Today, air heating systems for a private home are of interest to many people. Manufacturers of these systems present them as something new, effective and inexpensive. Is this information true? Let's figure it out
In reality, an air heating system in a private house does not represent anything good, since there are many more profitable and convenient options. Owners of private houses or those planning to build them are advised to become interested in the topic and check information about the operation of such systems.
However, so that the thesis about the inexpediency of using an air heating system in a private house is not unfounded, it is worth highlighting the disadvantages and advantages of these systems, as well as the places where their use is justified.
System installation features
If the calculations are carried out at a high professional level, and the design of the cottage air heating system is drawn up, you can carry out the installation yourself.
For this you will need:
- heating device;
- air ducts;
- fan;
- gratings;
- fasteners;
- tool for working with air ducts, etc.
A gas generator is usually used as a heater as the most cost-effective option. Air ducts can have a rectangular, square, round or oval cross-section.
Typically, suitable designs can be ordered from a company that manufactures ventilation systems.
The diagram shows the elements of the air heating system, which will allow installation of air ducts in strict accordance with the design documentation
Typically, air ducts are made of galvanized steel; they are light enough so as not to overload the supporting structures of the house, and also have increased resistance to wear and corrosion. For rigid air ducts, you will need special elements that provide a slope of 45 or 90 degrees. But for flexible products such elements are not needed.
Air ducts are also made from ordinary steel, copper, plastic and other materials. There are even textile designs of this type. In places with high humidity, it is recommended to use copper elements as they are more resistant to such conditions.
Plastic structures are relatively inexpensive and can be used away from potential sources of fire.
Air ducts are fixed under the ceiling and floor, as well as inside the walls. If there is a need to lay the air duct not inside, but along the wall, it is covered with a false panel. Ventilation grilles are installed in the ceiling and floor at the ends of the air ducts.

Rigid air ducts made of galvanized steel are very reliable and durable. For their successful installation, you will need elbows with a rotation angle of 45 and 90 degrees.
Air masses moving inside a structure can make some noise. To reduce this negative impact, it is recommended to hide the air ducts under a layer of sound insulation.
Typically, this material also has thermal insulation properties, which only increases the efficiency of the system.

To ensure that air heating structures make as little noise as possible during operation, it is recommended to cover them with a layer of insulating material
It is worth considering the option of purchasing air ducts that already have such an insulating layer applied. This will simplify and speed up installation work.
If there is a need to install a fan, or several such devices, then it is usually included in the system next to the heater. The fan is supplied with power and also provides a backup source of electricity.
The system also includes one or more filters. These can be mechanical cleaning filters that prevent the spread of dust particles. Along with these devices, it is recommended to install a carbon filter that absorbs various odors. Of course, filters need to be cleaned and/or replaced periodically.
Part of the air duct is led outside to provide fresh air. This section is supplied to the filter system, and then the air is supplied to the heat exchanger of the heating device. If installation work is carried out during the construction of a house, then its implementation usually does not cause any great difficulties. The main thing is a good project.
To improve the microclimate in the house, useful elements such as an air humidifier, ionizer, ultraviolet sterilizer, etc. are built into the air heating system. These elements are not mandatory, but if funds allow, you should not refuse them.
Another useful device is a ducted air conditioner. It is also built into the air duct system. This will allow you to use the system in the warm season to cool the air in the room.

Automatic control systems significantly improve the operation of the air heating system and reduce heat costs, as well as simplify the operation of equipment
The final stage is connecting the automatic control system. You will need air temperature sensors in the rooms and a control panel with a processor that will process the received data and regulate the operation of the heating equipment.
Installation recommendations
The most important point when performing installation is the order of actions. First of all, it is necessary to install an air heater with a heat exchange chamber. From it comes the wiring and mounting of the air heater. Thermal insulation of channels must be carried out without fail. Bends are made through flexible hoses. The sleeves, in turn, are mounted in the wall.
Advice! It is necessary to consult a specialist when choosing a good model of heat generator for air heating of a private house, the price of which depends on its technical parameters. It is better to place the devices in a specially designated room.
The heat source is the most important detail. In order to connect it, it is best to use the services of specialists. But if you want to do this work yourself, you should read and understand the instructions very carefully. It is recommended to install the structure in a separate room. A basement is perfect. The chimney should preferably have a sandwich structure. The heat exchanger itself is connected to the air duct, and the fan is located under the combustion chamber.

Placing the heat generator in a separate room
Installation of air heating systems is a complex and responsible process, which is preceded by painstaking calculations and selection of equipment. With proper theoretical preparation, it is quite possible to do the work yourself. In all other cases, contact specialists.
Types of air heating
If you are planning to install this kind of heating at home or in any room, then it is worth understanding what types of air heating there are. The classification of this kind of systems itself takes place according to the following parameters:
- Depending on the method of circulation.
- According to the size (scale) of the system.
- Directly by location.
- And according to the method of heat transfer.
Now it’s worth taking a closer look at each of the options, characterizing them a little and considering them separately.
By circulation method
The first parameter for classifying systems is the circulation method, and it can be presented in two versions:
- Forced.
- Natural.
In the first case, the circulation of coolant in the system is carried out using special fans. They disperse hot air throughout the network, while the process itself occurs as quickly as possible, and the flows cool minimally on the way to the room. Thus, the system becomes more profitable, since the air flow is delivered in the opposite direction while it has not yet cooled down, and therefore requires less fuel consumption for reheating.
