Reducing heat losses in heating communications of enterprises, utilities and private homes allows you to save significant financial resources on heating the coolant, so any methods of thermal insulation of pipelines are always relevant. In heating systems of private houses, the main way to maintain the temperature of the coolant in the system is thermal insulation for heating pipes; when used, it is installed on the outer surface of the pipeline.
It is useful for any homeowner whose heating boiler is located at some distance from heat exchange devices (for example, in a separate utility room on the street) to know the main types of heat insulators used to protect pipelines from environmental influences and how to insulate heating pipes. Depending on the material used to make the thermal protection, various methods of its installation are used; most of them are easy to do with your own hands if you know the appropriate technology.
Fig. 1 Thermal insulation for heating pipes in individual houses
Requirements for thermal insulation materials for heating pipes
Thermal insulating materials placed on hot pipes must meet the following requirements:
- Have low thermal conductivity - the lower its value, the more efficiently the shell retains heat. The material’s high resistance to heat loss helps save money on fuel for boilers.
- Heat resistance to high temperatures is the main requirement for an insulating coating; it should not melt or decompose when the object is heated to a boiling water temperature of 100 ° C.
- Water resistance is the main criterion for choosing a thermal insulation material when placed in soil; in this case, an insulator that is not capable of absorbing water is used.
- Biological resistance is important when using thermal insulators in any conditions; the insulating material should not be an environment for the development of various types of bacteria, microorganisms, mold and be of interest to rodents.
- Chemical resistance is also beneficial to insulating materials when installed under soil containing a wide range of chemically active components.
- The service life of thermal protective coatings is important from the point of view of financial savings - the material will not have to be changed too often, incurring additional cash costs for purchasing a new one.
- Physical and mechanical strength is the main criterion for choosing pipe coatings used in underground conditions.
- Environmental cleanliness is important when using thermal insulators indoors; they should not emit harmful chemicals both under normal conditions and when used on hot pipes.
Rice. 2 Thermal insulation of heating pipelines - comparison of thermal conductivity by thickness
Scope of application
First of all, thermal insulation is used for heating, since there, along with preventing frost, it helps to save an expensive energy resource. It is recommended to insulate pipelines not only outside residential premises, but also inside, as well as in the boiler rooms themselves. After all, this will eliminate the energy consumption for heating non-residential rooms.
There are four main groups of insulating materials for heating communications:
- roll;
- cylindrical cut;
- cylindrical uncut;
- halves of a cylinder (format is better known as "shell").

In any case, it is necessary to calculate the installation of insulating structures for the exact diameter of the pipe. The appearance of a gap significantly reduces the effectiveness of the protection and can even lead to its failure. Important: slag mineral wool is not suitable for heating, or even for water supply or sewerage. The service life of cotton wool insulation is relatively short (it reaches 10 years only if it is completely dry and protected from mechanical factors). Foamed polymers are completely resistant to moisture and significant cooling.

All polymers are characterized by increased flammability, which significantly reduces the scope of their application. If structures made from them will be placed on large pipes, you need to choose products with 3-4 locks. For small and medium-sized pipelines, 2 locks are enough. Polyurethane foam performs better than polystyrene foam, and that is why it is recommended for the most critical pipes. Polyurethane foam insulation materials intended for heating circuits in homes are supplied exclusively as strong shells with a steel shell.
You can use polyurethane foam only with reliable protection from light. Foamed rubber with similar characteristics is recommended not for heating pipes, but for ventilation pipes.

It also works well for protecting the pipes through which the coolant flows. Important: if there is even the slightest chance of rodents, you should use glass wool. They chew through all other substances faster than you can talk about it.
As for water supply, it is necessary to insulate it mainly when pipes are forced to be laid above the freezing line. Important: if the problem is mild, you can simply increase the speed of the water flow. This is done through the use of pumps or receivers. A heating cable is also sometimes used. Cable heating is considered the most reliable and powerful way to protect against the cold.

This is the method recommended for seasonally used cottages. The supply of heat through an electric cable helps to quickly prepare the water supply for use, and when it is no longer needed, it can be stopped.
Thermal insulation itself is most often carried out by using rigid materials, these include:
- expanded polystyrene;
- Styrofoam;
- penoplex.
Both the quality of protection and cost are directly determined by density. Soft insulation is placed in the foam shell to cover possible flaws and voids. Roll insulation of water pipes is made with mineral and glass wool, furniture foam rubber, foil foam. Problems may be associated with the hygroscopicity of the materials used. In addition to protection from harmful environmental factors, you will have to think about how to secure the roll to the pipe.

Professionals note that it is easiest to insulate water pipes using segmental materials. It is this option (sometimes also called casing) that maintains the highest tightness and reliability. Another way to protect your water supply is by spraying polyurethane foam. It initially provides absolute impermeability to water. The consumption of the component used depends on the thickness of the poured layer.
When choosing an option for insulating water pipes, you must take into account the difference between pipes laid underground and above it. The difference remains even when the same type of material is used. Plastic and metal pipes require different insulation. If you need to protect the water supply on the street (under houses, in distribution wells), use any means that will maintain the necessary tightness and will not be destroyed by water.
An aboveground pipeline needs thicker protection than its underground counterpart.

