Acts on external water supply and sewerage networks
Home |
Forms | Acts for external water supply and sewerage networks In this section you can download ready-to-use forms for drawing up as-built documentation. Source SNiP 3.05.04-85 “External networks and structures of water supply and sewerage”
- Certificate of acceptance hydraulic testing of the pressure pipeline for strength and tightness - download word | excel
- Certificate of acceptance hydraulic testing of a free-flow pipeline for tightness - download word | excel
- Act on the washing and disinfection of pipelines (structures) for domestic and drinking water supply - download word | excel
- Act on flushing pipelines - download word | excel
- Certificate of acceptance hydraulic testing of a tank structure for water resistance (tightness) - download word | excel
- Certificate of testing of external fire-fighting water supply system for water yield and operability of fire hydrants - download word | excel
- Certificate of inspection of hidden work (form RD-11-02-2006) - download word | excel
- Certificate of inspection of hidden work (form RD-11-02-2006), sample 2021. Download file in word
- Certificate of inspection of sections of engineering and technical support networks (form RD-11-02-2006) - download word | excel
In what cases is it compiled?
The act is required when:
- Commissioning of new equipment. The certificate will confirm that each element is in its place, the installation was carried out responsibly, and the system is working.
- The heating season is approaching. After a summer break in work, the pipes could fail. After checking their capacity, a report is drawn up.
- Already carried out repair work.
- The occurrence of contained emergency situations on the pipeline. In this way, specialists identify the amount of work required and the weak points of the existing heating network.
For the uninterrupted operation of the heating system, preventative control checks and reliable information about the quality functioning of the system upon startup are necessary.
The essence and types of crimping
Nowadays heating is most often carried out by a “water circuit” system. At the same time, heated water circulates through the works, imparting its thermal energy to the premises. Leaks are unacceptable; the pipeline must be completely sealed for normal operation. Pressure testing specifically creates a larger volume in the pipe than normal.
When this is done using air, it is called pneumatic pressing.
When using water, then hydropressing. The latter method is considered safer and therefore more popular. For this reason, an example of hydropressing is provided as a form.
When testing, it is recommended not to exceed the pressure inside the pipe more than 15 MPa. If we are talking about raising pressure with water, then there are limitations. The maximum possible pressure should not exceed the normal operating pressure by more than 30%.
In multi-storey buildings they resort to pneumatic pressure testing if the pipes are very old and there is a risk of flooding. But then there is a level of risk and all residents must be notified of the tests being carried out.
The work process is simple, but multi-stage. The algorithm looks like this:
- The necessary materials and equipment are being prepared.
- Draining the liquid that was previously in the heating system.
- Uploading a new one.
- Create the highest possible test pressure.
- Taking control measurements after 10 minutes.
- Flushing, adjusting the heating system to normal pressure levels inside.
- Documentation of work performed, generation of reports and acts.
But this is how the list of procedures looks only if there are no “thin spots” in the heating system and, accordingly, the tightness in it is not broken. If the pressure drops quickly and does not hold, then the system needs repair work. In such a situation, the specialist performs the necessary actions (replacing the pipe, sealing connections, cleaning, etc.), and then begins crimping from the very beginning. Only a heating system that has passed the test is allowed into the heating season.
Important nuance! Pressure testing should be carried out after cleaning and flushing the pipes. Otherwise, salt and other deposits inside them can mask possible external damage and breakthroughs.
If there are deposits of about 1 cm on the inner surface, then this reduces the overall heat transfer and efficiency by 15 percent or more of the overall indicators. To document the cleaning, a special report is also drawn up.
Components of the heating system pressure test report
At the top left is information about the organization that carried out the inspection. Ideally, there should be a signature for approval by the chief power engineer of the heating supply organization.
The top right should contain subscriber information. That is, about who is the client and consumer of heating services. This could be a partnership of residents of a particular house, any organization that occupies the building, the owner of a private house, etc.
It is important to provide names and other information accurately and in detail. In this case, an address is required.
The main part of the act states:
- City.
