Sometimes residents of the private sector make a very serious mistake when they install autonomous heating with aluminum radiators and do not think about the fact that in such cases ordinary water is not suitable as a coolant.
In addition, such a liquid is not the only one of its kind - there are different options and you cannot do without it, because ordinary water with its salts and alkalis will destroy aluminum, and this, of course, will not suit you, so in any case you need look for a way out.
Aluminum radiators
We will now tell you about the different types of this drug, the conditions for its use, and also invite you to watch the video in this article.
Types of coolant
Water is the most popular and accessible coolant for water heating circuits. However, due to its use as a coolant for aluminum heating radiators, the metal begins to rust, and scale and deposits appear inside the pipes. Therefore, such systems require periodic flushing and cleaning. Also, during winter shutdowns, there is a real danger of freezing: in such cases, it is necessary to drain the water. If this is not done, freezing of the liquid will certainly lead to rupture of pipes and batteries.

All this indicates that, in addition to correctly calculating the power of the batteries for the room, it is important to use exactly the coolant that is not afraid of freezing and chemical interaction with metal walls. It is important to keep in mind that such special solutions do not have a negative impact on human health when the circuit leaks.
We are talking about antifreeze: this coolant is not afraid of low temperatures, which is facilitated by additives and additives dissolved in the liquid, which act as inhibitors of corrosion and mineral deposits.
Antifreeze as a coolant
When solving the problem of which coolant to choose for aluminum radiators, it is important to find a specific composition intended specifically for the intended use.
It is important to consider the following disadvantages of antifreeze liquid for aluminum radiators:
- Low level of thermal capacity (inferior to water by almost 115%).
- A circulation pump is required. Without it, the system will not work due to the high viscosity of the antifreeze, which creates additional obstacles to the movement of the coolant along the circuit.
- Noticeable increase in volume when heated.
- Very high fluidity (50% more than water). Because of this, special attention has to be paid to welded (solder) and threaded connections.
- The toxicity of some compounds. We are talking, first of all, about ethylene glycol antifreeze, which must not be used in combination with hot water supply.
Types of coolants
The most common coolant in centralized and autonomous heating systems is water. Its popularity is explained by its general availability, low cost, environmental safety, and good thermal characteristics. However, there are also a number of significant disadvantages.
The presence of dissolved salts in water leads to the formation of scale on the internal walls of radiators. As a result, heat transfer is significantly reduced, the flow diameter of radiators is reduced, which impairs coolant circulation.
Another disadvantage is the rather high freezing point of water (0 °C). Freezing water leads to the destruction of radiators. Therefore, if interruptions in the operation of the system are possible, it is recommended to use a non-freezing coolant for heating radiators - antifreeze.
The freezing point of antifreeze can reach -65 °C. This is enough to operate the heating system in almost any conditions. In addition, even when frozen, it turns into a gel-like state, which does not lead to destructive consequences for radiators.
The operating temperature of antifreeze is about +75 °C, which is also quite consistent with the parameters of most heating systems. The use of antifreeze has a beneficial effect on the service life of gaskets, seals and other non-metallic elements of the system.
Today, antifreezes based on ethylene glycol and propylene glycol are most often used in heating systems. Ethylene glycol has optimal thermophysical characteristics, but is a strong toxin. Therefore, antifreezes based on propylene glycol, which is a harmless substance, are most widely used.
When using antifreeze, it is very important to control its acidity level. For most radiators, a pH level of 7-8 is recommended
If it is exceeded, the metal of the radiator can quickly corrode.
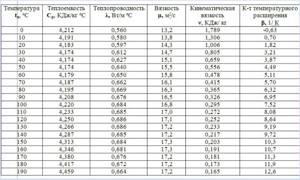
Comparison of working environment parameters of different types
| Characteristics | Unit change | Water | Antifreeze |
| Heat capacity | kJ/(kg*K) | 4,19 | 3,5-3,7 |
| Thermal conductivity at 20 °C | W/m*K | 0,605 | 0,433 |
| Density | g/cm3 | 0,998 | 1,04-1,075 |
| Prone to corrosion | There is activity | No activity | |
| Hazard Class | 5 safe | 3-4 moderately hazardous substance | |
| Viscosity | mm2/s | 1,002 | 5,8-7,1 |
| Freezing point | °C | 0 | -35…-65 |
| Boiling temperature | °C | 100 | 104-108 |
| pH level | 7 | 7,5-9 |
Some coolant features
It is important to remember that it is not recommended to use antifreeze in radiators where zinc is present. It is not recommended to use antifreeze in aluminum heating circuits containing copper or brass.
