Few people know that the choice of a chimney system directly depends on the temperature of the exhaust gases during fuel combustion in the boiler. Ignoring this important point leads to the fact that soon after assembling the chimney, the metal pipe or brick structure crumbles, so repairs and financial costs cannot be avoided. To understand why this happens, you need to understand the operating features of gas boilers.
Important nuances
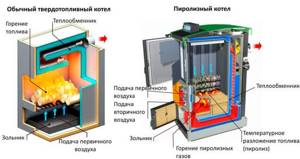
In solid fuel boilers, fuel burns at a high temperature, so the exiting gases have a high temperature (usually about 300 degrees, although the values may vary up or down). The situation is completely different with gas boilers.
Modern gas equipment used for space heating has an important feature - the temperature of the combustion products leaving does not exceed 120 degrees, and sometimes is significantly lower than this mark. This is due to the desire of manufacturers to increase the efficiency of gas boilers. This desire also has its negative sides. The lower the temperature of the exhaust gases, the more condensate forms inside the system. Condensate contains aggressive substances and therefore has a destructive effect even on stainless steel pipes. In general, unpleasant consequences can be prevented if you take into account several important nuances.
The temperature of the exhaust gases directly depends on the radiator settings. If heating radiators heat up to a temperature of 65 degrees, the combustion products will have a low temperature. When using a heated floor system, in which the water is heated to only 35 degrees, the temperature of the gases will be even lower and there will be more condensation.
Installing a gas boiler
According to statistics, of the total number of individual boilers operated in Russia, both near Moscow and in remote regions, about half run on gas, a third on diesel fuel, approximately 10% on electricity and approximately 5% on solid fuel. In other words, gas boilers predominate. It must be said that there are many such boilers supplied to the market, and different ones, and we have already written about this more than once. Therefore, now we will talk about choosing a gas boiler and its safe operation.
Heating boilers running on propane and natural gas
When choosing a place for a boiler when designing a house, you should be guided by the requirements of SNiP II-35-76 “Boiler installations” and the set of design rules SP 41-104-2000, which contain standards for organizing the operation of such systems.
The room for installing the boiler must be at least four square meters; the height of the ceilings in it is at least 2.5 m, the width of the external door is at least 80 cm. A window is required for natural light and an opening for the flow of outside air. When designing and constructing chimneys, to ensure draft and prevent blowing, it is advisable to place the upper cut of the chimney above the roof ridge. The chimney must have a cross-section corresponding to the equipment being installed (for a boiler with an open combustion chamber and a power of up to 30 kW, a pipe with a diameter of 130 mm is sufficient; for a boiler with a capacity of 40 kW, a pipe with a diameter of 170 mm is needed).
It is necessary to arrange a natural ventilation channel in the upper part of the room, and also have a power supply located on a separate circuit breaker. According to current building codes, in the room where the propane boiler is located, a gas analyzer should be installed to warn of a leak, and an emergency solenoid valve for emergency shutdown of the gas supply. All equipment is subject to annual maintenance by specialists in order to reduce the risk of emergency situations to a minimum.
The power of a gas boiler must be calculated at the stage of designing a house, since the diameter of the chimney and a number of other parameters of various engineering systems depend on it. Power is determined at the rate of: 1 kW per 10 sq. m with a ceiling height of 2.5 m. That is, for a house with an area of 100 sq. m. m you need a device with a power of at least 10 kW. Heating tap water takes approximately 25% of the power. But this calculation is very approximate, in practice it does not always pay off, so it is better if the equipment is selected by specialists who can calculate the heat loss of a house using the appropriate methods.
Gas boiler using propane and natural gas: selection criteria
When choosing a gas boiler, it is necessary to take into account a number of factors. First of all, this is the material from which it is made. Gas boilers can be either steel or cast iron. Steel is approximately two times lighter than cast iron of the same power and capacity. However, the service life of steel is 10–15 years, while cast iron lasts up to 50 years. Again, steel can rust, especially if the system is turned off or the temperature drops suddenly. Then condensation settles on its surface, which promotes corrosion. For large houses (over 400 sq. m), experts recommend cast iron devices.
It also makes sense to pay attention to the resistance value of the combustion chamber. In fact, this is the excess pressure at which gas should be supplied to the furnace. By this indicator you can judge how perfect the boiler firebox is. A good device has a combustion chamber resistance of 1–1.5 mBar, while a not very good one can reach 8 mBar. That is, imperfect fireboxes require higher gas pressure.