- The date of signing the act (and the pressure test itself).
- Heat supply organization: its form of ownership, name, full name of the representative.
- Which of the subscriber's representatives accepted the heating system after the test: full name, position.
- To what indicators the pressure in the system was raised is indicated in kgf/cm2.
- To what indicators did it drop after 10 minutes following the shutdown (the units of measurement here are also kgf/cm2, it is also permissible to measure it in mPa if accurate data on this matter is available).
- Whether the system passed or failed the test (the person completing the form needs to highlight the correct option).
The final part consists of the signatures and seals (if any) of the representatives:
- Subscriber.
- Heat supply organization.
- Service organization.
In general, the act of pressure testing the heating system is a convenient primary document, for filling out which the heat supply organization is responsible.
Fire test reports
During testing for the performance and safe operation of fire equipment, several reports are drawn up:
- checking fire hydrants;
- diagnostics of internal water supply;
- checking for the safety of use and compliance with labor protection rules of fire escapes.
Fire hydrants
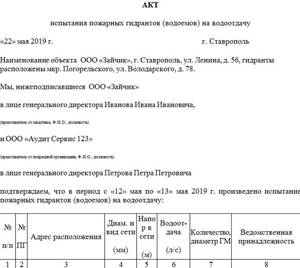
Testing the performance of hydrants for water loss is carried out twice a year and is often combined with checking the fire-fighting water supply system. Based on the results of the inspection, an act is drawn up and signed by the commission. Mandatory members: a representative of the fire inspection and a representative from the organization in which the inspection is taking place. Also, the commission may consist entirely of company employees.
The act states:
- general organizational information (information about the company, date and place of compilation);
- the main part describes the members of the commission and the progress of the test. Information about hydrants is presented in tabular form. The location address, diameter, pressure, water yield and affiliation of the hydrant are indicated;
- in the final part, compliance (or non-compliance) with the requirements of the hydrant condition is established.
At the end, the act is signed by authorized members of the commission.
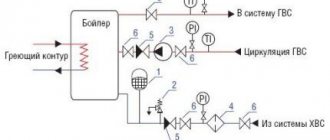
Internal fire water supply
The act establishes the presence or absence of defects and malfunctions in the fire water supply system. The inspection is carried out by responsible employees of the enterprise. Frequency – at least twice a year; for flammable industries, inspections may be scheduled more often.
Internal fire water supply (IFP) is a complex system of pipes, sensors, and switches. Therefore, it is often checked by a labor protection or fire safety specialist, as well as by persons who are trained in fire safety.
Certificate of acceptance of external sewerage. Hydraulic test report for water supply system: sample
After all installation work on the arrangement of water supply communications has been completed, it is necessary to conduct a final test of the entire system in order to put it into operation in proper form. Tests are carried out to identify possible defects in the operation of communications and their subsequent elimination. The stages of inspection work and complete information on it are entered into the form of the act approved by SNiP. A sample or example of a document can be seen in our material below.
Find out how to correctly fill out the water supply system testing document form and what such work entails in our article.
Important: tests of finished internal water supply are in most cases carried out hydraulically using a large amount of water under pressure above the general average. If you have to test the external water supply, then at a temperature of +5 degrees you can still use the hydraulic method, and at lower temperatures the pneumatic method is used (pumping the communication with air under high pressure). Both methods are called pipe crimping in professional circles.
Certificate of pneumatic testing of pipelines
Pneumatic method: diagnosis by pumping the system with high pressure air. Often the method is used for external systems if the temperature on the thermometer is less than +5 Celsius.
The procedure for crimping pipes by pneumatic testing is given in the same SanPiN; the test report is drawn up in the required form, which is given in Appendix No. 3.
Requirements for drawing up test documentation:
- Filling in the name of the city and the date of compilation.
- Indication of the members of the commission (as in the hydraulic test, three parties are involved).
- Description of the pipeline: length, diameter, material of pipes and joints.
- Information about the pressure value: calculated value, to what value the pressure in the pipes was increased, final pressure, amount of reduction. The crimping time is indicated.
