In a single-pipe system, it is possible to regulate the temperature of each radiator individually, but this requires a bypass with a needle or three-way valve, which complicates and increases the cost of the system, negating the savings in money for the purchase of materials and time for installation. Another disadvantage of the two-pipe system is the impossibility of repairing radiators without stopping the system.
This is inconvenient and this property can be circumvented by placing ball valves near each heating device on the supply and return. By blocking them, you can remove and repair the radiator or heated towel rail.
The system will function indefinitely.
Features of assembling a forced circuit
In order for the forced system to justify itself and function properly, it is necessary to select the right pump and correctly “embed” it into the heat supply main.
Selecting a circulation pump
The main parameters for choosing pumping equipment: device power and pressure. These characteristics are determined based on the area of the heated room.
Indicative indicators:
- for houses of 250 sq.m., a pump with a power of 3.5 cubic meters per hour and a pressure of 0.4 atm is suitable;
- in rooms measuring 250-350 sq.m, install the device at 4.5 cubic meters per hour with a pressure of 0.6 atm;
- if the area of the house is 350-800 sq.m, then it is advisable to purchase a pump with a capacity of 11 cubic meters per hour, the pressure of which is at least 0.8 atm.
In a more scrupulous selection, specialists take into account the length of the heating system, the type and number of radiators, the material of manufacture and the diameter of the pipes, as well as the type of boiler.
Installing the pump in the main
The pump is placed on the return line so that the coolant that is not too hot passes through the device. It is possible to install modern models made of high-temperature resistant materials on the supply line.
When inserting the pump, the water circulation should not be disrupted
It is important that at any point in the pipeline when the pumping unit is operating, the hydrostatic pressure remains excessive
Four acceptable schemes for heating systems with pump circulation and an open expansion tank. Hydrostatic pressure is maintained at the desired level
Option 1. Raising the expansion tank. A simple way to convert a natural circulation system to a forced one. To implement the project you will need a high attic space.
Option 2. Moving the tank to a distant riser. The labor-intensive process of reconstructing the old system and installing a new one is not justified. Simpler and more successful methods are possible.
Option 3. Expansion tank pipe near the pump nozzle. To change the type of circulation, it is necessary to cut off the tank from the supply line, and then connect it to the return line - behind the circulation pump.
Option 4. The pump is included in the supply line. The simplest way to reconstruct the system. The disadvantage of the method is unfavorable operating conditions for the pump. Not every device can withstand high temperatures.
Efficiency of a single pipe system
When developing a project for installing a single-pipe heating system, it is necessary to take into account many factors:
- Is there a constant power supply?
- Possibility of allocating a separate room (boiler room) for equipment.
- How many floors are there in the house?
- Design features and level of aesthetics of the future system.
Each individual situation is characterized by its own specific arrangement of equipment and methods of its switching. It is most practical to equip small premises (for example, a country house) with a simple gravity circuit with sequential switching of radiators directly into the main pipe. Using 2-3 batteries, you can do without a significant amount of shut-off valves: in this case, you can simply drain the water from the system if necessary.
If the building has a large area, a complex heating system with a number of branches is required. In such a situation, the best option would be a forced heating scheme of the Leningradka type. It is characterized by the use of diagonal switching of heat-releasing devices and the presence of adjustable bypasses.
Natural or forced water circulation: which is better for a high-rise building
Systems in which the coolant circulates according to the laws of gravity are for the most part limited to private houses (the heating scheme of a private house with natural circulation is described in the article), individual low-rise buildings located outside the city - or they are designed where there is no constant supply of electricity.

In such buildings, systems with natural circulation are often provided
The main advantage of such a system is that, provided there is a centralized water supply, it does not depend on electricity (read the article about the power supply of multi-apartment residential buildings).
There are other advantages, but there are also disadvantages:
| Advantages | Flaws |
|
|
Considering that in a one-pipe system there is an intense weakening of pressure, and the movement of the coolant slows down, without warming up the premises of a low building to the required temperature, providing for natural circulation, it is better to design a two-pipe system.
Please note: for high-rise buildings with gravitational heat circulation, a single-pipe system is more suitable.
The option with supply and return (two-pipe) is used only when forced movement of the coolant provided by the pump is provided.