In our conditions, boilers with fan rather than atmospheric burners work better. However, a boiler with a fan burner is more expensive.
Stable and long-term operation of gas equipment largely depends on the quality of the power supply. Experts recommend using a voltage stabilizer or surge protector. There are circuit breakers that protect against overvoltage in the network - they simply turn off if the voltage exceeds a certain value. Sometimes a differential circuit breaker (RCD) is installed, which protects equipment and people from a short circuit to the housing. Therefore, the boiler must be grounded and connected to a separate circuit breaker.
But don't panic when your equipment shuts down due to power outages. The absence of voltage in the network does not cause the gas boiler to block; after the power supply is restored, its systems automatically return to the desired operating mode. Thanks to the thermal inertia of the house in winter, the heating system is not in danger of freezing for several tens of hours.
For economical gas consumption, it is better to choose equipment with an electric ignition, rather than with a piezo ignition, the constantly burning ignition wick of which “awaits” for the boiler to be put into operation and wastes gas. In appliances with electric ignition, the burner ignites automatically when the hot water tap is opened and goes out after it is closed. In order to save money, special programmers are used that allow rational consumption of fuel. In short, when choosing, you need to take into account many little things and technical “bells and whistles” that are sold as a set or can be connected to this model. An ionization combustion control device that allows you to instantly block the gas supply if necessary. When using ionization control with electric ignition, there is no constantly burning pilot wick, which allows you to save even more gas. It is beneficial to use such controllers when working with liquefied gas, but it is not recommended to use them in dispensers installed in places with high humidity.
Remember that the gas boiler must be installed with a chimney and in a well-ventilated area with a separate exit to the street. It is necessary that the door to the room opens freely: for the wick and burner to burn, an influx of oxygen is required. Depending on the model and size, the device should be installed at a distance of 30–50 cm from the walls. The chimney must have a minimum of elbows and bends, and its internal diameter cannot be less than the diameter of the boiler neck.
In modern gas-fired devices, the outlet temperature of the flue gases is low: 100–120°C. When gas burns, water vapor, carbon dioxide, sulfur dioxide and other chemical compounds are formed, which cool down as they rise up the chimney. When the temperature drops to the dew point (55°C), the water vapor present in the gas mixture condenses. As a result, a very aggressive mixture of acids is formed, which, flowing down, quickly corrodes the walls of the chimney. The exhaust gases are usually cooled to the “dew point” temperature at a height of 4–5 m from the boiler neck. Therefore, chimneys that are longer are made of stainless steel and insulated.
Gas boilers are divided into floor-mounted and wall-mounted. Wall-mounted ones can be called mini-boiler rooms, since their body contains not only a burner and a heat exchanger, but also circulation pumps, an expansion tank, a pressure gauge, a thermometer and a security system. Gas boilers come with natural and forced ventilation. Those in which the gas is removed using a built-in fan are ideal for rooms without a chimney, since combustion products can be discharged through a regular hole in the wall. But such devices have a maximum power of 24 kW and are available only in a wall-mounted version. Gas condensing boilers with pulse combustion that have recently appeared on our market also do without a traditional chimney.
Propane and natural gas boiler: safety issues
Regulatory documents on the operation of boiler houses and the safe operation of boilers contain a number of requirements and restrictions that exclude or minimize emergency situations. Since complete combustion of gas is possible only at a certain ratio of air and fuel, one of the conditions is the organization of air flow to the combustion chamber. In a boiler of approximately 20 kW, for complete combustion of 2.5 cubic meters of gas per hour (this is exactly what is required to achieve the rated power), an air flow of approximately 30 cubic meters per hour must be provided. If there is not enough air, the fuel does not burn completely and as a result, carbon monoxide is formed, which is dangerous to human health. Burning gas with a lack of air increases fuel consumption.
During operation, the most dangerous thing is the spontaneous extinguishing of the burner and, as a result, the flow of gas into the room. The reasons for the attenuation may be: a drop in gas pressure in the network below the permissible level, a lack of draft in the chimney, a cutoff of the supply voltage, or the igniter going out. Such situations require immediate interruption of the gas supply to the burner.