- In the “Decision of the Commission” section, each of its members signs with a transcript if the pipeline has passed pneumatic diagnostics and is sealed and durable.
Filling out the first part of the act
Before performing testing (pressure testing) of a finished water pipeline, you must stock up on a report form in which all important data will be entered. The act is an official document from Appendix 1 of SNiP 3.05.04-85. The title of the document sounds like “Act on conducting an acceptance hydraulic test of a pressure pipeline for strength and tightness.”
The very first information that needs to be entered into the document is the city in which the testing work is being carried out and the date of the event. Below is a list of commission members who will test the internal/external water supply system.
As a rule, the commission should include:
- A representative of the organization that installed all communications;
- Representative from the customer's technical supervision service;
- Person representing the operating organization.
Moreover, it is worth registering the organization that the commission member represents, his position in it, and his last name with initials.
Below, it is mandatory to provide detailed information about the tested object. That is, enter its full name (can be taken from the project documentation), indicate the numbers of pickets located at the boundaries of the object, the total length of the water pipeline and its diameter, as well as the material from which the communication is installed and the pipe joints are made.
At this point, the “header” of the official document is considered completely filled out.
Carrying out system testing

- So, during the check, the water flow from each plumbing point is taken into account. It should be at least 0.2 liters per second.
- It is worth considering the water supply pressure. This is especially important for the highest water intake points. In this case, the pressure should be at least 2-3 meters.
- It is also worth checking the compliance of the parameters of the entire system according to the design documentation. Here they check the length, diameter of the pipeline, as well as the materials from which it is made.
- Visual initial inspection of external and internal communications also allows you to avoid strong gusts of the system as a result of testing.
- Pressure testing of a water supply system involves supplying water under high pressure to the system. Testing time is at least 10 minutes. The pressure when supplying water to the system should be one and a half times higher than the maximum permissible for a particular communication.
Example: household water supply can withstand a maximum gauge pressure of 0.45 MPa or just 45 meters of water column. Therefore, to test such sewerage and water supply systems, it is necessary to apply a gauge pressure equal to 0.675 MPa or simply 67.5 meters of water column.
Testing is considered successful if no leaks or ruptures in the water supply (sewer) pipeline are detected under the influence of water.
Important test details
In this case, the checks themselves can be carried out in one of two ways:
- manometric;
- hydrostatic.
The first testing method involves the use of pressure gauges that record and demonstrate the pressure in the system.
Please note: using pressure gauges, the amount of excess pressure is determined, which allows us to draw a conclusion about the reliability of the test.
The second method checks the real readiness of the system for operation by checking its performance at a pressure 50% higher than the standard. Any test lasts at least 10 minutes, the permissible pressure drop during pressure testing is no more than 0.02 MPa.
Good to know: the main document evidencing the conduct of tests is the corresponding act.
Further filling out the act

- After the pressure testing has been carried out, it is necessary to enter data on the nominal gauge pressure for a specific communication and data on the gauge pressure used in testing into the communication leak test report.
- It is also worth indicating the brand of pressure gauge that was used to test and measure the pressure readings in the system at the time of the test. Here it is necessary to indicate the height of the measuring device relative to the axis of the pipes.
- Another parameter that must be included in the leak test report for water supply or sewerage is the time during which the communication leak occurred.
- Further, the document indicates to what nominal value the pressure was reduced after the test. Lastly, members of the commission inspect the pipeline and sewerage and record the results in the report.
Important: the document should include all stages of communication research that were applied to a specific communication (did the pressure decrease periodically when water was supplied, was the water pressure changed, etc.).
- If there were no violations in the tightness of the water supply/sewage system, then in the “Check Results” column it is written down that at the time of the check no leaks or ruptures were found.
- Below is the item “Decision of the Commission”. If the tests are successful, the commission issues permission to put the water supply system into operation.
- Below, all members of the commission must put their signatures indicating their last name and initials, as well as their positions.