In the case of natural circulation, the air rises through the pipes due to its lightness (as you know, warm/hot air is much lighter than usual). Thus, it moves much more slowly, and therefore it cools down quickly and in this case the room will warm up quite slowly.
Location
The next step is the arrangement of the elements, which is also possible in several options:
- Hanging system.
- Floor-standing.
By type, floor systems are more popular and profitable. This is due to the fact that warm air rises upward, so if it is directed from the floor, then heating the room will begin from the bottom, which will make it as comfortable as possible.

The system itself is hidden behind decorative elements, so it won’t interfere with the interior. For the most part, it is hidden behind baseboards, or even under the floor.
In the case of a suspended system, air flows, on the contrary, go from top to bottom, and reach the floor already cooled; accordingly, coolness will be felt in the room at foot level.

Globality (scale) of heating
Here the division is also carried out into two options, these are:
- Local.
- Central.
In the first case, heating of a specific area of the building, a separate room, or a small building is assumed.
Central means fully equipping large-area buildings, in particular industrial and public buildings, with equipment for heating. For example, supermarkets, train stations, hangars and many other buildings.
By type of heat transfer
And the last classification option is the type of heat transfer. It can be divided as follows:
- Supply system. Here the equipment involves taking air only from the street, heating it and heating the premises with it. The cooled air inside is removed outside using equipped ventilation.
- Partial recirculation, which involves taking air from the street, as well as heating the internal air, which has already completely cooled down.
- And the last option is full recycling. This scheme involves constant circulation and heating of internal air. The streams are in constant motion, cooling and heating up again.
The most common option is complete recirculation of flows.
Equipment
The operation of an air heating system is based on heating air and redirecting it to heat rooms. For this purpose, the system is equipped with the following equipment:
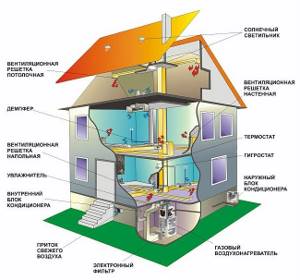
- gas air heater (or another model depending on the fuel) is the main source of heat;
- heat exchanger - heats the passing air and prevents mixing of flows with exhaust gases;
- air ducts - redirect warm air flows to the interior;
- filter, humidifier and air freshener – maintain air quality by cleaning it from dust and bacteria;
- central air conditioning - used to maintain comfort inside the building through the existing air duct system in the summer;
- automation system - monitors the temperature conditions of the room, controls the temperature, and the operating mode of the heat generator.
Where can combined systems be made?
The area and number of floors in our example are very arbitrary. It is also necessary to coordinate their operating modes.
It’s one thing: connecting a radiator heating system to a boiler when all the functionality for this is already included in the boiler. They propose to install polypropylene supply and return pipes in a layer of sand under the screed along the foundation. It can be single-pipe or double-pipe.
In some situations, when all the radiators are closed and the heated floor is running, the boiler pump and the underfloor heating pump work sequentially, interfering with each other. Installation of combined heating in a system with a gas boiler The most difficult moment in the process of installing combined heating is the need to supply coolant with different temperatures from the manifold for the heated floor and radiators through two pipes. Depending on the temperature at the outlet of the in-floor circuit, the mixing valve opens or closes, increasing or decreasing the amount of hot coolant from the supply in the recirculation circuit.
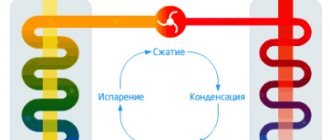
This is necessary to ensure the tightness of all joints made. Air heat pump is the main source of heat Air heat pump Before considering the positive and negative aspects of existing heating units, let's talk a little about air heat pumps.
Where can combined systems be made?
The collector is mounted in a special box made of galvanized steel that matches its size. In this case, the type of coolant or heat source does not matter.
Designation of the main elements of the circuit: wall-mounted gas boiler with built-in circulation pump and expansion tank; hydraulic separator thermo-hydraulic separator or hydraulic arrow ; collector - collector beam for connecting heating circuits; radiator heating circuit circulation unit; mixing unit kennel water thermoplastic floor; safety thermostat. The three-way thermostatic valve of the second type is distinguished by the fact that it provides regulation of the supply intensity of only the hot flow. In more complex systems, the controller is also guided by a weather sensor, making a preventive change in the heating power.
4 Proven water heated floor connection diagrams
As a result, the coolants are mixed as follows: liquid from the return pipe is supplied continuously, and hot liquid is supplied only when necessary. In this case, the in-floor structures will be durable, reliable and durable.
A special heat-sensitive device is used. Heating with a solid fuel boiler Combined heating with a solid fuel boiler is a closed gravity system with a heat storage device. We combine heating. Warm floor + radiators. A simple solution
Where is VO used?
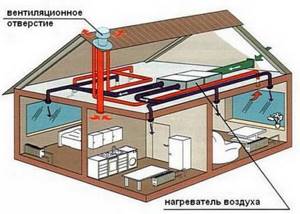
Diagram of air movement in the air heating system of a frame house, where the air duct is installed in hollow walls.
