No matter how zealous scientists and engineers are in searching for alternative heat storage and transmitters to liquid media from sources to end points of heat transfer, a worthy replacement for liquid media has not yet appeared. Water heating systems will remain the most common for a long time, as they are practical and quite efficient. They are called water-based, although it would be more correct to call them liquid, because they use not only water, but also other types of liquid substances as a coolant.
What should the coolant be?
Most often, ordinary water is used to fill household heating systems. However, there are situations when following such a traditional path is not only extremely inconvenient, but even dangerous. The reason lies in the specific chemical and physical characteristics of water: in this case, it is replaced by other liquids that are more suitable for the operational requirements put forward.
In order to correctly select the optimal coolant option for the heating system of a country house, you should familiarize yourself with the basic requirements for its properties:
- Effectively fulfilling its main purpose - to accumulate and transmit thermal energy. Simply put, the heat capacity of the liquid should be as high as possible. This will ensure that the energy released as a result of boiler operation will be transferred to the radiators with minimal losses.
- The components contained in the coolant should not stimulate active corrosion of boilers, pipes, heating radiators, shut-off and control valves and other elements included in the system. It is also important that there is no destruction of the gaskets and seals with which the connecting sections are equipped. If this aspect is not taken into account, it will reduce the service life of the system by an order of magnitude. In addition, if the coolant “corrodes” the gasket or seal, this can lead to flooding of the premises and damage to property.
- The presence of a wide temperature range of the operating state - from freezing to boiling, with release into a gaseous state. This will allow the liquid to be used in any climate zone.
- The coolant composition should not contain salts that provoke the formation of solid deposits inside the pipes or heat exchanger of the boiler. In case of frequent accidents associated with “overgrowing” of pipes from the inside, you should first check the chemical composition of the coolant used.
- The presence of a stable chemical composition. It is important that the heat transfer fluid is resistant to decomposition and breakdown into simpler elements under the influence of changing temperatures or over time. Stable operation of the heating system is possible only if the basic characteristics of the medium are constant - density, fluidity, heat capacity, chemical inertness.
- The heating fluid must be completely safe for the residents of the house. No toxic fumes, formation of explosive mixtures or fires are strictly permitted. Any liquid other than water must be thoroughly tested for safety.
- Since the volume of liquid poured into the system is quite impressive, it should not be too expensive. This is especially true for the so-called “antifreeze” - non-freezing coolants for heating systems with an increased operating temperature range.
These criteria and requirements are so simple and understandable that it would seem that finding a suitable coolant option would not be difficult. In practice, it turns out that the liquids currently used only partially satisfy the above-described requests, so choosing the appropriate option is not an easy task.
Based on this state of affairs, the search for an optimal solution involves taking into account the design features of the heating system and the specifics of its operating modes. Most often, the question of what coolant to pour into the heating system is decided when drawing up a project: this involves choosing one or another priority quality, which will be the main determining factor.
The following examples will help you understand this principle of the approach:
- In the case of a private house that is constantly in use and constantly under supervision, the best option for filling the heating system, based on economic and operational considerations, would be simple tap water.
- If in such a situation an electric boiler is used as a source of thermal energy, and the area is famous for interruptions in the supply of electricity, the presence of plain water inside the system in winter can become a serious risk. The fact is that if the boiler is idle, such a coolant can freeze, causing ruptures of heating pipes and radiators. Therefore, in such a situation, you need to decide for yourself what is better - coolant or water?
- A common situation is when a country house is used only from time to time, which requires long downtime of the heating system. If water is used, this causes serious risks of circuit damage. There is only one way out - to use a non-freezing liquid (antifreeze) as a coolant. In turn, this solution imposes additional requirements on the tightness of the system, since antifreeze often contains toxic substances.
- There are no eternal coolants, which requires their periodic replacement. Considering that we are talking about impressive volumes of liquid, it is desirable that its cost be acceptable.
- Certain types of boiler equipment are developed exclusively for a specific type of coolant (this point is indicated in the accompanying documentation). If you use another liquid to fill the network, the warranty on the boiler will expire: therefore, before choosing a coolant, this point should be clarified.
Taking into account all these considerations, when choosing the optimal solution, you do not need to rely on your intuition, but comprehensively evaluate all available options.
