Ventilation systems that provide the influx and processing of air masses coming directly from the street, as a rule, are used exclusively in the economic and industrial sphere. For domestic conditions, such systems are not provided by default. This is one of the reasons that makes ordinary users think about assembling something similar for home use. But is this possible and how can this problem be solved?
By and large, almost anything is possible. However, there are always a number of nuances that should be taken into account. And we will talk about this in our article - we will look at what do-it-yourself heated supply ventilation is and what main components it consists of. Let's discuss the issue of home heating with heating from the point of view of possible solutions to this issue, supplementing the article with visual photos and thematic videos.
Main design features
The system consists of several elements:
- Plastic grill. This decorative decoration of the structure filters out large debris that can get in with air masses.
- Valve or baffle. The function of the valve is to block the flow of air when the device is turned off.
- Filters. Filters trap small debris and dust. These filters must be replaced every few months.
- The heating element is a heater (water or electric).
For small rooms or houses it is better to use an electric heating element, and for large areas - a water one.
Design features
The design features of forced ventilation consist in the connection of several elements at once. Each of them performs separate functions:
- Ventilation ducts (air ducts) are pipes through which air masses circulate;
- Fans – organize air supply into ventilation ducts.
- Air intake grilles - mounted on the outside of air ducts, protect them from the penetration of dirt, unwanted insects and rodents.
- Filters – clean the air of contaminants, and especially thin ones prevent even the entry of pollen.
- Sound absorbers - absorb noise from the mechanisms themselves and aerodynamic noise in ventilation ducts.
- Air valves - regulate the air flow supplied from the outside, protecting the structure in cold weather.
- Heaters – used to heat supply air in winter.
- The automatic block is an optional element, but its presence allows you to control the system without human intervention. You need to set the necessary settings. Otherwise, you will have to turn on and adjust the fans manually.
Supply ventilation device with air heating
There are two types of units for supply ventilation:
- Monoblock - they are made up of one block, which is installed at the inlet of the air duct. This block contains all the necessary devices, without exception, that ensure high-quality and reliable service of the ventilation structure. This type of device is often installed in the wall or in window frames. This method is considered the simplest and least expensive. But in practice it is quite ineffective, since the placement of its intake fans does not make it possible to cover many areas of the building.
- Installation - these supply ventilation systems are powerful enough to cover high-rise buildings, large industrial premises, and apartment buildings.
Supply ventilation schemes
The simplest type of installation:
- Air filter,
- blower fan,
- A heating element.
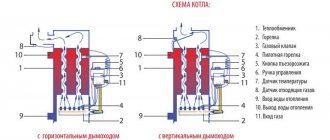
Standard scheme of supply and exhaust ventilation with heating
How to heat the supply air using a recuperator?
Recuperators are divided into 2 types:
- Rotary - work using electricity. They have a cylindrical body in which a rotor element is mounted. It constantly rotates between the “incoming” and “exhaust” air valves. Quite a large item. Efficiency – up to 87%.
- Lamellar. Such recuperators consist of united plates. Supply and “exhaust” air move towards each other through different valves. This helps prevent recirculation. Such recuperators are usually small in size.
Parts that make up the ventilation system
Supply ventilation with air heating for an apartment includes several main parts on which the quality of operation of the entire system depends. Such details include:
- Air filter.
- Shut-off valve.
- Heater.
- A fan that blows air.
- Noise muffler. It makes the entire device operate as quietly as possible.
The most important parts in the supply ventilation are the air (shut-off) valve, the filtration element and the heater. With the help of an air valve, air will enter the ventilation only when necessary. Filtration cleans all incoming air as much as possible and prevents dust particles from entering the house.
Thanks to the fan, air enters the room from inside. If the device is turned off, air intake will not take place.
Based on the principle of operation and its characteristics, a heated air supply for an apartment is not suitable for those rooms where there is too much moisture and gas is constantly formed. Therefore, it is better not to hang the vent in the kitchen and bath.
We recommend that you read: Ventilation in the incubator
Systems with recuperator
The supply air can also be heated using a recuperator. These devices are divided into two types:
- Rotary recuperators operate using electricity. A rotor element is mounted inside the cylindrical housing, which continuously rotates between the supply and exhaust air valves. The size of this type of recuperator is quite large. Efficiency reaches 87%.
- Plate recuperators consist of plates that are joined together. Fresh air and “exhaust air” pass through separate channels towards each other. They do not mix, the cold supply air is heated by the warm exhaust wind flow. Such recuperators are compact.
Another solution
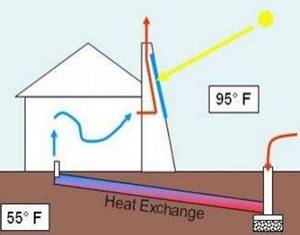
In conclusion, we can offer another option for heating the supply air, which is used less often in practice - a solar collector. It runs on the sun.
The solar collector, where the air is heated, is usually large. After all, it must ensure heating of the required amount of air, even with minimal operation. Collectors of this type are more profitable than water ones; they do not freeze.
Connection diagram