Air heating is recommended to be installed in frame-type private houses. Since the design of such a house provides for the presence of voids between the outer cladding and the inner covering, the air duct system can be installed in the hollow spaces of the wall without affecting the decoration of the house.
Another option for installing an air system is to include it in the project of a future construction. So, when erecting walls, technical niches are left between them for further installation of the system . If you plan to install air heating in a finished building without such preparations, you will have to launch large-scale construction and rebuild the walls.
Installation
The construction of a fireplace can be done with your own hands, but for this you will need to correctly draw up design documentation and accurately calculate the amount of building materials. It is also necessary to determine the type of heater being installed and its expected dimensions.
Standard fireplaces are attached to brick walls, installed deep within them, or mounted separately. It is not advisable to place the firebox of a wood-burning unit against a wall with windows. If their thermal insulation is not at a sufficient level, this will lead to drafts and energy losses.
Preparation
Before starting masonry, it is necessary to calculate the area of the room in which the installation will take place. The volume of the combustion opening should not exceed a fiftieth of the size of the room. The depth of the fuel chamber and the height of the fireplace portal are related to each other as 1 to 2. Excessive firebox capacity will lead to a decrease in heat transfer, and small dimensions will cause smoke.
The dimensions of the smoke channel depend on the size of the furnace and should be 10-15 times smaller. The optimal pipe diameter is 10 centimeters with a length of 4-5 meters.
Material
Making your own air-heated fireplaces for efficient space heating involves choosing high-quality materials. For installation you will need:
- whole stove bricks;
- pre-washed coarse sand;
- clay for finishing the hearth;
- Portland cement for pouring the foundation;
- medium-sized crushed stone;
- two dozen reinforcing bars with a diameter of 8 mm and a length of 70 cm;
- smoke damper of suitable size.
Foundation
All types of fireplaces that can be built at home require a preliminary pouring of the foundation, which is built separately from the base of the building. Its width is equal to the front base row with the addition of five centimeters of reserve.
Before pouring, you will need to dig a hole with dimensions 10-15 centimeters wider than the foundation of the house and a depth of 60 cm. After filling the crushed stone on the bottom and compacting it, the horizontalness of the base is measured.
Having made a formwork box without a bottom, it must be sheathed from the inside with roofing felt, firmly placed on the base and filled with cement-sand mortar. Having leveled the top of the foundation, it is covered with film and left until completely dry.
Bricklaying
The next step in constructing a wood-burning stove is laying individual bricks edge-on on the mortar. The geometric dimensions of the future fireplace are controlled using a square. All diagonals must be equal, angles must be clearly vertical, and rows must lie in a horizontal plane.
Laying continuous layers is carried out using a trowel or any suitable construction tool. Wooden slats that limit the size of the future fireplace are removed after building several rows of tightly laid bricks. The third layer also contains a pair of pins, on which the fireplace grate will later be placed. The thickness of the side projections of the portal is half a brick, and they are laid straight away.
Interior arrangement
Since the construction of the fireplace eliminates the need for internal plastering, the walls of the wood burning chamber and smoke collector are wiped down from the inside and thoroughly cleaned of any leaking solution. Smoke collectors and vaults with curved surfaces are laid out with a gradual overlap of bricks up to six centimeters. The portal openings are covered with brick lintels, which are installed separately.
In the process of laying a chimney with your own hands, it is necessary to control its verticality by switching to a cement-sand mixture as soon as the installation moves to the roof. To ensure better heat reflection, the fireplace walls are placed at an angle from the inside. At the same time, the side parts turn outward, and the back part leans forward slightly. The smoke chamber is installed above the firebox with an additional cornice. Its device prevents sparks and soot from flying out and reliably protects the room from smoke penetration.
Air heating options
So, our task is to heat the air masses and supply them to the premises of a country cottage or apartment. How to organize air heating:
- From the fireplace, wood stove.
- Use VRF systems using freon. Simply put, inverter air conditioners, air source heat pumps.
- Install a combined boiler + chiller + fan coil air conditioning system.
- Organize centralized air heating (abbreviated as VO), combined with ventilation of a private house. Use an electric heater or a gas air-heating furnace as a heat source.

A veranda with a large glass area can be conveniently heated with hot air supplied from the floor
Reference. The latter option is often implemented in American and Canadian cottages built using frame technology. The heater is a gas oven.
For heating/cooling large production workshops, a slightly different scheme is implemented. There are 2 networks of air ducts built in the premises - supply and exhaust. Both converge to a ventilation unit - a central air conditioner, consisting of the following blocks:
- 2-3-stage filters purify air masses before being supplied inside the building and emitted outside;
- heat exchanger-heater No. 1 heats the flow using hot water from the boiler room;
- heat exchanger No. 2 serves to cool the air and works in conjunction with a chiller;
- a plate cross (or rotary) recuperator removes heat from the exhaust flow and transfers it to the supply flow, saving 50...80% of energy;
- humidification unit;
- Centrifugal fans force flows through sections of the central air conditioner and further along the air ducts.
Why did we describe the design of an industrial climate control system? So that you immediately understand: installing full-fledged air heating + ventilation + cooling is not an easy and expensive task. But, as the owner of a country house, you can consider all heating methods, choose the simplest and cheapest, or return to the water scheme - heated floors, radiators.