Its reaction with these metals can cause an electrolytic reaction
It is not recommended to use antifreeze in aluminum heating circuits containing copper or brass. Its reaction with these metals can cause an electrolytic reaction.
When using antifreeze, you should use polymer rather than rubber seals as gaskets between radiator sections.
Antifreeze must also be used in circuits that have more than one section, because this coolant has a low heat capacity, and therefore it needs more space.
When choosing a coolant, you should decide on the required volume of solution, the power of the boiler and circulation pump, and you also need to carefully check the general condition of the heating system before filling it.
The use of antifreeze in aluminum heating radiators has a number of positive aspects compared to other types of fillers. Thanks to the use of antifreeze, the heating circuit will last a long time and will consistently provide the required level of heat.

You can find out what is better to fill the heating system with water or antifreeze from the video below.
How to pour antifreeze into the heating system
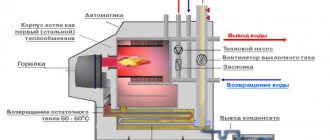
As professionals advise, a heating system using antifreeze should be planned before installing it. It must take into account such nuances as the power of the boiler, the material of the pipes and shut-off devices, the presence of an expansion tank through which the coolant is supplied to the system.
If the product is introduced into a system that previously operated on water, then a lot of work will have to be done to recalculate the power and size of its radiators, thoroughly rinse or replace the pipes.
If you need to add coolant to the heating system, you can only use the same brand as when filling it for the first time. Different types of antifreeze enter into a chemical reaction, causing the formation of sediment, and the additional additives they contain will be neutralized.
To summarize, we can say that non-freezing coolant has a number of advantages that attract many consumers. Thanks to antifreeze, aluminum radiators last much longer. It is important to follow safety rules and not use the product without protective gloves, and in the case of an ethylene glycol-based carrier, also a mask.
Until recently, all houses were heated using conventional cast iron radiators. Today the situation has changed and they have been replaced by aluminum, steel and bimetallic heating radiators, i.e. there was a choice.
Let's look at the advantages and disadvantages of each type, try to determine which one is better suited for an apartment or a country house and calculate the heating radiators.
Types and properties of heat-carrying liquids
The working fluid of any water system - the coolant - is a liquid that takes a certain amount of energy from the boiler and transfers it through pipes to heating devices - radiators or underfloor heating circuits. Conclusion: the efficiency of heating depends on the physical properties of the liquid mediator - heat capacity, density, fluidity, and so on.
In 95% of private houses, ordinary or treated water is used with a heat capacity of 4.18 kJ/kg•°C (in other units - 1.16 W/kg•°C, 1 kcal/kg•°C), which freezes at a temperature of about zero degrees. The advantages of traditional heating fluid are availability and low price, the main disadvantage is the increase in volume when frozen.
Crystallization of water is accompanied by expansion; cast iron radiators and metal-plastic pipelines are equally destroyed by ice pressure
The ice that forms in the cold literally splits pipes, boiler heat exchangers and radiators. To prevent the destruction of expensive equipment due to defrosting, 3 types of antifreeze made on the basis of polyhydric alcohols are poured into the system:
- Glycerin solution is the oldest type of non-freezing coolant. Pure glycerin is a transparent liquid of high viscosity, the density of the substance is 1261 kg/m³.
- An aqueous solution of ethylene glycol - dihydric alcohol with a density of 1113 kg/m³. The starting liquid is colorless and is inferior in viscosity to glycerin. The substance is toxic, the lethal dose of dissolved glycol when taken orally is about 100 ml.
- The same, based on propylene glycol - a transparent liquid with a density of 1036 kg/m³.
- Compositions based on the natural mineral - bischofite. We will analyze the characteristics and features of this chemical separately (below in the text).