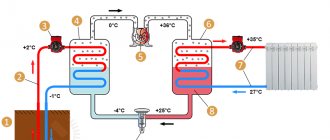
Individual heat distribution unit in a multi-storey building with forced circulation
Note: in order to create normal pressure in a two-pipe system with gravitational movement of the coolant, it is necessary to increase the distance from the heat exchanger to the lower heating devices. At a minimum it should be 3 m.
We recommend reading: autonomous heating of apartment buildings.
Features of heating high-rise buildings
High-rise buildings are those with more than 25 floors. This number of floors causes certain difficulties both in supplying water upstairs and in arranging a heating system.
To make this even possible, such buildings are zoned into sections of a certain height, between which there are technical floors, as shown in the photo.
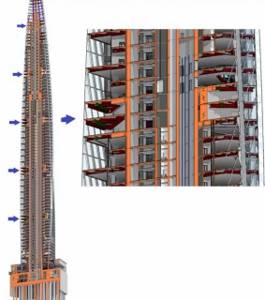
Arrows show the locations of technical floors
This number of technical floors is required in order to accommodate the equipment that ensures the operation of utilities - including heating.
In high-rise buildings, the service area cannot exceed a certain height.
The parameters of technical floors are determined based on the value of the hydrostatic pressure of the coolant in the heating devices of the lower level. Their height must correspond to the dimensions of the equipment placed in them: air ducts, boilers, pumps, heat exchangers.
If the hydrostatic pressure in heating devices varies between 0.6-1.0 MPa, the height of service areas usually does not exceed 55 meters (17-18 floors).
Each of them has its own heating system, connected to an external heat pipeline, but isolated from other systems, has its own heat exchanger, expansion tank, make-up and circulation pump.
In high-rise buildings, individual heating units (IHP) are usually equipped, which are located in the basement floors, where the main pumping equipment and heat exchangers are located. They are almost always rated for a maximum pressure of 1.6 MPa, at which a hydraulically isolated system has a limit of 160 meters.

Technical floor equipment
In a building with such a height, either two zones of 80 m each, or three of 55-50 m each, each with its own contour, are arranged. Moreover, water-water heating can only be in the first two zones - in the third and higher (if there are more floors) steam-water or combined heating is designed.
Note: steam is used instead of water because it does not produce high hydrostatic pressure.
It is supplied to the technical floor preceding the upper zone, which is equipped with its own ITP with a full set of equipment, including control equipment. In buildings whose height exceeds 250 m, electric-water heating can be used.
Heating systems of high-rise buildings are often divided by facades (horizon sides), and each department has its own automated system that regulates the temperature of the coolant.
Classification of two-pipe systems
Two-pipe systems have various installation options and can differ in the type of expansion tank (open and closed wiring), mounting method (upper and lower), layout options (vertical and horizontal system) and method of coolant supply (dead-end and sequential wiring).
Open and closed wiring
Any heating system is a closed circuit, in which there is an expansion tank. It is necessary because the coolant expands when heated, which leads to an increase in pressure in the pipes.

When using open wiring, a tank is installed in the circuit, which has contact with the atmosphere, due to which the pressure in the system is stabilized, but part of the liquid evaporates, and therefore it is so important to regularly monitor the volume of water, which creates additional problems when servicing the system. Another disadvantage of open wiring is the ability to use only water to heat the batteries.
Glycols and antifreeze cannot be used in such a wiring; when they evaporate, toxic vapors are formed, which is unacceptable for an open expansion tank
Another disadvantage of open wiring is the ability to use only water to heat the batteries. Glycols and antifreeze cannot be used in such a wiring; when they evaporate, toxic vapors are formed, which is unacceptable for an open expansion tank.
The main difference between closed wiring is the presence of an expansion tank in the heating circuit, which has no contact with the atmosphere. A membrane-type tank effectively compensates for high and low pressure in the system, and also allows the use of antifreeze and glycols for heating.
In a closed wiring there is always a stable pressure, which eliminates the failure of the pump and boiler, and extends the life of the heating equipment.
The ability to use antifreeze prevents the coolant from freezing in winter - this is another bonus from using closed wiring.
Vertical and horizontal system
A two-pipe heating system can be horizontal or vertical. The horizontal organization is used in one- or two-story buildings, and Mayevsky taps are used to bleed air from the circuit on the radiators.