The most difficult section is the one where the pipe rises to the surface. Here either the most powerful insulator is used, or weaker options are laid out in several layers. Covering the main insulating layer from moisture is achieved by wrapping it with plastic film or roofing felt. If both solutions are unacceptable, form a plastic box. In any case, care is taken to reduce to a minimum the number of joints, each of which forms a cold bridge.
The problem can be solved by laying out an insulating coating in the form of two mutually offset layers. But it’s not just the outer parts of the water supply that need to be protected from the cold. The covering of pipes connected to air conditioners also has its own subtleties. The purpose of protection in this case is to maintain the same performance of climate control equipment. When using uncovered pipelines, a considerable part of the energy is consumed through heat transfer. Calculations are made in advance and the location of the air conditioner and all associated pipes are determined. In this case, the required diameter of the insulating layer is calculated.
In most cases, channels serving climate control equipment are protected with synthetic rubber that does not have pores or polyethylene foam. But the hygroscopicity of mineral wool prevents its use in this case. It is much better to use mineral fiber products with a water-repellent layer.

Many pipelines in apartments and private houses are made of polypropylene structures.
The need to insulate them arises when placing:
- in the floor screed of the first floors;
- in floor screeds above unheated rooms;
- near external door and window openings.
It is also necessary to protect polypropylene pipelines entering the water supply and heating risers. They can be covered with basalt cylinders. But this is a rather expensive material, which limits its use. Foam is more versatile.
Another advantage of this material is the ability to use it many times in a row.

Insulating outdoor water pipes using glass wool is significantly complicated by the danger of its dust particles for the skin and respiratory system. Preparing the casings becomes a prerequisite. All metal pipes laid outside must be painted at the preparation stage. As for the insulation of sewage systems, it must be carried out in unheated rooms and in open areas. The only exception to this rule is in areas where in winter the temperature is guaranteed not to drop to negative values.
Of course, in Russia this is only a theoretical assumption, since in reality there are no such areas.
In most cases, sewer pipelines, including those from HDPE, cover:
- mineral wool in various formats;
- expanded polystyrene;
- expanded clay;
- polyurethane foam.
Liquid insulating elements are occasionally used. All such options are considered passive varieties. But sewerage, like other types of pipelines, is often protected using cable heating. Mineral wool should be used with caution to protect sewer systems because it contains formaldehyde resins and can be destroyed under significant mechanical stress. This makes it significantly more difficult to achieve effective thermal insulation.
Cotton insulation is used when it is necessary to cover the free areas of the channels. They cannot be laid in the soil. Wet cotton wool of any type very easily loses its characteristics. And if the pipes are made of metal, they often begin to rust quickly. To install it yourself, you need to use polystyrene foam.
Utility systems often include copper pipes, which have impressive practical properties. But even they need effective thermal protection. In most cases, copper pipelines are covered with foam materials. Such products are suitable not only for air conditioning ducts, but also for all water supply systems and heating lines.
Thermal insulation is also important for heated floors. As calculations show (and practice confirms), floors without insulation in an identical configuration under similar conditions consume 20% more energy. Cork substrates are widely used to stop heat flow. Their advantage is ideal environmental quality and excellent strength. Please note: cork has zero adhesion to cement screeds and blocks.
Installation of cork heat-shielding elements is possible if the ceilings allow it. Cork inevitably raises the floor by 40-50 mm. Therefore, it is unacceptable in rooms with low walls. The most popular method of thermal protection for heated floors is extruded polypropylene. The structure of its plates contains closed cells.
Polypropylene is well processed, it will not be difficult to install it even where the floor configuration is very sophisticated. In addition, the synthetic material does not absorb water and can be used at temperatures up to 130 degrees. Water-heated floors are mainly protected using polystyrene foam. Important: when choosing polymer structures, you need to carefully study their chemical composition. Sometimes it contains toxic components that will be released when heated.
To complete the overview of the areas of application of thermal insulation, it is appropriate to protect chimney pipes placed inside walls.
Help prevent heat loss and damage to the chimney from condensation:
- mineral wool;
- fiber products;
- slag concrete and structures based on it;
- brick break;
- foam glass.
Materials that are easily flammable and can be destroyed by heat are naturally prohibited. Professional builders try to use cinder blocks. This option is quite heavy and requires careful design taking into account the load on the roofing and load-bearing elements.
For independent work, flexible and soft mineral wool is much better suited. Attention: no matter what, where and with what is insulated, it is necessary to take into account the instructions for pipelines and insulating materials.
Functions of heat insulators for heating pipelines
If we consider a private house, the heating boiler can be located inside the building in the basement or outside in a separate technical extension. The latter option is often used in the absence of a gas pipeline and the use of solid dirty materials as fuel - coal, firewood, peat, briquettes, pellets.
Many private houses have outdoor baths or saunas, so as not to complicate the design by installing a separate tank for heating water; it is supplied into the premises from the boiler, and the distance between the objects can be quite significant. When deciding how to insulate heating pipes, choose materials that meet the conditions below.
Reduced heat loss
The principle of operation of any insulation is to protect the insulated surface of the protected object from contact with the environment. At the same time, due to the low thermal conductivity of the insulator, heat loss is reduced, and the equalization of air temperatures and the hotter pipeline proceeds much more slowly than in the absence of a heat insulator.
Any heating main can be placed on the surface of the earth or under the ground; in the first case, soft insulation is usually installed for heating pipes in the open air; when placed underground, protection from hard materials is installed due to soil pressure.

