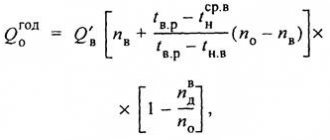Principle of operation
The heat of the earth is used to heat the house in countries where there are a large number of hot springs.
There, the coolant is pumped into pipes and supplied for heating to residential and administrative buildings. This option is not suitable for a separate building, since no one will make millions of investments that will never pay off. Two heating circuits - external and internal
A geothermal heating system for a private home works differently. It is based on the law of energy release when combining carriers with different temperatures. In this case, heat is released, which is used to heat the premises. Geoheat has a similar operating principle to refrigerator and air conditioning technology, where energy is distributed to produce heat and cold. The difference is that the low temperature is already present.
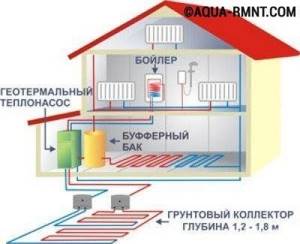
Thermal heating is a system consisting of the following parts:
- External contour. It is a closed pipeline in which liquid circulates. During the current flow, it acquires ambient temperature, thereby becoming a carrier of energy.
- Inner circuit. This is a standard piping consisting of pipes and radiators. Heated liquid enters it. To operate in cooling mode, convectors are installed.
- Heat pump. A compact device that compresses a liquid, giving it a given temperature, ensuring circulation of the coolant along the internal and external circuits.
Geothermal heating equipment
The implementation of a system of this type is only possible with special equipment. It accumulates heat from soil or water and transfers it to the coolant of the building’s heating system.
It includes:
- Heat pump;
- compressor;
- buffer tank;
- heat exchanger
The compressor helps bring the antifreeze to the required temperature. The buffer tank accumulates it after heating and transfers its heat to the coolant. The composition includes an internal tank, coolant water and a coil through which antifreeze circulates. This element is also necessary for the reason that the temperature of the antifreeze can vary from -5 to +20 degrees. At the same time, it expands and a container is needed to accommodate the increased volume.
Costs and payback prospects
The costs of equipment and its installation during the construction of geothermal heating depend on the power of the unit and the manufacturer.
Everyone chooses a manufacturer based on their own considerations and information about the reputation and reliability of a particular brand. But the power depends on the area of the room to be served.
This figure summarizes the benefits of using a geothermal heating system. It is precisely this ratio of incoming and outgoing energy that allows the system to first quickly pay for itself and then save its owner’s money (+)
If we take power into account, the cost of heat pumps varies in the following ranges:
- for 4-5 kW – 3000-7000 conventional units;
- for 5-10 kW – 4000-8000 conventional units;
- for 10-15 kW – 5000-10000 conventional units.
If we add to this amount the costs that are needed to carry out installation work (20-40%), then we will get an amount that for many will seem absolutely unrealistic.
But all these costs will be recouped in a very reasonable time frame. In the future, you will only have to pay minor expenses for the electricity needed to operate the pump. And it's all!
Due to the insufficient efficiency of geothermal systems for heating residential buildings, they are used as an addition to the main heating networks or built in complex with two or more heat exchangers
As practice shows, geothermal heating is especially beneficial for houses with a total heated area of 150 square meters. m. Within five to eight years, all costs for installing heating systems in these houses are fully recouped.
If geothermal heating is not particularly in demand among owners of private houses, then the effectiveness of solar systems has already been appreciated by residents of the southern regions. The technology for constructing solar heating is quite simple, and its efficiency and practicality are confirmed by many years of experience in use by Western countries and our compatriots.
Horizontal collectors for heating a house with earth's heat
They are used in regions with a relatively warm climate, where the depth of soil freezing does not exceed 1-1.5 meters. In this case, organizing heating of the house from the ground is much simpler, because you can dig trenches yourself, and the cost of the work will be significantly reduced.
But this scheme also has its drawbacks. First of all, heating from the ground with your own hands is not so easy: for example, for a house with an area of 275 square meters, you will need to lay 1200 meters of pipes in trenches. In addition to the fact that you will have to spend a lot of time digging trenches, the pipes will also take up a large area. This area cannot be used, for example, for a garden or vegetable garden: the roots of the plants will freeze due to the way the collector operates.
