What should the ideal coolant be?
Today there is no ideal universal coolant. Everyone decides for himself what suits him best, depending on the mode of operation.
Basic requirements for coolants:
- should not form precipitation, provoke the appearance of corrosion or other destructive factors;
- good thermal conductivity (the ability to transfer a significant amount of heat over a certain period of time with small losses);
- must be safe, not emit toxic substances and not ignite at operating temperatures.
A little about substances that carry heat
Before we get acquainted with the types of coolants and find out their characteristics, let’s figure out what good and high-quality liquids of this type should be like? What is this anyway?
Coolants for heating systems
So, the coolant is a substance that is inside the heating system and is responsible for preserving heat and redistributing it in a residential (or non-residential) room from the heating boiler through pipes and radiator batteries . Typically, either water or antifreeze is used for this. Each of these substances has positive and negative aspects of use - unfortunately, an ideal coolant does not exist. That is why the decision about what is best to pour into the heating system should be made depending on certain factors: the conditions of use of the entire system, the quality of the heating equipment, other equipment, and so on.
Antifreeze or water?
Attention! The operation of any coolant is highly dependent on the boundaries of a certain temperature range - in cases that are not suitable for a specific substance, the coolant will simply refuse to work correctly, and the quality characteristics will change significantly.

Heating system of a private house
But, despite the fact that ideal coolants do not exist, let’s still think: what would it be like if it existed?
In general, the substance that will retain and transfer heat through the heating system must have the following properties:
- high heat capacity;
- good thermal conductivity;
- low viscosity;
- the ability to transfer the maximum amount of thermal energy with minimal heat loss for a certain time;
- freezing only at very low temperatures;
- stability of properties during use;
- lack of ability to cause rust;
- low toxicity;
- high combustion temperature;
- lack of tendency to form a layer of scale;
- inertness towards various materials used in the heating system;
- low price;
- long service life.

Filling the heating system with coolant
Unfortunately, a coolant has not yet been invented that would fully meet all these requirements. However, it is still possible to make the right choice of this substance. But for this it is important to know what properties water and antifreeze have as coolants.

Antifreeze for heating systems
Water as a coolant for heating systems
Water is the simplest and cheapest coolant. Usually, under normal conditions, it is practically not consumed (remains in the system). In many ways, it depends on its quality.
If the heating system operates constantly, freezing of the system is impossible. In this case, it is better not to drain the water from the system, even in the summer, to avoid corrosion of the system.
If the water contains additional impurities (metal particles, salts, etc.), it must be passed through a special filter. This will protect your heating system from sudden breakdowns.
The main disadvantages of water as a coolant include its ability to form scale, sediment, etc. In this case, heat transfer decreases, as a result of which fuel consumption increases (be it gas, waste oil, etc.).
Water as a coolant
Hydrogen oxide or simply water is the most common and accessible substance on the planet. And by an amazing coincidence, it is precisely this that is one of the best contenders for the title of “ideal coolant”. However, not all so simple.
Main advantages of water
- Maximum heat transfer efficiency.
The thermal conductivity of water under normal conditions is 0.6 W/(m K), which is a record value among all liquids (if you do not take into account mercury and some alloys). The situation is similar with the heat capacity of water – 4.2 kJ/(kg K), which also has no analogues in liquid media.
If you heat 1 liter of water to 90°C, then when cooled in a radiator to 70°C it will transfer 20 kilocalories of heat - no other coolant liquid can achieve such results.
- Availability.
If you don’t take extreme cases (desert), then the cost of water is almost zero. At least in Russia, everyone has free access to it in any quantity. Alternative coolants are not even close to being able to compete in this indicator.
- Safety.
The water is non-toxic and absolutely environmentally friendly. No leaks from the heating circuit can lead to serious consequences for human health or the environment. Of course, we are also not talking about any fire or explosion hazard.
Main disadvantages of water
- Limited temperature range.