In modern heating devices, a number of automatic devices are designed for this: a flame detection sensor, a draft control sensor, a boiler blocking device when the gas is turned off or the pressure drops below the permissible level, a shutdown device when there is no power supply, a shutdown device when the coolant volume decreases. All these devices are part of the security system.
The problem of ensuring the safe operation of a gas boiler should be considered within the framework of the operation of the entire heating system. It also includes pipelines, pumps, shut-off and control devices, automation and control equipment that create optimal conditions for reliable and trouble-free operation of the equipment.
A modern propane gas boiler must have a whole set of control and safety devices. This kit includes an electronic self-diagnosis system, ionization control for the presence of flame, a pump blocking protection system, and a protective thermostat against water overheating in the primary heat exchanger. There must be a safety valve in the heating circuit, an anti-freeze protection system in the heating circuit (triggered when the coolant temperature drops to 5°C), as well as a system for reducing scale formation.
The list, as we see, is impressive, and if the homeowner had to buy it all, install it, and even make it function, he would hardly be able to cope. Fortunately, gas boiler equipment manufacturers take care of protective systems. Most leading companies equip their equipment with all of the above devices. And when a digital programmer is connected to a gas boiler, the owner of the house has the opportunity not only to remotely control the heating system, but also to automatically diagnose its components and identify faults with information displayed on the display, which also increases operational safety.
When selecting a gas heating device for a country house, it is necessary to take into account three values: heat loss of the building; the amount of heat required to prepare hot water (number of water points); the amount of heat required to heat the supply air (in the presence of forced ventilation). The sum of these values determines the power of the device. A reserve of 10–15% of thermal power should be provided. Exceeding the required thermal power leads to extremely negative consequences: increased cost of the heating system; inefficient operation of the boiler system; formation of condensation in chimneys; failures and rapid wear of automation system elements, etc.
Heating with propane and natural gas
All modern household boilers can operate on both natural gas (methane) and liquefied gas (propane-butane). They are divided into wall-mounted thermoblocks and floor-standing boilers. Modern wall-mounted gas thermoblocks, in turn, are divided into water-heating thermoblocks and condensate modules. The latter have a higher energy efficiency and are therefore more economical to operate. The thermal power of conventional thermoblocks ranges from 8 to 32 kW, condensate - from 4 to 60 kW. One of the main advantages of wall-mounted thermoblocks is their compactness and the absence of the need to organize a separate room for the boiler room (they are often installed in the kitchen as one of the elements of wall furniture).
Floor ones are made of steel and cast iron. The power range is from 15 to 150 kW. To install such boilers, a separate room is required. One of the advantages of cast iron devices is greater corrosion resistance and the ability to order in disassembled form, which allows it to be delivered through narrow doorways to the boiler room. Modern devices are distinguished by a high level of automation: weather-dependent programmable operating modes; a set of gas safety measures; a set of measures to prevent failure, etc.
Choosing a gas boiler for heating and hot water supply is a responsible task that must be solved by specialists. But the consumer should know some simple selection rules that will not replace design calculations, but will protect against gross mistakes:
- It is reasonable to combine the power for heating with the necessary power for heating water;
- a double-circuit boiler (preparing hot water in the second circuit of the boiler heat exchanger or in a secondary heat exchanger) is cheaper, with a boiler - more expensive, but more comfortable to use;
- there is no point in taking a device with a double or triple power reserve; it is best if its power is 30% more than the calculated load;
- wall-mounted gas appliances with a closed combustion chamber and a special “coaxial” pipe (combustion air from the street, smoke to the street) are produced with a power of 14 to 45 kW and can be combined in a cascade of up to 500 kW;
- a modern device can be equipped with an outside temperature sensor for weather-dependent control and a room temperature programmer;
- when choosing, it is better to give preference to a device with a self-diagnosis function;
- the use of wall-mounted condensate devices is justified only if “warm floor” is used as a heating method;
- in simple heating systems (1–2 circuits) it is more profitable to use a wall-mounted device, in complex systems (3 circuits or more) - a floor-standing one; wall heat exchangers are made of copper, floor heat exchangers are made of cast iron or steel;
- in areas where electricity is often cut off, you can use special converters that will ensure autonomous operation of the device for up to three days;
- devices manufactured in European countries and having Russian and European certificates of conformity are safe for humans and equipped with all the necessary levels of protection from adverse external factors, especially from the penetration of gases into the room;
- It is better to give preference to equipment from a brand that has proven itself well in the region, and from a company that has trained service engineers.