Upon completion of the installation of engineering systems, the interested parties must sign the appropriate document - an inspection report for hidden work. Acts can be signed by representatives of the installation organization, general contractor, technical and architectural supervision, representatives of the Customer, representatives of the design organization, representatives of the operation service, authorized persons and others.
Certifies that the relevant engineering system is installed in accordance with the design. The act indicates what work has been submitted for inspection, who completed the detailed design, materials and equipment used during installation, the start and end dates of the work, the commission’s decision to accept the work and permission for further repair and construction work. If deviations from the design occurred during installation, this is also reflected in the report.
The hydraulic test certificate confirms
that the test was carried out and the system passed it. Hydraulic tests are carried out in accordance with building codes and regulations. Heating and water supply systems are tested using the hydrostatic or manometric method in accordance with SNiP 3.05.01-85 (internal sanitary systems). The hydrostatic method is more preferable. The test is carried out at a pressure equal to 1.5 times the maximum operating pressure. For different heating and water supply materials, the test time is different, but in any case not less than 10 minutes.
The water supply system is considered to have passed the test if, within 10 minutes of being under test pressure using the hydrostatic test method, no pressure drop of more than 0.05 MPa (0.5 kgf/cm?) and drops in welds, pipes, threaded connections, fittings and leaks are detected water through flush devices. For a heating system, the pressure drop should not exceed 0.02 MPa (0.2 kgf/cm?).
Internal sewerage test
is carried out by pouring water by simultaneously opening 75% of the sanitary fixtures connected to this section of the sewer system. The system is considered to have passed the test if no leaks are detected through the walls of the pipelines and through the joints. Testing of internal drains is carried out by filling them with water to the highest point. The test time must be at least 10 minutes. The test is considered successful if no leaks are found during inspection and the water level in the risers has not decreased.
REPORT OF INSPECTION OF HIDDEN WORKS AND REPORTS OF HYDRAULIC TESTS (FORM)
Installation work, hidden work certificate
and the hydraulic test report are carried out by us in accordance with all building codes and regulations. When contacting “construction teams” and private craftsmen, you will not receive any agreed-upon working documentation, no correctly completed installation and as-built diagrams, or test reports on the actual work performed. Therefore, you will not receive any guarantees for installation work. As a rule, private teams do not have the qualifications, experience and knowledge to perform engineering and technical support of work. There are often cases when these unfortunate installers are not even able to speak Russian. What kind of compliance with building codes and regulations can we talk about? Therefore, if you want engineering systems to work correctly, last a long time and not cause you unnecessary trouble, contact qualified specialists.
guarantees high quality of work, clear documentary support for installation and design, and most importantly, attentive attitude towards you!
Hydraulic tests are carried out after completion of installation work; they are mandatory for pressure and non-pressure water supply networks. To carry out the tests, a pump is needed that pumps high pressure into the water supply, which reveals defects. The data obtained is included in the water supply testing report. Only after signing the act can the water supply be used.
Certificate of testing of external and internal sewerage for spillage
A test report for internal and external sewerage is drawn up as a result of checking the operability of the system. It confirms the position of the commission that the system has withstood the test of a spill of water, and the design complies with the design documentation, GOSTs and standards.

Diagnostics of the normal functionality of the sewer system is necessary when installing a new facility or after carrying out repair work on an existing system. Information about the performance check is entered into the report. The form is drawn up in the form specified in Appendix “D” to the Code of Rules 73.13330.2012.
The act specifies:
- name of the system and the facility in which it is installed;
- information about the members of the commission. Representatives of three organizations are needed: the general contractor, the customer and the installation company;
- information about the name of the project is written down;
- the results are entered: the number of simultaneously connected devices, as well as the connection time or filling of water on the floor (unnecessary ones are crossed out);
- the third paragraph states that no leaks were detected at the joints and through the walls. This means the system is suitable for use.
The decision is signed by the members of the commission.
Purpose and order of testing
Hydraulic tests of water supply and wastewater systems are carried out to check the tightness, reliability of the water supply system and detect defective parts. Testing is prescribed before putting into operation a newly constructed network or after reconstruction (overhaul). All detected defects are immediately corrected, and tests are repeated until a satisfactory result is obtained. Tests are carried out twice: first preliminary
, after them
final
.