Everyone knows that at 0°C water turns into ice, and at 100°C into steam. Moreover, both options for changing the state of aggregation lead to a significant increase in volume.
And if you can somehow cope with boiling water by limiting the maximum heating temperature, then with freezing things are much worse. If you leave the system unattended in winter (for example, at the dacha) and the water will simply burst all the pipes and radiators.
- Oxidation.
Water is an excellent oxidizing agent because the valence bond between hydrogen and oxygen atoms is small. Therefore, sooner or later destructive corrosion processes will develop.
The only way out is to buy pipes and radiators made of stainless steel or having a protective coating inside. You can approach the problem from the other side - add so-called corrosion inhibitors (special chemical components that reduce its corrosiveness) to the water.
- Sediment.
If you use ordinary rather than distilled water (which is far from free), then over time the salts dissolved in it settle on the surfaces of the pipeline, reducing their throughput and impairing the efficiency of heat transfer. This leads to increased heating costs and accelerated wear and tear of equipment.
However, there are ways to soften water. The simplest of them is boiling. But in order to eliminate all impurities, you will have to use a more complex chemical method of separating salts followed by filtration.
- Need for frequent replacement.
It is advisable to change the water in the heating circuit annually, while alternative coolants can be used for 5 years or more.
Antifreeze as a coolant for the heating system
Antifreeze is an artificially created substance that acts as a coolant. It is usually made from ethylene glycol.
The main advantages of antifreeze include a low freezing point. It is approximately -65 degrees Celsius.
This allows you to turn off the heating for a while without harming the system. The system will not freeze, and as a result, the batteries and other things will remain intact (in the case of water, the batteries will simply burst).
In addition, due to its base, antifreeze does not form scale and sediment. This will have a positive effect on the service life of the system.
Despite this, antifreeze has a number of significant disadvantages. Its heat capacity is approximately 15-20% lower than that of water. In addition, the viscosity is approximately 2-3 times higher.
As a result, antifreeze is not recommended for use on low-power boilers due to its ineffectiveness.

Also, it does not tolerate overheating very well. Due to high temperatures, antifreeze may begin to decompose into its components and form a small soot.
If antifreeze is made from ethylene glycol, toxic fumes are possible. This phenomenon is especially common in boilers with double-circuit chimneys.
In addition, it is necessary to replace the coolant approximately every 4-5 years.
Antifreeze heating system
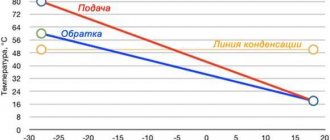
With the onset of cold weather, “anti-freeze” - a non-freezing liquid for the heating system - becomes relevant. Pipes filled with such a coolant will not burst at low temperatures - this point is important for homeowners who use the house irregularly. The carrier of this type of thermal energy is antifreeze. As a rule, it is designed to operate down to temperatures of -30°C or -65°C.
If the temperature drops below normal, antifreeze for heating systems, unlike water, does not harden, but turns into a gel-like state. Returning to a liquid state, it does not lose its original properties and does not pose a threat to the heating circuit.

Some types of antifreeze can function at extremely low temperatures.
To remove scale or pockets of corrosion, manufacturers add additives to the liquid - special inhibitors. Thanks to them, the service life of the heating system increases by several years. However, it should be remembered that antifreeze for heating is not a universal liquid, and additives are only suitable for certain materials of construction. Some of them are capable of destroying polymer pipes, others can cause electrochemical type corrosion.
Attention! The average service life of antifreeze is 5 years (10 seasons). After this period, the entire volume of coolant must be replaced. Manufacturers recommend a working life of 3 years.
If you compare antifreeze with water, in addition to the advantages, you can identify a number of disadvantages:
- increased viscosity requires heating equipment to be equipped with a powerful circulation pump;
- 15% lower heat capacity, therefore, the amount of heat given off is less;
- Detachable connections should be sealed more carefully;
- radiators are required that are 50% larger in volume than their water counterparts;
- a closed expansion tank is required, since increased expansion occurs during heating;
- The toxicity of a substance (for example, ethylene glycol) in antifreeze requires its use in single-circuit boilers.