There are many schemes and methods for placing equipment and organizing air exchange. The choice of a specific scheme depends on the type of room (apartment, private house, office), the dimensions of the system, and its equipment (read about the arrangement of ventilation in an apartment here).
For example, when organizing ventilation in a private house, the simplest scheme with an air supply device in the corridor or hallway is often used. In houses and apartments, the hallway communicates with almost all rooms, so heated, purified air can be supplied into it, which will be distributed throughout all rooms.
Before you begin to develop or apply a circuit, you need to carefully calculate the air flow.
Attention
If the calculation is made for private housing construction, then the air flow for the operation of the boiler room is added to the result obtained using the standard formula. If the house has local exhaust devices (pipes, hoods), then their performance values will have to be included in the calculation.
Step-by-step instruction
Diagrams and pictures
Before installation, craftsmen recommend making a sketch of the future ventilation system on paper. The drawing should include all dimensions and directions to make it more convenient to install the finished system and make calculations. The valves are marked with grilles and flaps.
Any scheme takes into account:
- The air flow should go from clean rooms to contaminated ones: from the bedroom, children's room, hallway to the kitchen and bathroom (how to install ventilation in the kitchen and bathroom?).
- A heated supply ventilation valve must be located in all rooms and spaces not equipped with an exhaust hood (how to install an exhaust hood?).
- The exhaust ducts must be the same size everywhere, without expansions or contractions.
Diagram of ventilation air ducts with heating in a private house: Supply ventilation on the wall with heating and a supply valve in section: A simple drawing of ventilation with check valves on the air ducts: Drawing of the location of air ducts in an apartment:
Calculations
In order for the system to work properly, it is necessary to calculate its power as accurately as possible. To do this, you will need all the parameters of the room through which the flow will move. Take into account:
- number of floors in the house;
- area of rooms;
- room layout;
- number of people living in the total area;
- availability of household appliances (computers, televisions, machines).
The calculation of the ventilation system begins with determining the air capacity, measured in cubic meters per hour. For calculations, you need a plan of the house or apartment, where the rooms and their areas are indicated.
For each, the amount of air supplied is determined.
Important: Calculation is usually carried out in accordance with the requirements of SNiP. For example:
For example:
- for residential premises where windows do not open, the flow rate should be at least 60 m³/h per person;
- for a bedroom - at least 30 m³/h per person.
When calculating, only those people who are in the premises regularly (permanent residents or employees) are taken into account.
The next stage is the calculation of air exchange by multiplicity. This parameter shows how many times a complete change of air occurs in the room within one hour.
It is important to provide at least one air exchange
Installation
To install the equipment you will need the following tools:
- Hammer or diamond drill.
- Hammer or sledgehammer, screwdriver or screwdriver.
- Wrenches of different sizes and a ratchet wrench.
Stages:
- Prepare a plane for the through hole.
- Choose its dimensions, mark out the space.
- Drill a through hole with a diamond drill or hammer drill. Prime the walls of the hole.
- Insert the air duct pipe into the through hole. A housing and a fan are mounted to it.
- After installing the duct, fill all cracks around the pipe with sealant.
- Lay channels for wiring to automate the operation of the device.
- Install all remaining parts: filters, sound absorbers, temperature sensors, grille.
- Check the system for functionality.
More details about the stages of installing a ventilation structure in different types of premises, about the essential and significant nuances of ventilation installation work are described in a separate publication.
You can do fresh air ventilation with an air heating function yourself, even if you have no experience working with ventilation devices. The main thing is to act step by step, carefully prepare for work by drawing the necessary diagrams and making the correct calculations.
Ventilation systems that provide the influx and processing of air masses coming directly from the street, as a rule, are used exclusively in the economic and industrial sphere. For domestic conditions, such systems are not provided by default. This is one of the reasons that makes ordinary users think about assembling something similar for home use. But is this possible and how can this problem be solved?
By and large, almost anything is possible. However, there are always a number of nuances that should be taken into account. And we will talk about this in our article - we will look at what do-it-yourself heated supply ventilation is and what main components it consists of. Let's discuss the issue of home heating with heating from the point of view of possible solutions to this issue, supplementing the article with visual photos and thematic videos.
Passive influx
If the windows are old, they let a lot of air through the cracks and improve ventilation. A dubious plus. It is better to install double-glazed windows to maintain the temperature both in summer and winter. Then ventilation will be required, but in winter the room will cool down, condensation will form, and it takes at least half an hour to completely renew the air. Add here drafts and sudden changes in temperature - the result will be very disastrous. Automatic supply ventilation will be very relative - “to the extent that”. The forced system, at a higher cost, gives a much better result.