Industrial series heating system running on natural gas
Direct air heaters
Direct air heaters are based on the principle of heating a room with red-hot porous ceramic tiles emitting infrared radiation, in the depths of which natural gas is burned. These are nothing more than gas fireplaces, near which it is pleasant to spend time, basking in the flow of radiant energy. Usually these are relatively inexpensive devices with a power of 3-4 kW, the production of which has been mastered by some manufacturers of heating devices (about the selection and placement of heating devices).
The biggest disadvantage of heating devices of this type is that oxygen “burns out” in heated rooms, and gas combustion products remain in the room. Therefore, such devices serve more for decorative purposes and cannot be recommended as the main source of heat.
Indirect air heaters
The above disadvantages can be partially or completely avoided by using indirect air heaters. This equipment is a convective-radial heat exchanger and heat exchangers with a built-in combustion chamber. When heated, the air becomes lighter and rises, and in its place comes cold air, which heats up, etc. (picture 1). Thus, the idea of a convector that warms a room without using forced air circulation devices arose.
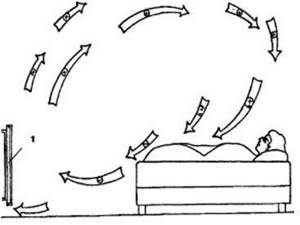
Figure 1. Convector air exchange in the room: 1 - convector; (+) - warm air; (+/-) — cooling air; (-) - cold air.
Gas convectors and heaters
Gas convectors are independent heating equipment that represents a real alternative to traditional heating devices. They provide not only the ability to maintain a set temperature in the range from 8 to 33°C in a heated room, but also allow you to set different temperatures in different rooms.
We recommend: Do-it-yourself hydrogen generator - diagram, installation design, drawings
Convectors operate on the principle of burning natural gas in a metal heat exchanger, which ensures highly efficient heat transfer to the room. At the same time, combustion products are removed outside and combustion air is taken in. This ensures the environmental cleanliness of the room and its effective ventilation. Compared to a traditional heating system, which requires boilers, radiators, room piping, fittings, pumps and other components, when using convectors, all this equipment is not required, since there is no water circuit. It is this feature of gas convectors that allows them to be used for efficient heating of country houses, cottages, garages, greenhouses, etc. The gas-air mixture in these devices is ignited either by a spark from the electronic unit or by the wick of the pilot burner, which, in turn, ignites when the button of the built-in “piezo lighter” is pressed. In the latter case, no electrical energy supply is required.
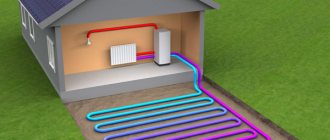
Duct air heating
In the practice of cottage construction in regions with cold and temperate climates, ducted air heating systems have been widely used (Figure 2). This system allows you to heat the premises of the house with warm air supplied through special channels without traditional pipelines and radiators. The advantages of this method over traditional ones are the low inversion of the system, which allows you to raise the temperature in the house from -10 to +22°C in 35 - 40 minutes.
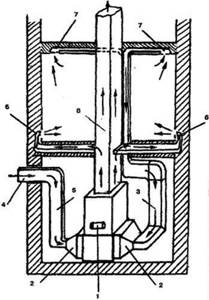
Figure 2. Scheme of air heating of a house: 1 - stove; 2 - filters; 3 - air intake pipe from the premises; 4 — fresh air intake; 5 — fresh air supply pipe; 6 — supply of warm air to the premises; 7 - air intake from premises; 8 - chimney.
After quickly warming up the premises, the automation switches on, allowing you to maintain the temperature at a given level. The advantages of air heating systems include:
- uniform heating of the room throughout the entire volume with a slight “pressure” of air, which completely eliminates drafts and the possibility of penetration of street dust;
- the ability to ventilate rooms, filter heated air to eliminate odors, germs and other foreign matter;
- low operating costs, allowing to increase efficiency up to 93%;
- ability to work in economical mode.
Gas or liquid heaters with safety automatics are used as heat generators. If the house is well thermally insulated, the heater is turned on 3-4 times a day to maintain the set temperature, which saves fuel and, consequently, money for heating residential premises. For example, to heat a small country house, one cylinder of liquefied gas is enough for about 8 - 12 days.
In almost all heating systems, the heat generated by the heat generator is transferred to the consumer by air. Even in a water heating system, water acts only as an intermediate coolant, and the final distribution of heat from the radiators still remains with the air. The only exceptions are heating devices from which heat is transferred by radiation - open fireplaces, infrared emitters, etc. But they play a limited role in heating residential buildings in our country.
The air is heated on heat-releasing surfaces (the surfaces of water heating radiators, convective-type electric heaters, “mirrors” of stoves, etc.) and enters the heated room, where it cools, giving off heat to walls, ceilings, and pieces of furniture. After this, the air should heat up again. This air circulation can occur under the influence of natural forces (warm air is lighter and therefore rises) or forcefully - due to a fan. In the future, we will use the term convection heating (by the way, here is general information about heating) for systems with natural air circulation and air heating (AH) for systems with forced air circulation.
This definition of VO is not generally accepted. A heating system is often called air-based if there is a system of air ducts for distributing heated air from a heat generator (without a fan). Wood-burning stoves such as “Buleryan” and “Professor Butakov” also fall under this definition, since they have the ability to connect air ducts and distribute warm air to other rooms due to convection.