Anti-freeze products are sold in two forms: ready-made solutions designed for a certain subzero temperature (usually -30 ° C), or concentrates, which the user dilutes with water himself. Let us list the properties of glycol antifreezes that affect the operation of heating networks:
- Low crystallization temperature. Depending on the concentration of polyhydric alcohol in an aqueous solution, the liquid begins to freeze at a temperature of minus 10...40 degrees. The concentrate crystallizes at 65 °C below zero.
- High kinematic viscosity. Example: for water this parameter is 0.01012 cm²/s, for propylene glycol - 0.054 cm²/s, the difference is 5 times.
- Increased fluidity and penetrating ability.
- The heat capacity of non-freezing solutions lies in the range of 0.8...0.9 kcal/kg °C (depending on concentration). On average, this parameter is 15% lower than that of water.
- Aggressiveness towards some metals, such as zinc.
- The substance foams when heated and quickly decomposes when boiling.
Propylene glycol antifreeze is usually colored green, and the prefix “ECO” is added to the marking.
In order for antifreezes to meet operational requirements, manufacturers add additive packages to glycol solutions - corrosion inhibitors and other elements that maintain antifreeze stability and reduce foaming.
Advantages of radiators with antifreeze
If you fulfill all the above requirements, then:
- A radiator with antifreeze will last 10 years or more.
- It is environmentally friendly and harmless to human health.
- A huge selection of aluminum radiators suitable for filling with antifreeze.
- High-quality antifreeze from the manufacturer (well-known brands), in a large assortment.
- Indispensable in schools, hospitals and residential premises in case of sudden power outage or gas supply.
Bimetallic heating radiators Flat heating radiators Heating radiators or heated floors Heating radiators with bottom connection
Advantages and disadvantages
When choosing antifreeze to fill into a radiator, you should select a special composition intended for these purposes. Antifreeze refers to a special liquid that does not freeze at low temperatures. Special solutions for heating circuits contain special impurities and additives that do not harm the radiator and maintain its stable operation.
Among the negative aspects of antifreeze, several factors can be noted.
The thermal capacity of antifreeze is low. Such liquids are 115% inferior to water in this indicator. To use this coolant in a radiator, a special pump is required to start the entire system, since fluids for heating circuits have a high viscosity. Therefore, they must be accelerated by a pump for the system to start working. Antifreeze has high fluidity
For this reason, special attention should be paid to welds and connections on the radiator. Some compounds are extremely toxic and harmful to human health.

But despite the above-mentioned disadvantages of this type of coolant, it is perfect for use in aluminum circuits with an autonomous heating system.

Benefits of ethylene glycol antifreeze
How do antifreezes differ in general? They do not freeze at fairly low temperatures. Pure ethylene glycol is a viscous, oily, colorless liquid with little odor. Its boiling point is +197 and its freezing point is -13 degrees Celsius.
But in a dacha that is closed for the winter, the room temperature can be much lower.
In order to prevent the ethylene glycol concentrate from freezing and causing the heating system to fail, it is diluted with water and a solution is obtained, the freezing point of which can be as low as -70 degrees Celsius.
For the production of coolants, not only ethylene glycol, but also propylene glycol is used, but the latter ingredient has the highest viscosity, and therefore the highest density.
And according to the laws of physics, it will have the highest freezing temperature. That’s why experts often recommend the antifreeze composition G11 G12 based on ethylene glycol.
Coolant
A coolant is a liquid intended for use in heating systems to transfer heat. In most cases, water or antifreeze is used as a coolant. It comes in two types - regular ethylene glycols and food grade propylene glycol. The type of coolant largely influences the service life of the heating device itself. This is why modern heating systems often use water. Despite the fact that it is highly corrosive and prone to salt formations, the water is environmentally friendly. In addition, it has high thermophysical properties. To reduce its corrosive properties and reduce salt formation, inhibitor additives are added to it. This improves its properties and allows you to increase the service life of the heating system. If there are concerns that you will need to defrost the system, then it is definitely better to choose antifreeze. Such a coolant also has high technical properties, which are inferior to water only in terms of thermophysical properties. Antifreeze is divided into several types, depending on the substance used for production, the crystallization temperature and the set of additives.