Features of using water as a coolant
From the point of view of heat transfer efficiency, water is an ideal coolant. It has a very high heat capacity and fluidity, which allows it to deliver heat to the radiators in the required volume. What kind of water should I fill? If the system is closed, you can fill it with water directly from the tap.
Yes, tap water is not ideal in composition; it contains salts and a certain amount of mechanical impurities. And yes, they will settle on the elements of the heating system. But this will happen once: in a closed system, the coolant circulates for years, and replenishment with a small amount is very rarely required. Therefore, some amount of sediment will not cause any tangible harm.

Water as a coolant for heating systems is almost ideal
If the heating is of an open type, the requirements for the quality of water as a coolant are much higher. Here, gradual evaporation of water occurs, which is periodically replenished by adding water. Thus, it turns out that the concentration of salts in the liquid increases all the time. This means that sediment also accumulates on the elements. That is why purified or distilled water is poured into open-type heating systems (with an open expansion tank in the attic).
In this case, it is better to use distillate, but getting it in the required volume can be problematic and expensive. Then you can fill in purified water that has been passed through filters. The most critical is the presence of large amounts of iron and hardness salts. Mechanical impurities are also useless, but they are the easiest thing to deal with - several mesh filters with cells of different sizes will help catch most of them.
In order not to buy purified water or distillate, you can prepare it yourself. First, pour and let sit until most of the iron settles. Carefully pour the settled water into a large container and boil (do not cover with a lid). This removes hardness salts (potassium and magnesium). In principle, such water is already well prepared and can be poured into the system. And then top up with either distilled water or purified drinking water. This is no longer as expensive as the initial fill.
Water
Water is used as a coolant in autonomous systems in 60% of cases, which is explained by the following objective reasons:
- Universal availability and low cost . Most often, there is no need to pay for this coolant at all, since most regions of the country do not experience serious interruptions in water supply. This makes it possible to repair, replace or install heating circuits at any time of the year - water is always freely available.
- High level of thermal performance indicators . The level of heat capacity of water is impressive, and this despite its high density. If we take the tabular value of heat capacity (4200 J/kg×ºС or 1 cal/g׺С), then with a typical temperature difference of 20 degrees for a heating system, one liter of water, when cooling, is capable of transferring 20 kcal = 83.43 through heat exchange devices kJ or about 23.26 watts of thermal energy. Such parameters are unique: all other liquids lag noticeably behind in this regard.
- Complete safety for humans and the environment . This allows you to calmly deal with leaks and accidents: apart from standard everyday inconveniences, such incidents do not bring anything more serious. That is, there is no risk of chemical burns, toxic poisoning, fire and other more serious consequences. Only water can be used as a coolant for an open heating system.

When using water as a coolant, the following disadvantages should be taken into account:
- High freezing point . Russian realities are such that winter in most regions of the country is accompanied by frosts. This, in turn, carries serious risks of freezing of the liquid inside the system in the event of interruptions in the operation of the boiler equipment. The consequences of such incidents are usually quite serious, including complete failure of the heating system.
- Corrosive aggressiveness towards products made of ferrous and some non-ferrous metals. Water by nature has strong oxidizing properties, which are enhanced by the presence of oxygen.
- Presence of impurities . In addition to H2O, tap or natural water usually contains a sufficient amount of various impurities - salt, dissolved iron, hydrogen sulfide, etc. One part of these substances may precipitate during operation, silting up the system. Other components gradually build up as hard deposits on the inner walls of the pipes, reducing their permeability. All this leads to a decrease in the thermal conductivity of radiators and heat exchangers, and a decrease in the efficiency of heating elements. As a result, the consumption of fuel materials increases by an order of magnitude against the backdrop of a decrease in the performance of boiler equipment, with the threat of its failure.
Lowering the freezing threshold of water is not very easy, but the other listed disadvantages can be eliminated. Before pouring water into the system, it is softened and cleared of salts, making their concentration non-hazardous.
Various methods are used for this:
- Boiling . Not a very effective approach that allows you to get rid of only weak carbonate compounds, although this is also important. This procedure is best carried out in a metal vessel with the widest possible bottom, which provokes the precipitation of dissolved carbonates in the form of insoluble sediment and carbon dioxide. This method is complicated because organizing boiling of a significant amount of water is quite problematic. In addition, not all salts can be removed this way.
