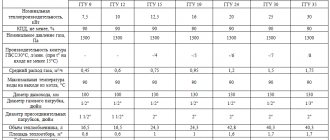
Few people know that the choice of a chimney system directly depends on the temperature of the exhaust gases during fuel combustion in the boiler. Ignoring this important point leads to the fact that soon after assembling the chimney, the metal pipe or brick structure crumbles, so repairs and financial costs cannot be avoided. To understand why this happens, you need to understand the operating features of gas boilers.
Important nuances
In solid fuel boilers, fuel burns at a high temperature, so the exiting gases have a high temperature (usually about 300 degrees, although the values may vary up or down). The situation is completely different with gas boilers.
Modern gas equipment used for space heating has an important feature - the temperature of the combustion products leaving does not exceed 120 degrees, and sometimes is significantly lower than this mark. This is due to the desire of manufacturers to increase the efficiency of gas boilers. This desire also has its negative sides. The lower the temperature of the exhaust gases, the more condensate forms inside the system. Condensate contains aggressive substances and therefore has a destructive effect even on stainless steel pipes. In general, unpleasant consequences can be prevented if you take into account several important nuances.
The temperature of the exhaust gases directly depends on the radiator settings. If heating radiators heat up to a temperature of 65 degrees, the combustion products will have a low temperature. When using a heated floor system, in which the water is heated to only 35 degrees, the temperature of the gases will be even lower and there will be more condensation.
Corrosion. Eliminate risks
We don’t argue that corrosion is an unpleasant phenomenon that can jeopardize the safe operation of a boiler installation and significantly shorten its intended service life.
When the flue gases are cooled to the dew point temperature and below, condensation of water vapor occurs, along with which NOx and SOx compounds pass into a liquid state, which, when reacting with water, form acids that have a destructive effect on the internal surfaces of the boiler. Depending on the type of fuel burned, the acid dew point temperature may vary, as well as the composition of the acids precipitated as condensate. The result, however, is the same - corrosion.
The exhaust gases of boilers operating on natural gas mainly consist of the following combustion products: water vapor (H2O), carbon dioxide (CO2), carbon monoxide (CO) and unburned flammable hydrocarbons CnHm (the latter two appear during incomplete combustion of fuel when the mode combustion is not adjusted).
Since atmospheric air contains a large amount of nitrogen, among other things, nitrogen oxides NO and NO2, collectively called NOx, appear in combustion products, which have a detrimental effect on the environment and human health. When combined with water, nitrogen oxides form corrosive nitric acid.
When fuel oil and coal are burned, sulfur oxides called SOx appear in the combustion products. Their negative impact on the environment has also been widely researched and is not in doubt. The acidic condensate formed when interacting with water causes sulfur corrosion of heating surfaces.
Traditionally, the flue gas temperature, as shown above, is selected in such a way as to protect the equipment from acid precipitation on the heating surfaces of the boiler. Moreover, the temperature of the gases must ensure condensation of NOx and SOx outside the gas path in order to protect not only the boiler itself, but also the flues with the chimney from corrosion processes. Of course, there are certain standards limiting the permissible concentrations of emissions of nitrogen and sulfur oxides, but this does not in any way negate the fact that these combustion products accumulate in the Earth’s atmosphere and fall out in the form of acid precipitation on its surface.
The sulfur contained in fuel oil and coal, as well as the entrainment of unburned particles of solid fuel (including ash) impose additional conditions for the purification of flue gases. The use of gas purification systems significantly increases the cost and complexity of the process of utilizing heat from flue gases, making such measures poorly attractive from an economic point of view, and often practically not profitable.
In some cases, local authorities set a minimum flue gas temperature at the mouth of the stack to ensure adequate flue gas dispersion and no plume. In addition, some businesses may voluntarily adopt such practices to improve their image, since the general public often interprets the presence of a visible smoke plume as a sign of environmental pollution, while the absence of a smoke plume may be seen as a sign of clean production.