Antifreeze is mainly produced on the basis of ethylene glycol. This is a fairly toxic liquid that can cause corrosion in pipes and radiators. That is why it is diluted with other substances, including water. The coolant in the form of antifreeze is suitable for powerful boilers, since its heat capacity is 10-15% lower than that of water. It also has increased viscosity, it is necessary to select the correct pipes and fittings, they must have a larger diameter. Antifreeze can have different freezing temperatures -30°C and -65°C. In this case, a concentrated liquid with a temperature of -65 ° C can be diluted to the concentration you need. This coolant can be used in various heating systems, including underfloor heating systems. Antifreeze can be diluted in any proportions, this will reduce its corrosive properties and reduce the formation of salts inside heating systems. There are a huge number of different types of antifreeze, so you can easily choose the composition you need. It is distinguished by high quality and high technical properties, which goes well with an affordable price. The coolant has a warranty period, which averages 2 years, depending on its type and technical capabilities.
Compatibility of radiators and coolants
Modern heating radiators can be used in heating networks where both water and antifreeze can perform the functions of a coolant. However, when choosing a working environment, you need to take into account some features that are determined by the material used to make the radiators.
Steel
Steel heating devices are sensitive to the composition of the coolant and the content of oxygen dissolved in it. To reduce the likelihood of corrosion processes, it is necessary to install air vents on the batteries to bleed air. The reason for the appearance of rust in steel radiators can also be the reduced acidity of the working environment. Therefore, to fill a heating system with such radiators, you need to use antifreeze with additives or water with a pH level of at least 7. In this case, over time, a dense protective layer is formed on the inner surface of the metal, slowing down the occurrence of corrosion.
Aluminum
Aluminum radiators are also sensitive to the composition of the working environment. If its functions are performed by water, then oxygen accumulates in the system over time and increases the risk of corrosion. Installing a special valve or Mayevsky tap allows you to promptly remove excess air from the network and protects the batteries from damage.
When using antifreeze, you need to take into account its viscosity, which is higher than that of water. It helps to increase the load on the circulation pump and increase the maximum operating pressure in the network. To avoid damage to batteries due to water hammer and ensure uninterrupted operation of the equipment, it is necessary to control the pressure in the system. It should not exceed the level permissible for aluminum radiators and specified in the product data sheet.
Cast iron
Due to the thickness of the metal, cast iron batteries are not prone to rust and are not demanding on the composition of the coolant. The risk of corrosion can only arise if the permissible pH level is significantly exceeded, which is recommended by the manufacturer and is usually 7-8. In addition, cast iron radiators have high thermal inertia and do not cool down for a long time, so any coolant can be used for them.
However, the choice of working environment is limited due to the overall dimensions of heating devices. The volume of the cast iron battery section is up to 1.5 liters and using antifreeze as a coolant is unprofitable from an economic point of view. Radiators are often installed in apartments of multi-storey buildings and how long they last depends on the quality of water preparation for central heating networks.
Bimetallic
Bimetallic heating devices are universal equipment. They are able to withstand high operating pressure and are resistant to corrosion. Due to the absence of a pronounced dependence of the service life on the composition of the coolant, bimetallic radiators can be used with both antifreeze and water. The main thing is that the pH level of the coolant remains within 6.5-9.5. To fill bimetallic heating devices, more antifreeze will be required than for aluminum models, but less than for cast iron batteries.
Lammin offers aluminum and bimetallic radiators of its own production, represented by the Premium and Eco series. They comply with the requirements of GOST R 31311-2005 and are designed for a long service life. Resistance to corrosion and low sensitivity to coolant quality is achieved thanks to manufacturing technology.
The design of bimetallic radiators eliminates contact of aluminum with the working environment. The protective properties of aluminum batteries are due to the use of an alloy with an optimal ratio of copper, iron, silicon, zinc and magnesium. The inner surface of heating devices is coated with zirconium, which forms a dense layer and prevents the settling of particles contained in the water.
Safety rules when working with antifreeze
It is not recommended to mix products from different brands. If such a need arises, first check for compatibility. In addition, not all manufacturers use the same additives. These components can mutually neutralize. Then the anti-corrosion properties of the coolant are lost.
Experts do not recommend pouring antifreeze into an open system. The reason is an open expansion tank. Through it, harmful substances can enter the atmosphere. Therefore, when using “anti-freeze” it is recommended to make the system closed.