Vadim SAKHAROV
When choosing a chimney, consider the boiler power
When choosing a chimney system, it is necessary to take into account the power of the gas boiler . The higher the power, the higher the combustion temperature of the fuel will be. This is sure to be reflected in the escaping gases. The power value helps to choose the correct pipe diameter and length. For example, a 300 kW boiler requires a pipe with a diameter of 150 mm.
Typically, the instructions for use indicate not only the technical characteristics of the heating equipment, but also provide recommendations for the selection and installation of a chimney system. If necessary, seek help from a specialist if you yourself cannot correctly calculate the optimal parameters of the chimney pipe.
Properties of wood
Different tree species have the following physical properties:
- Color – it is influenced by climate and wood type.
- Gloss depends on how the heart-shaped rays are developed.
- Texture – related to the structure of wood.
- Humidity is the ratio of removed moisture to the dry mass of wood.
- Shrinkage and swelling - the first results from the evaporation of hygroscopic moisture, swelling - the absorption of water and an increase in volume.
- Density is approximately the same for all tree species.
- Thermal conductivity - the ability to conduct heat through the thickness of a surface, depends on density.
- Sound conductivity - characterized by the speed of sound propagation, depends on the location of the fibers.
- Electrical conductivity is resistance to the passage of electric current. It is influenced by breed, temperature, humidity, direction of fibers.

Before using wooden raw materials for specific purposes, first of all, they become familiar with the properties of wood, and only then does it go into production.
Which material should you prefer?
Nowadays, stainless steel chimneys are very popular on the market. They are used for boilers of various types, although this approach is fundamentally wrong. If you plan to install a gas boiler , you need to decide what material the chimney should be made of. Don't rush to buy metal pipes. They are excellent for solid fuel boilers, as they can easily withstand high temperatures.
For gas boilers, which are characterized by low temperatures and large amounts of condensate, it is preferable to choose plastic or polymer pipes. Their main advantage is good resistance to moisture. Because of this, they usually last longer than metal chimneys. FuranFlex pipes are excellent for gas boilers, which are characterized by excellent resistance to aggressive substances, strength and durability.
If you use a gas-wood combination boiler , you will have to abandon the use of FuranFlex. The fact is that polymer pipes are produced in two versions - for high and low temperatures (solid fuel and gas boilers, respectively). Polymer stockings cannot be used effectively at high and low temperatures at the same time.
What factors influence the burning temperature of wood?
The combustion temperature of wood depends on the tree species that were used to prepare fuel. The key factors are the grade, moisture content of the wood and the volume of air mixture supplied to the fuel compartment of the stove, fireplace or boiler.

Humidity level
Fresh firewood has a moisture level ranging from 42 to 66%, the average being 54%. The combustion temperature of such fuel will not be high, since the heat produced is spent on evaporating excess moisture. As a result, this can lead to a decrease in the heat transfer of the fuel material.

You can achieve maximum temperature values when burning wood fuel in the following ways:
- to heat the house, organize hot water supply and prepare food, use double the volume of fresh firewood, which will entail an increase in the cost of purchasing fuel and maintaining the heating system;
- Properly prepare and dry freshly cut wood - cut the logs into logs and store them under a protective shed for drying in the open air. The optimal drying time is 12 months;
- carry out a wholesale purchase of ready-made, well-dried fuel.
Of course, the maximum specific heat of combustion of wood is possible only by implementing the latter method.
Metered air supply
To ensure complete combustion of the fuel and achieve a high temperature, an excess air supply must be provided in the fuel compartment.
Ideal combustion of wood can be described by the following formula:
C+2H2+2O2=CO2+2H2O+Q (heat)
When oxygen is introduced into the fuel chamber of a wood stove, the combustion process produces hydrogen and carbon (left side of the formula), which release heat, steam and carbon dioxide (right side of the formula).
In order for the fire temperature to be maximum, the volume of the air mixture supplied to the firebox must be 130% of the volume required for burning wood.

Closing the smoke dampers leads to a decrease in the volume of incoming air and the formation of carbon monoxide. As a result, the combustion temperature drops and the heat transfer of the fuel decreases.