Thus, heating with earth's energy is a good idea, but very difficult to implement. The situation is similar with solar heating. It is for this reason that alternative energy sources are not widespread today.
Classification by construction type
The operating principle of geothermal heating is similar to that of an air conditioner or refrigerator. The main element is a heat pump included in two circuits.
Operating principle of a geothermal (heat) pump
The internal circuit is a traditional heating system consisting of pipes and radiators. External - an impressively sized heat exchanger located underground or in the water column. Both a special liquid with antifreeze and ordinary water can circulate inside it. The coolant takes on the temperature of the medium and, “warmed up,” enters the heat pump, the accumulated heat is transferred to the internal circuit. In this way, water is heated in pipes and radiators.
The geothermal (heat) pump is a key element of the system. This is a compact unit that takes up no more space than a washing machine that is familiar to us. If we talk about performance, then for every 1 kW of electricity consumed, the pump “produces” up to 4-5 kW of thermal energy. While a conventional air conditioner, which has a similar principle of operation, will “respond” to 1 kW of heat for 1 kW of electricity consumed.
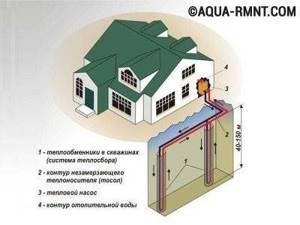
Scheme of geothermal heating in a private house
It must be admitted that the installation of this type of heating is the most expensive and labor-intensive to date. The lion's share of its cost is the purchase of equipment and, of course, excavation work. Naturally, a thrifty owner wonders whether it is possible to save money, for example, on installation and make geothermal heating with his own hands? In order to answer this question, it is necessary to understand which systems are used most often and understand the features of their design.
Horizontal heat exchanger
Quite often, a horizontal circuit is used, in which pipes are laid in trenches to a depth greater than the freezing level of the soil in a given area.

The disadvantage of a geothermal heating system with a horizontal circuit is the large area occupied by the collector
The disadvantage is that the area occupied by the circuit must be much larger than the house itself, so to heat a building with an area of 250 m², about 600 m² will go under the pipes. Not every developer can afford such luxury.
In addition, inconveniences arise if the site is already landscaped; for example, you have to observe the distance from trees (1.5 m) and many other nuances.
Vertical heat exchanger
A more compact, but also more expensive option is a vertical heat exchanger. Its installation does not require a large area, but it will require special drilling equipment.
Installation of a vertical heat exchanger requires the use of special drilling equipment
The depth of the well, depending on the technology, can reach 50-200 m, but its service life is up to 100 years. This method is especially relevant when planning geothermal heating of a country house with a developed adjacent territory; it allows you to preserve the landscape almost in its original form.
Water-based heat exchanger
The most economical geothermal installation uses thermal energy from water. It is recommended if the distance to the nearest body of water does not exceed 100 m.
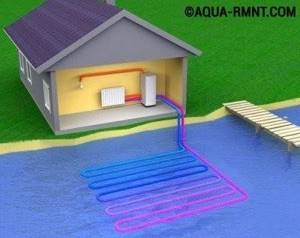
A water-based heat exchanger is the most advantageous and therefore more appropriate for the device
A circuit of pipes in the form of a spiral is laid on the bottom; the depth should be less than 2.5-3 m, that is, deeper than the freezing zone. Reservoir area – from 200 m². The main advantage is that there is no need to perform labor-intensive excavation work, but it is necessary to obtain permission from special services. Having spent significant amounts of money on expensive equipment, you should not skimp on high-quality installation. After all, the quality and efficiency of the entire system will depend on it.
As you can see, installing geothermal heating at home with your own hands is not so easy. Of all the listed types, perhaps only the last option will be quite easy to implement on your own. But even in this case, it is worth weighing all the pros and cons.
Methods for collecting the Earth's energy resources
Today there are three main methods for collecting geothermal energy: dry steam, hot water and the binary cycle. The dry steam process directly drives the turbine drives of electricity generators. Hot water flows from the bottom up, then is sprayed into the tank to create steam to drive the turbines. These two methods are the most common, generating hundreds of megawatts of electricity in the US, Iceland, Europe, Russia and other countries. But location is limited, as these plants operate only in tectonic regions where access to heated water is easier.
