Until recently, flow-exhaust ventilation with recuperators was used quite rarely in Russia and neighboring countries. In recent years, various premises have begun to be equipped with them en masse, which is primarily due to the reliability and efficiency of such systems.
Their main feature is the return of part of the heat from previously exhausted air. Leaving the room, it slightly heats the oncoming flow in the heat exchanger. As a result, not only fresh, but also slightly heated air enters the room, creating comfortable conditions for people.
What is an air recuperator?
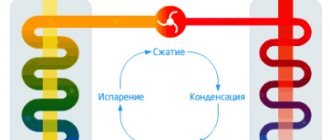
The air recuperator is a surface type heat exchanger. It is used to reuse the heat from the exhaust gases. This occurs continuously through the wall, which acts as a separator. Unlike a device such as a regenerator, the flows in a recuperator do not change their location.
An air recuperator is a device that minimizes losses through the ventilation system. As a result, this device can be called an energy-saving device. It involves the reuse of heat in the implementation of one technological process.
How the device works
The design of the air recuperator is quite simple. This affects the operation of this device. Its functioning is as follows:
- The flow of air into the room and its exhaust from the room occur simultaneously - in parallel with each other.
- Warm exhaust air is sucked into the device by a fan, thus entering the heat exchanger.
- Passing through the heat exchanger, the warm exhaust air exits to the outside of the structure itself.
- Cold fresh air is sucked into the room using reverse draft, passing through other parts of the heat exchanger.
- The heat from the air in the room is thus used to heat the cold flow that enters the room through the device.
Constant, non-intersecting air flows of different temperatures can provide recovery efficiency of more than 90%.

Why do you need a recuperator?
The popularity of air recuperators is due to several factors. They are used for the following purposes:
- improving the functioning of supply and exhaust ventilation in premises;
- providing apartments, private houses, businesses and offices with clean air;
- normalization of the temperature of the air flow entering from the outside;
- creating an optimal microclimate for human life in the room.
A recuperator is an effective and reliable device that is much better than standard supply and exhaust ventilation systems. It allows you to remove exhaust air from the premises, using its heat to heat the flows coming from outside the building. In turn, in the summer, the device works in the opposite way. In such situations, the cooler air in the room cools the warm flow that enters the room from outside.
System power calculation
Ventilator for large rooms with high power
The dimensions and power of the recuperator affect the performance of the device. The larger the area of the ventilated room, the more powerful the recuperator will be required. Therefore, before purchasing a device, you should calculate the power of the recuperator.
For this, the formula is used: Q = 0.335 x L x (T1 – T2), where:
- Q (W) – device power;
- L (m3/h) – the volume of air required for normal human life. According to the norm, one person requires 60 m3/h;
- Т1 (оС) – air temperature after recovery;
- Т2 (оС) – air temperature before recovery.
For example, let’s calculate the power of a recuperator for an apartment inhabited by 3 people. The temperature of the air transported to the premises must be at least 20 ° C, and air supplied from the street with a temperature of -10 ° C. Q = 0.335 x 180 x 32 = 1929.6 W.
When carrying out the calculation, you should take the minimum possible temperature (on average over 5 years), which was observed in the region where the recuperator is planned to be installed. If the device is not planned to be used as the main source of heating the room, then the temperature indicators are selected individually.
Types of recuperators
Currently, there are several different types of air recuperators. They differ from each other in such features as:
- Coolant flow diagram. In this regard, recuperators are counter-flow, cross-flow, etc.
- Design. Depending on their design, the devices can be tubular, plate, rotary, ribbed, finned plate type OPT, etc.
- Material of manufacture. The most common types of recuperators produced are metal, membrane and plastic.
- Purpose. Devices may have functions such as air heating, liquid heating, moisture evaporation, condensation of excess liquid, etc.
The most popular in their design are plate and rotary recuperators. Before purchasing one of these types of models, you need to pay attention to all their features and main differences.
Plate recuperator
Plate recuperators are in greatest demand today. This is due primarily to the simplicity of their design and low cost. Despite this, the efficiency of heat exchangers of such devices, as a rule, does not exceed 50%.
The main advantage of any plate recuperator is the complete isolation of air flows from each other. As a result, the exhaust air does not mix into the supply air. The heat of the flow removed from the room is transferred through aluminum plates to the air mass that enters the room.