All this leads to the fact that, under certain weather conditions, enterprises can specially heat flue gases before releasing them into the atmosphere. Although, understanding the composition of the exhaust gases of a boiler operating on natural gas (it is discussed in detail above), it becomes obvious that the white “smoke” that comes from the chimney (if the combustion mode is correctly configured) is mostly water vapor formed in as a result of the combustion reaction of natural gas in the boiler furnace.
The fight against corrosion requires the use of materials that are resistant to its negative effects (such materials exist and can be used in installations that use gas, petroleum products and even waste as fuel), as well as the organization of collection, processing of acidic condensate and its disposal.

When choosing a chimney, consider the boiler power
When choosing a chimney system, it is necessary to take into account the power of the gas boiler. The higher the power, the higher the combustion temperature of the fuel will be. This is sure to be reflected in the escaping gases. The power value helps to choose the correct pipe diameter and length. For example, a 300 kW boiler requires a pipe with a diameter of 150 mm.
Typically, the instructions for use indicate not only the technical characteristics of the heating equipment, but also provide recommendations for the selection and installation of a chimney system. If necessary, seek help from a specialist if you yourself cannot correctly calculate the optimal parameters of the chimney pipe.
Main mistakes when choosing and operating a solid fuel boiler

Unfortunately, many people make mistakes both when purchasing a boiler and when operating it, which results in troubles. Such problems and troubles include: poor heating of the room and constant low temperatures, excessive waste of fuel and financial resources, the need for frequent cleaning or frequent boiler repairs. Dear customers, we ask you to read this article to avoid mistakes when choosing, installing and operating a solid fuel boiler.
What is the operating principle of a solid fuel boiler? Why clean the boiler?
A modern solid fuel boiler is a combination of tubular or plate heat exchangers through which heated gases move. The metal walls of the boiler heat exchangers are simultaneously the walls of the water circuit through which the coolant constantly moves, and the walls of the flue. As a result, on the one hand, the surface temperature of the heat exchanger is increased by the flue gases, and on the other hand, it is decreased by the cooled coolant. Thus, heat is transferred to the coolant through the boiler heat exchangers.
The combustion process of solid fuel is accompanied by the release of flue gases. Flue gases always contain a percentage of soot and tar, which settle on the walls of the chimney and inside the boiler during its operation. It is impossible to completely get rid of the formation of plaque on the surfaces of heat exchangers. Therefore, it is necessary to regularly clean your solid fuel boiler at least once a month.
If you do not regularly clean the boiler, the boiler will consume more fuel to heat your room, since a layer of soot on the surface of the heat exchanger of only 2-3 millimeters reduces the boiler power by 20-30%.
This is explained by the fact that soot and tar on the walls of the heat exchangers act as a heat insulator, which reduces the efficiency of the boiler and prevents the exchange of heat between flue gases and the coolant. Soot and resins also settle on the walls of the chimney, and their accumulation in a critical volume inside the chimney can lead to a fire. Intense combustion of deposits heats up the chimney and the roof and attic floors catch fire.
What are the reasons for the accumulation of soot and tar on the boiler heat exchangers and on the chimney walls?
1. Fuel.
The choice of fuel is a fundamental factor in the correct and stable operation of the heating boiler - Firewood.
The main indicator is humidity.
High-quality firewood is wood with a moisture content of no more than 20%. Firewood with higher humidity burns longer, but worse. And accordingly, more such firewood will be needed to maintain a comfortable temperature in the house, since part of the thermal energy released during combustion is spent on evaporating excess moisture in the wood. The use of raw firewood significantly speeds up the process of planting the boiler, as it produces very large tar emissions. Many “experts” write on forums that you should lay firewood with a humidity of 40% or higher. Such firewood actually burns longer, but the rate at which heat exchangers are planted increases significantly, which entails a loss of boiler power and additional fuel consumption. - Coal.