With binary cycle technology, warm (not necessarily hot) water is brought to the surface and combined with butane or pentane, which has a low boiling point. This liquid is pumped through a heat exchanger where it is evaporated and sent through a turbine before being recirculated back into the system. Binary cycle technologies provide tens of megawatts of electricity in the United States: California, Nevada and Hawaii.
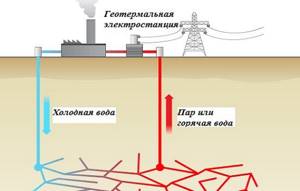
The principle of energy production
Disadvantages of Geothermal Energy
At the utility level, geothermal power plants are expensive to build and operate. Finding a suitable location requires expensive well surveys with no guarantee of hitting a productive underground hot spot. However, analysts expect this capacity to nearly double over the next six years.
In addition, areas with high underground source temperatures are located in areas with active geological and chemical volcanoes. These "hot spots" form at the boundaries of tectonic plates in places where the crust is quite thin. The Pacific region, often referred to as the ring of fire for many volcanoes, has many hot spots, including in Alaska, California and Oregon. Nevada has hundreds of hot spots covering much of the northern United States.
There are other seismically active areas. Earthquakes and the movement of magma allow the water to circulate. In some places, water rises to the surface and natural hot springs and geysers occur, such as in Kamchatka. The water in the geysers of Kamchatka reaches 95° C.

One of the problems with an open geyser system is the release of certain air pollutants. Hydrogen sulfide is a toxic gas with a very recognizable "rotten egg" smell - small amounts of arsenic and minerals released in the steam. Salt can also pose an environmental problem.
In offshore geothermal power plants, significant amounts of interfering salt accumulate in the pipes. In closed systems there are no emissions and all liquid brought to the surface is returned.
Economic potential of the energy resource
Seismically active spots are not the only places where geothermal energy can be found. There is a constant supply of useful heat for direct heating purposes at depths anywhere from 4 meters to several kilometers below the surface almost anywhere on earth. Even the ground in your own backyard or local school has economic potential in the form of heat to be released into your home or other buildings.
In addition, there is a huge amount of thermal energy in dry rock formations very deep below the surface (4 – 10 km).
Using the new technology could expand geothermal systems, where people could use that heat to produce electricity on a much larger scale than conventional technologies. The first demonstration projects of this principle of generating electricity were shown in the United States and Australia back in 2013.
If the full economic potential of geothermal resources can be realized, it will represent a huge source of electricity for production capacity. Scientists estimate that conventional geothermal sources have a potential of 38,000 MW, which can produce 380 million MW of electricity per year.
Hot dry rocks occur at depths of 5 to 8 km everywhere underground and at shallower depths in certain places. Access to these resources involves the introduction of cold water, circulation through hot rocks and the removal of heated water. There are currently no commercial applications for this technology. Existing technologies do not yet allow the recovery of thermal energy directly from magma, very deeply, but this is the most powerful resource of geothermal energy.
With the combination of energy resources and its consistency, geothermal energy can play an indispensable role as a cleaner, more sustainable energy system.
Hydrothermal heating design diagram
Today, three fundamentally different schemes for arranging underground heating are most widespread. To ensure maximum efficiency of heating a house, the total area of the external underground circuit should be 2.5 times larger than the heated area of the residential building.
The following types of geothermal heating are used in autonomous heating:
- Underwater option.
- Horizontal bookmark.
- Construction of wells.
In each specific case, the choice of one or another type of geothermal heating will depend on the area of the house, the financial capabilities of the homeowner, and the characteristics of the area. The underwater option can be used in cases where there are deep bodies of water nearby that do not freeze to the bottom in the winter.
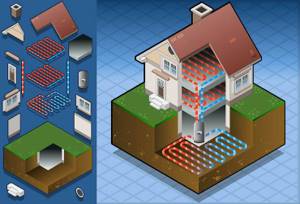
There are several types of such heating.