The advantage of the horizontal layout is ease of installation and minimal costs for components. There is only one drawback - the high probability of airing the system.
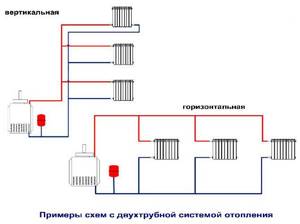
Vertical layout is more often used in multi-story buildings. Its main advantage is the removal of air from the heating circuit automatically.
Air pockets go up the pipes, where they are released through a release valve or expansion tank. Connection to the riser is carried out on each floor separately, which increases the reliability and efficiency of heating.
Upper and lower wiring
A two-pipe heating system uses upper and lower wiring. In the first case, the heating system is mounted under the ceiling, and branches from the main circuit go to the radiators fixed near the windows and doors of the balcony (areas where cold air accumulates). The lower, outlet heating circuit receives water that cools during circulation.
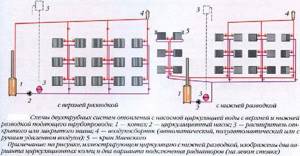
Top wiring is recommended for large rooms where the quality of heating dominates the interior. In residential buildings, this type of wiring is practically not used.
With bottom wiring, the supply and discharge channels are located near the floor, which makes the pipes invisible. Let us highlight the following advantages of such an organization:
- Easy installation,
- Battery connections and wiring points are on the same level,
- Installation is on the same level and requires minimal pipe consumption.
Passing and dead-end systems
In two-pipe heating systems, a passing and dead-end supply of coolant is used. Multidirectional supply of hot water and return water is used with a dead-end heating method. With this circuit design, bypasses are installed, and the batteries are fixed in closed areas, which allows you to turn off each of the radiators without disrupting the heating operation.
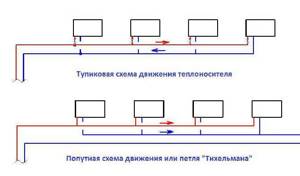
The associated system is called the Tichelman loop
In this case, balancing and adjustment are easier, which is especially important when the heating circuit is long. The coolant moves in the same direction, which increases the efficiency of the heating circuit
Features of the heating system of apartment buildings
When installing heating in multi-storey buildings, it is imperative to comply with the requirements established by regulatory documentation, which include SNiP and GOST. These documents indicate that the heating structure must ensure a constant temperature in the apartments within 20-22 degrees, and humidity must vary from 30 to 45 percent.
Despite the existence of standards, many houses, especially older ones, do not meet these indicators. If this is the case, then first of all you need to install thermal insulation and change heating devices, and only then contact the heat supply company. The heating of a three-story house, the diagram of which is shown in the photo, can be cited as an example of a good heating scheme.
To achieve the required parameters, a complex design is used, requiring high-quality equipment. When creating a project for the heating system of an apartment building, specialists use all their knowledge to achieve uniform heat distribution in all sections of the heating main and create comparable pressure on each tier of the building. One of the integral elements of the operation of such a design is operation on a superheated coolant, which provides for the heating scheme of a three-story building or other high-rise buildings.
How it works? The water comes directly from the thermal power plant and is heated to 130-150 degrees. In addition, the pressure is increased to 6-10 atmospheres, so the formation of steam is impossible - high pressure will drive water through all floors of the house without loss. The temperature of the liquid in the return pipeline in this case can reach 60-70 degrees. Of course, at different times of the year the temperature regime may change, since it is directly related to the ambient temperature.
What is meant by a closed system in low-rise private houses
The main feature of classifying the heating system of private houses as closed/open types is the design of the expansion tank. An open tank connected directly to the atmosphere is an open system. A hermetically sealed membrane tank is a closed system. This classification has developed in the Russian-language segment of the Internet in fact.
The purpose of the expansion tank is intuitively clear - to compensate for changes in the volume of coolant liquid in the heating system when its temperature fluctuates. Heating the coolant (water, antifreeze) causes an increase in its volume (water heated from 0 ° C to 100 ° C increases in volume by 4.33%), the pressure in the pipes increases (on average by 1.2 - 2.2 bar/ °C) and radiators, increasing the likelihood of emergency situations. The expansion tank installed in the system is capable of temporarily absorbing excess heated coolant. The cooled liquid contracts and leaves the internal volume of the tank.