Thus, before filling the heating system with antifreeze, it is necessary to consider installing a more powerful pump and a capacious expansion tank. Radiators should be voluminous, pipes should be of larger diameter. To seal detachable connections, it is better to use Teflon or paronite gaskets. If you decide to dilute the antifreeze, you only need distilled water. Each successive filling of antifreeze requires a complete flushing of the heating system, including the boiler.
What's better? Water or antifreeze?
Let's summarize. Each of these coolants has a number of advantages and disadvantages. Everyone chooses the most suitable option for themselves. If the system will operate continuously - water is the best option, if the heating will turn off at sub-zero temperatures - antifreeze will suit you.
You can also find a compromise - a mixture of antifreeze and water. Approximately 50 to 50. This will shift the freezing temperature of the mixture to -30 degrees, and at the same time reduce the negative factors that appear when using antifreeze.
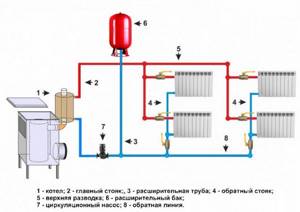
When installing a boiler using waste oil in service stations, garages, greenhouses and other technical premises, antifreeze is often used, because in some cases, the boiler does not operate around the clock, but during the working day. Often, when using fan heaters (air-heating units) in the heating system, the boilers are started in the morning, warming up the room in the first 30-40 minutes of operation, and turned off at night.
There are also combined systems: the main circuit is water coolant, and the heated floor circuit is antifreeze. The circuits are separate, the warm floor in this case is heated through an intermediate heat exchanger of appropriate power, while pumping antifreeze under pressure.
If you have any questions or need advice, you can always contact us using our contact details
- User's blog 5energy
- Login or register to post comments
For heating, as a coolant, in the Russian climate, antifreeze is considered to be a “panacea” for all ills. Is it so? Let's consider the advantages and disadvantages of water and antifreeze as a coolant.
Content
- Water is the coolant
- advantages of water as a coolant
- disadvantages of water as a coolant
- Antifreeze - coolant
- advantages of antifreeze as a coolant
- disadvantages of antifreeze as a coolant
- New generation antifreezes
- Results of the dispute
Water is the coolant
When filling the heating system with water, the owner must foresee possible negative consequences.
Under normal conditions, practically no liquid is consumed in the heating system, but here the quality of the water comes to the fore.
advantages of water as a coolant
Water itself is not an aggressive element.
If the water contains few salts and other impurities, and before filling the system, the water is passed through a filter to remove the above impurities - this is an excellent coolant.
If the owners live in the house permanently, they can monitor the condition of the heating system - they will not allow the heating system to freeze.
If the boiler is an open system and does not depend on the power supply, power outages do not affect the operation of the gas boiler.
The best option is to constantly fill the system with water; even in the summer, the system should be constantly filled - this will prevent corrosion and other problems.
disadvantages of water as a coolant
If the water contains salt and other impurities, then when heated, all these salts will settle on the internal elements of the heating system - this will reduce heat transfer.
If the boiler is used periodically, residents move to the city during the cold season - the coolant in the form of water is drained, the system is preserved.
As a result, new water is poured every season - the amount of scale increases.
All this gradually reduces heat transfer and increases gas consumption.
Antifreeze - coolant
Antifreeze is an artificially created chemical coolant.
The basis of antifreeze is an aqueous solution of salts, alcohols, ethylene glycol with additives.
These additives can adjust the physical properties of the solution.
In Russia, ethylene glycol-based antifreezes are most widespread.
advantages of antifreeze as a coolant
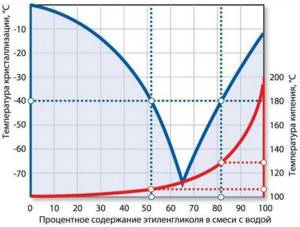
The main advantage of antifreeze is its low freezing point, down to -68*C.