Horizontal bookmark
This option of hydrothermal heating involves making a pit next to the house, the depth of which will be 2 meters deeper than the freezing point of the soil. Accordingly, to heat a private house with an area of 100 square meters, you will need to dig a pit with a depth of more than 3 meters and a total area of 250 square meters.
If the available area of the site allows for such a foundation pit, then a horizontal foundation will be the best option for geothermal heating of a private house. A system of pipes is laid inside the pit through which non-freezing coolant circulates. The external heating circuit is brought into the house and connected to a heat exchange unit.
Among the advantages of this geothermal heating scheme, it is customary to highlight its efficiency, ease of arrangement, and reduced costs for installing the external circuit. At the same time, it is necessary to take into account the mandatory requirements for the correct calculation of the volume of the pit, which is not always possible to place on a small plot of land.
Geothermal home heating:
Underwater option
Owners of private homes who live near lakes and rivers often choose hydrothermal heating using an underwater option. It is only necessary to correctly consider the location of the external contour, which is placed at a depth of more than 4 meters, which eliminates the possibility of freezing of a lake or river to the bottom. The underground and above-ground parts of the circuit, which goes directly from the shore of the lake to a heated private house, are necessarily insulated, and underground pipes are laid at a depth below the freezing point of the soil.
The use of an underwater option makes it possible to simplify the arrangement of the heating system of a private house, since there is no need to carry out expensive and complex excavation work. The external circuit will be heated by the heat of the water, after which the heated coolant is supplied to the system, ensuring the operation of the equipment.
Execution of hydrothermal wells
The installation of geothermal wells for organizing autonomous heating is the best option, allowing to significantly reduce the costs of the homeowner. The well is drilled to a depth of 30-50 meters, which increases the heating efficiency, since at great depths the temperature of the earth will be higher than at the surface itself.

Drilling a well is one of the effective methods of installing such heating
Today, many homeowners, when installing an autonomous geothermal heating system in a private home, choose the option of drilling wells, which greatly simplifies the installation of the circuit. In this case, maximum efficiency of the equipment used is ensured, allowing you to use all the capabilities of such modern technologies even if you have a small area.
Heating a private house by laying an external circuit in deep wells allows you to reduce the total cost of installing autonomous heating in a house by 20-30%. Due to the high heating temperature of the coolant in the deep circuit, it is possible to use heating installations that are small in power, which simplifies the installation of equipment, reduces its cost, while simultaneously ensuring maximum convenience of living in a private home.
How to do it yourself?
It is quite difficult to make geothermal heating, some semblance of power plants (geoPP), on your own, but it is quite possible. In the row next to the house, you need to build a structure from a closed piping system and place it at a considerable depth. The size of the collector and the design of the coil depend on the degree of thermal conductivity and the depth of the soil. If you undertake the installation of geothermal heating at home with your own hands, then it is better to purchase the external circuit ready-made.
To create minimum operating conditions for a geothermal system, the following conditions must be met:
- The temperature of the soil layer where the pipe circuit will be located should not fall below +5°C.
- Throughout the entire piping with antifreeze, insulation must be made to protect the circuit from freezing.
- Thermal heating of a building is carried out after careful calculations and design.
Given these requirements, it becomes clear that geothermal heating can be effective. However, for the northern regions, the use of such an installation is justified for heating small buildings - up to 200 sq.m.
Let's consider only ways to create horizontal geothermal heating at home with your own hands under ground or water. Mounting the collector vertically is much more difficult and very expensive.
A heat pump will not take up much space, because this equipment is comparable in size to a conventional boiler. Connecting the sediment to the internal contour of the building is also not difficult. The main task is to arrange the external contour.
It is best to install the collector in a reservoir at a distance of no more than 100 meters. It is necessary that the area of the pond be more than 200 sq.m., and the depth should be at least 3-3.5 meters. If you do not have rights to use this reservoir, you will first have to obtain permission to install the necessary equipment.
If the pond is on your property, then it will not be difficult for you to drain it for a while so that you can easily lay and secure the pipes in a spiral at its bottom. Excavation work consists only of digging a trench necessary to connect the external circuit to the geothermal pump. Having completed all installation work, the reservoir can be filled again.
If your site does not yet have green spaces and many structures, then you can design a horizontal method of placing the heat exchanger underground. To do this, you need to calculate how much area the future collector will occupy, taking into account the parameters indicated above: 250-300 sq.m. contour per 100 sq.m. building area.