An open expansion tank is an unsealed container with a removable (lifting) lid and a drain pipe, installed at the top point of the system, where, under the influence of the Archimedean force, bubbles of air dissolved in water move through the risers, escaping into the atmosphere. The reverse movement also takes place - atmospheric air saturates the volume of heated liquid in the tank, entering the system when the coolant is compressed after cooling.
Modern membrane expansion tanks, the design of which is shown in the figure below, prevent the entry of atmospheric air into heating systems.
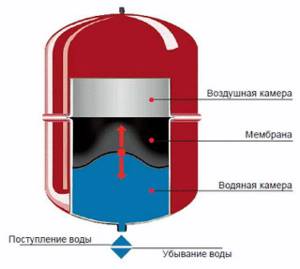
5. Design of a membrane expansion tank.
Inside it there is an elastic membrane (diaphragm), dividing the internal sealed cavity of the tank into air and water chambers. Advanced models contain nitrogen instead of air. Gas is pumped into the tank under excess pressure, which bends the membrane towards the inlet water pipe. The growing pressure of the heated coolant causes the membrane to compress the gas. The process continues until both pressures (liquid and gas) are balanced.
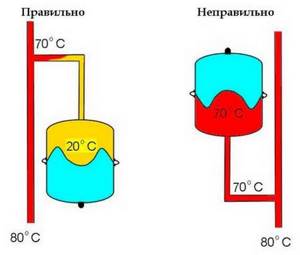
The membrane tank can be installed anywhere in the system. The best place is considered to be a point on the return pipeline in front of the circulation pump. The liquid reserve inside the tank prevents the occurrence of cavitation in the pump inlet pipe.
In an effort to prevent the water chamber of the expansion tank from being “aired” by air dissolved in the coolant, the inlet pipe is turned upward, as shown in the figure below.
6. Methods for installing an expansion membrane tank.
Additionally, this installation method reduces the temperature of the coolant in the tank, protecting the membrane from thermal loads. High-quality membranes are able to withstand any coolant temperature for a long time, which allows us to recommend both methods of installing expansion tanks.
Upper wiring
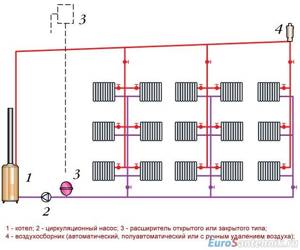
Pipes supplying coolant are installed at the top of the room. Most often closer to the ceiling, above the windows. This contributes to the appearance of high pressure in them. The pipes supplying coolant back to the boiler run along the bottom of the room, as close to the floor as possible.
A two-pipe heating system for a private house with overhead wiring requires an expansion tank. Sealed or not is the owner's choice.
The disadvantage of the top wiring is that some of the heat goes up. It is not intended for heating large areas. But the coolant is transferred at high speed.
Forced circulation
Neutralization of almost all of the listed disadvantages is achieved by introducing a circulation pump into the system. As a result, the coolant receives an additional impulse, thanks to which it effectively overcomes the hydraulic resistance of the pipeline. Single-pipe heating system wiring is currently the most popular solution in private homes.
The installation location for the pump can be any section of the highway. However, it should be borne in mind that when rubber elements (gaskets) are exposed to hot water, the service life of the pump is noticeably reduced. Therefore, they try to install the device on the return pipe, because The coolant there is not so hot. A coarse filter must be installed in front of the pump to prevent various contaminants from entering the mechanism. When connecting all instruments and devices, it is recommended to use shut-off valves and bypasses. This will significantly simplify repair and maintenance activities at individual units: in this case, there is no need to stop the entire system and completely drain the coolant.
Strengths of forced circulation heating circuits:
- Possibility of using more complex branched circuits, leading to an increase in the total length of the circuits.
- There is no need to increase the diameter of the pipes. Thanks to the pump, sufficient pressure is created inside the system for movement and uniform distribution of liquid.
- The circulation has a stable speed. This indicator is not affected by the level of heating of the coolant and the installation of the accelerating manifold.
- There is no need to organize inclination angles on horizontal sections of the pipeline, because A pump is used to stimulate the movement of the coolant.