Based on our definitions, these ovens should be classified as convection-type systems.
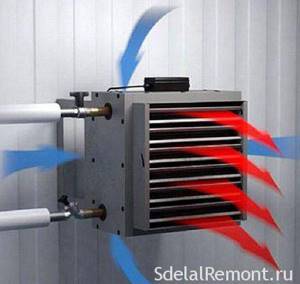
VO systems can be divided into two types - channel and local. Ducted systems require a system of air ducts, both supply and return. For local systems, air ducts are usually not needed. The simplest local heating systems are fan heaters and heat guns.
Figure 3. Direct heating heat exchanger: 1-hot air; 2- heat exchanger; 3-fan; 4-cold air; 5-burner; 6-chimney.
Figure 4. Indirect heating heat exchanger: 1 - hot air; 2 - heat exchanger; 3 - fan; 4 - cold air; 5 - burner; 6 - intermediate coolant circuit; 7-chimney.
How to organize stove heating
An important advantage of any stove: it simultaneously heats the air and surrounding surfaces with intense infrared radiation. No batteries or coolant pipes are needed.
Clarification. Stoves or fireplace inserts with a water circuit can be used to heat 2-3 small rooms. The coil is connected to a gravity or closed system with a pump.
How to use a stove for pure air heating:
- For 1 room it is enough to install a cast iron or steel potbelly stove.
- To heat 2–3 rooms with a total area of up to 40 m², place a brick stove of a suitable design in the wall between the rooms.
- It is not easy to build a stove in a lived-in house. If there are no high aesthetic requirements, we install a potbelly stove, attach convection casings to the firebox and connect air ducts.

Option No. 3 involves laying air ducts into adjacent rooms and installing duct fans that can withstand the temperature of the moving medium 100–150 °C. Air can move through the pipes on its own, but too slowly, and the ventilation duct must slope upward. How such an air heating system works, see the video below.
The first two options are well known, but not always applicable:
- It is generally unrealistic to install a stove in an apartment;
- even a large Russian stove is not able to cover an area of more than 50 square meters (on one floor), so it is suitable for heating a dacha or a small house;
- the foundation plus a brick stove-fireplace is erected during the construction or major renovation of the building;
- a metal potbelly stove takes up space and is dangerous for small children (in terms of burns).
You can install an iron stove with your own hands - this is a tangible plus. But you will also have to heat it, which results in a lot of inconveniences: frequent loading, the smell of firewood and smoke in living rooms, dust. The author of the video acted wisely by placing the potbelly stove in a separate furnace room. We do not recommend repeating one thing after the home craftsman - installing air ducts made of aluminum corrugations. Such pipes create high aerodynamic resistance and greatly slow down the flow. It is better to use galvanized boxes.
We recommend: Cast iron stoves for baths: great popularity and its reasons
Preliminary conclusion. Solid fuel stoves are a budget option for air heating with their own advantages and disadvantages. Suitable for small buildings - country houses, garages, greenhouses.
Application of air conditioners and heat pumps
As you know, modern split systems are able to operate in heating mode, consuming three times less electricity than a conventional electric boiler of the same power. Hence, a completely workable solution is to buy and install an inverter air conditioner in each room.
Reference. Why an inverter? The compressor in such “splits” does not stop, and therefore does not freeze in the cold. The air conditioner successfully heats the air down to -5 °C outside, after which the efficiency noticeably decreases.
The advantages of this scheme are obvious:
- lack of batteries, pipes, boilers and other heating equipment;
- relative ease of installation;
- aesthetic appearance of the indoor unit;
- cooling mode in summer;
- Possibility of installation in apartments.

The air-conditioned heating method is viable in the southern regions, where the temperature rarely drops below -15 °C. To the north, “splits” are used only during the transition period – in spring and autumn.
Other disadvantages of heating with a split system:
- Air conditioners will have to be installed in all rooms, which is unacceptable for cottages of 2–3 floors. A multi-split VRF system will cost more than the same number of single coolers/heaters.
- The device “can” clean, dry and change the temperature of the air flow. Rare models are designed to mix in outside air. This means that you will have to do separate ventilation.
- When the external unit of the air conditioner is operating, the distinct noise of the fan and the hum of the compressor can be heard from behind the wall.
The problem of efficiency at low temperatures is solved by an “air vent” heat pump, whose performance remains intact down to -30 degrees below zero. The design and operating principle are identical to the split system, the differences being the larger size and price. If the external unit is installed on the ground and carried 2-3 m from the building, the noise of the unit will become inaudible.
Brief conclusion. VRF systems are good for apartments and small houses located in the southern regions. Heat pumps can also be installed in northern latitudes, but the cost of the equipment plays a role here. If desired, you can install the air conditioner yourself.
Combined multi-zone systems
In this case, the coolant is still used, which is why the system is called combined. How this equipment works:
- Each room has an air heating/cooling unit - a four-pipe fan coil unit that looks like an indoor air conditioner unit.
- One pair of pipes supplies the units with coolant from the boiler. Hot water passes through a heat exchanger blown by a fan, causing the room air to heat up.
- When it is necessary to switch to cooling, the automation switches the fan coil to the second pair of pipes supplying cold water from the chiller.
