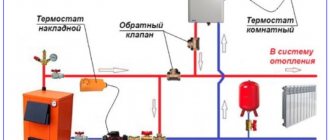
Why are balancing valves needed?
Let us immediately make a reservation that not every system requires balancing as such. For example, 2-3 short dead-end branches with 2 batteries on each can immediately switch to normal operating mode, provided that the pipe diameters are selected correctly and the distances between the devices are small. Now let's look at 2 situations:
- 2-4 heating branches of unequal length with a number of radiators from 4 to 10 are connected to the boiler.
- The same layout, but with batteries equipped with thermostatic valves (described in another publication).
An example of a dead-end circuit with arms of unequal length and load.
The last radiator of the short branch also needs a balance valve. Since the bulk of the water always flows along the path of least hydraulic resistance, in situation No. 1 the first heating devices located close to the boiler will receive more heat. If the flow of coolant to these radiators is not limited, then the last batteries in the chain will heat up much less, the temperature difference between them can be 10 ° C or more.
To direct the required amount of coolant to distant batteries, radiator balancing valves, shown in the photo, are installed on the connections to nearby devices. They restrict the flow of water, partially blocking the flow area of the pipes and increasing the hydraulic resistance of the area.

In the same way, the coolant supply is regulated in systems with five or more dead-end branches. Manual balancing valves intended for pipelines are installed on the tie-ins close to the heat generator. Partially blocking the passage of water, they direct the main flow further along the highway.
Situation #2 is more complicated. Installing radiator thermostats with heads allows you to change the coolant flow automatically as needed. But imagine that in the room closest to the boiler the window opened, the air temperature dropped, and the thermostat opened completely. Then the last room will also become colder, because it will not have enough heat taken away by the first battery.

The purpose of the valves is to limit the coolant flow to the risers (or horizontal branches)
On long branches with a large number of heating devices equipped with thermal heads, balancing valves are combined with automatic differential pressure regulators, as is done above in the diagram.
Regulators connected by capillary tubes to balance valves respond to a decrease/increase in water flow and maintain the return pressure at the same level. Then all consumers have enough coolant, despite the activation of the thermal valves. The benefits of such control taps are described in detail in the video:
Types of valves and their design features
All new heating systems using radiator thermostats are considered dynamic. During operation, the thermostat installed on the heating device responds to any slight changes in the temperature conditions inside the room, thus changing the flow of heating water.
This creates a changing or dynamic operating mode in the heating system. It is a prerequisite for the introduction of automatic/dynamic balancing devices.
Classification of balancing valves by parameters:
- Type of coolant working medium: water, steam-water mixture, glycol composition;
- standard coolant parameters for volume flow, T and pressure;
- location points on the heating network: supply, return or bypass;
- purpose and number of floors of the heating facility; residential/public, single-story/multi-story;
- working function: automatic/mechanical.
- Their combination according to connection options is also practiced: threaded or flanged.
A variety of materials can be used to release valves. Static valves are most often made of brass, with a flanged/threaded connection, or cast iron, exclusively with a flanged connection. For dynamic modifications, in addition to brass/cast iron, they also use carbon steel, which is capable of providing the highest quality standard thermal and hydraulic characteristics of the system.
Manual balancers are required in order to adapt the heating network after installation, and automatic balancers change the characteristics of the heating network during the heating period.
When choosing a balancer modification, it is necessary to take into account various parameters:
- Type of heating circuit with natural/forced circulation.
- Thermal and hydraulic parameters of the network.
- installation point in the in-house system.
- adjustment parameters.
Mechanical balancer
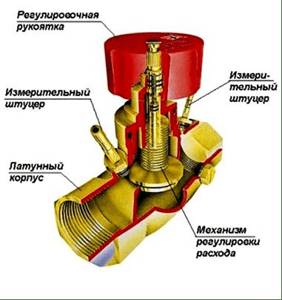
The mechanical valve has manual adjustment and works perfectly in a stable heating network. Works well for residential properties with not a very large number of heating devices. It facilitates repair and adjustment work, since when repairing a separate heating section there is no need to turn off the entire system.
Such modifications are very often equipped with measuring nipples capable of measuring the pressure in the system in the area where the valve is located. The main advantage of such regulators is their low price.
Mechanical balancer - the device works effectively in those facilities where the number of radiators is no more than 5 units. With more, the mechanics cannot cope and causes an imbalance in the heat supply circuit. When the thermostat on the 1st battery is closed, the coolant flow on the second increases. Due to this, the temperature of the water in some heating devices may rise to the boiling point, while in others it will remain cold. Only automatic balancers can solve this problem.
Automatic balancer