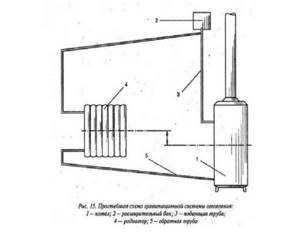
Open type heating systems are of little use for the use of antifreeze.
The home owner does not always know which product was used to fill the heating system last time. In this case, the pipes are completely freed from the previous product, and only then the system is filled.
Distilled water is used to dilute the concentrate. It should not contain calcium and magnesium salts. If you use tap water with a hardness higher than 5 mg-equivalent, there is a possibility of sedimentation.
If it is assumed that antifreeze will be used in the heating system, then you should pay attention to the characteristics of the radiators. Preference is given to models with higher heat transfer rates, internal volume and diameter
The pump power should be 60% higher than that of equipment working with water.

Hard water should not be used to dilute concentrated products.
Automatic air exhaust devices are not designed to work with such coolants. To make it possible to free the system from air, Mayevsky taps are installed on the radiators.
In the system, it is better to use inserts made of materials resistant to glycol media - paronite, Teflon, etc. Threaded connections are laid with flax tow, and a special sealing paste is used as a lubricant. Oil paint is not suitable. The active components of the coolant are good solvents for paintwork materials, as a result of which the system begins to leak.
Antifreeze concentrate is mixed with water in a separate container, and only in this form is the system filled. If you first add coolant and then water, the system may fail. Consequences of ignoring this rule:
- uneven heating of the system, and some radiators may be completely cold due to uneven distribution of the product;
- failure of the circulation pump;
- foaming, which makes it necessary to repeatedly empty and refill the system.
If by mistake you add concentrate and water separately, the circulation pump should not be turned on at full power. Take a wait-and-see attitude and periodically bleed air from the system through the radiators. After some time, more or less uniform mixing of water and antifreeze will occur. If the heating system is gravitational with a gravity function, then this process lasts longer.
Video - Disadvantages of using antifreeze in heating systems
Antifreeze should not be used in systems that do not have an accurate temperature controller. When the temperature rises to 70 °C and above, the coolant disintegrates, which is dangerous for the heating system.
After draining the antifreeze and before filling a new portion, the system is washed with clean water or special solutions.

Before refilling antifreeze, it is recommended to flush the heating system
Bimetallic heating radiators
Bimetallic heating radiators, as the name implies, consist of two metals and combine their best properties.
As a rule, they have a steel core, which allows them to withstand high pressure, as well as an aluminum shell, which has high heat transfer.
Can be installed in a central heating system.
Such bimetallic batteries have a modern design, quickly heat up and cool down, and have high efficiency.
In appearance they are not much different from aluminum radiators.
Advantages of bimetallic radiators:
- high heat transfer;
- withstands high pressure;
- modern design;
- greater reliability;
Calculation of heating radiators
In order to correctly calculate the number of required sections, you need to know some reference data. These data show how much heat needs to be spent to keep the room warm. All values are given for an area of 10 m2.
- For a panel house you need 1.7 kW;
- For a brick house 1 kW;
- For corner rooms, we multiply this data by a factor of 1.2.
Now you can easily calculate the required number of heating radiator sections.
Example: Room 15 m2, corner, brick house. We divide the area of 15 m2 by the estimated area of 10 m2 and multiply by 1 kW.
15m 2 /10m 2 *1kW=1.5 kW.
Because We have a corner room, then this value must be multiplied by a factor of 1.2. We find that to heat such a room, 1.8 kW of heat is needed. Then you need to select the required heating radiator. This data must be contained in the battery data sheet. Here are just some approximate capacities for various radiators.
- cast iron - 160 W one section;
- aluminum - 190 W one section;
- steel - 450-5700 W for the entire panel;
- bimetallic - 200 W one section.
It turns out that if you decided on bimetallic heating radiators, then you will need 1.8 kW/0.2 kW=9 sections. Take more stock in one section because... It is easier to reduce the temperature in the room than to install an additional section.
What to put in the heating system
This question arises only for private developers, because only they have a choice. What is better to fill with water or antifreeze depends on the boiler and pumping equipment, heat exchangers, heating pipes, etc.