Rice. 3 Mineral wool is a popular thermal insulation material for heating pipes
Frost protection
If hot water in an individual heating system is supplied from the boiler to an object located at a considerable distance from it, the water supply is usually laid underground at a distance from the surface below the freezing point. At the same time, it is not always possible to place the pipeline at a sufficient depth, so if the supply of hot water is interrupted for a long time, the remaining and cooled liquid in the pipes may freeze in severe frosts. To protect the underground line from freezing, it can be thermally insulated by placing it in hard shells or soft shells located in pipe channels.
Prevents condensation formation
Construction regulations prohibit the laying of metal pipes in the ground in the absence of insulation or protection of the outer shell with auxiliary materials; the situation is different indoors, where steel, galvanized steel, and copper pipelines are quite often laid. When the heating is turned off, the liquid in the metal pipes cools down and condensation appears on their surface, water drops cause corrosion of the outer wall and, if there is a large accumulation, fall down to form puddles on the floor - this can cause damage to the flooring.
To combat this phenomenon, porous heat-insulating materials for pipelines that are resistant to water or with good vapor permeability are used.

Rice. 4 Foamed polyethylene - thermal insulation for outdoor heating pipes
Protection against thermal burns
In municipal and household services, the temperature of the coolant transported through pipes can reach values close to 100 ° C, so the task of protecting service personnel or residents of a private house from burns when coming into contact with pipes becomes urgent. To do this, their outer walls are covered with thermal protection from various types of heat insulators, the shell of which cannot have a high temperature by definition.
Neutralization of geometric deformations
The ability of all materials to expand when heated is well known, so a hot pipeline, when passing through walls or floor slabs, is placed in steel sleeves of larger diameter. A heat-insulating shell is placed on the pipe, protecting the assembly from hard contact of the enlarged shell with the wall of the sleeve.
When laying pipelines in walls or under the floor, their expansion can lead to cracks in the plaster or screed, so the use of an elastic shell that absorbs part of the thermal expansion helps to avoid problems associated with geometric deformation of the pipes.

Rice. 5 Expanded polystyrene shell - thermal insulation for heating pipes in the ground
Why do you need thermal insulation of pipelines?
Steel and plastic pipes used for water supply, sewerage and heating systems do not always require insulation. But in many cases it is necessary if the owners of the house are not ready to be left without water or heat in the middle of winter and spend money on repairing communications.
- Thermal insulation for water supply pipes is required if they are laid below the freezing level of the soil, on the surface of the ground, or pass through unheated rooms. Without it, the water in them will freeze in winter, which will most likely lead to damage to the pipes and components themselves. This is fraught not only with inconvenience associated with the lack of water, but also with the need for repairs, which is preceded by a search for damaged areas. In the case of steel pipes, insulation has another goal: eliminating condensation in hot weather.
Broken faucet
- Insulation of heating pipelines is also necessary when they pass through a cold zone: in walls, underground or along the street (for example, from a separate boiler room into a house). In such cases, high heat loss occurs, and the coolant reaches the consumer very cold, which negatively affects the efficiency of the heating system and increases the cost of maintaining a comfortable temperature.
The heating main in the basement needs insulation
- Insulation is least often required for gravity sewer systems, since they have an open spout and work to remove warm wastewater. The need for insulation arises if the pipes are laid shallow, with too little slope, or have a large length or turns. And also if the house is not equipped with hot water supply. Traffic jams and jams may appear in them, creating ideal conditions for freezing.
Note! Thermal insulation materials, in addition to their main function, can perform another function - sound insulation. Therefore, sometimes they are used precisely for this purpose.
Types of thermal insulation materials for heating pipes and their characteristics
For thermal insulation of pipes, industry and individual production produce a wide range of materials that differ from each other in their physical and chemical characteristics, scope of application, and installation features.
Mineral wool
Mineral wool fibers are thermal insulators often used in the construction industry; for example, basalt slabs cover the external facades of buildings; in individual houses they are laid under the roof and floors of attics. Often, pipelines are wrapped with soft sheet insulation made of any type of mineral wool, which is fixed with protective films and ties.
Usually they use glass and basalt wool, made respectively from fine glass threads and natural fibers of mountain basalt; in residential buildings, the third type of wool for technical premises - slag - is not used, due to its harmful acidic effect on metals and environmental hazards.
Stone mineral wool is formed from fibers with a length of about 16 mm and a thickness of 4 - 12 microns, it corresponds to the following technical parameters:
- thermal conductivity depends on the form of manufacture and ranges from 0.033 to 0.05 W/m K
- heat capacity: 1059 J/kg K;
- moisture absorption: within 24 hours no more than 0.01% of the volume;
- operating temperature range: from -60 to +450 °C for mineral wool made of glass fibers and from -100 to +700 °C for basalt fiber;
- density depends on the form of manufacture (rolls, plates, cylinders) and ranges from 30 to 225 kg/m3;
- sound absorption coefficient: 0.75 - 0.95;
- flammability class: NG – non-flammable;
- content of binding components (formaldehyde resin): 0.25 - 10% by weight.
Mineral wool is produced in the form of rolls, mats, slabs; for use on pipelines, hard varieties made of basalt are made in the form of shells from individual segments.
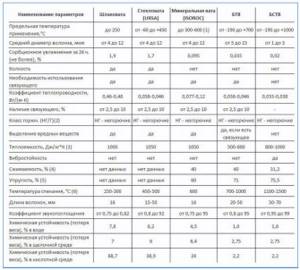
Rice. 6 Physical characteristics of various grades of mineral wool
Foamed polyethylene
Materials made from PE foam polyethylene are widely used in the construction industry; it is used for water and sound insulation, as substrates for laminate flooring, insulation outside and inside buildings, and objects of various shapes. Foamed polyethylene has the following physical characteristics:
- thermal conductivity depends on the brand name of the product and is associated with the manufacturing technology (cross-linking) of PE, the range of its values is from 0.30 - 0.55 W/m K;
- operating temperature range: from -60 to +75 °C and above;
- the density of PE depends on the brand and lies in the range of 25 - 100 kg/m3;
- vapor permeability: 0.001 mg/m·h·Pa;
- water absorption coefficient: no more than 1%;
- flammability group: G1 – low flammable, G2 – moderately flammable;
- if there is a foil coating, its reflectivity for infrared radiation: 80 - 97%;
- water absorption: 0.6 - 0.9% of volume
Pipeline design
Design documentation for the installation of pipelines through which steam, gas or hot water is transported must be carried out exclusively by competent authorities on the basis of certain standards specified in SNiP.
When making calculations, a number of parameters must be taken into account:
- temperature regime;
- expansion of the materials from which communications are made under the influence of high temperatures;
- the value of the maximum or working pressure;
- weight of the structure.
Based on the data provided, specialists determine the operational life of the pipeline and enter it into the communication passport. The structure must be designed so that it is convenient to carry out medical examinations and control. The joining of pipeline elements is performed using welding.