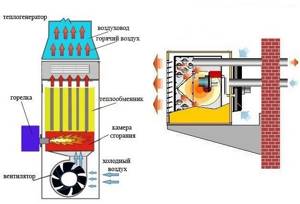
Modern solid fuel wood boilers are additionally equipped with heat accumulators. They allow you to accumulate excess thermal energy, which is generated during the combustion process with high efficiency and good chimney draft.
In some cases, it is enough to purchase a heat generator unit with forced air circulation.
The design of wood-burning stoves does not allow saving fuel, since the entire volume of thermal energy is immediately spent on heating the room or heating water. However, an increase in draft in stoves can be achieved by increasing the intensity of combustion of wood, as well as its calorific value.
Also, the combustion temperature depends on the design features of the heating devices. For the manufacture of boilers and furnaces, wear-resistant materials with varying levels of thermal expansion are used.

In a large brick heater, wood fuel burns slowly and completely. Metal devices ensure an accelerated burning process of wood. They are characterized by low ash content and high heat transfer.
Features of repair work to restore the chimney
If repair of a gas boiler , or rather its chimney system, is required, the most effective solution would be to use FuranFlex technology. When installing a polymer stocking, there is no need to perform dismantling work. The FuranFlex pipe is inserted into the chimney from the inside, and after hardening it serves as support and protection. It prevents further destruction, while the material itself has excellent performance characteristics. The main thing is to choose the right type of material, but our employees are always ready to help in resolving this issue. They will advise you on all your questions.

What kind of wood is best to heat the stove?
When choosing the best option for lighting a fireplace, heating a room, cooking or lighting a fire, you should take into account the combustion qualities of different types of wood. You can use combinations, follow the ignition sequence and gradually introduce other types of logs into the burning firebox.
For home heating
If the stove heats a small room, then fruit or coniferous wood is suitable (for closed type solid fuel boilers). Fireplaces love alder, linden, oak and birch. For large areas, oak, birch, alder, and larch are suitable.
After birch, pine or cedar, alder or aspen will help clean the chimney from soot. They are advised to be added to the firebox after combustion is complete, as well as mixed with oak logs, birch or acacia.
For the bath
A real find for sauna lovers is linden wood: its delicate aroma has healing properties, and the high heat will quickly heat the steam room and retain heat. To maintain combustion longer, birch logs or aspen are added to the linden tree.
Alder gives a pleasant aroma, burns with great heat output, saves time on kindling, and has been used since ancient times by wealthy boyars and merchants for heating.
A hot sauna will be created by birch, alder and ash firewood, as well as logs from fruit trees
The sauna cannot be heated very much on pure aspen, but if you add it to birch or alder logs, the effect will be excellent. The air will receive disinfecting properties, the chimney will be cleared of soot.
Birch wood is used most often by true fans of the Russian bath. This firewood produces stable heat, retains heat for a long time, does not smoke, and gives the steam room the atmosphere of a birch grove. It is worth removing the bark from a birch tree that is not dry enough before burning it, but it is better to start with oak or ash.
Ash firewood is perfect for traditional black-style sauna fires.
For barbecue
For the perfect barbecue, gourmets choose fruit woods in combination with linden and birch chips. If you have veal or fish on the grill, there is nothing better than linden and birch firewood. There are also lovers of the aroma of fruit trees: plums, cherries, apricots and pears.
Chefs in Italian restaurants always use oak firewood to cook real pizza in their heat. In this case, an apple or pear tree can replace oak. And lamb meat requires, according to technology, the presence of alder, linden, plum or cherry smoke.
Suitable for poultry meat: cherry, plum, apple tree and grapevine; for pork and lamb: cherry, birch and linden; and for veal and fish: birch, linden, pear, plum and peach
Many recipes with poultry, rabbit and pork include cherry smoke. Peach, apple and grapevine also add piquancy.
Combustion
After all, the chemical action of oxygen should give soot particles a brighter color, even white. However, this phenomenon is understandable, since the size of the particle affects its temperature, and the smaller it is, the lower the temperature.
Therefore, burning small particles of wood have exactly the same temperature as the gas surrounding them.
Also, it should be noted that the heat transfer of each type of wood is different, and in order to find out in more detail there is a special table that shows the thermal conductivity indicators for each type of wood.
What is better to heat the stove: with wood or briquettes, see the following video:
Fuel procurement
It is a mistake to think that any wood can be put into a stove. That is, you can load it, but what effect will it give when burned? To obtain maximum heat transfer, wood for the stove must have a humidity of no higher than 25%, maximum 30%. During the combustion of raw wood, the lion's share of thermal energy will be spent on the evaporation of moisture, in addition, soot will be intensely released, settling on the inner walls of the flues.