- It becomes possible to insert control devices on all batteries, which ensures the maintenance of an optimal heating level, reducing energy consumption and heating costs.
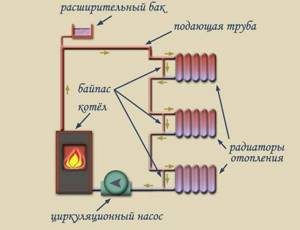
There are also disadvantages:
- The need for electrical power.
- Noise from a running pump.
- The need for additional capital investments (when compared with the gravity scheme).
Neutralizing them usually does not cause difficulties. To maintain a stable energy supply, an autonomous electric generator is being installed. Systems that provide the possibility of switching to a natural circulation mode have proven themselves very well. To reduce the noise from a running pump, it is usually installed in a non-residential area.
Heating the house with a double-circuit gas boiler

If you are looking for a universal way to provide your home with heat, then you should think about purchasing a double-circuit gas boiler. It can not only heat the room, but also heat water for domestic needs.
It is worth keeping in mind that boilers are not entirely suitable for large houses. The heating capacity of hot water in double-circuit boilers allows servicing only one point. If you plan to have several bathrooms, then the power will not be enough. In such cases, you should resort to indirect heating boilers or conventional heating element tanks.
Operation of a closed heating system
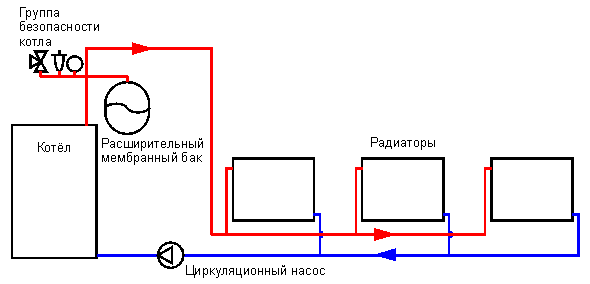
The role of the expansion tank is played by the membrane tank. Excess hot water enters it, pushing through the rubber membrane. At the same time, the nitrogen in the air chamber is compressed. The coolant is removed from the tank using a special pump. The absence of oxygen contact with circuit elements extends their service life. The coolant does not evaporate and does not require frequent replenishment. The closed circuit allows the connection of additional heat supply sources with their integration into the overall system. The temperature is regulated by reducing or adding coolant.
A closed system requires constant access to electricity to keep the pumps running smoothly. Despite this difference, it works more effectively in small homes. Multi-storey buildings require a large number of membrane tanks and complex calculations.
System pressure testing
It is impossible to put the heating system into operation without performing a pressure test - testing the strength of pipelines and their connections to the equipment, carried out hydraulically or pneumatically.

Preparing the system for pressure testing
In addition to the tests that are carried out before putting the building into operation, pressure testing is carried out:
- Before the onset of each heating season. The goal is to identify weakened or depressurized areas and push through the pipes in order to free them from sludge that reduces permeability.
- After repairs, during which sections of the pipeline, fittings, and gaskets were changed.
- Post-installation pressure testing is carried out twice: first to identify the presence of leaky connections, and a second time to ensure the operability of the system.
This maintenance helps keep the circuit in working order at all times, which keeps the building warm in the winter.
Subsequence
Actions to test heating pipelines are carried out only outside the heating season, when the coolant is completely removed from the system. Since pressure testing involves increased loads, you have to monitor the pressure using instruments.
The procedure may vary depending on the condition of the heating circuits.

Equipment for crimping
Taken into account:
- pipe material and wall thickness;
- characteristics of fittings;
- number of floors served by the system;
- supply pipeline layout option.
The process consists of several stages:
- Preparations.
- Exposure of the circuit to water or compressed air under pressure half the WP (working pressure).
- Entering data into the accounting journal and drawing up a report.
- Pre-start flushing.
If problems are identified, repair work is carried out, after which the circuit must be tested again.
After the test is completed, the pressure is not reduced for another 30 minutes, during which it becomes clear whether there are leaks.
Features of installation of a one-pipe system
When installing a single-pipe heating system, it is important to consider the following points:
- Use of pipe products of a certain diameter.
- Maintaining the slope of the heating pipe with natural circulation around the entire perimeter of the system.