When purchasing windows, you can add a window valve to the design or cut a through pipe with an adjustment valve into the wall. In the first case, cold air falls to the ground, mixing with warm air. In the second, the pipe can be inserted immediately behind the battery, so that the air warms up immediately when it enters the house. The valve can be supplemented with a humidity and temperature sensor for better climate control, and a cleaning filter can be added. The downside is that such a system depends on wind speed - strong gusts pump in excess air, creating additional pressure. If the wind changes and blows into the hood, it is necessary to close it, otherwise the reverse draft from the kitchen and toilet will spread dirty air.
Types of systems

Heated ventilation comes in several types; they are classified according to different criteria: heating method, mounting location, design, etc.
Central and individual ventilation

All types of ventilation can be divided into 2 main types: central and individual (compact, or breather).
Central ventilation is used when it is necessary to supply clean air to a large room. It has high performance.
It is used in industries and installed on general building ventilation systems. The air is heated from a water or electric heater; a recuperator is less often used. Such equipment is expensive.
Breathers are used for individual ventilation. These are compact devices that are installed in apartments and private houses. They are usually placed on the wall.
Installation is quick and takes no more than an hour. You can install such equipment in any home. The device has many settings, a climate control function, and a multi-stage cleaning system.
Active and passive ventilation
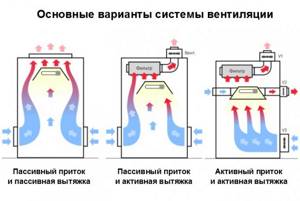
In this case, separation is used to regulate the supply of fresh air.
Passive designs do not have this feature. Air masses arrive due to the pressure difference between the room and the street.
The amount of air supplied depends on the speed of its movement, temperature differences and humidity levels. Most often, the device is mounted on a wall; it consists of a small box.
Active ventilation systems allow you to control the air supply. Outwardly, they are similar to passive ones, but the control unit allows you to regulate not only the temperature, but also the intensity of the flow.
By heating type

Supply ventilation may differ in the method of heating the air.
The following types of devices are distinguished:
- with recovery. In this case, the incoming air is heated by the outgoing air. Used in passive ventilation systems. Suitable for regions with warm winters, because with large temperature differences it is ineffective;
- with water heating. In this case, central heating or a boiler is used for heating. Allows significant savings on electricity;
- electric. Ventilation uses a heating element that runs on electricity. It heats the passing air to the desired temperature.
Other types