In the case of coal, there are more basic quality indicators than with firewood. — Brand of coal. For example, for boilers with layered fuel combustion, the best option is to use DO grade coal. Brand – long-flame, piece size – walnut (25-50mm). It is also possible to use the DOM (long-flame nut with small) and DKO (long-flame large nut) coal varieties. But the use of these varieties is not recommended on an ongoing basis, since in one case fine coal will block the access of air through the grate, and in another case large pieces can cause coal to hang in the loading chamber. — Calorific value. Another important indicator is the calorific value of the fuel. The specific heat of combustion of the selected coal must be at least 5800 kcal/kg. The use of fuel with a calorific value below the specified limit will lead to a decrease in boiler power and, as a result, an increase in fuel consumption. In some cases, there may be a low temperature of the water leaving the boiler. - Ash content. High ash content of the fuel leads to clogging of the grate with ash and a premature decrease in the heating output of the boiler. If there is a large amount of sand and other inclusions in the fuel, the amount of ash residues increases and the fuel cokes. - Caking. The high content of dust and fine fractions in the fuel prevents the flow of air for its efficient combustion. This leads to sintering of the fuel and a decrease in the heating output of the boiler. - Humidity. Fuel must be stored in a dry place at a temperature of at least 5°C, avoiding contact with moisture. High humidity and low fuel temperature lead to a significant reduction in the heating output of the boiler and its operating time on one load. At the same time, the temperature of the flue gases decreases, the amount of deposits on the heat exchange surfaces of the boiler and chimney increases, which is extremely negative for the operation of the boiler. If it is not possible to store a large amount of fuel in a warm and dry place, organize intermediate storage of a portion of fuel equal to one full load into the boiler in your boiler room.
2. Miscalculations in choosing boiler power
One of the main mistakes is the incorrect selection of a boiler. In this case, the boiler power will not be enough to achieve the optimal temperature of the coolant in the heating system. Errors in the selection and installation of a heating boiler are especially expensive. Often, when choosing a heating boiler, serious importance is not attached to the competent calculation of the required boiler power and simplified calculation schemes are taken as a basis. To choose the right boiler, you need not only to know the area of the room - it is important to take into account the thickness of the walls, the size of the windows, and the material used in the construction of the building. An important condition is the presence of another type of heating, for example, “warm floors” or hot water supply.
3. Low supply and/or return temperature in the heating system. Errors in heating system calculations.
The heating system is a closed circuit, all links of which - the heating boiler, pumping equipment, pipelines, fittings and radiators - work in close interconnection with each other. It is very important that no serious mistakes are made at the design, selection and installation stages of these elements. The main mistake of boiler users in this case is underestimating the boiler supply temperature, as well as low return temperature. When using a draft regulator together with a boiler (to automate combustion), users often set the temperature on the combustion regulator to less than 65°C. This often happens in the off-season to reduce the air temperature in the room, when the temperature outside rises, or when the number of radiators in the heating system was incorrectly selected and/or the total amount of coolant does not correspond to the boiler power. There are violations when the amount of coolant in the heating system much exceeds the required amount. In this case, the temperature of the circulating water decreases to a temperature below 60°C and intense condensation and soot deposition occurs on the heat exchange surfaces of the boiler. To maintain a nominal return water temperature of at least 60°C, it is necessary to install a mixing valve or a recirculation pump.
4. Lack of oxygen
Often, as a result of incorrect selection of boiler power, boilers in private homes operate in a suppressed mode. This mode is ensured by limiting the air supply to the combustion chamber of the boiler. This technique allows you to extend the duration of fuel combustion and limits the intensity of combustion if the system is already in a warm state. The lack of oxygen during fuel combustion has its consequences - incomplete combustion of the fuel. For proper operation of the boiler, it is necessary to ensure the flow of fresh air into the room where the boiler is installed through the ventilation holes in the walls of the room. Due to the lack of air for fuel combustion, tar formation, formation of semi-coke gas and deterioration of traction are possible.
Boiler room requirements:
- The volume of the boiler room cannot be less than 15 cubic meters. For each kilowatt of boiler power, an additional 0.2 cubic meters of area should be allocated;
- Ceiling height – at least 2.5 meters;
- Supply and exhaust ventilation is required.
Ventilation requirements:
- The exhaust intensity should provide three air exchanges per hour.
- The return air flow must completely compensate for the volume of the exhaust and exceed it by the amount of air necessary to maintain combustion of the energy carrier;
- The boiler room needs supply and exhaust ventilation. The cross-section of the supply and exhaust ventilation windows is at least 0.25 square meters. meters.