Installation of automatic units is carried out on branches/risers with a significant number of batteries. They differ from mechanical devices in the order of their operation. The balancer is adjusted to the position of the greatest throughput. When the hot water flow rate decreases by the thermostat on one of the batteries, the pressure increases. Then the impulse tube mechanism is activated, which analyzes the magnitude of the pressure drop. This approach allows for fine-tuning of the network.
The main advantages of automatic equalizers:
- The presence of a capillary tube that facilitates instant adjustment;
- the control unit does not change the pressure during operation, thereby preventing hydraulic vibrations in the network from disrupting the set mode;
- if necessary, special temperature independent zones can be installed in the general network;
- the high speed of adjustment of the balancer does not allow thermostats to rearrange their operation, which guarantees balanced operation of the entire intra-house heating system.
Where should the valve be installed?
In most private homes, only manual radiator valves are used. They are quite enough to set up normal operation of water heating in cottages up to 500 m². Installation of main-type balance valves is carried out in the following cases:
- in buildings with an extensive heating network consisting of many risers;
- in apartment buildings heated by their own boiler room;
- when connecting a solid fuel boiler with a heat accumulator.
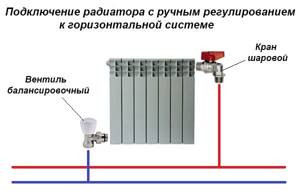
Once we have figured out the purpose of balancing valves, we will indicate specific locations for their installation. Radiator taps should be installed at the outlet of the batteries, and main taps should be installed on the return pipe with cooled coolant. If the element is used in conjunction with an automatic pressure regulator, then it can be installed on both the supply and return pipelines, depending on the designed circuit.

An example of a scheme with group balancing of risers
Reference. In aluminum and steel radiators with bottom connections, the balancing valve is built into special fittings designed for connecting connections to such devices.
Let us highlight the moments when it is not necessary to install control valves:
- in dead-end systems of short length with hydraulically equal “shoulders”;
- if all batteries are equipped with preset thermostatic valves;
- on the last (dead-end) radiator;
- in collector-type heating systems.
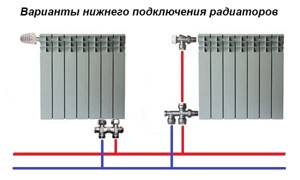
Temperature regulators with presetting, located on the water supply to the battery, simultaneously play the role of a balancing valve, so it is enough to install a shut-off ball valve at the outlet of the heater.
The same fittings are mounted on the connections of the last radiator in the chain, since there is no point in adjusting it; it must be completely open.
Mechanical balancer
The manual valve works great with stable pressure. Ideal for apartments and houses with a small number of heating radiators. It simplifies repair work because it does not require shutting down the entire heating system. Effective action is carried out in those rooms where the number of radiators does not exceed 5 units.
With a significant number of batteries, mechanical devices cause the valves to malfunction. At the moment when the thermostat on the first radiator is closed, the fluid flow on the second increases. Then the temperature of the coolant in some batteries rises to a boil, but in others it heats up too little. Only automatic valve models can cope with this problem.

Design and operating principle
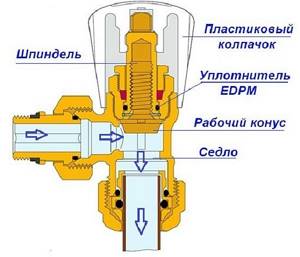
The radiator tap, designed for manual balancing of heating, consists of the following parts:
- Brass body with threaded pipe connections. Inside, a saddle is made using the casting method - a vertical round channel, slightly widening towards the top.
- A shut-off and regulating spindle with a working part in the form of a cone, which enters the saddle when twisted and limits the flow of water.
- O-rings made of EPDM rubber.
- Protective plastic or metal cap.
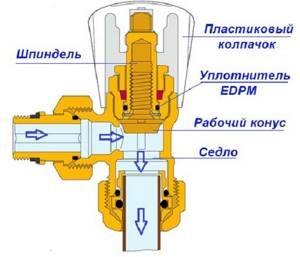
The figure shows a valve from Caleffi (website – https://www.caleffi.com)
Note. All well-known manufacturers - Danfoss, Herz, Caleffi and others - offer 2 types of valves - straight and angular. The principle of operation is the same, only the shape changes.
The device of the balancing valve is shown in more detail in the diagram above. It shows that rotation of the spindle leads to an increase or decrease in the flow area, and this is how the adjustment is made. The number of revolutions from the closed to the maximum open position is from 3 to 5, depending on the valve manufacturer. To turn the rod, you need to use a regular or special hex key.
Main taps differ from radiator taps in size, inclined position of the spindle and fittings designed for:
- coolant drain;
- connecting measuring instruments;
- connecting the capillary tube from the pressure regulator.
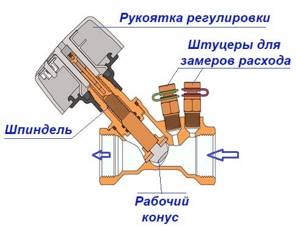
Main valve device for balancing heating branches
For reference. Radiator valve models, for example, from the Oventrop brand, are also equipped with a drain pipe.
The range of balance cranes is constantly expanding due to the emergence of new high-tech products. An example is an Italian-made Caleffi vertical valve equipped with a flow meter.