- Users in rooms can set different air temperatures, but they cannot turn on cooling and heating at the same time. Hence the second name of the air conditioning system – multi-zone.
Note. Chiller is a type of refrigeration machine designed to cool liquid. Usually located on the street under a canopy or in an open place (depending on the design).
Various fan coil units are used inside the building - wall-mounted, duct-mounted, floor-mounted, ceiling-mounted. It all depends on the wishes of the homeowner and aesthetic requirements. Duct-type units can be built inside ventilation ducts to heat/cool the supply air.

Connection diagram of a cassette, duct and floor fan coil to a chiller and boiler
Advantages of multi-zone air systems:
- applicable in large buildings with 20 or more rooms - administrative and residential buildings, warehouses, and so on;
- can work in conjunction with forced ventilation of the cottage;
- any heat generator is used for air heating - a boiler using solid fuel, gas, electricity, diesel fuel;
- pipes with coolant (coolant) take up little space, air units are easily built into the ceiling, hung on the wall or hidden behind the cladding;
- closed terraces with stained-glass windows covering the entire wall are heated by in-floor convectors or wall-mounted fan coil units;
- possibility of adjusting the temperature in individual rooms, remote control.
We believe that the boiler + fan coil + chiller scheme is the most universal and successful from the point of view of aesthetics and operation. Of course, you can’t do this type of air heating yourself; this is a minus. It is necessary to make calculations, select equipment, install, adjust... without knowing the basics, it is extremely difficult to carry out these works.
Let's list other negative points:
- high price of air conditioning units;
- the boiler and chiller are quite large devices, occupying 2–3 m² of area;
- the operation of the system depends entirely on electricity; when the lights are turned off, the heat supply will stop.
Conclusion. A multi-zone combined scheme is the best way to air-heat a home. But implementation will require significant investments.
Heating combined with ventilation
This is a classic method of heating buildings with air, used in enterprises since the last century. Subsequently, manufacturers began to produce small-sized analogues of industrial ventilation units installed in private homes. Thanks to less stringent requirements for air purity, the treatment scheme has also been simplified.
Let us explain the principle of operation of the “ventilation + heating” system step by step:
- The heat source is a stove, usually a gas one. A burner, an air heat exchanger, a fan and an electronic control unit are installed inside.
- The first network of ducts radiates from the furnace, distributing heated air throughout the rooms. With the help of diffusers, grilles and other supply devices, jets are supplied to the premises (usually to the upper zone).
- The second network of channels collects polluted/cooled air from the lower zone of the rooms into a common collector connected to the stove from below.
- Having passed through the collector, the exhaust air masses are cleaned in a mesh or cell filter, then sent to a heat exchanger, where they are heated by a burner.
- Electronics monitor the safe operation of the gas air heater, maintain the outlet temperature, and signal when the filters are dirty.
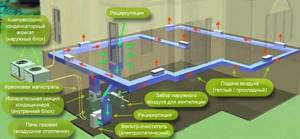
Typical air heating circuit with recirculation. The heater is a furnace and an air conditioner with a ducted indoor unit
Addition. Since the heater dries the air, an automatic humidifier with an electronic hygrometer is usually installed on the supply duct. The latter is located on the return air duct to measure the humidity of the flow.
The air heating stove is a rather noisy unit, so it is installed in a separate room. Combustion products are removed through a conventional or coaxial chimney (depending on the design of the heater). Air ducts made of galvanized steel are laid in several ways:
- in the basement or ground floor;
- hide in floors and wooden ceilings;
- in the attic;
- vertical channels run along the walls and are covered with facing materials.

Large ventilation ducts are laid under plasterboard finishing
The supply air temperature reaches 40...45 °C, the speed of movement through the ventilation ducts is 4-5 m/s. You can't go any faster; there will be additional noise. In this situation, the diameter of the main collector reaches 300 mm, we took a typical flow rate of 1000 m³/h, although it can be more.
We recommend: Which gas boiler should you choose: wall-mounted or floor-standing?
A logical question: why heat air masses to 40 °C if 22 degrees is sufficient in the house? We answer: the heating system must compensate for 2 types of heat loss - through building structures and energy consumption for heating the inflow, since ventilation is needed in any case. Accordingly, we bring the air to a temperature of 20–24 °C (compensating for losses at home), then overheat it to 40…45 °C.
Conclusion. The “ventilation + heating” scheme is the most cumbersome and expensive. The building must be prepared in advance - even at the design stage, otherwise the air ducts will go directly through the rooms. Operating efficiency is highly dependent on the way the building is ventilated, which we will discuss next.
Arguments for choosing an air system
Compared to conventional systems operating on a liquid coolant, air circuits have significant advantages. Let's take a closer look at them.
- High efficiency of air systems. The productivity of air heating circuits reaches about 90%.
- Possibility to turn off/on equipment at any time of the year. Work interruption is possible even in the most severe winter cold. This means that a switched-off heating system will not become unusable at low temperatures, which, for example, is inevitable for water heating. You can put it into operation at any time.
- Low operating cost of air heating. There is no need to purchase and install quite expensive equipment: shut-off valves, adapters, radiators, pipes, etc.
- Possibility of combining heating and air conditioning systems. The result of the combination allows you to maintain a comfortable temperature in the building in any season.
- Low system inertia. This ensures extremely fast heating of the premises.