Devices are also divided according to the method of pumping air masses into natural and forced. In the second case, fans are used to supply them.
Devices are also divided by type of control. There are automatic devices that are controlled from a remote control or through an application on a smartphone. The second type is manual, the operation settings of which are set on a stationary control unit.
According to their design, they are divided into monoblock and mounting ones. The first ones consist of one block installed at the entrance to the ventilation duct. They are used when installing an air inlet in a wall or window frame.
The devices have low performance and are suitable for small rooms. Mounting devices consist of many elements.
They are used in the arrangement of central ventilation. Their power is enough to supply multi-storey buildings and production workshops with fresh air.
What you need to know about installing systems and their specifics
There is no need to equip large buildings with local supply units. Using air conditioners is also pointless; it is much more correct to supply fresh air to the entire building. Air supply from the supply units for individual zones occurs through air ducts. Given the complexity of modern ventilation units, it is almost always necessary to entrust installation to professionals. When designing, you must first calculate the total power, and then determine other parameters.
If you plan to ensure a flow of fresh air into a city apartment, you should give preference to compact devices. But ventilation of private houses needs to be carried out using more powerful devices, since there are many more problems there. But you cannot chase abstract power, because the influx of fresh air and the removal of waste mass must be coordinated. If their volume varies greatly, then even formal compliance of ventilation with people’s needs does not save. Valves through which air flows in should be installed only in specially designated places.

You need to select the area from the window to the heating radiator. It is not recommended to create duct ventilation systems. Their practicality is questionable, and the total space required is quite large. Most often, pipes with a cross-section of 10 cm and fans with a total capacity of up to 150 cubic meters are used for heated supply ventilation. m of air per hour. Filter housings are mounted with rubber gaskets that help reduce the intensity of vibration.