Water is the cheapest and most accessible liquid. It is used for heating in private and multi-storey construction, but it has a number of disadvantages.
It must be operated at positive temperatures. When freezing, a breakdown of pipes, boiler, etc. may occur, which will lead to failure of the entire heating system. Therefore, if you turn off the heating of the house, you will have to drain all the water from the system.
The water used for heating is usually not distilled and has many different impurities. When heated, various chemical reactions occur, which leads to the appearance of salts on the inner surface of pipes and heating radiators. As a result, efficiency is lost and efficiency decreases.
In heating where water is used, any type of radiator can be installed : cast iron, aluminum, steel, bimetallic .
The main property of antifreeze is freezing at lower temperatures compared to water. The service life is about 10 heating seasons, after which it is better to replace it.
With such heating, elements containing zinc cannot be used, because it will disintegrate and settle on the inner walls of pipes, boilers, batteries, etc.
Let us remind you once again that if you use antifreeze, it is better not to install aluminum heating radiators, but instead purchase steel or bimetallic heating radiators; you can, of course, use cast iron ones, but they are increasingly becoming a thing of the past.
Quite often, many owners of autonomous aluminum radiators use ordinary water to fill them. This negatively affects the operation of the heating circuit, reduces its service life, promotes corrosion, and ultimately disables the system. Today, you can use many other liquids designed specifically for use in radiators. The most common of these is antifreeze.
Types of antifreeze
The market for these specific products is very large. Recently, due to the increased demand for anti-freeze products, manufacturers have greatly expanded their range.
Antifreeze liquids are made based on various chemical compounds:
- Glycerin;
- Ethylene glycol;
- Propylene glycol;
- Bishofite brine;
- Saline solution.
The most common household anti-freeze products are made from aqueous solutions of ethylene glycol, glycerin and propylene glycol. Since these substances are highly aggressive, special components are added to them - additives.
The purpose of which is to prevent damage, corrosion, scale and foaming.
- Ethylene glycol is the most popular among our consumers. Their main advantage is their low price. But at the same time, it is the most toxic non-freezing liquid, the use of which is prohibited in double-circuit boilers, due to the high probability of entering the water supply system, which is dangerous to human health. It is worth considering that when the boiling point increases above 110 degrees, ethylene glycol gives a precipitate that can damage some elements of the system.
- Propylene glycol is similar in properties to the first type, but is harmless and safe. They are recommended by most manufacturers.
- Glycerin is absolutely non-toxic and environmentally friendly, providing maximum protection against corrosion. It does not increase in volume when it turns into a solid state, and to start the system it is enough to simply heat it.
- Antifreezes based on natural bischofite solution have unique physical and chemical properties. Low freezing point and high boiling point, as well as greater heat capacity and heat transfer than water, which is not typical for most of these products.
- Salt coolants are produced on the basis of solutions of mineral salts (magnesium, calcium, sodium and their compounds). A significant disadvantage of these liquids is their high corrosiveness to equipment.
Antifreezes are sold either already diluted and ready for use (experts recommend using a coolant with a freezing point of -20 to -25 degrees), or in the form of concentrates, and then the solution must be prepared independently.
Example of dilution of ethylene glycol liquids. They come in two types:
- With a freezing threshold no higher than -30 degrees (then, to reach a freezing temperature of -25, the mixture must be diluted with distilled water in a ratio of 9:1);
- With a freezing threshold no higher than -65 degrees (to get a freezing threshold of -25, antifreeze and water are mixed in proportions of 6:4).

Water as a coolant
The use of water in the heating system is optimal if people constantly live in the house - even if there are some problems or a long power outage in the winter, if you cannot quickly fix the problem and connect the electricity, you can simply drain the water from the system.
The ideal option for filling the heating line is distilled water, but obtaining it or purchasing it in large quantities is too expensive. A way out may be to collect rainwater and use it further after filtration; you can also soften the water by boiling or use chemical reagents for this.
Pros and cons of water as a coolant
Water is the most common element among heat transfer fluids used and has the following properties:
- Availability. Water is everywhere, it costs practically nothing, and in emergency situations it can always be drained and the system refilled.