If there are trees and temporary buildings on your site, but you really want to install horizontal geothermal heating, then all the buildings and green spaces will have to be cut down and demolished. The process is complex, time-consuming, but necessary.
Distribution of geothermal heating system
Heating using the heat of the earth began to spread in the late 80s in US cities, which were particularly hard hit by the crisis. At first, this system was used by wealthy people, who in this way saved on heating their homes, but soon the system began to become cheaper, and poorer Americans became interested in it. And soon the use of earth's heat for heating became the prerogative of most Americans who owned private homes. In European countries, 20 years ago, statistics indicated that approximately 12 million citizens used geothermal heating systems. And during all this time until today, this figure has only increased.
Although the gas heating system is the most popular, for the same reason, every year the reserves of natural gas decrease, the cost of it increases and increases. And using solid fuel to heat a house is labor-intensive. In addition, as a result of burning wood and coal, harmful carbon dioxide is released, soot and tar are formed. Therefore, geothermal heating is becoming increasingly common in Russia.
Scope of application
Energy
The use of underground heat for energy purposes is the traditional main area of application of geothermal resources, as evidenced by the following figures:
- The increase in the capacity of GeoPP geothermal power plants in 2018 amounted to 540 MW.
- Their total generation reached 13,329 MW.
- There are 22 petrothermal GeoPPs operating in the world, most of which are located in Europe.
The obvious advantages of this type of energy are: practical inexhaustibility, independence from weather and climatic conditions, the possibility of direct and indirect use of steam and hot water.
Industry
Industrial use of geothermal resources can have several directions:
- Energy. The enterprise consumes heat from a boiler house or electricity from a mini-GeoPP, which uses the thermal energy of the Earth.
- Direct use of hot water or steam for technological needs.
- Indirect use of thermal energy from underground sources through the creation of double-circuit systems.
Agriculture
By 2015, 38 countries around the world were actively using geothermal energy for agricultural needs. It is used for sterilization, pasteurization and drying of food products; carries out heating of ponds and greenhouses, increases the temperature of air, water and soil in agricultural structures.
District heating
The use of geothermal resources for heating settlements, buildings and structures is quite practical and effective. Iceland, a country that has no other energy resources, has achieved great success in this direction. Similar experience already exists in the countries of the Pacific Rim and in southern Russia.
Balneology
Perhaps the most ancient way of using the Earth's heat for medicinal purposes, known to residents of many regions of the world that have healing hot springs. But not only. There are places in the world where hot steam or even air comes out of rocks, which is used to treat a number of diseases.
It is clear that over time, this natural heritage has been placed on a more technically and medically professional basis. There are many resorts and hospitals providing their services in this direction. And the number of these institutions using underground heat to restore and improve health continues to grow continuously.
Efficiency and payback
Geothermal energy cannot be called a free gift from nature. The creation of heating systems based on it can cost over a million rubles, excluding the cost of a heat pump. It all depends on the required heating volumes, its functional purpose and type. Typically, the economic feasibility of geothermal heating systems is calculated by comparing the costs of its maintenance.
The cost of any type of energy used is not constant and will never decrease. In this regard, their alternative replacement by using the heat of the internal layers is, of course, economically profitable and expedient, since heat pumps do not consume a lot of energy, and to extract and process thermal reserves there is no need to build expensive factories and power plants.
Moreover, each generation of scientists finds new solutions for creating equipment and technologies in this direction. In addition, it is more correct to estimate the cost of heating systems equally for all types of fuel from zero without the use of existing centralized supply systems, for example, gas. And then the payback of the system in 5 years will become a real value.
The use of geothermal heating systems is reminiscent of the question, why not drive a Zaporozhets car nowadays. Of course, you can, especially off-road and into the forest to pick mushrooms. But you want it faster and more comfortably. So it is in this case. The mere thought that your own heating system does not disturb the environment and does not interfere with the lives of even the smallest and most unknown creatures in nature will confirm the correctness of choosing a geothermal system.
