside and backfilling trenches outside, the drainage network must be tested to ensure the tightness of the nodes, pipelines and their connections. The external system and internal network are checked in various ways, regulated by the fundamental document of builders - SNiP. How to test the tightness of pipes and sewer connections by pouring, filling, and other methods, and what data is entered, if necessary, into the inspection report, you will learn by reading the article.
The entire sewerage system in each building is divided into an internal sewage disposal network and an external sewerage system. Internal sewer wiring includes the following components to be checked:
- plumbing fixtures and their connections with outlet pipes;
- local sections of a horizontal pipeline with pipes flowing into it from plumbing fixtures;
- sewer risers;
- outgoing pipe.
In the external part of the sewer system, sections of the pipeline (between cleaning and auxiliary equipment) are tested for leaks, as well as:
- operability of wells, tightness and slope of the pipeline;
- condition of treatment or storage facilities (reservoirs);
- storm sewer.
Certificate of testing of external and internal sewerage for spillage
A test report for internal and external sewerage is drawn up as a result of checking the operability of the system. It confirms the position of the commission that the system has withstood the test of a spill of water, and the design complies with the design documentation, GOSTs and standards.
Diagnostics of the normal functionality of the sewer system is necessary when installing a new facility or after carrying out repair work on an existing system. Information about the performance check is entered into the report. The form is drawn up in the form specified in Appendix “D” to the Code of Rules 73.13330.2012.
The act specifies:
- name of the system and the facility in which it is installed;
- information about the members of the commission. Representatives of three organizations are needed: the general contractor, the customer and the installation company;
- information about the name of the project is written down;
- the results are entered: the number of simultaneously connected devices, as well as the connection time or filling of water on the floor (unnecessary ones are crossed out);
- the third paragraph states that no leaks were detected at the joints and through the walls. This means the system is suitable for use.
The decision is signed by the members of the commission.
Testing basic principles
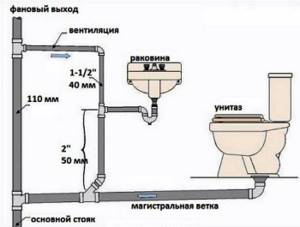
The internal system includes the following objects:
- All plumbing points and household appliances that drain water;
- The entire pipeline connected to the central manifold;
- Central sewer riser.
The external test system includes:
- A pipeline placed outside a building to transport wastewater to a point of accumulation or disposal;
- All inspection and rotary wells;
- Storm drainage channels.
In order for the testing to pass efficiently and fully reflect the condition and performance of the sewer communication, it is necessary to adhere to the basic rules:
Thus, all plumbing points must be cleared of possible construction and natural debris before carrying out work; It is worth checking all points for cracks, chips and other damage; It is important to monitor the evenness of all straight sections of the network. There should be no deflections or bends; All vertical risers must be checked using a plumb line; To check the pipeline, you can use either a hydraulic method (spill method) or a pneumatic method (pumping the system with air); Important: drainage of sewer lines can only be carried out if the air temperature around does not fall below +5 degrees
If the outside temperature is below the specified parameter, then a pneumatic testing method is used. It is worth conducting a separate communication check for each floor of the building. To do this, audit plugs are installed on all other floors.
During testing of external sewerage using the spill method, the same document is drawn up as during testing of the internal sewage system. The form of the act itself is not a form of strict reporting and can be drawn up by the customer, contractor or subcontractor.
Also, during experiments on an external water drainage system, one of the forms of SNiP 3.05.04-85 can be used, which is a general form of document for acceptance of work performed when installing or repairing a drainage system.
Fire test reports
During testing for the performance and safe operation of fire equipment, several reports are drawn up:
- checking fire hydrants;
- diagnostics of internal water supply;
- checking for the safety of use and compliance with labor protection rules of fire escapes.
Fire hydrants
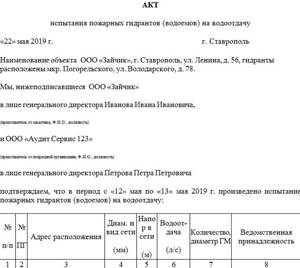
Testing the performance of hydrants for water loss is carried out twice a year and is often combined with checking the fire-fighting water supply system. Based on the results of the inspection, an act is drawn up and signed by the commission. Mandatory members: a representative of the fire inspection and a representative from the organization in which the inspection is taking place. Also, the commission may consist entirely of company employees.
The act states:
- general organizational information (information about the company, date and place of compilation);
- the main part describes the members of the commission and the progress of the test. Information about hydrants is presented in tabular form. The location address, diameter, pressure, water yield and affiliation of the hydrant are indicated;
- in the final part, compliance (or non-compliance) with the requirements of the hydrant condition is established.
At the end, the act is signed by authorized members of the commission.
Internal fire water supply
The act establishes the presence or absence of defects and malfunctions in the fire water supply system. The inspection is carried out by responsible employees of the enterprise. Frequency – at least twice a year; for flammable industries, inspections may be scheduled more often.
Internal fire water supply (IFP) is a complex system of pipes, sensors, and switches. Therefore, it is often checked by a labor protection or fire safety specialist, as well as by persons who are trained in fire safety.