- High specific heat capacity. Among all liquids, water has the highest heat capacity with an average value of 4200 J/kg*K. (4.2 KJ./kg.*K.) - this means that it heats up slowly and cools down slowly.
- Low viscosity. Water has a low kinetic viscosity of 1.006 m2/s (10-6) at a temperature of 20º C, with increasing viscosity it decreases and at a boiler operating temperature of about 70 C. this indicator has a value of about 0.4 m2/s .(10-6). This means that there is less resistance to water as it is pushed into the system by the impeller of the electric pump.
- Low coefficient of volumetric expansion. When heated, water increases slightly in volume; compared to zero temperature at 80 degrees, its volume increases by 2.8%.
- Environmentally friendly. The use of water is harmless to health; in case of emergency leaks, it will not cause harm to human health.
- Neutrality. Water is chemically neutral in relation to all synthetic materials; it does not have a harmful effect on the currently widely used pipelines made of cross-linked polyethylene (metal-plastic) used for heating systems.
Rice. 5 Physical properties of water
The disadvantages include the following properties of water:
- High freezing point. This is the main drawback that does not allow the heating system of the house to be operated in the off state in winter.
- Corrosive effect on steel. The use of water does not allow the use of cheap steel as a pipeline material for a long time; it is necessary to use pipes made of more expensive materials and plumbing fittings made of non-ferrous or stainless alloys.
- Scale. As the temperature rises, the salts contained in the water settle on pipes, radiators and plumbing fixtures - this leads to a decrease in the cross-section of the working channel and disruption of the shut-off and control valves.
Antifreeze properties
Consumers are so accustomed to using water as a coolant that they do not even suspect that there is water of better quality.
Water's biggest advantage is its cost and non-toxicity, but otherwise it can be an adversary for a heating system. Its ability to cause corrosion of metals has “ruined” more than one generation of radiators.
In addition, in the event of a tragedy on a heating main in winter, when the heating is forced to stop working, it can freeze in the pipes even at zero temperature. Its ability to expand, both when frozen and heated, causes them to rupture.
Antifreeze, enriched with special additives for use in heating systems, has some advantages next to water, but it also has negative properties:
- This coolant freezes at -70 degrees.
- It does not harm aluminum, which is extremely important for such a “sensitive” metal.
- It has a good level of thermal conductivity, although it takes slightly longer to heat up than water.
These were the positive properties of antifreeze.
Among its disadvantages:
It has greater viscosity, so to move it through the heating system you need a fairly powerful boiler. The fluidity of antifreeze is dangerous if the integrity of joints or parts of the heating network is compromised. Antifreeze is toxic, so precautions should be taken when using it.
Many consumers are wondering, knowing about these shortcomings, whether it is possible to use antifreeze in duralumin radiators. In this case, it is even preferable when it comes to an autonomous heating system. The durability of this coolant is enough to heat a house for 10 winters, which in itself is good news. During this period, aluminum batteries do not change at all under its influence, which also has a positive effect on their service life.
Find out useful information about duralumin batteries on our website:
Benefits of ethylene glycol antifreeze

Antifreeze does not freeze at low temperatures. Pure ethylene glycol is a viscous, oily, colorless liquid with little odor. Its boiling point is +197 and its freezing point is -13 degrees Celsius. But in a dacha that is closed for the winter, the room temperature can be much lower.
To ensure that the ethylene glycol concentrate does not freeze and cause the heating system to fail, it is diluted with water and a solution is obtained, the freezing point of which can be as low as -70 degrees Celsius.
To make coolants, not only ethylene glycol is used, but also propylene glycol, but the latter ingredient has a higher viscosity and, therefore, greater density. And according to the laws of physics, it will have a higher freezing point. Therefore, experts often recommend the antifreeze composition G11 G12 based on ethylene glycol.
Types of antifreeze
All antifreezes differ from each other in two parameters - composition and added additives. As a result of this distribution, the following compositions can be distinguished:
- glycerin The products are completely harmless and non-toxic. They dissolve well and have a long service life. The product does not form harmful deposits;
- ethylene glycol. This foundation requires special caution on the part of users as it may be toxic. The cost of the substance is low. The composition can be used in heating circuits;
- propylene glycol. Such substances are very expensive, but also completely harmless. Suitable for long periods of operation and completely prevent the formation of precipitation.
