Basic information about thermal insulation
In Russia and many post-Soviet countries, insulators are used on various engineering systems. Main examples are sewerage installations, ventilation systems, heating systems, water supply installations, air conditioning systems. Also, insulators are often mounted on boiler installations, where high heat consumption is observed.
In addition, thermal insulators have also become widespread in some special sectors of the economy - the food industry, chemical production, gas purification.
Thermal insulation of pipes can be used in various areas - outdoors, underground, indoors. It is necessary to take into account the peculiarities of the temperature regime in a particular area. Example: outdoor heat loss will be significant in winter, so it is recommended to use a stronger dense insulator. Whereas inside factory workshops and premises the air temperature can be quite high even in winter. Therefore, simpler thin insulators can be used there.
When choosing an insulator, you must also take into account its physical properties and technical features. We list the main parameters:
- Thermal conductivity coefficient - the lower this indicator is, the lower the heat loss during transportation will be.
- Fire resistance - it is recommended to give preference to non-flammable materials that will not ignite during transportation of the coolant.
- Sensitivity to ultraviolet light - it is recommended to choose insulators with low sensitivity, as they are more durable.
- The ability to maintain shape - it is better to choose materials that do not crumble and retain their shape for a long time
- Chemical inertness - this indicator is critical in the case of an atypical coolant (gas, chemicals). And the higher this indicator is, the longer the insulator will retain its shape and physical properties.
In practice, thermal insulation of a pipeline is usually carried out using the following materials - glass wool, basalt fiber, natural or synthetic rubber, polystyrene foam, heat-protective foam.
Recently, composite materials have become widespread. They have good physical and chemical properties, are easy to install, and are not too expensive.

Polyethylene foam
Polyethylene foam has a lower cost and a smaller scope. It cannot be used to insulate so-called “cold objects” as it has low resistance to the penetration of water vapor. This type of thermal insulation does not allow achieving complete tightness of the thermal insulation layer, which leads to heat loss. Poor gluing of seams is also noted as a disadvantage.
To avoid these disadvantages, it is necessary to use heat-insulating pipes made of polyethylene. Together with sheet materials, they provide reliable thermal insulation of any pipelines. Such pipes are easy to use and install, and have a low price. Polyethylene pipes can be used both on new and existing systems. Thanks to the presence of a special latch, they are easy to dismantle, which is convenient when carrying out repairs.
During installation, the insulation is cut along the technological seam and then glued together. In this case, it is necessary to make a slight tension in order to compensate for the shrinkage of the polyethylene. This insulation is easily installed on elbows and arches; the pipe length is 2 meters.
Thermal insulation of pipelines allows you to save heat, and you get an economic effect already at the beginning of the system’s operation.
Pipe laying methods
On the street, insulation of heating pipelines is required both when installed above ground and when laid hidden - underground. The latter method is a channel method - a reinforced concrete trench is first laid in the trench, and pipes are already placed in it. Channelless placement method - directly in the ground. The insulating materials used differ not only in thermal conductivity, but also in steam and water resistance, durability and installation methods.
The need to insulate cold water supply pipes is not so obvious. However, you cannot do without it when the water supply is laid open above ground - the pipes must be protected from freezing and subsequent damage. But inside buildings, water supply pipes also have to be insulated - to prevent moisture condensation on them.
Thermal insulation of foam glass tanks
Thermal insulation of bottoms, walls and roofs of steel and reinforced concrete tanks.
The high compressive strength of foam glass makes it possible to use it to insulate the bottoms of tanks of any volume - in Russian practice, up to 50,000 m3.
When insulating tank walls with foam glass, there is no need for through-fastening of blocks, which makes it possible to completely eliminate heat loss associated with the presence of the so-called. "cold bridges"
Purpose of thermal insulation of steam pipelines
It turns out that on an uninsulated section of pipes with an area of 10 m², in order to maintain the operating parameters of the carrier, the annual fuel consumption increases by 10-20 tons! But these are huge reserves of fuel “flying down the drain.”
You should pay very close attention to the thermal insulation of fresh steam pipelines, switchgear, steam shut-off valves, protection of pipes supplying steam to the turbopump and ejectors operating at a temperature of 400-500°C.
Without proper thermal insulation of industrial steam pipelines, a considerable amount of energy is lost in the area from the steam generator to the steam injection well. Pipelines are insulated with heat-resistant materials made of rubber and mineral wool before the turbines are put into operation.
Thermal insulation of underground pipeline without duct laying
Thermal waterproofing is a thermal insulation system that protects underground pipelines from corrosion.
Anti-corrosion materials used in the insulation of underground pipelines of channelless installation (such as FRUCS, BIURS, etc.) cannot be used at temperatures on the surface of the pipe above + 60 ° C. At the same time, at various industrial facilities there are underground pipelines with higher operating temperatures.
The thermal insulation structure shown in the figure can also be used as thermal insulation, capable of replacing traditional anti-corrosion coatings.
The use of such a system is especially important in permafrost areas, where, in addition to anti-corrosion protection, it is necessary to take into account the likelihood of soil cooling.
You can also find out about installation materials on our website.