The moisture content of freshly cut wood ranges from 45 to 55% depending on its species. It is believed that drying firewood to the required humidity requires storage in a barn or under a shed for 1-1.5 years. The logs must be prepared so long that they fit into the firebox with a gap of several centimeters. It wouldn’t hurt to make some of the firewood shorter and thinner, so it will be more convenient to stack it for kindling.
The coal used to fire the stove also requires close attention. If it is briquetted anthracite, then there will be no problems, but fuel with a high content of dust fraction must be sorted. Otherwise, dust and coal fines will partially spill through the grates into the ash pan and go to waste. In this case, the other part will block the passage of air through the grate, and the combustion process will proceed sluggishly. You can make homemade briquettes from fine coal mixed with dust.
Exotic
As you know, there are quite a lot of tree species, and to list all their types, you could write a thick book, or even more than one.
Therefore, in addition to the varieties listed, it is worth touching on at least a few more:
- Elm. It produces a lot of smoke, is difficult to split and takes a long time to ignite.
- Poplar. Like firewood for a stove - nothing at all. They prick easily, just scatter sparks and burn quickly.
- Beech. It is also difficult to light and split, but can be used raw.
- Fir. Like poplar, it is easy to prick and ignite, but you cannot do without a lot of smoke and sparks.
- Sycamore. Wood is easy to kindle, but difficult to split.
What is the combustion process
An isothermal reaction in which a certain amount of thermal energy is released is called combustion. This reaction goes through several successive stages.
In the first stage, the wood is heated by an external fire source to the ignition point. As it heats up to 120-150 ℃, the wood turns into coal, which is capable of self-ignition. Once the temperature reaches 250-350 ℃, flammable gases begin to be released - this process is called pyrolysis. At the same time, smoldering of the top layer of wood occurs, which is accompanied by white or brown smoke - these are mixed pyrolysis gases with water vapor.
At the second stage, as a result of heating, the pyrolysis gases ignite with a light yellow flame. It gradually spreads over the entire area of the wood, continuing to heat the wood.

The next stage is characterized by ignition of the wood. As a rule, for this it should warm up to 450-620 ℃. For wood to ignite, you need an external heat source that is intense enough to rapidly heat the wood and speed up the reaction.
In addition, the rate of firewood ignition is influenced by factors such as:
- craving;
- wood moisture;
- cross-section and shape of firewood, as well as their quantity in one stack;
- wood structure - loose firewood ignites faster than dense wood;
- placement of the tree relative to the air flow - horizontally or vertically.
Let's clarify some points. Since wet wood, when burning, first evaporates excess liquid, it ignites and burns much worse than dry wood. Shape also matters—ribbed and jagged logs ignite more easily and quickly than smooth, round ones.
The draft in the chimney must be sufficient to ensure the flow of oxygen and dissipate thermal energy inside the firebox to all objects located in it, but not to blow out the fire.
The fourth stage of the thermochemical reaction is a stable combustion process, which, after the outbreak of pyrolysis gases, covers all the fuel in the furnace. Combustion goes through two phases - smoldering and burning with flame.

During the smoldering process, the coal formed as a result of pyrolysis burns, while gases are released rather slowly and cannot ignite due to their low concentration. The condensation of gases as they cool produces white smoke. As wood smolders, fresh oxygen gradually penetrates, causing the reaction to further spread to the rest of the fuel. The flame occurs as a result of the combustion of pyrolysis gases, which move vertically towards the outlet.
As long as the required temperature is maintained inside the furnace, oxygen is supplied and there is unburnt fuel, the combustion process continues.
If such conditions are not maintained, then the thermochemical reaction enters the final stage - decay.
Types of firewood
There are no bad or good types of wood for lighting a stove. In fact, it all depends on the design and purpose of the heating device.
Good firewood is characterized by high heat transfer and a high degree of flammability
Conifers
The resins in softwood fibers do not allow them to be used for open fireplaces. Dense wood burns with the release of thick smoke, and there is a danger of cracking and scattering of embers.
Pine, spruce and larch are often used to fire closed stoves. They burn with great energy intensity and emit a healing aroma. Among the disadvantages, it is worth noting a large amount of soot and soot, as well as a fire hazard.