Threaded and flanged connections are used when pipeline parts have flanges. Then they will use cast iron pipes with a cross-section of no more than 100 millimeters, belonging to category IV. Making connections using tees is permissible if the system belongs to categories III - IV.
Pipeline elements must be protected from corrosive processes. At the same time, all areas of communications that operate with an ambient temperature of more than 55 degrees and are open to specialists must be properly insulated.
Thermal insulation for external heating pipes
The insulation of pipes laid outside buildings on the street is exposed to environmental temperatures, direct solar radiation and precipitation, therefore, for their insulation, materials are used that are not influenced by the factors listed above.
From the above list of all insulation materials, polystyrene foam shells can be excluded due to their decomposition under ultraviolet irradiation. Mineral wool and polyethylene foam, which absorb moisture without external protection, can also be excluded from the list of suitable ones.
In municipal and industrial services, for the external laying of heating mains, pipelines in polyurethane foam insulation with a steel shell are used; in everyday life, with the cheapest and most accessible option, the surface of the pipes is wrapped with soft glass wool in combination with an outer polyethylene film, which can be secured with tape.
A slightly more expensive option for household use is the use of soft shells made of polyethylene foam with a foil or PE film surface, which at the same time protects the material from moisture penetration. During installation, the shell is placed on the pipeline, and the joints are wrapped with tape for reliable fastening and sealing from precipitation. Shells made of foiled glass and mineral wool are used and installed in the same way.

Rice. 13 Spraying polyurethane foam
Materials for insulation of hot water supply pipelines
Communications transporting hot water require insulation, which has a low thermal conductivity coefficient. This is necessary to reduce heat loss from pipes. Without proper thermal insulation, the pipeline will dissipate heat into the environment, showing low efficiency.
Let's consider what types of insulating materials can protect the pipeline transporting hot water:
- Polymer foam mineral pipe insulation (PPM) is an insulating material obtained by mixing polyurethane foam and mineral filler.
PPM insulation is used, as a rule, only for hot water supply pipelines. PPM insulation consists of three main layers having different densities. PPM insulation is a multifunctional protective structure, since each of its layers performs its own function: corrosion protection, thermal insulation and waterproofing. This monolithic structure is resistant to temperature changes and also has good strength, which allows you to protect the pipeline structure from mechanical influences.
Helpful information! Pipeline insulation can be either external or internal. Internal pipe insulation performs two main functions: protecting the pipe from corrosive influences and increasing the throughput of the pipeline.
- polyurethane foam (PPU). This material is used primarily to enhance the waterproofing properties of communications. It has good heat resistance and is able to withstand temperature changes. In addition, it is worth noting that heat loss when organizing polyurethane foam insulation is no more than 5%.
- very reinforced insulation (VUS). This is a special type of insulation, which consists of two or three layers and is used to protect pipeline communications from the harmful effects of corrosion. It is also worth saying that the VUS is resistant to low temperatures and can be used in unfavorable climatic conditions.

Very reinforced insulation is used to protect highways operating in difficult climatic conditions
Thermal insulation for underground heating pipes
GOST 30732-2006 regulates the direct underground installation of heating networks using pipelines with polyurethane foam insulation in a polyethylene shell or sealed channels with a galvanized steel outer protective layer.
For domestic use, laying steel pipes underground with unsealed protection is prohibited; if a pipeline made of PP polypropylene is used, it can be placed in a rigid shell made of regular or extruded PS polystyrene foam, PPU polyurethane foam.
In underground installation, many companies and individuals use a combination of a large-diameter external rigid pipeline and soft polyethylene foam insulation, similar to factory pipes with a PPU thermal insulator and a protective PE sheath. When laying a pipe, a tube made of soft foam polyethylene is placed on the pipeline, secured with tape, and then the resulting structure is inserted into sewer pipes of larger diameter.