At the same time, by changing the ratio of concentrate and water, the freezing temperature also changes from -10*C to -68*C.
When the antifreeze temperature decreases in the range from -20*C to -30*C - 35%, the concentration of ethylene glycol acquires a “sludge” state.
The use of various additives in antifreeze helps protect metal from corrosion, dissolves and removes scale that has formed, and prevents the destruction of seals in threaded connections.
But this is ideal. But in fact, all European manufacturers of heating boilers do not recommend using antifreeze as a coolant.
Manufacturers always emphasize in their passports that the coolant is only water.
Many sellers simply hush up this problem, and the buyer reads the passport after the boiler is purchased.
Why is antifreeze not recommended as a coolant?
disadvantages of antifreeze as a coolant
The heat capacity of antifreeze is 15-20% less than the heat capacity of water.
The viscosity of antifreeze is 2-3 times higher than the viscosity of water.
Volumetric expansion is 40-60% greater. Many other characteristics also differ.
In practice, it turns out that if you decide to use antifreeze in the heating system, you need to make changes to the design of the heating system in advance.
Namely: it is necessary to purchase larger batteries, a more powerful circulation pump, and a larger storage tank.
And most importantly, you need to purchase a more powerful boiler.
Accordingly, the power of the entire system increases, gas consumption and, accordingly, the payment for it increase.
In addition to the above, ethylene glycol-based antifreeze is not stable in operation when overheated, since thermal decomposition of the antifreeze into its components occurs, acids are formed and solid precipitation occurs.
Carbon deposits form on the heating elements of the boiler, which subsequently leads to the destruction of the heat exchanger.
Acid provokes metal corrosion, gaskets are corroded at threaded joints, and leaks appear at joints.
When overheated, the antifreeze begins to foam and the system becomes airy.
Overheating is a very big danger for ethylene glycol-based antifreeze.
Antifreeze has increased permeability or fluidity properties.
When the heating system is turned off, during cooling, leaks often appear at the joints.
Ethylene glycol-based antifreeze is a toxic material, so it is not recommended for use in double-circuit boilers in hot water supply systems.
If the heat exchangers are not sealed, there is a risk of antifreeze getting into the hot water.
New generation antifreezes
Currently, new generation antifreezes have become more widespread in Russia; in Europe they became widespread in the late 90s of the last century.
The basis of these antifreezes is food-grade propylene glycol - it is an environmentally friendly substance.
This antifreeze is absolutely harmless; it is allowed for use in dual-circuit heating systems.
Although the thermal and hydraulic characteristics are equivalent to those of ethylene glycol-based antifreeze, they are less aggressive to metals and heating system materials.
Many leading gas boiler manufacturers allow the use of propylene glycol antifreeze in their boilers.
The price of new antifreeze is quite high.
Results of the dispute
Whether it makes sense to increase the cost of the entire heating system is a question that does not have a clear answer.
With the correct operation of any boiler, freezing of the coolant is simply impossible, since almost all wall-mounted boilers have an automatic heating mode.
If the boilers are non-volatile, the best coolant is water.
If you have a backup power source, it will be able to ensure the operation of the heating system.
But if your house is located in an open field, is powered by a single cable, and there are long power outages, fill it with antifreeze.
When pouring antifreeze, check whether it precipitates when interacting with water.
In case of precipitation, fill with distilled water.
Do not dilute antifreeze by more than 50%.
Do not pour antifreeze into galvanized pipes, as this will create a huge sediment and the heating system will fail.
After 4-5 years, the antifreeze is changed as it ages.
Author: Sergey and Svetlana Khudentsov
10
How to fill your heating system with antifreeze

Filling CO with antifreeze can be roughly divided into three stages: preparing the system; diluting the concentrate in the required proportion; directly filling.
The first stage is preparation.
- Check the tightness of the connections in the CO. If required by the manufacturer, replace seals and materials incompatible with this active substance.