Heaters that receive heat from the heating system are made on the basis of metal tubes. Further movement of the heated air is provided by a fan. Important: such systems can take up quite a lot of space. They are used mainly in greenhouses and industrial facilities of various kinds. Connection to central heating networks is not recommended because the temperature needs to be precisely controlled.
Design features of the device
Main elements of supply ventilation
- Air intake grille. Acts as an aesthetic design and a barrier that protects debris particles in the supply air masses.
- Supply ventilation valve. Its purpose is to block the passage of cold air from outside in winter and hot air in summer. You can make it work automatically using an electric drive.
- Filters. Their purpose is to clean incoming air. I require replacement every 6 months.
- Water heater, electric heating elements - designed to heat incoming air masses.
- For rooms with a small area it is recommended to use ventilation systems with electric heating elements, for large spaces - a water heater.
Supply and exhaust ventilation elements
Additional items
- Fans.
- Diffusers (contribute to the distribution of air flow masses).
- Noise muffler.
- Recuperator.
The design of ventilation directly depends on the type and method of installation of the system. They come in passive and active action.
Passive ventilation systems.
This device is a supply ventilation valve. The scooping of street air masses occurs due to a pressure difference. In cold weather, the temperature difference contributes to the discharge; in warm periods, the exhaust fan assists. Regulation of such ventilation can be automatic or manual.
Automated regulation directly depends on:
- the flow rate of air masses passing through the ventilation;
- air humidity in the room.
The disadvantage of the system is that in winter, such ventilation for heating the house is not effective, since a large temperature difference is created.
On the wall
Refers to the passive type of supply ventilation. This installation has a compact box that is mounted on the wall. To control heating it is equipped with an LCD display and a control panel. The operating principle is to recuperate internal and external air masses. To heat the room, this device is placed near the heating radiator.
Active ventilation systems
Since in such systems it is possible to regulate the intensity of the fresh air supply, such ventilation systems are more in demand for heating and warming up the room.
According to the heating principle, such a supply heater can be water or electric.
Water heater
Powered by a heating system. The operating principle of this ventilation system is to circulate air through a system of channels and tubes, inside of which there is hot water or a special liquid. In this case, heating occurs in a heat exchanger built into the centralized heating system.
Electric heater.
The operating principle of the system is to convert electrical energy into heat using an electric heating element.
Breezer
This is a compact device, small in size for supply ventilation, with heating. To supply fresh air, this device is attached to the wall of the room.
Breezer Tion o2
Breather design tion o2:
- A duct consisting of an air intake and an air duct. This is a sealed and insulated tube through which the device draws air from the outside.
- Air delay valve. This element is an air gap. It is designed to prevent the outflow of warm air while the device is turned off.
- Filtration system. It consists of three filters that are installed in a certain sequence. The first two filters clean the air flow from visible contaminants. The third filter is a deep cleaning filter from bacteria and allergens. It purifies incoming air from various odors and exhaust gases.
- Fan for air supply from outside.
- Ceramic heater, which is equipped with climate control. Responsible for heating the air flow and automatic temperature regulation.
Additional components in the “inflow” scheme
Having decided on the selection of the main components of the apartment supply system - a fan and a heater, you should consider options for providing other accessories. In particular, equipping the air handling unit with a coarse air filter. That is, we are talking about creating equipment in a complex.
The rules for the installation of fresh air ventilation necessarily require the introduction of an air filter of cleaning class “EU3”, no less, which must be placed in front of the electric (water) heater. One of the main functions of the filter is to separate small dust particles from the incoming air.
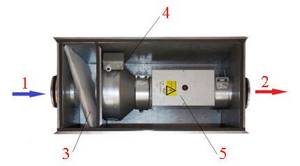
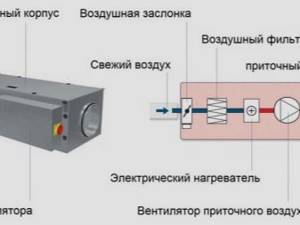
Apartment supply ventilation with the function of heating the air flow (classic scheme): 1 – outside air inlet; 2 – output of treated air; 3 – filter class “EU3”; 4 – channel axial fan; 5 – heating module with round pipes
If there is no filter, the electric heating element or water heater quickly becomes dirty, which is fraught with a serious loss of heating power, and for the electrical structure there is also a risk of fire.
The filter installed in the system must be periodically replaced with a new one as it becomes dirty. Accordingly, a do-it-yourself home structure should provide for the ability to quickly and easily change the filter element.
It is worth noting that industrial air supply structures are usually equipped with differential air pressure sensors. In turn, the sensors are connected to automatic control, which signals the user that the filter is dirty.
In fact, it is also advisable to supplement a serious home air supply system, made by yourself, with a filter condition monitoring function.
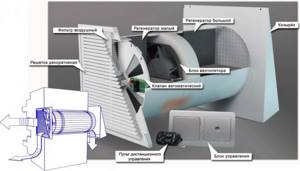
Operating principle of compact ventilation.
- Masses of street air pass through the air intake, which is equipped with a closed plastic grille. Thus, air masses are filtered from debris and insects.
- The air then passes through the duct into the body of the device. To protect the walls from freezing, it is made of sound-heat-insulating plastic pipe. In this case, all joints are sealed.
- Then, coarse and medium dust are filtered using special filters built into the device.
- After which the air mass passes into the heater and warms up to the temperature set by the climate control. On such a device you can set the desired temperature (up to +25°C) and the system will maintain it automatically.
- After heating, the air undergoes two-stage filtration to remove fine dust, odors, gases and allergens, enters the fan and is discharged into the room.
This supply ventilation can be controlled remotely using a remote control.
The bottom device is installed within one hour.
Principle of operation
Heated supply ventilation is very simple in operating principle. At the first stage, air is drawn in through the air intake and filtered from large debris and insects. After this, air is transferred directly to the device body.
At the next stage, the incoming air is specifically purified from all small particles. To do this, there are several thin filters in the inlet for varying degrees of purification.
After thorough cleaning, the air flows directly to the heating elements. If the device has the ability to control heating, then it occurs only within the specified parameters. After heating, another cleaning process starts, during which the air is freed not only from dust, but also from pollen, other allergens and odors.
As a result, purified and sufficiently warm air enters the room, the temperature of which can be controlled from the control panel.
Blowing the car
To speed up the drying of passenger cars, blowing with cold or heated air is used.
After washing, cold air is blown using a powerful blower installation of Sirocco type fans, which force air into air distribution pipes with slotted nozzles at an angle of 60° to the surface being blown.
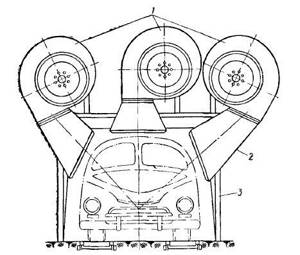
The installation for blowing air after washing cars consists of three fans 1 brand EVR-6, driven by electric motors with a power of 20 kW. To direct the air stream, each fan is equipped with a rectangular shaped nozzle 2. The installation is mounted on frame 3 and enclosed in a casing.
The disadvantage of drying with cold air is the significant energy consumption (the power of the fan motors reaches 60 kW). However, the use of warm air due to its low thermal conductivity (250 times less than the thermal conductivity of iron) is also not effective enough due to the too low heat utilization coefficient.
A promising method of drying a car can be considered the use of lamps with infrared rays, as well as thermoradiation drying with dark infrared panels with high efficiency. and slight heat loss.
Kinds
Heaters for supply ventilation are classified according to the type of heat source and can be water, steam and electric.
Water models
They are used in all types of ventilation systems and can be of two- or three-row design. The devices are installed in ventilation systems of rooms whose area exceeds 150 square meters. This type of heater is absolutely fireproof and least energy-consuming, due to the possibility of using water from the heating system as a coolant.
The principle of operation of water heaters is as follows: street air is taken in through air intake grilles and supplied through an air duct to coarse filters. There, the air masses are cleaned of dust, insects and small mechanical debris, and enter the heater. A copper heat exchanger is installed in the heater body, consisting of links arranged in a checkerboard pattern and equipped with aluminum plates. The plates significantly increase the heat transfer of the copper coil, which significantly increases the efficiency of the device. The coolant flowing through the coil can be water, antifreeze or a water-glycol solution.