Rice. 14 Factory insulated pipe with PPU insulation
Separation of pipelines according to category
According to the main operating characteristics of the transported medium, communications are divided into 4 categories.
The parameters according to which categories are determined are:
- For systems that transport steam from boilers - the value of its pressure and temperature at the exit point.
- For steam pipelines operating from turbines, the highest temperature and back pressure are observed when operating at idle speed.
- For designs of unregulated or adjustable types of extracting pairs - the highest value of pressure and temperature in the extraction.
- For communications that move the medium from reduction-cooling and pressure-reducing units - the highest pressure and temperature.
- For structures that move water after diaerators - the nominal pressure taking into account the system indicators.
- For supply and return communications of hot supply - the highest indicator of temperature and pressure, taking into account pumping facilities and terrain.
Advantages and disadvantages of individual insulation materials
Each of the insulation materials has its own advantages and disadvantages that limit their scope of application; these factors are taken into account when choosing a suitable material for specific conditions.
Fiber wool
Insulation materials made from glass and basalt wool are widely popular among consumers due to their affordability and environmental friendliness, allowing their use inside residential premises. Mineral wool has the following properties:
- Fire-resistant, in case of fire they do not burn and release substances harmful to health; they melt when exposed to too high a temperature.
- Glass wool has low rigidity and easily wrinkles, basalt-based material is stiffer, both types restore their shape after physical impact.
- Mineral wool has a high degree of moisture absorption; because of this disadvantage, shells made of quartz and basalt are not laid directly underground.
- Cotton wool is resistant to most aggressive chemicals and the biological effects of microorganisms, bacteria, fungi, and mold.
- With the exception of slag wool, mineral wools are environmentally friendly natural materials and are safe for human health.
- The material allows air to pass through well and prevents the accumulation of moisture and condensation under its surface.

Rice. 15 Thermal insulation of heating pipes on the street
Soft foam materials
Foamed polyethylene materials for pipeline insulation are produced in the form of tubular shells with a longitudinal slot; their characteristic differences from other types of insulation are:
- Polyethylene in its normal state is harmless to health.
- PE is a chemically and biologically neutral material that is not subject to rotting and resists the appearance of fungus and mold.
- It is moisture-proof, therefore it is often used as vapor and waterproofing in combination with materials with high adhesion (mineral wool).
- Depending on the manufacturer, foamed polyethylene does not support combustion or is slightly flammable (groups G1, G2), while during its ignition substances that are harmful and dangerous to human health are released.
- Foamed polyethylenes and rubber do not shrink and quickly regain their shape after applying physical force.
- Porous rubber is designed to adhere to metal surfaces - thus providing long-lasting and reliable insulation of pipelines.
- For ease of use, some tubes at the longitudinal seam are coated with an adhesive composition (self-adhesive varieties) - this allows you to hermetically isolate objects without cold bridges.
- For external use, tubes made of foamed polyethylene are produced in moisture-protected versions with surface films of various colors.
- Protection made of tubular foam polyethylene is quickly installed, has a beautiful aesthetic appearance of a closed shell, and is therefore widely used in households.
- Due to its low rigidity, the material is used on surface pipelines, popular brands: Energoflex, Jermaflex, Porilex, Vilaterm.

Rice. 16 Application of mineral wool for pipe thermal insulation
Hard shells made of polystyrene foam and polyurethane
Durable and rigid foam plastic, polyurethane shells in the form of a shell from several segments have the following qualities:
- The manufacturing material is biologically inert and resists most aggressive chemicals.
- They do not allow water and moisture to pass through, being vapor and water insulators.
- Polystyrene foam is one of the cheapest materials.
- The material is divided into several groups according to density and rigidity; its extruded variety has the highest parameters.
- Foam plastics are low-flammable; in case of fire they release a large amount of toxic substances in the form of black smoke.
- Due to the destructive effect of ultraviolet radiation on their structure, foam and polyurethane foam shells are recommended for use in underground pipeline laying.
- The low maximum permissible temperature of foam plastic, about 70 °C, is an obstacle to the use of PS in metal pipelines transporting steam or boiling water.
- For outdoor use, given the low strength and fear of ultraviolet radiation by polystyrene foam and polyurethane foam, they are placed in a hard shell made of thin-walled galvanized casings.
- Almost all foam shells are manufactured by commercial small businesses, so if a suitable diameter is not available, the protection can always be made to order in the required size and configuration.

Rice. 17 PE insulation on a heating pipe in a private house
Thermal insulation paint
Domestic manufacturers produce a wide range of thermal paints, the most famous brands being Bronya and Corundum, which have the following advantages and disadvantages:
- Thermal paints are applied to objects by brush or spraying; due to their high adhesion, they adhere well to surfaces made of any materials.
- The cost of paints sold in plastic buckets is too high due to imported raw materials; the price for a 5-liter bucket starts at 1,500 rubles.
- Manufacturer's recommended paint consumption: 1 liter per square meter to obtain an optimal layer of 1 mm thickness.
- Thermal paint is convenient to use on surface hard-to-reach and non-standard sections of pipes, insulation of flange joints, and its underground use is practiced for insulating steel pipelines.
- In addition to thermal insulation, thermal paint provides anti-corrosion protection for objects.
Oil pipeline insulation
Trunk pipelines transporting liquid fuels must meet strict requirements regarding thermal insulation and fire resistance. The required level of protection is provided by:
- PPU. Foamed polymer reliably protects pipes and their contents from temperature fluctuations. The material has a porous structure, but is quite light and does not load the pipes. Combines low vapor permeability and thermal conductivity with fire resistance, resistance to temperature changes and chemicals.
- Foamed rubber. Another polymer with positive performance properties makes installation easier and faster. Due to its plasticity, it is convenient for insulating curved sections of oil pipes. Protects metal from corrosion and destruction under the influence of an aggressive environment.
- Liquid insulation with special paints and varnishes. Protect underground pipes from water and salts dissolved in the soil. Paints for oil pipeline insulation have high electrical insulating properties and increased resistance to chemicals and overheating. Liquid insulators are applied by spraying or painting with brushes; the final layer is very thin and does not create unnecessary load on the system.
Technology and installation of insulation in everyday life - the best options
Owners of private houses, in order to save money on heating their premises, often have to decide how to insulate heating pipes, considering various types of pipeline insulation. In this case, heating networks can be located anywhere on an individual plot: inside a house or outbuilding, underground or on its surface.