- Check the CO for leaks, scale on heat exchangers and lime deposits in the piping and radiators.
- Calculate the required volume of coolant.
This is quite simple to do: fill your CO with water, then drain it and measure the amount using a measuring container.
History of origin
Once upon a time, people used stove heating, heated the stove with wood and warmed themselves from the stoves. Later, when industry began to develop and the process of industrialization took place, people began to move to cities. And this question became especially acute there.
How to heat a room, how to heat people’s homes? Because it was almost impossible to heat it all with stoves and wood. For this purpose, they began to use boiler rooms and distribution of heating systems in houses, where water was used as a coolant. Water was poured into tanks, then this water was heated using fire, and it was then supplied under pressure through the heating system.
Later, this heating system began to be actively used in private housing construction. But here certain nuances arose. In a private house, firstly, a person does not live permanently, and, secondly, the heating system in country houses is almost always autonomous, because it is located far from any city communications.
What is easier - antifreeze or water?
Is it possible to mix antifreeze with water? Let's look at this issue by going back a little into history and studying the origins of antifreeze. A long time ago, water was poured into car radiators. To prevent it from freezing, it was diluted with ethylene glycol. Such a mixture could not break the cylinders, since it became viscous and contained ice crystals. Even such a liquid did not cause trouble for ancient cars in the form of rust. But after some time, they created a special non-freezing liquid - antifreeze. I will talk about it in the article.
Application of water

The method of transferring heat from a source to radiators using water is the simplest and at the same time the least expensive . Water accounts for at least 70% of the total number of liquids used.
Despite the apparent simplicity of application, there are a number of points that must be taken into account:
- Rigidity. There are solid particles in water. When heated above 70 degrees, the crystallization process begins, which, in turn, leads to the appearance of scale on the internal surfaces of the boiler heat exchanger, pipelines, and batteries. To combat this phenomenon, there are water softening devices that also purify water from mechanical pollution. Such devices are connected directly to the water supply. When connected in this way, there is no need to install an additional pump to fill the system. Filling occurs due to pressure in the water supply network.
- Temperature regime. When providing heat to a separate building, the supply temperature rarely exceeds 95 degrees. Most domestic heating boilers are also designed for this temperature as the maximum. At this temperature, the liquid does not boil. It must be remembered that at a temperature of 80 degrees, the process of deaeration begins (the release of air particles from the water). To prevent airing of the system, it is necessary to install air valves that will automatically release the air that appears.
- Freezing temperature. If the room is heated regularly, then this problem will not arise. If the heating of the room is not carried out on an ongoing basis, but from time to time, then it is necessary to take into account that at 0 degrees the water will freeze. Freezing of water in heating devices can lead to their failure for a long time or even to complete unusability.
Positive aspects of using water:
- Environmentally friendly substance.
- Has a high heat capacity.
- Does not require additional energy costs to ensure circulation.
- If it is necessary to fill the system , it is always available.
- Low cost.
Negative sides:
- Turns into ice at 0 °C.
- The need to install a water treatment device.
What kind of water is poured into the heating system?
Before pouring into the heating system, water from a tap or natural sources requires preparation. This is necessary to eliminate possible negative effects of the liquid on the surfaces with which it interacts. During water treatment, it is filtered and softened. But this is not available to all boiler house owners. The simplest thing is to buy water prepared for heating systems. Be sure to study the documentation for your boiler and heating radiators - it should indicate the requirements for the coolant.
Why is untreated water dangerous? Calcium and magnesium salts cause deposits on the internal surfaces of pipes and the heat exchanger. As a result, the heating system becomes overgrown with scale. Over time, this can lead to a decrease in the bore diameter, a decrease in heat transfer, an increase in energy consumption and the destruction of individual elements of the heating system. Dissolved oxygen in water increases the risk of corrosion, but in a properly designed system the air is effectively removed, reducing the risk to a minimum.
— If water is the best coolant, why is there any talk about antifreeze?