- Inserting radiators parallel to the main pipeline without breaking it. In this case, you do not need to worry about the lack of circulation in the heating devices; many years of research have proven the effectiveness of the system assembled using a single-pipe design.
- The expansion tank and each heating device must be equipped with an air bleed device. This is especially true for closed-type systems that are isolated from atmospheric air. However, there is one more feature of such systems: if air is not completely bled from one of the radiators, the expansion tank can be excluded from the system.
- Installing chokes and thermostats on heating devices helps to evenly distribute heat between radiators located in close proximity to the boiler and the furthest heating devices.
Single-pipe water heating system for a multi-storey building
a steel pipe is used as the main material (in private heating systems, the use of polypropylene or metal-plastic is acceptable).
- the design of the system and its design are calculated in accordance with SNiP for laying pipelines;
- sections of the main line running outside or in the basement are insulated so that the heat does not go to waste;
- buildings use a vertical single-pipe system - a cheap and effective heating option;
- design and calculations are carried out at the construction stage - the optimal option, diagrams and drawings with calculations related to heating are approved by the relevant authorities before the start of construction;
- Before putting into operation, pressure testing and commissioning are carried out.
Advantages and disadvantages
The demand for a dual-circuit heating system is explained by the presence of a number of significant advantages. First of all, it is preferable to a single-circuit one, since in the latter the coolant loses a noticeable part of the heat even before it enters the radiators. In addition, the double-circuit design is more versatile and suitable for houses of different floors.
The disadvantage of a two-pipe system is its high price. However, many people mistakenly believe that the presence of 2 circuits requires the use of twice the number of pipes, and the cost of such a system is twice as much as a single-pipe system. The fact is that for a single-pipe design it is necessary to take pipes of large diameter. This ensures normal coolant circulation in the pipeline, and therefore the efficient operation of such a design. The advantage of a two-pipe system is that for its installation, pipes of smaller diameter are used, which are significantly cheaper. Accordingly, additional elements (pipes, valves, etc.) are also used with a smaller diameter, which also somewhat reduces the cost of the design.
The installation budget for a two-pipe system will not be much larger than for a single-pipe system. On the other hand, the efficiency of the first will be noticeably higher, which will be a good compensation.
Closed wiring
The system is based on an expansion tank. Inside it is divided transversely into two parts by an elastic partition, which is called a membrane. The required pressure is maintained in the upper part, and the volume of water is maintained in the lower part. The lower part is connected to the heating system through a pipe.
Water and any ethylene glycol-based liquid are suitable for filling a closed dual-circuit system. The advantage of the latter is that it does not freeze even at fairly low temperatures. Disadvantage: it is not egological and requires disposal. And there are problems with this in the CIS countries.
An expansion tank with a membrane can be installed anywhere in your home, not necessarily at the highest point.
A sealed tank is more dangerous than a leaking one. The pressure can increase greatly, and gases, having no outlet, accumulate. Therefore, a closed system must be carefully monitored and air vents installed.
Accurate calculation of a two-pipe heating system
Before starting work, it is necessary to draw up a heating scheme, decide on the material, and make a hydraulic calculation. It is necessary to calculate the pressure drop in the rear section or to calculate the diameter of the pipe.
The calculation is carried out taking into account the following factors:
- Inner surface of pipes and its roughness;
- Section diameter;
- Number of pipe bends;
- Pressure difference between supply and return;
- Number of radiators and their cross-section;
- Locking elements.
When making calculations, use formulas and an axonometric table. You can use a special software program. The most loaded ring or contour is taken as the main object. As a result of calculations, the optimal speed of movement should be from 0.3 to 0.7 m/s.
After the calculations have been made, pipes of effective diameter, the required number of radiators, a boiler, fittings, pipes, an expansion tank, and a circulation pump, if necessary, are purchased.
Calculation
When planning a two-pipe system, it is important to carry out a preliminary calculation of the two-pipe heating system, using such a guide as a preliminary diagram of the system (all elements must be indicated on it) and special axonometric formulas and tables.
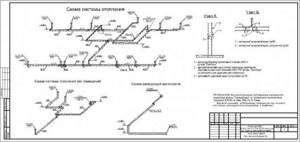
Heating calculations are made based on the plan
This simple hydraulic calculation of a two-pipe heating system allows you to determine the optimal diameter of the pipes necessary for the normal functioning of the system and the volume of radiators used. The most commonly used types of calculations are:
- by pressure loss. This method assumes an equal level of coolant temperature in all parts of the system.