Do-it-yourself geothermal heating at home
It is quite possible to install and put into operation geothermal heating yourself. However, difficulties may arise during the work. First of all, this concerns the installation of the external circuit in the ground. Therefore, if you do not have the necessary skills, it is recommended to entrust setting up the system to professionals who will make a competent calculation and install the entire geothermal heating system.
Preliminary calculations
In order for geothermal heating to bring the planned effect, it is necessary to make calculations. They will help you choose the power of pumping equipment. Approximate figures for buildings with different levels of thermal insulation differ. So, to heat one square meter you will need:
- without thermal insulation – 120 W;
- with conventional thermal insulation – 80 W;
- with energy-saving insulation - 40 W.
For calculations, you will also need figures determining heat loss in the house. For example, if for a residential building with an area of 180 sq. meters with high-quality thermal insulation, heat loss is 9 kW/day, then the equipment must provide a power of 216 kWh (9 kW x 24 hours). Taking into account the fact that heat losses may differ at different times, an increase of 10-20% is made. Therefore, the final pump power of the geothermal heating system should be 10.8 kW.
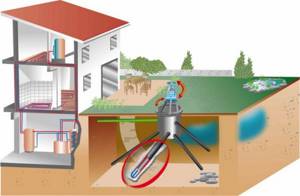
When making calculations, it is important to consider some points. These include the soil temperature at the well level
In central Russia it stays within +8...+10 degrees (at a depth of 15-20 meters). With a horizontal arrangement of the external circuit of the heating system, a power of 50 kW per meter is taken into account. The exact numbers depend on geological conditions (humidity, presence of groundwater). Different soils give different indicators:
- Dry soil – 25 W/m;
- Wet substrate – 45-55 W/m;
- Hard rocks – 85 W/m;
- Presence of groundwater – 110 W/m.
How to install a heating system
Water systems are rare; geothermal heating through the ground is most in demand. Therefore, the first stage of work involves drilling wells or digging a pit. Recesses are made to a depth of 20 to 100 meters using special equipment. The bottom of the pit is covered with sand. Next, plastic pipes that can withstand a pressure of about 6 bar are placed in the prepared recesses or trenches. These pipes will act as probes.
During installation, pipe piping of three or four lines is used, with the edge sections connected in the form of the letter “U”. The external contour can be purchased ready-made or assembled yourself.

When the most difficult part of the work on installing a geothermal heating system is completed, they begin to connect the pump. The wiring with this method is similar to the wiring of a traditional heating system.
Benefits of Geothermal Heating
This type of system is an excellent way to supply heat to buildings. This is an opportunity to save money and energy. The main advantages of geothermal heating include:
- Energy efficiency
- A geothermal heating system generates 5 units of energy from 1 unit. The efficiency of such a system is 530%. The efficiency indicator of a modern gas boiler is 98%.
- Economic efficiency
- Due to the large difference in energy efficiency of such a system, on average, investments in it pay off in several years.
- Environmental Safety
Geothermal energy sources are recognized as the most environmentally friendly. They minimize the threat of air pollution. Installing one geothermal pump is the environmental equivalent of planting 750 trees.
- Fire safety
Since the heat pump does not use natural gas to operate, there is no source of flame or carbon monoxide.
- Everywhere Availability
The equipment can be installed anywhere. The main condition is the availability of electricity in the house.
- High reliability
The geothermal circuit is located underground at a constant temperature. It is not exposed to thermal loads during fuel combustion. The declared service life of heat pumps is 25-30 years.
Sources and principle of operation of thermal heating
To generate heating, high-temperature and low-temperature sources of ground thermal energy are used. The first include thermal springs with hot water, but this type is rare. The second includes all other sources - air, earth, water.

Energy is produced using special equipment. Heating with a heat pump involves mounting the device on the surface, and the heat exchanger is lowered into the shaft, so the coolant in the external circuit is heated to the ambient temperature in which it is buried and is supplied to the heat pump. And from here, concentrated heat is transported through pipelines and radiators in the rooms.
The dimensions of the heat pump are comparable to the size of a conventional washing machine; the unit requires electricity to power it. For 1 kW of electricity consumption, the pump generates up to 5 kW of heat.