The air requirement for a coal-fired boiler is calculated using the formula: Vв=1.86*P
, cubic meters/hour where P is the boiler power (kW)
How to properly fill the system with coolant? Should I choose water or antifreeze?
To avoid damage to the boiler due to material stress resulting from temperature differences, the heating system must only be filled (or topped up) when it is cold (flow temperature should not exceed 40°C). During the filling process, it is necessary to bleed air from the heating system. For this purpose, automatic air valves must be installed in the heating system. It is IMPORTANT to install the valve at the highest point of the heating system. The most common type of coolant is water, which has a high heat capacity and can maintain temperature for a long time. Meanwhile, water contains dissolved oxygen, which is released over time and contributes to metal corrosion, which reduces the value of this liquid when used in heating systems. Water must be clean and colorless, without suspensions, oil and chemically aggressive substances, with a total hardness of no more than 2.0 mEq/l. The use of hard water as a coolant causes the formation of scale in the boiler, which reduces its thermal parameters and also causes damage to the heating element unit (if it is installed in the boiler). The deposition of 1 mm of limestone on the internal surfaces of the boiler reduces the transfer of heat from metal to water in a given location by 10%. If the water hardness does not meet these requirements, it must be treated. If the boiler and heating system are not protected from freezing, it is recommended to fill the system with antifreeze with a low freezing point and anti-corrosion additives. When using these coolants, it is necessary to comply with the requirements for their use in heating systems. In addition to its main function - heat transfer - antifreeze in heating systems prevents freezing of radiators and heating system pipes. Most often, antifreeze for the heating system is used in country houses, which are heated inconsistently during the cold season.
Heating antifreeze is selected according to the following parameters:
- main substance
- the presence of additives,
- crystallization temperature.
Antifreezes for heating systems have two main performance characteristics:
- viscosity,
- operating temperature range.
The antifreeze in the heating system must be changed at least once every three years. Antifreeze: advantages and disadvantages
Using antifreeze in the heating system of your home provides a number of advantages over using ordinary water:
- does not freeze at low temperatures;
- does not cause corrosive processes;
- eliminates scale formation.
Antifreeze for heating systems has a number of characteristics that may require upgrading the system and a slightly different approach to its operation:
- the heat capacity of antifreeze is 15% lower than that of water, so heat transfer will occur more slowly;
- higher viscosity requires the use of a more powerful circulation pump;
- a more significant expansion of antifreeze when heated requires the presence of an expansion tank and larger radiators in the system;
- antifreeze is more fluid, so all connections in the system must be carefully sealed;
- When using antifreeze that contains ethylene glycol, you should remember its toxicity and use it only in single-circuit systems.
Remember the basic rules!
- It is prohibited to disassemble the coolant from the boiler and heating system for different needs.
- It is prohibited to use liquids not intended for heating systems as a coolant.
Flushing the heating system. Water used for heating systems must be softened to reduce the risk of scale formation inside the pipes, but sediment still remains on their internal walls, which must be removed in a timely manner. Experts recommend washing at certain intervals:
- hydraulic – annually;
- hydropneumatic – once every 4 years;
- chemical – once every 5 years.
A special liquid for flushing heating systems is used only in the latter case.
When the cleaning agent enters the pipes, it enters into a chemical reaction with deposits, dissolves them and allows them to be removed during subsequent purging. How to choose the right chimney?
The combustion process is impossible without the release of smoke, but also without a constant supply of oxygen. This means that boiler equipment cannot operate without a chimney. It is this unit that is responsible for removing exhaust gases and supplying fresh air to the system. But for it to function effectively, it is necessary to choose the right chimney for a solid fuel boiler. Which model will be the best? What to look for when choosing? What should the exhaust gas removal system be like? The quality of boiler operation directly depends on the presence of draft. It is created as a result of different temperatures inside the chimney duct and outside. The greater the difference between them, the better the traction, and therefore the more completely the fuel burns. But besides temperature, this parameter is also affected by other characteristics:
- Height
- Form
- Availability of turns
- Surface roughness
- Location of the wind support zone
The straighter and narrower the pipe is, the better its traction, and turns and slopes significantly worsen this indicator. The height of the chimney for a solid fuel boiler is regulated by regulatory documents and cannot be less than 5 m
, this is due to the fact that the smoke rises upward in a spiral, gradually increasing speed.