- calculations taking into account the value of conductivity and resistance. In this case, different values of temperature indicators are assumed.
As a result of using the first method, you can obtain very accurate data showing the level of resistance in the circuit. The second method shows the temperature in each individual segment of the system, as well as the approximate coolant flow.
Pressure testing of the heating system
If you want your heating system to work smoothly and without any problems, it needs to be well designed and installed. But as it turns out, this is not enough. The equipment must be put into operation.
And for this, nothing more than pressure testing is done - hydraulic tests, pressure testing of the OKPD heating system - a necessary test that must be carried out not only when installing the system, but also when replacing or repairing a heating device and in preparation for the next heating season.
Such a tightness test will reveal all violations and the need for such work is obvious. Previously, crimping required more time and effort, but now it is much easier. The work is carried out using special equipment.
Next we begin crimping. It includes a number of activities. We carry out preventive maintenance of the system and its preparation. It is necessary to create pressure inside the system, it is necessary for the work. The final stage is to flush the entire heating system.
If the system has passed all tests, it is ready for use.

Single-pipe horizontal heating system
Methods for connecting radiators
What is horizontal heating distribution in combination with a single-pipe system, in what cases can it be installed? Among experts, it is considered the easiest to install and the most affordable. The principle of its design is that radiators are connected to the pipeline in series. Depending on the selected configuration, the connection of the pipes can be top or bottom.
But at the same time, the horizontal single-pipe heating system of a two-story house has the following disadvantages:
- Uneven heat distribution across the batteries. The further the radiator is from the boiler, the lower the water temperature in it will be;
- Difficulties in performing repair and maintenance work. When the radiator is disconnected from the general network in a horizontal single-pipe heating system with natural circulation, the flow of coolant further through the pipeline stops;
- Inability to regulate temperature in various rooms of the house.
During the design of this system, it is imperative to install a bypass in front of each radiator. In combination with shut-off valves, it will allow you to carry out repair work or replace individual heating elements.
For effective heat transfer, the batteries must be 2/3 covered by the window sill. This will promote optimal air convection in the room.
A single-pipe horizontal heating system with bottom wiring is installed only in houses with a small area - up to 150 sq. m. You also need to take care of additional thermal insulation of those rooms that are farthest from the boiler.
Features of connecting single-pipe heating in a two-story house
In two-story houses, natural air circulation, which is the rise of warm air to the 2nd floor and the flow of cooler air to the 1st floor, is especially pronounced and can create noticeable discomfort. To maintain approximately equal temperatures on different floors of the house, you need to carefully consider the order of connecting radiators and the number of sections in them.
You can, of course, solve this issue more simply: block the connection between the floors of the house with a door on the flight of stairs. However, this can ruin the interior of the house, although such a DIY solution to the problem is quite common.
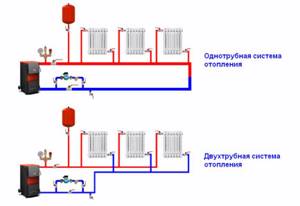
Scheme of one-pipe and two-pipe heating.
There is 2 options for uniform heat distribution throughout a two-story house, called forced ventilation. However, it cannot be taken seriously, because at the first power failure, the discomfort will return, and such a system will be quite expensive to install and operate.
In order for the temperatures on the floors of the house to be equal or at least become closer, on the 2nd floor, instead of heating radiators, you can install a water heated floor system made of metal-plastic pipes with a diameter of 20 mm.
It is almost impossible to solve the issue of equally comfortable heating of 2 floors, especially with your own hands, but a thoughtful layout of the house and installation of an autonomous heating system will allow you to reduce the difference in conditions. Moreover, a single-pipe heating system is best suited for heating a two-story building.