- Special filter softeners . Their work is based on reagents of the ion exchange or electromagnetic principle of action. These devices can be purchased at specialized stores that sell boiler cleaning equipment.
- Adding reagents to water . Soda ash or sodium orthophosphate have a softening effect. The proportion of such additives must be carefully adjusted, since an overdose will provoke the opposite effect when, instead of increasing, the thermal properties of water will decrease and its corrosive activity will increase.
- Mud filters . They are included in almost all heating systems, purifying water from insoluble precipitation. Filters need to be cleaned from time to time.
- Distilled water . It is freely available in construction stores in a variety of packaging. If you have enough money to purchase it (large volumes require wholesale discounts), then the system filled in this way will not need to be cleaned or re-equipped for a long time. This approach is an excellent option for which coolant to choose for a gas boiler.
- Rainwater . Although this liquid is far from ideal purity, natural distillation and purification bears fruit. In any case, it contains an order of magnitude less heavy salts and other impurities that contribute to the fouling of heating pipelines than water from the purest natural sources. You can easily collect rainwater on your site by preparing a coolant for heating with your own hands through filtration.
- Inhibitors . This is the name of special additives that reduce or completely remove the oxidizing properties of water. If everything is done correctly, the metal elements of the heating system will be completely protected from corrosion.
- Surface active additives . With the help of these components, old scale and rust are removed, and protection is created against the appearance of new ones. With the help of surfactants, specific water-repellent qualities are imparted to surfaces, resulting in a reduction in hydraulic resistance in pipes. This significantly reduces the cost of heating materials and extends the service life of gaskets.
Solutions of distilled water, inhibitors and surfactants are commercially available, although preparing these coolants for a heating system with your own hands is not very difficult.
Non-freezing coolants - antifreeze
Strengths and weaknesses of antifreeze liquids
After purification and enrichment with useful components, water turns into a good coolant. However, its main drawback, freezing, cannot be overcome in this way. Therefore, it is recommended to fill systems with unstable operation in winter with special liquids with a lower freezing level. They are called antifreeze: they are well known to car enthusiasts, as they are used in engine cooling systems and glass cleaning.
Advantages of antifreeze:
- Low freezing point . Moreover, which is very important, even their crystallization does not provoke hardening and volume expansion. Although the fluidity level of the gel-like substance does not allow the heating to function normally, it completely eliminates the risk of damage to pipes, radiators and heat exchangers. After the temperature normalizes, the non-freezing coolant completely restores its fluidity, which does not in any way affect its performance characteristics.
- Possibility of adding water . The freezing level in normal concentration is approximately -65 degrees. Such ultra-low temperature conditions are rare in nature, which makes it possible to dilute antifreeze with distilled water. As practice shows, the lower limit of -35 degrees will suit all regions of the country.
- Chemical stability . It is typical for most modern antifreezes. Although the range of operational temperature differences is quite significant, the service life of a high-quality coolant without replacement can reach 5 years.

When considering antifreeze for potential use as a coolant, it is important to know the negative aspects:
- High level of viscosity . It is an order of magnitude higher than that of water, so good circulation of non-freezing liquids along the circuit is possible only with powerful pumps. If the house is equipped with a heating system with natural circulation, the use of antifreeze as a coolant is completely excluded.
- Low heat capacity . Even the most effective non-freezing coolant for heating in this regard is usually inferior to water by at least 15%. This may not seem like a big figure, but on the scale of the heating system of an entire building, the consequences of such a difference are very significant, and are expressed in a decrease in efficiency, an increase in costs for maintaining the desired temperature, and the need for a larger number of powerful radiators.
- High level of gasket penetration . Despite the higher viscosity of antifreeze, even those seals that remained dry in water do not hold it. Therefore, if the coolant is replaced, be sure to repack all fittings and threaded connections. In this case, the aggressiveness of non-freezing liquids should be taken into account, which requires the use of only chemically resistant seals.
- Toxicity . Most antifreezes contain chemical compounds harmful to humans that can cause severe poisoning and damage to the skin and mucous membranes. Therefore, the systems where they are used must be as tight as possible to eliminate the slightest chance of leakage or evaporation of liquid. In any case, antifreeze cannot be used in double-circuit boilers, where there is a real risk of coolant getting into hot water pipes.