And in various kinds of branches, the direction of movement of gases changes, which can lead to turbulence. A round shape is considered ideal. But a square or rectangular one will lead to the rapid accumulation of soot, significantly worsening traction performance. However, the length and cross-section of the chimney should be selected depending on the individual characteristics of the equipment. When installing a chimney system, it is necessary to use round-section stainless steel chimney pipes with sandwich-type thermal insulation. They are resistant to aggressive environments and the formation of condensation. The recommended thickness of the chimney steel is at least 0.8 mm, steel grade AISI 316L, AISI 321, AISI 430. Installation of modern boilers in a brick chimney is not allowed, since condensate is formed during the combustion process, which can lead to to cracks or structural failure. Installing a chimney for solid fuel boilers is quite a complex matter, so without having the necessary knowledge of boiler equipment, it is better to entrust the selection and installation to specialists. The key influence on the operation of the boiler is the correct choice of the height and diameter of the chimney
.
When selecting the diameter of the chimney, no narrowing should be created relative to the boiler outlet pipe. When selecting a pipe, it is prohibited to increase the diameter by decreasing the height, this reduces the flow rate of flue gases. Low flow rates promote the formation of condensation on the walls of the chimney. The length of the horizontal section is not allowed to exceed 1 meter. It is recommended to place horizontal sections at a slope - this will help maintain constant traction. Do not forget! You cannot connect two boilers to one chimney! When installing a chimney, comply with all requirements regulated by regulatory documents.
The height of chimneys placed at a distance equal to or greater than the height of a solid structure protruding above the roof should be taken: - at least 500 mm above a flat roof;
- at least 500 mm above the roof ridge - when the pipe is located at a distance of up to 1.5 m from it; - not lower than the ridge of the roof or parapet - when the pipe is located from it at a distance of 1.5 to 3 m; - not lower than a line drawn from the ridge downwards at an angle of 10° to the horizon - when the pipe is located at a distance of more than 3 m from it. In any case, chimneys must be installed above the roof of taller buildings attached to a building with boiler heating.
Which material should you prefer?
Nowadays, stainless steel chimneys are very popular on the market. They are used for boilers of various types, although this approach is fundamentally wrong. If you plan to install a gas boiler, you need to decide what material the chimney should be made of. Don't rush to buy metal pipes. They are excellent for solid fuel boilers, as they can easily withstand high temperatures.
For gas boilers, which are characterized by low temperatures and large amounts of condensate, it is preferable to choose plastic or polymer pipes. Their main advantage is good resistance to moisture. Because of this, they usually last longer than metal chimneys. FuranFlex pipes are excellent for gas boilers, which are characterized by excellent resistance to aggressive substances, strength and durability.
If you use a gas-wood combination boiler, you will have to abandon the use of FuranFlex. The fact is that polymer pipes are produced in two versions - for high and low temperatures (solid fuel and gas boilers, respectively). Polymer stockings cannot be used effectively at high and low temperatures at the same time.
Gas boilers without traditional chimneys
Gas heating boilers without traditional chimneys are a solution for apartments. These are units with a closed combustion chamber; they have a special system built into them for removing carbon monoxide. These boilers do not need a chimney with natural draft, because a special turbine in forced mode removes exhaust gases from the firebox. The gas exhaust system for such gas boilers can be used from polyvinyl chloride with any number of turns, and it is not necessary to maintain a vertical position. This type of chimney is designed as a coaxial type, it is led out through a hole in the wall of the apartment, and is aesthetically attractive.

Standards for installing a chimney relative to the building facade
When choosing a chimney for a gas heating boiler, be guided by the parameters of your device and the requirements for the installation of chimneys. This will guarantee your safety, as well as the uninterrupted operation of your gas equipment.