Rice. 18 Applying Warm Paint
Insulation of heating pipes on the street
When deciding how to insulate heating pipes on the street with your own hands, you should first of all consider PE shells of a suitable internal diameter with closed cells. They have a surface film of various colors to cover the longitudinal seam, use tape, staples, self-adhesive types of tubes or any polyethylene glue. Depending on ease of use, PE tubes are purchased in standard lengths of 2 or 10 m; installation work is carried out in the following sequence:
- Clean the pipeline from dirt and dust and put a PE tube of the required size on it; when the seam is about to be coated with glue, it is placed at the top.
- If you use a non-self-adhesive variety, coat the walls of the longitudinal cut with glue and connect them until completely dry, then turn the shell over with the seam down.
- In a similar way, the ends of entire tubes or cut sections are glued together, resulting in a solid and aesthetically beautiful protective shell.
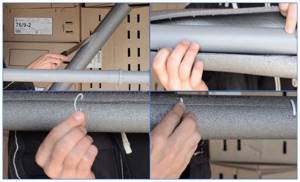
Rice. 19 Installation of PC tubes - main steps
Insulation of heating pipes in an unheated room
Indoors, to insulate pipelines, you can use PE tubes with open cells, which are cheaper than the option discussed above, and options for installing protection with a foil-coated surface layer are also often used. Some manufacturers, for example Energoflex, sell together with their tubes a special glue for joining PE products and an additional tool in the form of a special knife for cutting PE shells and a plastic miter box for cutting tubes straight or at an angle of 45 degrees. PE thermal insulation for heating pipes in an apartment or private house of the Energoflex brand is installed as follows:
- An additional longitudinal seam is cut in the tube using a special knife.
- Pull the seam apart and place the product on the pipe.
- The edges of the seams are secured with special plastic clamps in the form of half rings; to do this, they are connected together and clamping brackets are inserted in the amount of 4 - 5 pieces per linear meter.
- If it is necessary to insulate a corner section of the pipeline, proceed as follows:
- A piece of pipe is inserted into a special miter box and the middle fragment is cut out, and the ends of the joined elements are cut at the desired angle.
- The resulting parts are glued together, coating their edges with special Energoflex glue.
- The resulting corner element is cut lengthwise with a special knife, its longitudinal ends are coated with glue and the parts are placed on the corner of the pipeline; the halves can be wrapped with tape for 2 - 3 hours until the glue dries, after which the shaped unit is ready for use.

Rice. 20 Installation of Energoflex corner insulation element inside the building
Insulation of heating pipes underground
When deciding how to insulate heating pipes on the street when laying them underground in households, they usually use hard shells or place soft porous materials in polymer pipes of larger diameter. To thermally insulate pipelines with foam shells, proceed as follows:
- The pipeline lying on the surface is cleaned of dirt and shell segments are placed on it using a tongue-and-groove connection so that the upper and lower elements lie offset.
- As the fragments are laid, they are tied together with tape; for connection, you can also use special glue for foam plastic.
- After installation on the surface, the pipeline is placed in a trench on a pre-filled sand bed and covered with earth.

Rice. 21 Installation of hard shells
When thermally insulating heating pipelines, materials used in the construction industry are widely used; for ease of use on pipelines, they are produced in the form of cylindrical shells or hollow tubes of various lengths. To insulate external and internal heating pipelines, the most rational option is to use soft tubes made of polyethylene foam; the underground pipeline is usually insulated with hard shells made of polystyrene foam or polyurethane foam.
Pipe insulation technology
With the advent of thermal insulation cylinders, the insulation process itself has become very simple. Even an inexperienced beginner can do it with his own hands. To do this, it is necessary to select the correct shell according to the diameter of the pipe being insulated; its internal diameter must coincide with the external diameter of the pipeline. Pipes of small diameter are insulated with cylinders with a longitudinal dimension. The insulation procedure itself is quite simple - you need to put the material on the pipe, after which the cut ends are covered with protective tape or glued to each other.

It is necessary to ensure complete sealing of the seam. The joints of the two cylinders are connected to each other with the same tape or tape.
If thermal insulation of large diameter pipes is being carried out, then it is necessary to use cylinders of two or three parts. They are laid on the outer plane of the pipe so that they form a closed cylinder. The parts are fastened with tape, tape, wire or clamps. The distance between the fasteners is 30-50 cm. The joint between the two finished shells must be covered with tape or tape. The tightness of the joint between the parts of the insulation is ensured by a locking connection.
How to properly insulate pipes outdoors
The most dangerous areas prone to freezing in winter are those located outdoors. In principle, the technology for carrying out the thermal insulation process is practically no different from insulating pipes indoors. But, as mentioned above, many heat insulators lose their thermal insulation properties under the influence of sunlight and humidity, so pipes insulated outdoors are additionally covered with protective layers.
Algorithm of work carried out:
- If the pipes are metal, they must be painted or treated with bitumen mastic. If they are plastic, then you don’t need to do anything.
- Insulation is being installed. The thicker it is, the better. Using roll materials, installation must be carried out in several layers. The minimum thickness is 10 cm. For example, cylinders made of polyurethane foam are produced with a thickness of up to 720 mm.
- Fastening is done with foil tape.
- A protective coating is installed. This can be roofing felt laid in several layers, a galvanized steel casing, a plastic or rubber casing, an asbestos coating with a reinforcing metal mesh.