- Possibility of installing additional equipment that is used to maintain an optimal microclimate. These can be ionizers, humidifiers, sterilizers and the like. Thanks to this, you can choose a combination of devices and filters that exactly matches the needs of the residents of the house.
- Maximum uniform heating of rooms without local heating zones. These problem areas are usually located near radiators and furnaces. Due to this, it is possible to prevent temperature changes and their consequence - unwanted condensation of water vapor.
- Versatility. Air heating can be used to heat rooms of any size, located on any floor.
The system also has some disadvantages. Among the most significant, it is worth noting the energy dependence of the structure. Thus, when there is a power outage, the heating stops functioning, which is especially noticeable in areas with intermittent power supplies. In addition, the system requires frequent maintenance and monitoring.
Air heating is very economical. The initial costs for its arrangement are low, operating costs are also low
Another negative feature of air heating is that the installation of the structure must be carried out during the construction process. The installed system is not subject to modernization and practically does not change its operational characteristics.
If necessary, it is possible to install air heating in a constructed building, but in this case only suspended air ducts are used, which is not aesthetically pleasing and is not always effective.
Conclusions and useful video on the topic
Interesting information on calculations and design of air heating is shown here:
In this video you can see two options for relatively inexpensive installation of air heating systems using Russian-made devices and materials:
Air heating is a worthy and profitable option for heating a private home. It is more efficient than traditional water systems and can significantly improve the quality of life in your home. But to ensure the successful implementation of this idea, the system must be correctly calculated and professionally designed.
Do you have any questions? Or do you have personal experience using air heating for your home? Please share your own opinion on this issue. Leave comments, ask questions, share tips in the block below.
What is combined heating
Combined (mixed) is a heating system that contains both traditional high-temperature (conventional radiators, convectors) and low-temperature (warm floors, less often warm walls) heating devices.
Water floors in a combined system are connected in two ways:
- For existing heating boilers. The advantages of this solution are a reduction in the estimated cost of equipment and a reduction in installation time. Disadvantage - additional heating cannot function in autonomous mode. This causes an increase in thermal energy consumption, and the efficiency of using heated floors decreases.
- Install hotel boilers for floor heating. The disadvantage is a significant increase in cost. Advantages: complete autonomy; water floors can be used independently of radiators. This may be necessary for a small heating of the room when the batteries are already turned off, for example, in the autumn-spring period.
1st floor - heated floor, 2nd floor - radiators
Where to begin?
It is recommended to carry out the idea of air heating in stages, carefully checking your work, because the cost of a mistake is too high.
Of course, it is best to do this at the stage of designing a home, but if desired, this can also be implemented on the finished property. The sequence is as follows: We recommend: Antifreeze for the heating system of a country house - how to choose?
Carrying out calculations of the thermal power required to heat a house. Choosing an air heating system. Scheme development.
Having gone through these stages, you will select and purchase equipment, and then move on to installation work, which you can do yourself or with the help of specialized organizations.
Advice. Based on the results of your work, it is recommended to consult with specialists involved in the design of such systems. This will help clarify many nuances and also check your calculations.
Calculation of the home heating system
| Calculating the heating systems of a private house is the very first thing where the design of such a system begins. We will talk to you about the air heating system - these are the systems our company designs and installs both in private homes and in commercial buildings and industrial premises. Air heating has many advantages over traditional water heating systems - you can read more about this here. |
System calculation – online calculator
Why is a preliminary calculation of heating in a private house necessary? This is required to select the correct power of the required heating equipment, allowing you to implement a heating system that provides heat in a balanced manner to the corresponding rooms of a private house. A competent choice of equipment and correct calculation of the power of the heating system of a private house will make it possible to rationally compensate for heat loss from the building envelope and the influx of street air for ventilation needs. The formulas themselves for such a calculation are quite complex - therefore, we suggest you use the online calculation (above), or by filling out the form (below) - in this case, our chief engineer will make the calculation, and this service is completely free.
How to calculate the heating of a private house?
Where does this calculation begin? Firstly, it is necessary to determine the maximum heat loss of an object (in our case, a private country house) under the worst weather conditions (this calculation is carried out taking into account the coldest five-day period for a given region). It will not be possible to calculate the heating system of a private house on your own - for this purpose, specialized calculation formulas and programs are used that allow you to build a calculation based on the initial data on the structure of the house (walls, windows, roofing, etc.). As a result of the data obtained, equipment is selected whose useful power should be greater than or equal to the calculated value. When calculating the heating system, the required model of duct air heater is selected (usually a gas air heater, although we can use other types of heaters - water, electric). Then the maximum air performance of the heater is calculated - in other words, how much air the fan of this equipment pumps per unit time. It should be remembered that the performance of equipment differs depending on the intended mode of use: for example, with air conditioning the performance is greater than with heating. Therefore, if you plan to use an air conditioner in the future, then the air flow rate in this mode must be taken as the initial value of the required performance; if not, then only the value in the heating mode is sufficient.