Features of repair work to restore the chimney
If repair of a gas boiler, or more precisely its chimney system, is required, the most effective solution would be to use FuranFlex technology. When installing a polymer stocking, there is no need to perform dismantling work. The FuranFlex pipe is inserted into the chimney from the inside, and after hardening it serves as support and protection. It prevents further destruction, while the material itself has excellent performance characteristics. The main thing is to choose the right type of material, but our employees are always ready to help in resolving this issue. They will advise you on all your questions.
Installation of a chimney according to the rules
Based on where the gas boiler will be located relative to the house, the chimney installation is carried out in two ways:
Indoors. Installing such a system is quite troublesome, and it is also necessary to strictly comply with fire safety requirements, because such a chimney has an increased risk of ignition or carbon monoxide leaking into the room. If all the rooms through which the chimney pipes pass are heated, then only the pipe located on the roof will need insulation. Please note that such a chimney is difficult to repair.
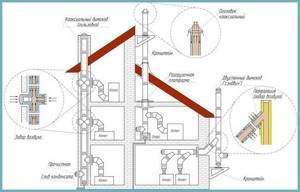
Coaxial pipe installation options
If you decide to install a chimney for a heating gas boiler yourself, then you first need to apply marks for drilling holes for the flue pipe in the ceiling and roof. Then double-check everything again, as they say: “measure seven times, cut once.” Cut out the opening. Now, let’s actually assemble the chimney:
- connect the heating boiler pipe to the adapter;
- Now you need to connect the tee and revision. After this, a sheet of steel is attached and the main holder is secured;
- we extend the gas outlet pipe from the bottom up, if necessary, use elbows;
- a special pipe is used in the place where the chimney crosses the floor of the house;
- Next, you need to throw a galvanized sheet over the chimney with a hole made in it, which is larger than the diameter of the chimney, and secure this sheet at the top and bottom of the ceiling;
- all places where gas outlet structures are joined must be additionally reinforced with clamps;
- We put a cap on the very top of the chimney - it will protect the chimney from bad weather.
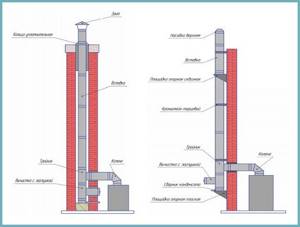
Outside. Due to the uniformity of the constituent elements of the chimney, it is easy to install and therefore easy to repair. Such a chimney requires thermal insulation along its entire length. If you are installing a chimney on the outside of the house, then the procedure is as follows:
- We mark the places for drilling openings and double-check. Then we thread the system passage through the drilled opening, one end of which is hermetically connected to the boiler pipe. The area that penetrates the wall is thermally insulated;
- we attach the revision and tee, then connect the plug;
- We install the flue elements from the bottom up. Don’t forget to attach the holders to the surface of the house;
- We reinforce all joints with clamps;
- Now you need to attach thermal insulation along the entire length of the chimney; this does not need to be done if you used a sandwich pipe.
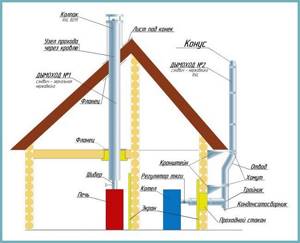
When installing a chimney, remember:
- all structural elements must be assembled correctly, gaps are unacceptable, and deflection of elements is also unacceptable;
- in places where the chimney crosses the structure of the house, it is necessary to install passage elements;
- The boiler and chimney are connected by applying heat-resistant sealant to the joints.
Advice. Thermal insulation of the chimney is performed with mineral wool, which is wrapped on top with foil or a sheet of galvanized steel. But there are ready-made products made from mineral materials on sale; you only need to measure the diameter and length of the pipe.
Which boiler to choose?
Chimneys for solid fuel boilers differ in several ways.
- Main (pipe risers standing on a separate foundation, connected to the boiler by an inclined gas duct).
- Mounted (installed directly above the boiler and serve as a continuation of the boiler flue).
- In the form of a channel in the wall (built during the process of laying load-bearing external or internal walls).
Depending on their location, boilers can be external or internal:
- External (mounted outside the building as free-standing or attached to an external wall in a radical design).
- Internal (mounted inside a building in any design).