The disadvantages of plate recuperators include the need to ensure drainage. As a result, the air dehumidifies.
In northern latitudes and the central climatic zone of Russia, experts do not recommend the use of plate recuperators. This is primarily due to their low efficiency. In addition, such devices do not function very well in such conditions due to constant freezing and thawing cycles.
Rotary recuperator
A distinctive feature of rotary recuperators is their high efficiency. As a result, such devices are sold at a higher cost than plate-type ones.
The operating efficiency of rotary recuperators is about 82%. Thus, if the air temperature outside is −28 degrees Celsius, it can be heated in the device up to +14 degrees Celsius.
The operating principle of rotary recuperators is based on heat recovery. The rotating drum of the device, made of foil, absorbs the thermal energy of the air flow removed from the room, transferring it to the supply air.

Rotary recuperators also have some other advantages. These include the absence of defrost cycles and the need to drain condensate. As a result, these types of devices have recently become increasingly in demand.
Main differences
Before purchasing a rotary or plate heat exchanger, you need to pay attention to the following main differences between them:
| Device Features | Plate recuperator | Rotary recuperator |
| Efficiency level | About 50% | About 82% |
| Device cost | Low | High |
| Defrost cycles | Present | None |
| Requirement for condensate drainage | Present | Absent |
| Design | Insulated aluminum fins designed for different air flows | A rotating drum made of aluminum foil absorbs heat from one air stream, transferring it to another |
| Payback | About 3-4 years | About 1.5-2 years |
| Saving rate | Small | Very significant |
The payback of recuperators directly depends on several factors. These include the climatic features of the region, room area, design efficiency, etc. In cold winters, some devices can pay for themselves in just one season. The system can significantly reduce household operating costs.
How the device works
The recuperation system consists of two main parts, one of which performs the function of taking air from the environment, pumping it into the premises, and the second moves the flow in the opposite direction - to the street. Thus, to install the system you need:
- Directly recuperator;
- A system of pipelines through which air moves;
- Diffusers that perform the function of controlling the movement of air.
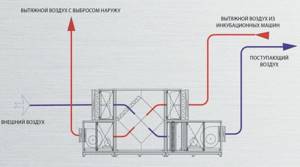
The recuperator itself contains several elements: a heat exchange module, a fan, a fan rotation mechanism to change the direction of the air flow, a damper, and a filter element. A heat exchanger is necessary so that the passing air gives off excess heat or heats up (depending on the season). Since the system eliminates the possibility of direct mixing of two air flows (moving from the room and into the room, respectively), clogging and the appearance of unpleasant odors are excluded.
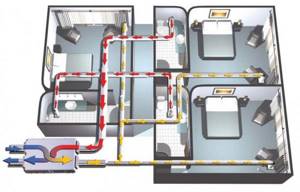
Thus, the regeneration system provides a favorable microclimate in the house without the need to install an indoor fan.
Step-by-step instructions for making a homemade recuperator with drawings
Despite the presence of a large number of air recuperators on sale, you can create such a device yourself at home. Before you begin this task, you need to pay attention to some important features. These include manufacturing materials, drawings and instructions.
Materials for production
Before the process of creating an air recuperator, it is necessary to purchase materials for its manufacture, such as:
- Sheet metal. It is best to use aluminum. Instead, roofing iron, textolite, getinax or cellular polycarbonate may also be suitable. In order to improve the level of heat transfer of the device, it is necessary to select the thinnest sheet metal.
- Wooden slats. They are required for laying between metal plates. Instead of wooden slats, it is allowed to use technical plugs or a simple cord. Their thickness should not be more than 2-3 millimeters. In this case, the width of the product should reach 10 millimeters.
- Sealant. It should not be based on acid, but on other substances.
- Glue. It is necessary to pay attention to what materials it is intended for. Glue intended for metal cannot be used to attach wood.
- Material for the device body. It can be plywood, metal or medium density fiberboard (MDF). Instead, experts advise purchasing a ready-made wooden box of the required hermetic dimensions.
- Four flanges. They must be exactly the same size as the previously selected pipes for the device.
- Mineral wool. The thickness of this product should be approximately 4 centimeters. This material is necessary to ensure thermal insulation of the room.
- Metal corner. They are designed to provide secure and efficient mounting of the device to the wall.
- Hardware. They are the fasteners that will be required to assemble the entire system.
- Fan or cooler. The main purpose of such a device is to ensure air flow into or out of the room.
To carve some parts during the work process, you may need a power tool. The width of the device body must correspond to the diagonal of the future heat exchanger. In turn, the height of the system directly depends on the number of plates that will be used to create the ventilation device.
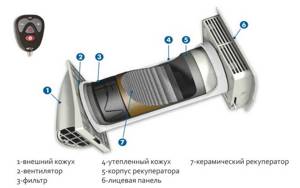
Step-by-step instruction
In order to create a truly reliable and efficient air recuperator, it is necessary to perform the following algorithm of actions:
- Initially, you need to cut the metal into squares with sides of 20-30 centimeters. You will need about 70 such plates.
- The slats should be covered with drying oil. After this, they need to be cut to the same size as the sides of the square sheets of metal.
- The slats must be glued on both sides to each plate. After this, you need to wait until the substance dries completely. There is no need to glue slats to one of the squares.
- Having coated the upper parts of the slats with glue, it is necessary to connect all the plates together. It is necessary to pay attention to the fact that each subsequent plate should be placed on the previous one with a rotation of 90 degrees. Thus, the channels formed between the squares will be perpendicular to each other.
- At the end, you need to glue the top square, on which there are no slats. To tighten and fix the assembled structure, you need to use metal corners.
- All resulting cracks should be carefully sealed using previously purchased sealant.
- Additionally, you need to make fastenings and four holes intended for mounting flanges.
- The heat exchanger must be inserted into the housing. In order for it to be well secured there, you need to first screw in the corners inside, which will ultimately serve as guides. It is worth paying attention to the fact that the heat exchanger must be positioned in such a way that its corners rest against the sides of the housing (the result will be a rhombus).
- You also need to make a hole into which to insert the hose. It will be used to drain condensate.
- It is best to provide a special mount at the inlet, which will be designed for installing a filter.
- The walls of the housing must be lined with mineral wool. In this way, the proper level of thermal insulation can be ensured.
- Finally, you need to install the fan. Once this is done, it is necessary to install the assembled structure into the ventilation system.
The finished device can be installed either on the wall or in a specially prepared niche. The noise level will directly depend on several factors. These include fan power, materials used, etc. In most cases, the device produces sounds that do not exceed the hum of a computer cooler.
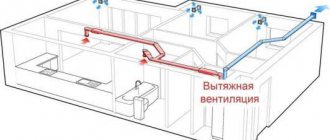
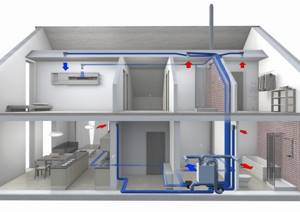
Methods for organizing recuperative ventilation
Recovery is arranged in one of the following ways: centralized and decentralized. In the first case, ventilation flows from the entire room pass through the heat exchanger, in the second - from one room.
Centralized complex – air handling unit
A centralized system is installed at the stage of construction or major modernization of the ventilation system.
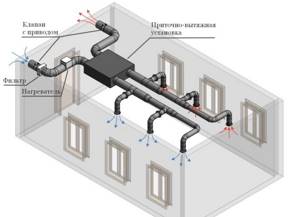
A forced supply and exhaust unit (PVU) with a built-in recuperator is selected. The main selection criterion is the overall performance of the complex based on the entire volume of air in the structure (+)
A PVU with a recuperator ensures sufficient air exchange even in houses with sealed windows. At the same time, air flows are distributed evenly without creating drafts.
Complex supply and exhaust units of monoblock type are equipped with:
- fans – round-the-clock supply of clean air and emission of jets saturated with carbon dioxide;
- heaters – preheating of inflow;
- filters – retain dust and microparticles;
- recuperator – different types of installations can be used.
The functionality of some PVUs is expanded with a delay timer, power regulator, humidity level sensors, etc.