When burned, logs from coniferous trees emit a large amount of smoke, so they are practically not used for heating houses.
Fir and cedar have a less dense structure and are difficult to extinguish. With good drying, combustion occurs evenly and heat is retained for a long period.
Hardwood
The epithets that the people bestowed on hardwood logs (royal, merchant, boyar) speak more than eloquently of their valuable qualities.
The most expensive option is middle-aged oak wood: it burns slowly and evenly, there is little waste, the aroma is subtle, pleasant, and the heat is very strong. The last property is used by Italians to obtain truly thin, crispy pizza. Despite the high price, oak logs are consumed more slowly than other hardwoods.
Birch forest is very popular as wood for firewood. Pathogenic bacteria disappear from the air, and colds are cured. The bark, due to its high tar content, allows the core to burn evenly and for a long time without leaving waste. Birch chips are often used to make ignition material. The disadvantage is that it cannot be stored for a long time, and after a couple of years the firewood turns into dust. Effective drying requires removing the bark.
Birch is known for its high heat transfer, but this type of log quickly loses its properties, and within two years after cutting the log becomes rotten
Aspen has the ability to produce a high flame and at the same time clear the chimney of soot residues. It burns slowly and does not burn for long, so it is suggested to combine it with birch or oak logs.
Alder was revered in Rus' as the best option for heating a home. There is a lot of heat, no smoke, and the aroma disinfects the air in the house.
Alder firewood is rightly called “royal”: the logs flare up very quickly, and in terms of heat transfer they are only slightly inferior to birch and oak
Linden firewood has a high combustion temperature and a persistent healing aroma. When properly dried, they provide versatile wood for lighting fireplaces, stoves, heating baths, saunas, and are often used in smokehouses. Firewood burns slowly, but retains heat for a long time.
Finding poplar logs will not be a problem. An extremely uneconomical option, but it easily forms a good flame.
Willow is a budget option. It burns well, but quickly. Doesn't smoke, no smoke. It’s not difficult to get, it takes longer to dry than birch, but it’s also much cheaper.
Fruit trees
Apple and pear trees under 10 years of age can be compared in terms of quality characteristics with oak. They burn well, have high energy intensity, no soot, little waste, and do not smoke. If you cut down fruit trees in late autumn or winter, when there is no sap flow, it will be easier to dry them.
Apple wood does not emit a lot of smoke and adds a wonderful aroma, which is why it is most often used in fireplaces
Cherries, like all stone fruits (peach, apricot), contain a large amount of juice and essential oils under the bark. It burns slowly and poorly, smokes, and does not produce good heat. Drying such firewood is difficult and takes several years. Storing longer than 20 months is problematic - pests will appear. Used for heating baths and cooking.
The nut takes a long time to flare up, but also burns for quite a long time. Wood is difficult to dry and split.
Calorific value table for logs
The calorific value is calculated based on the density of the wood and its moisture content.
| Dry firewood | Calorific value, kWh/kg | Calorific value, MJ/kg | Calorific value, MWh/storage meter | Bulk density, kg/dm3 | Density, kg/storage meter |
| Oak | 4,2 | 15 | 2,0 | 0,67 | 470 |
| Birch | 4,2 | 15 | 1,9 | 0,65 | 450 |
| Ash | 4,2 | 15 | 2,0 | 0,69 | 480 |
| Alder | 4,3 | 15 | 2,0 | 0,66 | 465 |
| Apple | 4,0 | 16 | 1,8 | 0,67 | 465 |
| From larch | 4,3 | 15,5 | 1,8 | 0,59 | 420 |
| Pine | 4,3 | 15,5 | 1,6 | 0,52 | 360 |
| Spruce | 4,3 | 15,5 | 1,4 | 0,47 | 330 |
| Aspen | 4,2 | 16 | 1,5 | 0,49 | 510 |
| Nut | 4,0 | 17 | 1,5 | 0,43 | 600 |
| Willow | 3,8 | 17 | 1,4 | 0,46 | 460 |
Primary requirements
The best firewood for heating stoves is dry. Humidity should be within 20%. This is the main requirement. The calorific value of wood depends very much on its moisture content.
Dry wood flares up and burns well, emits more heat, and smokes less. The logs should not be rotten or saturated with water. Water logs are not suitable for heating stoves.