Today, plastic casings for small-diameter pipes are increasingly used as a protective layer. This is practically the same cylinder with a longitudinal section. There is no need to attach it to the insulation; simply tie it with wire in two or three places. Large diameter pipes are most often protected with metal casings. Often outdoors, combined insulation is used: roofing felt and a metal casing.
As you can see, there are a lot of insulation materials for pipeline insulation. All of them are quite effective, and the method of installation is very simple, which pleases home craftsmen who are accustomed to doing everything in the house with their own hands. And the appearance of heat-insulating cylinders on the market reduced this insulation process to a minimum.
Fittings and other pipeline elements
According to regulatory documentation, all communications related to heating networks should be equipped with shut-off and control valves and the necessary measuring devices.
In this case, their settings must correspond to the required parameters. For example, the pressure level in a protective device cannot exceed the calculated value by more than 10%. If the pipeline operates at reduced pressure, it is necessary to configure safety devices in accordance with the operating conditions of the facility.

An important point is to equip the protective valves with diverting elements so that it is possible to redirect the medium when the protection is triggered. Discharge communications must be insulated in case of severe frosts and equipped with a structure for draining condensate. All fittings must have appropriate markings on their bodies.
The marking contains:
- trademark of the manufacturing company;
- diameter size (DN) of nominal bore;
- standard value of pressure and temperature of the transported medium;
- direction of movement of steam or water;
- steel grade.
Basalt (stone) wool
More dense than glass wool. The fibers are made from the melt of gabbro-basalt rocks. Absolutely non-flammable, can withstand temperatures up to 900° C for a short time. Not all insulating materials, like basalt wool, can be in long-term contact with surfaces heated to 700° C.
Thermal conductivity is comparable to polymers, ranging from 0.032 to 0.048 W/(m K). High performance indicators make it possible to use its thermal insulation properties not only for pipelines, but also for the installation of hot chimneys.
Available in several versions:
- like glass wool, in rolls;
- in the form of mats (stitched rolls);
- in the form of cylindrical elements with one longitudinal slot;
- in the form of pressed fragments of a cylinder, the so-called shells.
The last two versions have different modifications, differing in density and the presence of heat-reflecting film. The cylinder slot and the edges of the shells can be made in the form of a tenon joint.