The Caleffi valve with flow meter can be mounted in 2 positions - horizontal and vertical
What is a balancing valve: its principle of operation
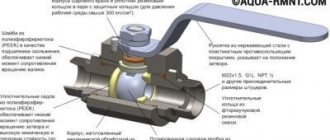
A balancing valve is a simple mechanical device that is part of a pipeline structure. In appearance it resembles a ball valve. The valve is made of bronze, brass or cast iron. It has a metal body with a latch inside. The spool is driven by an inclined rod.
The operating principle of the valve is based on full automatic level control or manual rotation of the shutter handle. When the handle is turned, the spindle rotates the spool located inside the valve, which changes its position, as well as the cross-section of the pipes.
How to balance a radiator network
Typically, installers of heating systems set the coolant flow rate on the batteries in a simple way: they divide the number of revolutions of the balancing valve by the number of heating devices and in this way calculate the adjustment step. Moving from the last radiator to the first, close the taps with the resulting difference in speed.
Example. On one “arm” of the dead-end system we have 5 radiators with Oventrop manual valves with 4.5 spindle turns. Divide 4.5 by 5, we get an adjustment step of about 0.9 turns. This means that we open the penultimate heating device by 3.6 turns, the third by 2.7, the second by 1.8, and the first by 0.9 turns.
The method is quite approximate and does not take into account the different power of batteries, and therefore can be used as a preliminary setting with adjustments during operation.
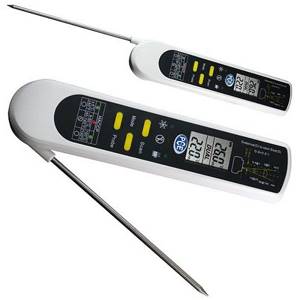
A contact thermometer that measures the surface temperature of pipes and radiators will help you balance your heating more accurately.
Our experienced expert Vladimir Sukhorukov offers another technique based on measuring the actual surface temperature of heaters. The step-by-step balancing instructions look like this:
- Open all balancing valves as much as possible and put the system into operating mode with a supply temperature of 80 °C.
- Use a contact thermometer to measure the temperature of all heating devices.
- Eliminate the resulting difference by tightening the taps of the first and middle radiators; do not touch the end ones. Open the near battery by 1-1.5 turns of the valve, the middle ones by 2-2.5.
- Allow the system to adapt to the new settings for 20 minutes and repeat the measurements. Your task is to achieve a minimum temperature difference between the battery farthest and closest to the boiler.
Note. The weather and outside temperature do not matter, only the difference in the heating of the radiators is important. By the way, in normal operating mode at 50-70 °C at the supply temperature delta will become even lower. How the system is hydraulically balanced using balancing valves, watch the video from an expert:
What is the difference between a tap and a valve?
A standard balancing valve for regulating fluid flow is a cheap analogue of the original valve, which allows you to regulate the flow area more smoothly and accurately. Also, the second one has holes in its design for measuring the amount of liquid passed by a flow meter.
The valve is essentially a simpler balancing valve, since it also serves to regulate the resistance of the passing liquid, but it does not have holes for measuring the amount of heated liquid material.
Another product that controls coolant flow is balancing valves. It works on the same principle as standard valves, although there are models with holes for measurements. The ability to take measurements is an important indicator for the correct installation of such devices, so when choosing products, focus on those that have holes in their design for this.
Final Conclusion
If you install heating yourself, you will probably encounter balancing problems. When all radiators, except the last one, have balancing valves, the procedure will not cause much trouble. It is better to take valves that are adjusted with a key or a screwdriver, rather than with a plastic handle, so that children cannot reach them. It is possible that in winter the position of the spindles will have to be adjusted, because heat loss in rooms varies. The only caveat: do not make sudden movements and open the taps in cold rooms slowly, ¼ turn at a time.
How to choose
If you decide to install a shut-off and balancing valve in your heating system, then decide in advance which product is suitable in your case based on four factors:
- Control type – automatic or manual balancing valve;
- Functions – why and for what purpose will you install the device; the product will be installed for a multi-story or one-story private house;
- Mounting method – fixing flanges or threaded;
- Popularity of the manufacturer - you should not purchase crafts from unknown companies; pay attention to models from such companies: Danfoss, Watts, HERZ, Cimberio.
When you have made your choice, you can safely purchase the product. You can carry out the installation yourself, but it is better to contact a specialist: the problem is that they are configured with a special device, without which it will not be possible to install the unit correctly.
Setting the balance valves