Design features
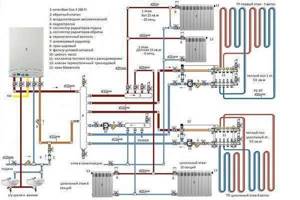
This CO is a closed circuit consisting of two branches along which the coolant moves. It is heated in a boiler plant. Next, along the supply branch (supply) of the pipeline, the heated water (brine, antifreeze) enters the heating devices (batteries, registers), thanks to which the air in the heated rooms is heated. Cooled water is discharged from all radiators into the return line (return), which is connected to the inlet of the boiler unit. The main differences are shown in the diagrams.
The main advantage is that with two-pipe heating, the temperature of the coolant remains practically unchanged.
Expert comment: There is a difference between the first and last batteries in the circuit, but it is quite insignificant and depends on the thermal conductivity of the pipeline from which the heating circuit is made.
The main disadvantage (which is always voiced by supporters of single-pipe heating) is the higher pipeline consumption, which means the higher estimated cost of the entire CO
Expert comment: The cost of a single-pipe heating system is not so small. Due to the sequential connection, as the coolant passes through each subsequent radiator, it cools down more and more. In order to obtain a sufficient amount of heat from the final radiators, it is necessary to increase the heat transfer area by increasing the number of battery sections. This is what increases the cost of single-pipe COs.
Installation
Conventionally, several stages of work can be distinguished. First, the type of heating is determined. If gas is supplied to the house, then the most ideal option would be to install two boilers: one gas, the second a spare, solid fuel or electric.
Next, you should agree on the installation of the heating system in the project documentation and begin purchasing the necessary materials, devices, and preparing tools.
Stages
Briefly, installation consists of the following points:
- a supply pipe is led upward from the boiler and connected to a compensating tank;
- a pipe from the upper line is removed from the tank, which goes to all radiators;
- a bypass (if provided) and a pump are installed;
- the return line is drawn parallel to the supply line, it is also connected to the radiators and cut into the boiler.
Boiler
For a two-pipe system, the boiler is installed first, for which a mini-boiler room is created. In most cases, this is a basement (ideally a separate room). The main requirement is good ventilation. The boiler must have free access and be located at some distance from the walls.
The floor and walls around it are lined with fire-resistant material, and the chimney is vented to the street. If necessary, a circulation pump, distribution manifold, control and measuring instruments are installed near the boiler.
Radiators
They are installed last. They are located under the windows and fixed with brackets. The recommended height from the floor is 10–12 cm, from the walls – 2-5 cm, from the window sills – 10 cm. The inlet and outlet of the battery is fixed with shut-off and control devices.
It is advisable to install temperature sensors - with their help you can monitor temperature indicators and regulate them.
Double-circuit heating system for a private house
Boiler power is calculated in kW, not in square meters. The collector wiring is something like this, but it needs to be calculated correctly. Although I am an opponent of GS, I advise you to use it in your case. Yes, you are right about kW per m2.
I just showed m2 for clarity, to make it clear. And the boiler power is 25 kW. I intended to make the first diagram.
Why do you recommend this particular scheme?
Water heating is mainly used to provide heat to residential buildings. When installing it, a one- or two-pipe system is installed. In the second case, two pipes are required for the heating to function. The heated coolant flows through one of them into the radiators, and through the other, cooled water from the battery returns to the boiler. With a two-pipe heating system, any heating boilers can operate using different types of fuel.
Design and principle of operation
Any water CO is based on heat exchange between the coolant (water, brine, antifreeze), which circulates along the circuit, and the air of the heated room. Depending on the architecture of the heated room, there are two options for supplying water to the radiators: through sun loungers (horizontal main pipeline) and vertical risers.
The principle of operation of a horizontal single-pipe heating system is as follows: the coolant circulates in the main pipe, forming a closed loop that begins and ends in the heat generator. It is to one main line that all the equipment necessary for CO operation is connected.
Double-circuit heating combined with heated floors
Closed options for double-circuit heating of a private house can be easily combined with a water heated floor system. It is important to consider that underfloor heating is a low-temperature system, and radiators are a high-temperature system. Therefore, it is necessary to provide underfloor heating so that the temperature drops from 60-80 degrees to a more comfortable 45-50.
If you want to heat all one room with a water floor, then this module will be useful to you:

The module has a thermal head, which, depending on the temperature, opens or closes the coolant supply to the system. The module is connected to the return of the dual-circuit system.
If you want to implement a solution: one floor has floors, another has radiators, then it’s worth distributing the coolant in the boiler room.