The body of monoblock models is covered with noise-absorbing material, making the operation of the PVU very quiet. Vertical, horizontal and suspended versions of ventilation units are possible
Vents (Ukraine), Dantherm (Denmark), Daikin (Japan), Dantex have proven themselves well .
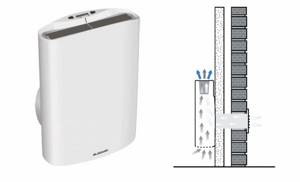
Local units - an addition to the existing ventilation system
To restore the circulation of air masses in the room being used, decentralized air inlets with heat recovery are suitable.
They cut into the façade of a building or are mounted through a window. Their main task is to improve the supply ventilation in the house.

Local recuperators are equipped with a fan and a plate heat exchanger. The inlet “sleeve” is insulated with sound-absorbing material. The control unit of compact ventilation units is located on the internal wall
Features of decentralized ventilation systems with recovery:
- Efficiency – 60-96%;
- low productivity - the devices are designed to provide air exchange in rooms up to 20-35 sq.m;
- affordable cost and a wide selection of units, ranging from conventional wall valves to automated models with a multi-stage filtration system and the ability to adjust humidity;
- ease of installation - no air ducts are required for commissioning; you can install the wall damper yourself.
Popular manufacturers of local recuperators: Prana (Ukraine), O.Erre (Italy), Blizzard (Germany), Vents (Ukraine), Aerovital (Germany).

Important criteria for choosing a wall inlet: permissible wall thickness, performance, efficiency of the recuperator, diameter of the air channel and temperature of the pumped medium