At the first stage, water is pumped into the water supply system under pressure; the pressure should be one and a half times higher than the working pressure. Preliminary hydraulic tests of water supply pipelines are prescribed with full access to the above-ground and underground parts of the pipeline, before the installation of plumbing fixtures.
Testing is scheduled before the final finishing of the premises. Hydraulic tests of drainage and water supply systems are carried out by specialists from the plumbing service.
Before the final stage of hydraulic testing of the water supply, the underground sections are closed, all installation work on the section is completed, but plumbing fixtures have not yet been installed. The exits are covered with plugs. During hydraulic tests of cold water supply, the pressure in the mains is increased by 1.3 times compared to the working one.
- Hydraulic tests of plastic water supply pipelines are allowed to be carried out a day after installation, at above-zero temperatures;
- To conduct hydraulic tests of drains in a house, the pipes are completely filled with water to the top of the risers. The condition of the pipes is first visually examined and noticeable defects are corrected. If a completely filled drainage system does not leak within 20 minutes, and the water remains at the marked level, the system has successfully passed the test.
The concept of crimping and timing
Pressure testing means a set of test measures to assess the tightness of the heating system.

Similar tests are carried out in the following cases:
- After assembling a new heating system before putting it into operation. In this case, the act is a permitting document for starting to use the networks.
- On previously installed and operating networks, hydraulic tests are carried out before the start of the heating season or immediately after completion.
- If preventive or repair work was carried out on the heating main, then hydrotesting is carried out upon completion.
- Mandatory pressure testing is carried out before replacing individual elements and equipment of the system, repairing radiators or pipelines. In this case, the measures taken make it possible to identify weak points in the system, which allows them to be replaced or repaired in a timely manner without waiting for an accident.
To carry out hydrotests, water or air is injected into the network under pressure. For this, a hydraulic or pneumatic pump is used. As a result, it is easy to identify areas and places with broken tightness of components and connections. If air is used, a characteristic whistle will be heard, and when pumping under water pressure, leaks will be detected. We can say that during hydrotesting, situations are artificially created that arise during water hammer, or during a critical increase in pressure in the line.
If the circuit elements and devices have a sufficient margin of safety, then increasing the pressure for half an hour will not harm them and will not affect their service life. But during this period of time at high pressure, weak areas, depressurized components and connections can be easily identified.
If the apartment has an autonomous heating system, it is recommended to periodically check it using a compressor. Such pneumatic pressure testing will protect against flooding of the lower floors while reducing the safety margin of the system.
Test conditions

It is necessary to carry out hydraulic tests of water supply and wastewater systems with full responsibility, recognizing the complexity of the procedure. The result of the tests largely depends on the skill of their implementation. Therefore, they are trusted only to specialists who know the safety measures and requirements for such checks.
- The temperature indoors or outdoors (if the external water supply is checked) is not lower than +5 degrees;
- The water pipeline is filled gradually, starting from the main section. Then the water is poured into risers and small local networks;
- The lower floors are filled first, gradually rising higher. This is necessary to displace air from the pipes and prevent the formation of air locks;
- At the end of the hydraulic tests, the used water is drained from the water supply and drainage system;
- During hydraulic tests of hot water supply, the temperature is measured at the extreme sections of the system. Water of the design temperature is poured into the system;
- During hydraulic testing of hot water supply, the condition of heated towel rails in bathrooms is tested;
- If it is necessary to test the efficiency of the water supply system, all points of use in the riser are turned on at the same time. This test step is optional.
Stages of implementation
This procedure is carried out in stages:
- First, all connections are checked, as well as the functionality of the locking elements. Their condition is visually assessed.
- After this, not only the boiler, but even the expansion tank is disconnected from the system. This is necessary to completely flush the pipeline and radiators from the possible presence of small debris in them.