Note! The operation of two or more solid fuel boilers on a common chimney is not allowed.
- metal (ferrous, galvanized, stainless or sandwich pipes);
- brick (ceramic or fireproof);
- ceramics (ceramic pipes and blocks);
- concrete (prefabricated reinforced concrete panels with special vertical channels of round or oval cross-section);
- asbestos cement (pipes made of asbestos cement);
- glass (special fire-resistant glass).
The most common ones when installing individual boiler rooms with solid fuel boilers are chimneys made of brick, ceramics and steel:
| Brick chimneys | Clay and refractory bricks are traditionally used in the construction of chimneys. Requires special masonry skills. | the ability to build them into an array of walls without taking up useful space in the room. |
Due to partial utilization of useful energy (t = 250-3000), additional heat radiation occurs in the rooms adjacent to the chimneys.
not subject to corrosion,
durability, do not require additional insulation.
Pipe height
This size is determined by SNiP, which sets certain parameters:
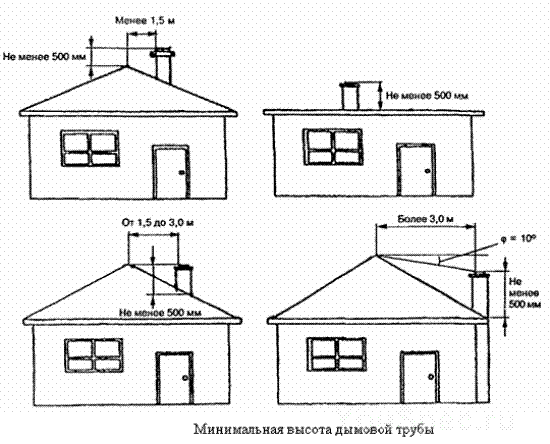
- If the roof is flat, the chimney should rise 1.2 meters above it.
- If the chimney is located near the ridge, and the distance is less than 1.5 meters, it should rise above the ridge by 0.5 meters or more.
- When the pipe is located in the range of 1.5 - 3 meters to the ridge, it should not be below the ridge line.
- If the location of the chimney from the ridge exceeds 3 meters, its height should be on a line extending from the ridge, maintaining an angle of 10 degrees relative to the horizon line.
Features of installation and connection of chimneys
Installation of a metal chimney is carried out in the following ways:
- along the smoke path - the elements are assembled by inserting the lower pipe into the socket of the upper one;
- along the condensate drain - in the reverse order, the higher one is inserted into the socket of the lower pipe.
The chimney is made of steel with a thickness of at least 1 mm and is installed vertically.
Permissible deviations in certain areas are no more than 30°. It is necessary to have a special acceleration section at least 1 m long after the boiler nozzle. It is permissible to have horizontal sections no longer than 0.5 m.
The elevation of the pipe head above the roof is set within 50 cm. The joints are sealed with heat-resistant sealant.
When installing on a wall, fastening is carried out in increments of at least 1.5 m.
When installing the pipe indoors, contact with flammable materials is unacceptable; the distance to walls and wooden floor structures is at least 0.25 m. It is necessary to install a special protective screen on the chimney.
Requirements for chimneys for solid fuel boilers
When equipping a home with a water heating system, the source of which is a solid fuel boiler, one of the most important issues is the correct choice of chimney. It largely depends on the design features of the house and the performance of the boiler unit.
It should be taken into account that the following requirements apply to any type of chimney:
- absolute tightness (preventing the penetration of flue gases into the premises);
- providing the necessary draft (creating a vacuum in the chimney that exceeds the gas resistance of the boiler);
- no difficulties during installation (manufacturability, no need for complex and expensive equipment, moderate labor costs);
- durability of the structure;
- low operating costs;
- thermal and corrosion resistance of the materials used;
- smooth inner surface (no seams, joints, differences);
- optimal aerodynamic section (circle or oval);
- high fire safety;
- minimal thermal conductivity of the chimney walls (to prevent the formation of condensation inside the chimney);
- successful design solutions.
Note! The round or oval cross-section and smooth internal surface prevent soot deposits in corners, joints and on rough surfaces of the chimney walls.