Cold air flows passing through the heat exchanger take heat from metal surfaces and transfer it into the room. The use of water heaters makes it possible to heat air flows up to 100 degrees, which provides ample opportunities for their use in sports facilities, shopping centers, underground parking lots, warehouses and greenhouses.
Along with obvious advantages, water models have a number of disadvantages. The disadvantages of the devices include the risk of water freezing in pipes when temperatures drop sharply, and the inability to use heating in the summer when the heating system is not functioning.
Steam models
They are installed at industrial enterprises where it is possible to produce large amounts of steam for technical needs. Such air heaters are not used in domestic supply ventilation systems. Steam acts as a heat carrier for these installations, which explains the instant heating of passing flows and the high efficiency of steam heaters.
To prevent this from happening, all heat exchangers undergo a leak test during the production process. Tests are carried out using jets of cold air supplied under a pressure of 30 bar. The heat exchanger is placed in a tank with warm water.

Electric models
They are the simplest option for heaters and are installed in ventilation systems serving small spaces. Unlike water and steam heaters, an electric heater does not require the installation of additional communications. To connect them, it is enough to have a 220 V outlet nearby. The principle of operation of electric heaters is no different from the principle of operation of other heaters and consists in heating air masses passing through heating elements.
Even with a slight decrease in this indicator, the electric heating element overheats and breaks down. More expensive models are equipped with bimetallic thermal switches that turn off the element in case of obvious overheating.
The advantages of electric heaters are simple installation, no need for piping, and independence from the heating season. The disadvantages include high energy consumption and the inappropriateness of installation in powerful ventilation systems serving large spaces.