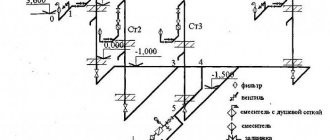
Testing of external sewerage networks
Preliminary tests Acceptance tests Pneumatic tests Preliminary tests Hydrostatic pressure in the pipeline during its preliminary testing must be created by filling the riser installed at its upper point with water, or by filling the upper well with water, if the latter is to be tested. In this case, the value of hydrostatic pressure at the top point of the pipeline is determined by the amount of excess of the water level in the riser or well above the pipeline shelyga or above the groundwater horizon, if the latter is located above the shelyga. The magnitude of hydrostatic pressure in the pipeline during testing must be indicated in the working documentation. For pipelines laid from free-flow concrete, reinforced concrete and ceramic pipes, this value, as a rule, should be equal to 0.04 MPa (0.4 kgf/cm2).
Testing of external network Testing of external sewerage is carried out mainly by hydraulic method. Work performed:
- pipeline slope control;
- the pipeline is tested for leaks;
- examination of wells and other equipment.
The slope level of the external sewer is checked by level.
The test is carried out between wells, in stages, each section is disconnected from the system using a plug. Test scheme for non-pressure systems::
- checking pipes for blockages and debris from construction, and flushing if necessary;
- spill test - a section of the system is filled with water; if no leaks are detected within 10 minutes, the test is passed.
Water is supplied to the pressure sewer under pressure. If the pressure at the inlet and outlet of the pipe is the same, the test is also considered passed.
The check includes:
- testing the pipeline for leaks (carried out as described above. For testing, sections of pipes located between wells or other elements of the system are taken);
- checking the pipeline slope level;
- testing of wells and other equipment;
- checking the performance of storm drains.
A level is used to check the level of pipe laying required for a gravity sewer system.
If a pressure sewer test is being carried out, then water must be supplied to the pipeline system at the pressure specified in the design documents. The test of pressure sewerage pipelines is considered successful if the pressure value in the flow into the network and at the exit from it is the same.
Roof fencing test report
Technical requirements and roof testing methods are enshrined in the same GOST as the standard for fire escapes and stepladders (53254-2009).
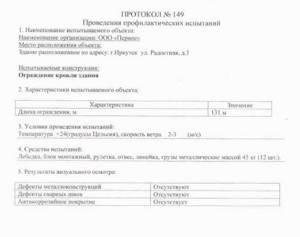
Tests are carried out at intervals of five years, integrity checks are carried out every year. The results are documented in acts.
The conditionally completed act can be divided into three parts:
- General information. Information about the tested object and the inspecting organization is entered here.
- Information about the inspection (what manipulations were carried out, what tools were used).
- Test results (compliance with GOSTs, integrity and safety of the structure).
The agreement of the commission members during testing is confirmed by their personal signatures.
Organizations with a license from the Ministry of Emergency Situations have the right to conduct inspections and tests. Defects found must be corrected.
Purpose of testing
Tests must be carried out after the creation of a new network or after major repairs, preventive maintenance and reconstruction of an existing one, and also before the start of the heating season.
After which new testing is carried out, and this continues until results that correspond to the norm are obtained. Actually, there are two stages of testing: preliminary and final.
Note:
Pressure testing is carried out to check tightness and integrity, as well as to detect possible defects in any section of the water supply system, including boilers.
Such checks are the most popular pressure testing process for heating systems. This happens by simulating water hammer, when pressure is pumped into the system several times higher than the standard one.
Specialist's note:
all defects and deficiencies discovered at the time of crimping must be eliminated immediately and without delay.
Test report for ladders, racks and stepladders
Inspection and testing of racks, ladders and stepladders is carried out at least once every six or twelve months (depending on the object being tested and the material from which it is made).
Tests and checks for safe operation can be carried out by specialized organizations from outside or a commission specially created at the enterprise. At the same time, its members must be trained; an occupational safety or fire safety engineer is usually appointed as the chairman of the commission.
As a result of the diagnosis, the commission draws up a report; it is better to document it with the date of the inspection. The header indicates the name of the document, date and place of compilation. It is also important to indicate the details of the organization, list the members of the commission: their positions and full names.
In the main part, describe the tests of stepladders, ladders and racks:
- how many were checked, their inventory numbers, belonging to the workshop and department;
- what load was used and for how long;
- presence and absence of defects;
- availability of an assigned inventory number.
As a result of the test, suitability (or unsuitability) for use is established: they are safe, can withstand the required load, do not have defects in connections and fastenings, do not have sharp edges or burrs.
The signing of the act by the commission members indicates agreement with the results of the inspection.
By the way! If after this article you still have questions about how to fill out the forms, contact the site’s on-duty lawyer.
How much do hydraulic tests cost?
Knowing how to pressurize a heating system, it will not be difficult for the owner of a private house to carry out the work on his own, but this solution is not optimal, especially when launching a new autonomous highway. It is better to contact a specialized company, whose master will show you all the stages of the procedure and tell you the nuances of the work.
The cost depends on the complexity of the process, the length and condition of the heating system. If the procedure is supplemented by washing, replacing metering and measuring instruments and eliminating leaks, then the service will cost more. On average, testing an apartment building will cost from $400 (from 30,000 rubles), a mansion will cost from $200 (15,000 rubles), one apartment on average from $65 (5,000 rubles).