For aluminum motors, it is worth choosing the safest and most harmless compounds. This is due to the fact that toxic antifreeze can begin to corrode thin metal.
Ethanol compounds
The significant cost of this antifreeze for aluminum radiators often becomes a serious obstacle to its use in private autonomous systems. The composition can be obtained from distilled water and 40% ethanol (ethyl alcohol). The quality of such a solution is superior to the factory analogue in certain parameters. The matter mainly concerns its low viscosity (although compared to water it remains quite high). There is also a decrease in fluid fluidity, which makes it possible to be less demanding on the connecting areas.
The use of homemade ethanol antifreeze for heating radiators has a beneficial effect on the safety of the rubber sealing gaskets that are present in any circuit. It is recommended to dilute alcohol with hard water: in combination with ethanol, it will become a serious obstacle to the formation of scale on the inner walls. In this case, you cannot do without solid sediment, but you can easily get rid of it by flushing the system. In cases where the percentage of ethyl alcohol in water does not exceed 30%, it will not evaporate.
Due to the fact that the coolant for aluminum radiators is similar in its characteristics to water, its boiling point is approximately the same as that of water. This suggests that when the temperature reaches + 85-90ᶷ, no steam release will be observed. Thanks to ethanol, the thermal expansion of water is reduced by an order of magnitude, which allows the system to more comfortably tolerate lower temperatures in the room.
Water and its properties
The popularity of using water in heating networks is due to the technical parameters and consumer properties of the liquid. It is accessible, safe to use and has a low price and good thermal conductivity and heat transfer. When the water level in the system decreases, its volume is easily replenished, and eliminating leaks does not require special skills. Among the disadvantages are:
- Tendency to scale. It forms on the inner surface of heating devices due to salts dissolved in water and leads to a decrease in the flow diameter. As a result, circulation in the network deteriorates and heat transfer decreases.
- Possibility of freezing. At temperatures below 0 °C, water becomes solid and expands, causing damage to batteries and pipelines.
What should a heating system be like, where the functions of the working medium are performed by water? Firstly, it cannot be left filled and disconnected from the heat source. This situation can arise in a private home due to a breakdown of the heating boiler, or in a central network due to a major accident at a heat distribution point. In addition, it is necessary to ensure that the water is prepared before filling the system, during which the chemical composition of the liquid is changed.
Which radiator to choose
Iron radiators are chosen for a personal home.
The most popular types of alloy for radiators are cast iron (in almost everyone’s old apartments), steel, bimetal, and aluminum.
- Cast iron batteries are made up of sections and are extremely strong and durable. But the appearance and design are somehow somewhat outdated, plus they are extremely heavy to move and mount.
- Steel radiators are the most beautiful and lightweight.
They can be either panel or tubular. The downside is that it is short-lived and more susceptible to corrosion.
- Aluminum batteries are lightweight, aesthetically beautiful, and comfortable for the garden. But they are extremely selective in the composition of the water that is heated in them. Therefore, when turning off batteries for the winter, you need to be especially vigilant in choosing antifreeze.
- Bimetallic radiators are made of an alloy of aluminum and steel and are the most successful solution in your home. Only the cost is high compared to duralumin radiators.
Cast iron heating radiators
Cast iron batteries were installed in all standard apartments. Now they are also in demand, although to a lesser extent, mainly for apartment buildings.
Cast iron heating radiators are highly inert, i.e. They take a long time to warm up when heat is applied and take just as long to cool down. It is necessary to take into account that one such cast iron section has a volume of 1.45 liters, which is a disadvantage, especially for suburban buildings.
A significant drawback is that water hammer is dangerous for such batteries, because cast iron itself is a rather fragile material. The average pressure that cast iron batteries can withstand is 9 kg/cm2 at a temperature of 130 0 C.
The appearance leaves much to be desired, so they are often covered with special screens for a more aesthetic appearance. They require constant painting, because... The cast iron on the outside is constantly rusting. They are heavy and inconvenient to use.
Positive properties include the price and the ability to expand additional sections.
Cast iron radiators are resistant to corrosion and have high thermal conductivity. One cast iron section produces 160 W of heat.