Methods for implementing a geothermal installation
This type of heating differs in the way the heat exchanger is installed. Today there are three varieties in use:
- Vertical heat exchanger: it is compact and has a higher installation cost compared to other types. To install a vertical heat exchanger, you do not need to use a large area, but you will need to use specialized drilling rigs. Depending on the chosen technology, the depth of the finished well can reach up to 200 meters, the minimum is 50 meters. The service life of the system is up to one hundred years. It is beneficial to install this type of geothermal heating if it is installed on an already developed area. The landscape of the area will remain virtually untouched.
- Horizontal heat exchanger: This type is used quite often. When installing a horizontal heat exchanger, the pipes are laid to a sufficiently large depth, which necessarily exceeds the level of soil freezing. The main disadvantage of using exactly this type of wiring is that it requires a large area to be used for installing the collector. It is difficult to install such a system on an already developed site.
- Water-based heat exchanger: this installation is the most cost-effective among all the variety of geothermal heating, as it works using the energy of water bodies. This system is relevant for those homeowners who have a body of water hundreds of meters away. Such a heat exchanger is the most profitable, which makes its installation the most appropriate among all types of similar heating.
Types of geothermal installations
Having understood what geothermal heating of a house is and the principle of operation of the equipment, let’s consider the types of systems.
There are 3 types of installations:
Earth-water is considered the most efficient system for heating residential premises. The operating principle boils down to the consumption of heat from the ground through probes, collectors and energy transfer to a heating system with a water coolant.
- Water-water uses warm water resources as energy. To ensure the functionality of the system, a source (pond, river, lake) is needed. Experts note that this design is the most stable in terms of temperature indicators.
- Air-to-air uses an unlimited and accessible natural supply for work. The functionality of the system is provided by fans and evaporators connected into one complex. The greatest efficiency is achieved at temperatures down to -15 C; when the air gets colder, part of the system’s power is lost.
Advantages and disadvantages
The objective advantages of geothermal heating can be considered:
- excellent efficiency;
- a solid service life (a heat pump lasts 2-3 decades, and geological probes last up to 100 years);
- stability of operation under almost any conditions;
- lack of connection to energy resources;
- complete autonomy.
There is one major problem preventing geothermal heating from becoming a truly widespread solution. This, as reviews from the owners show, is the high price of the structure being created. To heat an ordinary house of 200 square meters. m (not so rare), it will be necessary to build a turnkey system for 1 million rubles, up to 1/3 of this amount costs a heat pump. Automated installations are very convenient, and if everything is configured correctly, they can work for years without human intervention. Everything depends only on the availability of free funds. Another disadvantage is the dependence on the power supply of the pump unit.

Disadvantages of geothermal heating:
- The cost of a geothermal method of heating a house will require significant capital costs.
- Volatility - the system requires power to operate. To avoid interruption of heat supply to your home due to a power outage, you need to purchase a gasoline or diesel fuel electric generator.
- Subcooling of the soil occurs in the area where the heat collection collector is located (usually due to errors made during the design). Leads to disruptions in the operation of the system.
Advantages and disadvantages of geothermal heating pumps

Let's start with the negative aspects:
- High requirements for regulatory parameters of adjacent territories. The station cannot be installed at any point; geological exploration is first required to determine the feasibility of using the equipment.
- High price. One-time investments exceed the capabilities of many owners. There is an option to use government assistance, but it is issued only to a certain group of beneficiaries.
- Changes in the position of the circuit in the first year of use. The pipes sag, the circulation rate of propylene glycol decreases, which leads to a decrease in heat transfer rates and COP.
Advantages of the equipment:
- Economical. There is no need to stock up on solid fuel or connect a gas line. Electricity consumption is minimal. The costs can be recouped within 5 years.
- Functionality. The entire system provides heating in winter and air conditioning in summer. This is convenient and you don’t have to set up another system.
- Long service life. The pump itself operates for 100 years, but some key parts are replaced every 30-50 years, which is much less common than any other equipment.
You should know that in European countries geothermal pumps are used to produce heat not only for residential buildings, but also for manufacturing and industrial enterprises. The economic benefits become more obvious if we take into account the long service life, as well as the minimum costs for maintenance and repair of the system - the latter is practically excluded, since all components are reliably buried in the ground or water and are not subject to mechanical stress.