At the next stage, the calculation of air heating systems for a private house comes down to correctly determining the configuration of the air distribution system and calculating the cross-sections of the air ducts. For our systems, we use wafer-shaped rectangular air ducts of rectangular cross-section - they are easy to assemble, reliable and conveniently located in the space between the structural elements of the house. Since air heating is a low-pressure system, when constructing it it is necessary to take into account certain requirements, for example, to minimize the number of turns of the air duct - both the main one and the terminal branches going to the grilles. The static resistance of the route should not exceed 100 Pa. Based on the performance of the equipment and the configuration of the air distribution system, the required cross-section of the main air duct is calculated. The number of terminal branches is determined based on the number of supply grids required for each specific room of the house. In a home air heating system, standard supply grids measuring 250x100 mm with a fixed capacity are usually used - it is calculated taking into account the minimum air velocity at the outlet. Thanks to this speed, there is no air movement in the rooms of the house, there are no drafts or extraneous noise.
| The final cost of heating a private house is calculated after the design stage is completed, based on a specification with a list of installed equipment and elements of the air distribution system, as well as additional control and automation devices. To make an initial calculation of the cost of heating, you can use the questionnaire for calculating the cost of a heating system below: |
online calculator
How to warm up a house with air?
We can talk for a long time about how to warm a house with air. The essence of all air systems is one. There is some kind of powerful heating device that warms up and at the same time pumps air into the rooms through ducts with a powerful fan. As a result, this system will perform the following functions:
- heating;
- ventilation;
- air conditioning in summer.
Air conditioning is carried out by cool air, which is cooled through the boiler and passing through cooled channels. There is no need to install any additional equipment, because it solves everything. In this case, the boiler can operate at a minimum, because it will still not be possible to overheat the air, and this is not necessary.

Self-installation
You can do air heating yourself, which will help you save money. It is best to do this during the construction stage. Installation of an air heating system consists of the following steps:
https://youtube.com/watch?v=QO2mryOkg6E
Carrying out calculations
This is one of the most difficult and lengthy stages, requiring knowledge, skills and careful work. You need to consider several important factors:
- calculate heat loss separately for each room;
- choose the type of air heater and its power depending on the heat loss indicators;
- based on the heater power indicators, calculate the amount of warm air;
- perform an aerodynamic calculation of the entire system;
- calculate the required diameter of the air channels.
Purchase of equipment
You should start by purchasing the most important part - the heat generator. It should be selected based on the size of the heated area and fuel consumption indicators.
It is better to purchase air ducts, tie-ins and throttle valves from a special enterprise that produces ventilation equipment.
Everything else, namely aluminum tape, screws, mounting tape, insulation, etc., can be found on any decent market.
Installation features
During the installation of this heating system, the main air duct is first installed. Usually it is made of galvanized steel, after which it is covered with foil insulation with a thickness of about 3-5 mm.
After this, a system of smaller air ducts is installed, which branch off from the main one. To make the system easily adjustable, a throttle valve must be installed in each supply duct.
At the end of the main air duct, it is better to leave a section 50 cm long, in which there will be no insertion of thin air ducts. This way there will be uniform pressure along the entire length of the device and equal volumes of air will enter the side branches.
All this is followed by the installation of the air heater itself. It provides all mounting holes for additional equipment (filters, air conditioning, air sterilizer) and a fastening system. Assembly of the complex will take no more than an hour. However, connecting all this equipment will take time.
From all this we can conclude that air heating of a cottage is a modern and effective option that has long been used abroad and is slowly being introduced into Russian homes.
Date: September 25, 2021
How to draw up a heating project
If you decide to install a VO system, it’s worth understanding and developing a detailed project. Key points to consider when planning:
- heating speed (warm air supply) and room area;
- heat generator power, which is calculated based on the characteristics of the house and possible heat losses (condition of doors, windows, walls);
- dimensions of air ducts and the subsequent value of air pressure losses.
Please note that for optimal operation of the system, all calculations are carried out by competent specialists. Due to miscalculations and attempts to independently “figure out” the operation of the system, intense heat loss, strong noise and vibration during operation are possible.
Selecting a heat generator

When choosing a heating unit, first of all, the required power and the type of fuel used are taken into account.
Today, devices are produced in both mobile and stationary versions. In private homes, the second type is usually used, while the first can often be seen in industrial premises of enterprises.
Low-power household heaters are usually made wall-mounted. With this design they take up less space. High power units are installed on the floor.
If you are going to install solid fuel equipment, be sure to check its weight - this equipment is quite heavy.
Gas and liquid fuel heaters can have an open or closed combustion chamber.
In the first case, the air for burning fuel enters the furnace from the boiler room, therefore, sufficiently efficient supply ventilation must be installed in it. With a closed combustion chamber, this requirement can be neglected - air is pumped into it by a fan from the street through a special channel.
Today, non-traditional ones are increasingly being used in conjunction with traditional heat generator installations. These include:
- Solar collectors: in modern versions they look like batteries of tubes in which the heat of the sun's rays is absorbed by air or a coolant liquid. The most productive are vacuum collectors, the working surface of which, thanks to the vacuum shell, does not come into contact with street air (heat loss is reduced). Just be prepared for the fact that such collectors are more expensive than regular ones.
- Heat pumps: This heat generator is almost no different from the heat pumps found in air conditioners and refrigerators. By alternately compressing and expanding gas, it is possible to “pump out” thermal energy from a relatively cold environment - with a temperature of +7 degrees and below.
Of course, in the latter case, energy is required, but the “game” is worth the trouble: every kW of electricity spent brings from 3 to 5 kW of heat.