- Next, the crimping itself begins. To do this, water is poured into the system from the water supply and a compressor is connected to the drain valve and the pressure is gradually increased until it reaches the desired value. If there are no downward changes in the indicators, this indicates that the system is completely sealed and can be put into operation. If there is a hole in the thermal pipe assembly, there will be a sharp drop in pressure in the system.
Please note: the average time for hydropress testing is one hour, while 20 minutes is enough for a pneumatic test.
- If malfunctions are found, they are eliminated and the procedure is repeated.
- When the system has confirmed its tightness based on the test results, a pressure test report is drawn up.
Please note: you cannot carry out such a procedure alone, because such a process requires special skills and knowledge
It is important to correctly follow all safety measures.
Preliminary test progress
The procedure for conducting preliminary hydraulic testing is regulated by the Construction Norms and Rules:
- The water supply is filled and left without pressure for two hours.
- Increased pressure is slowly created for half an hour. Then you can check for leaks at the joints.
- The pressure is reduced to the calculated values, and the condition of the route is examined.
- The route remains under this pressure of water for 30 minutes or more to stabilize the deformed shape of the pipes.
- The inlet taps are closed and the water is slowly drained from the pipes using a pressure testing pump.
- The route is checked for leaks and noticeable problems.
The water supply system has successfully passed inspections when no leaks are detected at increased pressure, connections and fastening elements are intact.
Before starting a hydraulic test of a water supply system in an apartment building, you should find out the standard operating pressure and check it with the pressure limits of the devices (manifolds, hoses, filters, sensors).
Progress of the final test
In multi-apartment residential buildings, the final hydraulic test of the cold water supply is carried out after the installation of plumbing fixtures:
- The working pressure is pumped into the water supply and maintained for two hours. If the pressure decreases by 0.02 MPa, it is raised to the initial level.
- In 10 minutes the pressure is increased to test values and maintained for two hours.
Hydraulic testing of the cold water supply system is considered successful if the leakage is not higher than the readings in the table.
| diameter , cm | Allowed leakage | |
| For welded joints | For connections on seals (sockets) | |
| 6,3-7,5 | from 0.2 to 0.24 | from 0.3 to 0.5 |
| 9-11 | from 0.26 to 0.28 | from 0.6 to 0.7 |
| 12,5-14 | from 0.35 to 0.38 | from 0.9 to 0.95 |
| 16-18 | from 0.42 to 0.6 | from 1.05 to 1.2 |
| 20 | 0,56 | up to 1.4 |
| 25 | 0,7 | up to 1.55 |
| 28 | 0,8 | up to 1.6 |
| 31,5 | 0,85 | up to 1.7 |
| 35,5 | 0,9 | up to 1.8 |
| 40-45 | from 1.1 to 0.5 | from 1.95 to 2.1 |
| 50-56 | from 1.1 to 1.15 | from 2.2 to 2.3 |
| 63 | 1,2 | up to 2.4 |
| 71 | 1,3 | up to 2.55 |
| 80 | 1,35 | up to 2.7 |
| 90 | 1,45 | up to 2.9 |
| 100 | 1,5 | until 3 |
| 120 | 1,6 | until 3 |
Table 1.
Permitted volumes of leaks on a 1 km section of water pipeline
The data obtained as a result of hydraulic tests is entered in as much detail as possible into the acceptance certificate of the water supply system. This also includes information about alterations and repairs made during the tests. The water supply testing report is proof of the quality and excellent condition of the water supply system and readiness for operation.
Upon completion of hydraulic tests, the following documents are required for commissioning of a cold or hot water supply system: working materials with notes on the features of the installation of the water supply system and the coincidence of the final result with the project, a description of the changes; hydraulic test certificate; act describing hidden work.
Drawing up a hydraulic test report for the heating system
An official certificate of hydraulic testing of the heating system, a sample of which is submitted by the supplying organization, indicates the successful completion of a comprehensive check. This is carried out to ensure the proper technical condition of the entire system. Even a minor malfunction will lead to significant problems during practical operation. The hydraulic test report for the system must be completed only by an authorized organization. Otherwise, the document has no legal force.