Types of materials for thermal insulation of heating pipes
Technical solutions for pipe insulation differ in design, materials and characteristics.
Mineral wool

Technical insulation made from basalt rock wool for insulation of high-temperature pipelines is produced in wound cylinders, slabs and mats, including those with one-sided foil. It is chemically inert, biostable, non-flammable, has a thermal conductivity of about 0.04 W/m*K and a density of 100-150 kg/m3.
The materials are effective, affordable, but have disadvantages. The use of mineral wool insulation for insulating heating pipes in attics, basements, and technical undergrounds is limited due to high humidity. The tendency to caking and absorption of moisture lead to structural damage, wetting, and rapid deterioration of heat-protective properties.
Installation
The pipe is wrapped or lined with cotton wool, ensuring uniform filling density over the entire surface. Then the insulation, without too much pressure, is fixed using a knitting wire. The material is hygroscopic and easily gets wet, so insulation of external pipelines made of mineral or glass wool requires the installation of a vapor barrier layer made of a material with low vapor permeability: roofing felt or polyethylene film.
PPU insulation production technology
The technology for producing heat-insulating shell half-cylinders includes the process of pouring material into a mold. In this case, additional covering of the shell with foil or fiberglass is acceptable. As a rule, polyurethane foam is produced in two main ways - pouring or spraying. The result of a product manufactured by any of these technologies is identical in its technical characteristics. However, the pouring method is recognized as the most productive and economical.
To obtain a polyurethane foam half-cylinder, a mixed composition is poured into the equipment pre-lubricated with an anti-adhesive substance. The material poured into a mold goes through several stages of transformation in 10-15 minutes, including foaming, expansion and hardening.
To obtain a polyurethane foam half-cylinder, a mixed composition is poured into the equipment pre-lubricated with an anti-adhesive substance. The material poured into a mold goes through several stages of transformation in 10-15 minutes, including foaming, expansion and hardening.
Advantageous characteristics of polyurethane foam shells
Experts note the significant advantage of insulating pipes with polyurethane foam shells compared to traditional thermal insulation with mineral wool.
- reduction of time required for installation of thermal insulation and commissioning of pipelines
- Possibility of installation and dismantling in any climatic conditions
- preferential increase in the service life of the thermal insulation characteristics of pipelines
- significant reduction in heat loss in pipelines
- Possibility of reusable insulation material
- quick access to damaged areas
- high productivity (2 specialists can carry out up to 150 linear meters of PPU insulation per work shift)
Variation in the density coefficient of thermal insulating shells (50 - 120 kg/m³) and thermal conductivity coefficient (0.025 0 027 W mK).
Pipes and steam lines with temperatures exceeding 120°C should be insulated in stages. At the first stage, it is necessary to carry out work to reduce the surface temperature (basalt felt, felt), and at the second stage, carry out thermal insulation with polyurethane foam.
Mineral wool
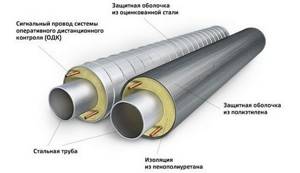
Scheme of thermal insulation of steel pipes.
This is a fairly common insulation material; many pipelines are insulated with mineral wool slabs and covered with foil. Such thermal insulation looks unaesthetic, and the quality of heat conservation is very dependent on how carefully the work on installing the thermal insulation material is carried out. Currently, mineral wool cylinders with a diameter ranging from 18 to 273 mm are used to insulate the pipeline. Such pipeline insulation ensures high quality and practically does not depend on the contractor.
Mineral wool, which is used in the manufacture of heat-insulating cylinders, is produced from molten rocks. All raw materials, before mineral wool is made from them, undergo radiation control. The insulation does not emit harmful substances during operation, it is non-flammable and non-explosive.
Such heat-insulating cylinders are used to insulate above-ground and underground pipelines. They are very convenient for installation, as they have a notch, they can be used in the temperature range from -180 to 600°C.
Return to contents
Pre-insulated pipes