Good firewood leaves little ash. It is advisable to harvest wood in late autumn or winter, when sap flow stops and the wood is denser.
The size of firewood for the stove depends on the size of the firebox, usually 35-40 centimeters long. The thickness is medium, thick logs split. Small logs are easy to light. They also burn quickly, which must be taken into account when preparing them.

Flammability
An important role for the appearance of fire is played by the power of the heating source, the cross-section of the wood, the speed of the air flow and the density of the material.
Light wood with high porosity can cause a flame to appear as quickly as possible. As for wet wood, it ignites more slowly because it must dry before an open fire appears.
Expert advice: choose dry places to store firewood, away from moisture. Otherwise, they will take a long time to dry in the oven.
Also, combustion will depend on the shape of the logs, since round shapes of wood will not burn as well as rectangular logs with a small cross-section, sharp ribs and a developed side surface. Unplaned wood from birch logs is more likely to ignite than smooth wood.
A very important condition for the combustion of any type of wood is a normal flow of oxygen. In some respects, wood combustion is even superior to coal combustion.
About the fire:
There will be no firewood - no fire! This means that in order for the fire to burn for a long time, preparation is needed. Or rather, the preparation of firewood. The bigger, the better. Having a little experience of spending the night in the forest, you can know in advance the approximate amount of firewood needed. Of course, you can mathematically calculate how much wood is needed to keep a fire going for a certain number of hours. Convert knots of one thickness or another into cubic meters. But in practice, such a calculation will not always work. There are a lot of factors that cannot be calculated, and if you try, the scatter will be quite large. Only personal practice gives more accurate results.
Strong wind increases the burning rate by 2-3 times. Humid, calm weather, on the contrary, slows down combustion. A fire can burn even during rain, but for this it is necessary to constantly maintain it. When it rains, you shouldn’t put thick logs on the fire; they take longer to burn and the rain can simply put them out. Don't forget, thinner branches flare up quickly, but also burn out quickly. They should be used to light thicker branches.
Before I talk about some of the properties of wood during combustion, I want to remind you once again that if you are not forced by the need to spend the night in close proximity to a fire, try to burn a fire no closer than 1.5-2 meters from the edge of your bed.
Most often we come across the following tree species: spruce, pine, fir, larch, birch, aspen, alder, oak, bird cherry, willow or willow. So, in order.
Weeds

Now is the time to consider alternative types of natural fuel that can be used to fuel a campfire.
Sometimes it happens that there is no dead wood near the camp, but conscience does not allow green trees to be cut (foresters do not allow them), or there is a decent distance to them. Then you have to get out with the help of herbaceous plants. As a rule, if the area is more or less wild and open, such large species of grass as:
- Sagebrush;
- Burdock;
- Thistles, thistles and others like them;
- Blooming Sally;
- Large umbelliferae: hemlock, kupir, angelica, hogweed (including the notorious giant one);
If the area is marshy or borders water, then the above list is supplemented by the following plants:
- Cane;
- Rogoz;
In rural areas, the following options are possible:
- Straw;
- Sunflower stems;
The best thing, of course, is thick, non-hollow stems (wormwood, burdock, sunflower). All this nonsense usually dries out in the fall, stands all winter, spring and the first third of summer, then - as the green herbs grow, most of last year's dry stems rot and fall off. However, you can collect a certain amount of such “wood” for a fire at any time of the year.
Dry weeds burn quickly and hotly; they actually do not form coals, because their density is very low. For a full-fledged night fire you will need ten cubic meters and a specially trained farmhand who will constantly throw this thing into the fire. It is also possible to use ingenuity: twist the grass into dense sheaves with twine. It will burn longer.
But in order to light a mini-bonfire, for example, for boiling water, weeds are quite suitable. The only thing you need is a few stones. So that you can lay out a small fireplace and not radiate heat into space in vain, thereby increasing the efficiency of the fire.
Next are the parameters of weeds as fire fuel (during the calculations, straw indicators were used as the initial parameters).
- Fire power: 0.1de.
- Calorific value: 378 kWh/m³.
- Combustion temperature: 800-900 °C.
- Burning time: very short.
- Flame: even, with a characteristic crackling sound. It smokes, the less dry the material, the stronger it is.
- Coals: does not actually form.
- Difficulty of lighting: extremely low, dry weeds are excellent kindling.