The worst dream of any owner of his own boiler room is its shutdown in winter. If the temperature in the house drops below zero, the water in the heating system will freeze. This can cause irreparable damage to pipes and units.
Another, not so obvious reason for talking about antifreeze lies in the myths that exist in the heating industry. Antifreeze is perceived as a specially developed coolant, and water is perceived as a regular, cheap option. This is exactly how manufacturers position their products.
When does danger occur? The most common reason is a power outage causing the pumps to stop. It also happens that the heating in the house is not constant, there is downtime during the heating season.
How serious is it really? In our latitudes it really can be very cold. Periodically, the light goes out in every house - sometimes less often, sometimes more often. Then the idea arises of using not water as a coolant, but a liquid that does not freeze. In reality, a power outage may not cause any harm. It all depends on the air temperature and the duration of the system downtime. In case of frequent shutdowns, the heating system is equipped with an uninterruptible boiler power supply system.

I want to install a new boiler in my house - which one should I choose?
How to properly dilute antifreeze with water?
The engine cooling system must have a sufficient level of coolant, otherwise the engine will overheat and will not last long. Therefore, experienced car owners answer in the affirmative when asked whether antifreeze can be diluted with water. However, a number of simple rules must be followed.
Recommendations for diluting antifreeze
Article on the topic: How to wash a car correctly?
There are two restrictions here:
Questions often arise about whether it is possible to add antifreeze during force majeure, if the technical composition is more than half gone (a broken hose, a large leak, an accident). Experts unanimously say: in such cases it is better to completely change the main composition. In the summer, as a last resort (if everything happened far from the benefits of automobile civilization), you can go with distillate. But then, in any case, you will have to replace the technical fluid.
How to drain the liquid
The answer to this question is very simple. The coolant requires draining in the following cases:
- If necessary, replace according to the season.
- When replacing the cooling radiator.
- When installing a new thermostat.
The work is done in two steps, since there is antifreeze in the radiator and in the engine. This work has already become familiar to owners of domestically produced cars.
You need to start draining the fluid from the radiator:
- Turn off the engine.
- Wait 15 minutes for the engine to cool down slightly.
- Switch the interior heater control to the extreme right position. This will open the stove drain valve.
- Next, you need to open the expansion tank cap.
- Unscrew the radiator drain plug.
- Wait about 10 minutes until the liquid is completely drained.
Coolant is drained from the engine as follows:
- Take a spanner and unscrew the drain plug on the engine block.
- Wait about 10 minutes until the liquid is completely drained.
- Wipe the drain plug and check the quality of the rubber seal, replace it if necessary, and screw the plug into place.
When draining antifreeze, care must be taken as this liquid has a sweetish odor that attracts children and pets. Therefore, antifreeze or antifreeze must be poured into a container and disposed of, and not poured onto the ground
Application of coolants
There are usually no special difficulties when choosing antifreeze. But when using it, some peculiarities arise.
When preparing a solution of coolant and concentrates, the proportion requirements must be met.
Antifreeze must be replaced as needed or as part of the maintenance schedule unless replacement is required during engine repair. Do not mix coolants of different properties and types, as malfunctions of the cooling system may occur.
If the brand of antifreeze poured into the engine is unknown, then it is better to drain it all and purchase new antifreeze. It is undesirable to mix different brands of antifreeze, since different sets of additives have different properties, and as a result of chemical reactions they will become unbalanced. When mixing different reagents, malfunctions and ballast sediment may occur, water pump failure, engine overheating, clogging of the cooling system, and major repairs of the power unit. You should not save on buying antifreeze, as engine repairs will cost much more.
Antifreeze for car engines is sold in finished or concentrated form. Many car enthusiasts are accustomed to purchasing concentrate in order to make the solution themselves in the required proportion. But we must not forget that to dilute the solution, only distilled water is needed, and the proportion should be determined by the freezing temperature. Each time you need to use only the concentrate manufacturer’s instructions.