This method of pipeline insulation is considered the most promising. The method consists of filling the space between the insulated pipe and a larger pipe with polyurethane foam. The result is a monolithic three-layer structure with excellent thermal and waterproofing properties.
Comparative analysis of technical and economic efficiency when using polyurethane foam products and traditional mineral wool
Indicators Polyurethane foam Mineral wool
| Coefficient of thermal conductivity | 0,019-0,027 | 0,05-0,07 |
| Coating thickness | 35-70 mm | 120-220 mm |
| Effective service life | 25-30 years | 5 years |
| Manufacturing jobs | From 5°C to 30°C | From 5°C to 30°C |
| Moisture, aggressive environments | Stable | Thermal insulation properties are lost and cannot be restored |
| Ecological cleanliness | Safe. Approved for use in residential buildings by the Ministry of Health of the RSFSR No. 07/6-561 dated December 26, 1986 | Allergen |
| Productivity brigade 2 - people | 100-300 m.p. per shift | 20-5 - m2 per shift |
| Actual heat loss | 1.7 times lower than the normative SNiP 2.04.14 88 Energy Saving, No. 1, 1999 | Exceeding regulatory standards after 12 months of operation |
| Technological advantages | Transition to ductless installation of heating networks SNiP 2.04.07-86 (heat networks) SNiP 2.04.17-88 (thermal insulation of equipment and pipelines) TU RB 00012262-181-94 <products made of="" polyurethane foams=""> SNiP 11 -3-79 (Construction heating engineering) TU 3497-44406476001-99 | No |
Thermal insulation Average density (kg/m 3) Thermal conductivity coefficient (W/m*K) Porosity Service life (years) Operating temperature range.
| Polyurethane foam (PPU) | 40-60 | 0,019-0,027 | Closed | 30 | -200°С +120°С |
| Mineral wool | 55-150 | 0,052-0,058 | Open | 5 | -40°С +120°С |
| Cork board | 220-240 | 0,050-0,060 | Closed | 3 | -30°С +90°С |
Foamed polyurethane (polyurethane foam, PPU)
Reduces heat loss by more than half compared to glass wool and mineral wool. Its advantages include: low thermal conductivity, excellent waterproofing properties. The service life declared by the manufacturers is 30 years; The operating temperature range is from -40 to +140 °C, the maximum withstandable for a short time is 150 °C.
The main brands of polyurethane foam belong to the flammability group G4 (highly flammable). When the composition is changed by adding fire retardants, they are assigned G3 (normally flammable).
Although polyurethane foam is excellent as an insulating material for heating pipes, keep in mind that SP 61.13330.2012 allows the use of such thermal insulation only in single-family residential buildings, and SP 2.13130.2012 limits their height to two floors.

Thermal insulation coating is produced in the form of shells - semicircular segments with tongue and groove locks at the ends. Ready-made steel pipes insulated with polyurethane foam with a protective sheath of polyethylene are also available for sale.
Installation
The shells are secured to the heating pipe using ties, clamps, plastic or metal bandage. Like many polymers, the material does not tolerate prolonged exposure to sunlight, so an open ground pipeline when using PPU shells requires a covering layer, for example, galvanized steel.
For underground ductless placement, thermal insulation products are laid on waterproof and temperature-resistant mastics or adhesives, and the outside is insulated with a waterproof coating. It is also necessary to take care of the anti-corrosion treatment of the surface of metal pipes - even the glued joint of the shells is not tight enough to prevent the condensation of water vapor from the air.
Thermal insulation of steam pipes
Thermal insulation of steam pipes for a long time was carried out using mineral or glass wool. This is logical - such materials have good performance characteristics, and they are very cheap.
Installation is also simple - the cotton wool is glued to the pipe using glue; For additional strength, wrapping with thick tape can also be used. However, over the past 20-30 years, alternative materials have appeared and have also become widespread:
- Liquid insulators. They are cheap and easy to apply to pipe structures. The installation process looks like this: the mixture is applied to the pipe over its entire surface, and after the insulating paint has hardened, a new layer is applied. The higher the temperature of the coolant, the more layers need to be made.
- Foil non-combustible insulation. The main advantages are a long shelf life, high quality insulation. It consists of sheets of insulator, which is covered with a layer of foil on top for additional protection. The material is mounted as follows: the top surface of the pipe is covered with insulating foil - the edges of the foil are folded up and fastened to each other using buttons, pins or staples. At the end, it is necessary to apply a waterproofing agent to avoid rust on the foil.