SP 61.13330.2012 contains instructions that the thermal insulation of pipelines must comply with safety and environmental protection requirements. Basalt wool itself fully complies with this instruction.
Manufacturers often resort to tricks: to improve consumer performance - to make it hydrophobic, more dense, and vapor permeable, they use impregnations based on phenol-formaldehyde resins. Therefore, it cannot be called 100% safe for humans. Before using basalt wool in a residential area, it is advisable to study its hygienic certificate.
Installation
The insulation fibers are stronger than glass wool, so it is almost impossible for its particles to enter the body through the lungs or skin. However, it is still recommended to use gloves and a respirator when working.
Installation of rolled sheets is no different from the method of insulating heating pipes with glass wool. Thermal protection in the form of shells and cylinders is attached to the pipes using mounting tape or a wide bandage. Despite some hydrophobicity of basalt wool, pipes insulated with it also require a waterproof, vapor-permeable shell made of polyethylene or roofing felt, and an additional one made of tin or dense aluminum foil.
How to insulate pipes in the basement with your own hands
You should think in advance about how and with what to insulate pipes in the basement of a private house, how to insulate a columnar foundation, and what thermal insulation material to use for various materials. Requirements for the materials used should take into account the ease of installation of insulation, long service life, water-repellent characteristics, environmental and fire safety of the material.
You should not have any difficulties in your work; anyone can handle this issue. No special skills or special tools are required to insulate pipes in the basement. Read the video instructions at the end of the article on this topic, and you will understand the stages of sewer insulation. The main thing is to be careful when performing all repair work.
Insulation with pressure and air
To prevent water pipes from freezing, you can use more specific methods. A pipe rupture occurs due to ice forming in it, so the main task is to eliminate the cause of the rupture. This can be achieved by keeping water under pressure - in this case it cannot change the state of aggregation, so ice will not appear in the system.
Unfortunately, it is not possible to use this method everywhere - it is only suitable for reliably preserving the system for the winter. This is not relevant for private houses, but dacha owners may well take advantage of such insulation.
To create pressure in the water supply system, the following algorithm is used:
- First of all, you need to check whether the system can withstand a pressure of 5 atmospheres. This information is indicated in the documentation attached to the water pipes. In addition, it is imperative to carefully inspect the pipeline for cracks or other defects that would make it impossible to maintain pressure in the system.
- The immediate start of work is to insert a submersible pump into the pipeline, which will provide pressure in the system. A check valve must be installed directly behind the pump.
- Then all that remains is to turn off the tap on the installed receiver and start the pump. When the required pressure in the system is reached, the pump must be turned off.
The insulation of water supply pipes using pressure is now complete, and the system can easily stand all winter without damage. To return the pipeline to normal condition, you will only need to bleed the air from the system.
Another rather unusual method of insulating a water supply involves using ordinary air as a heat insulator. It is located in the free space between the water supply main and the larger diameter pipes in which the former are laid. A layer of air will reduce the effect of frost on the pipes.
To increase the efficiency of air insulation, the pipes must be deepened into the ground at least a meter, since they are heated by the heat located in the thickness of the earth. It is not practical to install such a system at a shallower depth.
You need to understand that insulation of water supply pipes due to a layer of air is easiest to arrange when laying a new pipeline or replacing an old one. In addition, the cost of such a design is quite high, and installation is very difficult.
Types of garden aqueduct
There are two ways to lay a pipeline at a dacha - summer and seasonal (major). Each of them has its own advantages and disadvantages.
Summer option
The method of ground installation of a water supply system in summer cottages is used to organize watering of vegetable beds, berry bushes, and fruit trees. Ground water supply is used for supply to a bathhouse, summer kitchen, and garden house.
The seasonal water supply system is a ground loop with pull-in fittings at the branch point. If the site is used exclusively during the warm season, it is reasonable to lay pipes on the surface. Such a system can be easily disassembled for the winter to prevent theft of materials during the off-season.
On a note! To avoid damage to communications by agricultural equipment, summer water supply is laid on special supports.
The main convenience of a seasonal polyethylene water supply is its mobility. If necessary, the configuration can be changed in 10-15 minutes. It is enough to add or remove a few meters of pipe or run it in a different direction.
Irrigation system
Scheme
Temporary summer water supply at the dacha from HDPE pipes is assembled and disassembled with your own hands according to the principle of a children's construction set.
Typical diagram of a country water supply system
The network diagram is drawn up in relation to the detailed site plan. The drawing marks the location of green spaces, water intake points, a house, a shower, and a washbasin.
Important! Pipes are laid with a slope towards the water intake point. A drain valve is installed at the lowest point of the system
Capital system
If the site is thoroughly developed and used all year round, it is reasonable to spend time and money on installing a capital water supply system. The principle of connecting elements in this case does not change. The difference lies in the additional installation of compressor equipment and the closed arrangement. To install a permanent water supply system, communications are laid in trenches below the freezing depth of the soil.
Inserting HDPE pipes into the house
Insulation
The depth of soil freezing in different regions of the Russian Federation differs significantly. To avoid rupture of communications during sudden temperature changes, it is recommended to insulate them.
To insulate the capital water supply system from HDPE at a summer cottage, the following materials are used:
- Basalt insulation in the form of ready-made cylindrical modules.
- Fiberglass sheet in rolls. You will need to purchase additional roofing material to protect the warm layer from getting wet.
- Expanded polystyrene. Reusable folding modules of two halves, which are used repeatedly, are assembled simply and quickly.
Insulation for pipes made of foamed polyethylene According to statistics, the depth of soil freezing in winter in Russia exceeds 1 meter. For clay and loam in Moscow and the region this is...
On a note! Water under high pressure does not freeze. If a receiver is installed in the system, there is no need for additional thermal insulation of the water supply system.
In capital construction, when laying a pipeline to a shallow depth, a heating cable is laid parallel to the system and connected to a grounded source of electricity.
Defrosting water supply and sewerage pipes Russia is located in a harsh climatic region, so in winter and early spring there is a risk...
How to choose?
Manufacturers offer several types of polyethylene pipes to choose from. First of all, products are distinguished by the type of transported medium.
For the production of gas pipes, special additives are used that change the composition of water. Gas pipes with yellow markings are strictly prohibited for use in the plumbing system!
To assemble the pipeline underground, two types of polyethylene are used:
- HDPE PE 100, manufactured in accordance with GOST 18599-2001. The diameter of the products is 20 to 1200 mm. Such pipes are made black with a longitudinal blue stripe along the entire length.
- HDPE PE PROSAFE, produced in accordance with GOST 18599-2001, TU 2248-012-54432486-2013, PAS 1075. Such pipes have an additional mineral protective shell, 2 mm thick.
For the main line, blanks with a diameter of 40 mm are selected. For secondary - 20 mm or 25 mm.
This is interesting: Rimless toilets - pros and cons, reviews from owners
Foamed polyethylene
The temperature range at which the use of high-density polyethylene foam is allowed is from -70 to +70 °C. The upper limit is not compatible with the maximum temperature of the heating pipe, usually accepted in calculations. This means that the material is of little use as thermal insulation for pipelines, but can be used as an insulating layer over a heat-resistant one.
Polyethylene foam insulation has found virtually no alternative use as protection against freezing of water pipes. Very often it is used as a vapor barrier and waterproofing.
The material is produced in the form of sheets or in the form of a flexible thick-walled pipe. The latter form is more often used, as it is more convenient for insulating water pipes. Standard length is 2 meters. Color varies from white to dark gray. There may be a coating of aluminum foil that reflects IR radiation. The differences relate to internal diameters (from 15 to 114 mm), wall thickness (from 6 to 30 mm).

The application ensures the temperature on the pipe is above the dew point, which means it prevents the formation of condensation.
Installation
A simple way with worse vapor barrier results is to cut the foam material along a small depression along the side surface, open the edges and put it on the pipe. Then wrap it along the entire length with mounting tape.
A more complex solution (and not always feasible) is to turn off the water, completely disassemble the insulated sections of the water supply system and put on solid sections. Then put everything back together. Secure the polyethylene with ties. In this case, only the junction of the segments will become a vulnerable point. It can be glued or also wrapped with tape.