Design and types of fan heaters
To preliminarily estimate the amount of work and select the materials necessary for assembly, it is worth familiarizing yourself with the design of a factory-assembled fan heater. The elements present in the design of all models are:
- Protective housing made of plastic or metal.
- Electric motor.
- Impeller with blades.
- A heating element.
- Protective grille.
- Adjustment and control elements.
Depending on the chosen design and purpose of the device, additional components are selected. You can make almost all types of electric heaters with your own hands. For domestic needs, you can make a mini heat gun with your own hands to warm up and dry the room, a do-it-yourself electric fireplace will allow you to realize your own design ideas and give the room a cozy atmosphere, and a ducted air heater is built into the supply ventilation or air conditioning system.
Connection diagram

The choice of a specific scheme depends on the type of room (apartment, private house, office), the dimensions of the system, and its equipment (read about the arrangement of ventilation in an apartment here). For example, when organizing ventilation in a private house, the simplest scheme with an air supply device in the corridor or hallway is often used. In houses and apartments, the hallway communicates with almost all rooms, so heated, purified air can be supplied into it, which will be distributed throughout all rooms.
Before you begin to develop or apply a circuit, you need to carefully calculate the air flow.
Attention If the calculation is made for private housing construction, then the air flow rate for the operation of the boiler room is added to the result obtained using the standard formula. If the house has local exhaust devices (pipes, hoods), then their performance values will have to be included in the calculation.
Supply ventilation device
Ventilation is a method of ventilating a confined space, which helps:
- fill the room with fresh air;
- create a special microclimate;
- prevent the appearance of mold and mildew on the walls and ceiling.

- temperature control;
- adjusting the air flow power, etc.
Ventilation devices are compact and fit into the residential interior. Heated ventilation devices consist of a heating element, a filter grille that cleans the incoming air masses from debris, dirt, dust, and additional elements that not all systems are equipped with (humidifiers, antibacterial filters).
Attention A high-quality ventilation system regularly fills the room with fresh, warm, purified, humidified air
Supply and exhaust ventilation with air conditioning
Sometimes this option is called central air conditioning, since the air is distributed not in one room, but throughout the entire apartment, where the ventilation ducts are laid. The advantage of this system is that this option is cheaper than equipping each room with a separate air conditioner. Outdoor unit installation options may be limited. One external unit with a heat exchanger of a powerful air conditioner does the job better than several weak ones.
Central air conditioning lacks the characteristic indoor unit with a drum fan and curtains. Instead, the freon line from the compressor goes to the duct distributor. Air is supplied to the distributor through supply ducts, and is exhausted, already cooled, to those places that are beneficial to the owners - usually to the kitchen and living rooms. Another system of exhaust air collection pipelines concentrates it and removes it outside. The distributor is not equipped with fans. They are supplied separately in the quantity required by the project. Unlike the usual split system, central air conditioning combined with ventilation is a construction kit, from the components of which you can create a solution for any living space.

Internal distributor
How to use a fan heater
The main purpose of a fan heater is to heat air masses. For more intense circulation of flows, the fan forces air into the air. This makes this device universal.
Options for operating the fan heater:
- This device can be used as the main source of heat supply to a room that does not have central heating.
- The fan heater can complement the main heating system.
- For heating construction sites and workers on them.
- For quickly heating air in a small room.
- The fan heater can be used as a regular fan: in winter for heating, in summer for cooling the air.
- For ventilation and heating of enclosed spaces.
How to heat air using recirculation?
The principle of operation of the device due to recycling:
- The air flow comes from outside into the duct. Part of it, using a special system, is removed back outside the room, and the remainder ends up in the mixing compartment (read separately about the specifics of installing ventilation outlets that lead the air flow outside).
- In the compartment, fresh air enriched with oxygen is mixed with exhaust air, that is, that which was already in the room. Mixing, the air masses are warmed up and sent to the heater or air conditioner, and then into the room.