Modern universal heat insulators
Today, there are also universal heat insulators on sale that are suitable for protecting pipes of all types (sewage, steam, water). An example of such an insulator is polyurethane sealant. It has many advantages - a high degree of protection, a long shelf life, corrosion protection, resistance to chemicals. The main disadvantage is inconvenient installation:
- In a technical sense, polyurethane sealant is a paste-like liquid that is used with a protective casing.
- To create thermal insulation, the casing is carefully pulled over the pipe. Polyurethane liquid foam is poured into the gap between the casing and the pipe structure. Finally, a special component is added to the foam, which causes the foam to swell, which creates a thick layer of insulation.
- Before installation, it is necessary to carry out very accurate calculations so that the casing does not turn out to be larger or smaller than the main pipe. You also need to correctly calculate the volume of foam - if there is too much of it, the protective casing may crack and break. If there is insufficient foam, the quality of thermal insulation will be poor.
Calculation of the volume and area of the heat insulator
To make thermal insulation, it is necessary to correctly calculate the required amount of insulator. For this, two indicators are used - volume or area.
The first indicator is used to count flat sheets (polystyrene, foil in the form of plates).
The second indicator should be used in cases where we are talking about materials that are packaged in cylinders (wool wool, basalt).
Two formulas are used to calculate volume and area. For area: S = 3.14 x (A + B) x B x C. Volume: V = 3.14 x (A + 2B) x C. Explanation:
- A is the diameter of the pipe on which the heat insulator will be attached.
- B is the thickness of the insulator that is mounted on the pipe structure.
- C is the total length of the pipe structure that will be covered with insulating material.
Please note that such formulas are used exclusively for calculating sheet or cylindrical insulators. If you plan to create insulation using other materials (paints, liquids, polyurethane, rubber), then the calculations are carried out differently. Example: the consumption of insulating paint is often indicated on the can itself.
Examples
- You want to buy a flat sheet of thermal insulation. Your pipe has a diameter of 10 cm and its length is 20 meters. You like a material whose thickness is 5 cm. How much insulator is needed to cover such a pipe? We need to determine the coverage area using the formula S. Let's convert the diameter and thickness into meters. 10 cm = 0.1 m, 5 cm = 0.05 m. Substitute into the formula: S = 3.14 x (A + B) x B x C = 3.14 x (0.1 + 0.05) x 0.05 x 20 = 0.471 sq. m.
- You need to purchase cylindrical material. You have a pipe with a diameter of 20 cm; its length is 25 meters. You have chosen a material whose thickness is 10 cm. How much of this material should you buy? In this case, the second formula V will be used. Let us convert to other measurement systems. 20 cm = 0.2 m, 10 cm = 0.1 m. Substitute into the formula: V = 3.14 x (A + 2B) x C = 3.14 x (0.2 + 2 x 0.1) x 25 = 31.4 cu. m.

Application of rubber casings for thermal insulation of steam pipelines
Rockwool thermal insulation is installed for heating mains and low-pressure steam pipelines. For unmounted products, the cylinders are put on the pipes and smoothly, using the method of axial rotation, move to the installation site. One of the ends of the heat-insulating material is glued to the pipe. The end parts of the insulation are fixed with glue.
When installing or overhauling installed pipelines, the cylinders are cut lengthwise and loosely placed on the pipe. The longitudinal parts of the thermal insulation of steam pipelines are lubricated with glue and pressed after the setting period begins. The cut-in piece of insulation is cut 2 mm longer than required.
Useful tips for thermal insulation of steam pipes
- When considering the proposed thermal insulation technologies and materials, choose options with suitable technical characteristics. For example, at an oil refinery there was such a case: molten paraffin, when it hit the glass wool thermal insulation of a steam pipeline, began to ignite.
- To reduce losses of transferred heat, insulated pipes are required. The cost of insulation consists of the sum of the price of insulation and the cost of its installation.
- Thermal insulation of underground and overhead pipes performs the functions of steam and water protection.
Recommendations for choosing thermal insulation materials
For an inexperienced person, it is quite difficult to decide on the choice of thermal insulation material, both for steam pipelines and for other communications. Very often people pay attention to bright advertising and do not look at the characteristics of the thermal insulation material.
Thermal insulation for steam pipelines and other pipelines is subject to certification; it can be mandatory or voluntary.
Mandatory certification involves checking the thermal insulation material for compliance with health and environmental safety standards, as well as the fire safety of the material.
During voluntary certification, technical and operational characteristics are checked. Before purchasing thermal insulation material, you need to check whether it has undergone voluntary certification, and if so, familiarize yourself with its results. Voluntary certification must be confirmed by relevant acts and protocols.
To insulate the pipeline, materials such as glass wool, foamed synthetic rubber, mineral wool, polyurethane foam and other materials are used. Each material has its own advantages and disadvantages and differs in technical and operational characteristics.
Return to contents