To balance the heating in a private house, select manual devices of the required diameter, selecting and configuring them using the appropriate diagram included in the passport. The initial data for working with the graph are the supply volume, expressed in cubic meters per hour or liters per second, and the pressure drop, measured in bars, atmospheres or Pascals.
For example, when determining the position of the adjustment indicator of the MSV-F2 modification with a nominal bore DN equal to 65 mm. at a flow rate of 16 cubic meters per hour. and pressure drops of 5 kPa. (Fig. 11) on the graph, connect the points on the corresponding flow and pressure scales and extend the line until the conventional scale intersects the coefficient Ku.
From the point on the Ku scale, draw a horizontal line for diameter D equal to 65 mm, find the setting with the number 7, which is set on the handle scale.
Also, for the selected diameter of the device, its adjustment is carried out using the table (Fig. 12), from which the number of spindle revolutions corresponding to a certain flow is determined.
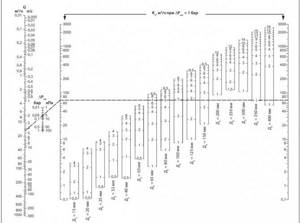
Rice. 11 Determination of the position of the valve scale at a known pressure and a certain water supply
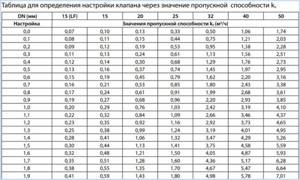
Rice. 12 Example table for manual configuration
What types of balancing valves are there?
Standard ball valves for heating radiators are unable to regulate the distribution of thermal energy in pipes and radiators. But nevertheless, in order to distribute heat evenly in the rooms, such adjustment is simply necessary.
There are two types of balancing valves - manual and automatic. Manual ones are necessary in order to configure the network during its installation, and automatic ones change the parameters of the heating network at the time of heating.
When selecting a valve, you need to take into account many characteristics, which include:
- type and characteristics of the coolant;
- installation location in the system;
- adjustment characteristics;
- adjustment parameters;
- classification of buildings;
The types of heating systems directly depend on the coolant they use. It can be antifreeze, steam, water. They directly affect the performance of the system.
An important characteristic is the purpose of the system. The parameters of hot and cold water supply and heating systems differ quite greatly. For example, in a domestic hot water system only thermostatic balancing valves are used.
The type of building where the balancing valve will be installed is of great importance. The installation location of the valve also plays a fairly important role, since the return and supply pipelines differ quite significantly from each other in characteristics. And because of this, the balancing devices that will be mounted on them will have significant differences.
Installation. Where is it installed?
Installation is carried out in the return branch circuit, which ensures a permanent supply of liquid to the batteries when operating one circuit for hot water supply and space heating. When installing balancing valves on each battery, installation is carried out in the lower part on the outlet pipe diagonally from the spherical coolant supply valve, which is mounted on top.
In a private cottage, differential pressure regulators are used for each battery, and for each outlet pipe they are provided with union nuts or another type of threaded connection. Automated installations do not require configuration. When using a two-valve design, the passage of the thermal energy source to the batteries furthest from the boiler is automatically increased.
Balancing is achieved by increasing the pressure on the circuits leading to the batteries closest to the boiler. The need to accurately calculate the indicators that are set on the valve is due to the features of the model. Manual valves typically require adjustment using calculations or measuring equipment.
In high-rise multi-storey buildings, valves are mounted on each common vertical pipeline (in the return line). When carrying out calculations, the given quantities of heat energy source supplied by an electric pump and the number of risers are used.
Purpose of the device
All branches of the heating system must receive the calculated amount of coolant. Previously, simple systems were controlled by using pipes of different diameters. In complex ones, special washers were installed, by moving which it was possible to change the cross-section of the pipeline. Today, a special valve is used that operates on the principle of a valve.
The balancing valve is equipped with two fittings, thanks to which
:
- the pressure of the coolant flow is measured before and after passing through the valve;
- a capillary tube is connected to allow adjustment.
Based on the readings of the device, it is possible to determine the pressure drop when water passes through the regulator, and calculate, according to the instructions, how many turns of the handle are required to optimize the operation of the heating system.
Note! A number of manufacturers offer balancing valves with a digital display, but such devices are more expensive.

Cross-section of balancing valve