- High level of thermal expansion . This indicator for antifreeze is an order of magnitude higher than for ordinary water. Because of this, it is necessary to use larger volume membrane expansion tanks. The use of cheap open-type expanders in this case is completely excluded, because this threatens not only the evaporation of expensive coolant, but also the release of toxins into the indoor air. Currently, three types of non-freezing coolants are widely used - based on ethylene glycol, propylene glycol and glycerin.
What is antifreeze and its types
Antifreeze is a class of liquids that cannot crystallize at low temperatures; their main purpose is to cool automobile engines and operate in low-temperature installations.
There are two main types of antifreeze: propylene glycol and ethylene glycol (glycerin-based formulations are also commercially available); they have different chemical and physical properties and areas of application.
The use of non-freezing liquid in heating systems is justified in cases where the owners of individual houses are absent from them for some time in the winter - in the event of an emergency (breakdown, power outage), the heating system may defrost. As soon as the temperature of the water in the pipes drops to zero degrees, it will freeze and expand by 10%, due to the lower density of ice compared to water by a similar amount. In this case, you will have to change the entire pipeline, completely filled with water, heating radiators and a heating boiler - the losses will be enormous.
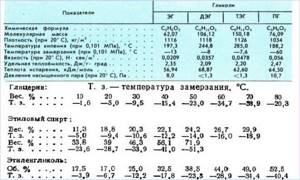
Rice. 6 Physical properties of glycols and freezing points of antifreezes
Pros of using antifreeze
In addition to preventing the pipeline system from defrosting, the use of antifreeze has the following advantages:
- The temperature range of operation of antifreeze compositions for heating systems, which lies in the range from -70º to +110º C, ensures the preservation of the pipeline at any low temperatures existing in nature and effective operation as a coolant.
- When the cooling temperature of glycols is below crystallization, they become jelly-like, expanding slightly in volume - this does not lead to defrosting of the system and its failure. After the pipes have thawed, the liquid can be thawed and reused without loss of quality.
- The presence of special additives (corrosion inhibitors and others) in the glycol composition prevents the appearance of scale, rust, foam, and airing, thereby increasing the service life of the system.
- The use of dyes makes it easy to detect leaks, and a change in the color of the fluid indicates the need to replace it.
Disadvantages of using antifreeze
The use of antifreeze has the following disadvantages:
- When using antifreeze compounds, it must be remembered that ethylene glycol antifreeze is poisonous; the lethal dose for humans when ingested is 2 mg. per 1 kilogram of body weight. In this regard, environmentally friendly and absolutely safe propylene glycol was developed.
- The big disadvantage of non-freezing liquids is their too high price; a standard 20-liter container of ethylene glycol with a maximum temperature of 65º C costs on average about 30 USD. A 20-liter canister of propylene glycol with a maximum temperature of -30º C has the same cost - in fact, this means that the propylene glycol composition costs 2 times more.
- The use of relatively inexpensive poisonous ethylene glycol is impossible in a house with an open expansion tank.
- Non-freezing liquids have a limited service life, on average it is 5 years or 10 heating seasons, after which the liquid must be drained, the pipeline flushed and a new composition filled in, and when using poisonous ethylene glycol, the issue of its disposal will have to be additionally addressed. This procedure leads to significant financial costs and loss of time.

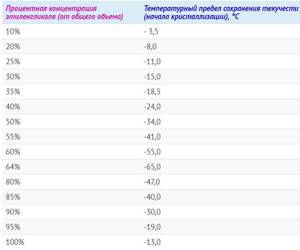
Rice. 7 The influence of the percentage of ethylene glycol in a solution on its crystallization temperature
- The use of low-quality antifreeze or its use after the expiration of its service life can cause damage to water supply fittings, clogging of pipes and fittings - there are a considerable number of similar examples on the Internet.
- One of the critical disadvantages of using antifreeze compounds is that many boiler manufacturers refuse the consumer further warranty service after adding antifreeze to the system.
- When using glycols, you will have to install a more powerful circulation pump; propylene glycol will require an increase in its pressure by 10% and productivity by 60%; similarly, a larger expansion tank will be needed.
- It is not recommended to use propylene glycol compounds in electrolysis boilers (Galan) and heating systems with galvanized pipes.
Ethylene glycol
The most popular antifreezes, which is explained by the simple technology of their production and low price. They are available for sale in concentrated form and in the form of a ready-to-use solution. Depending on the climatic characteristics of the area, the characteristics of the coolant can be slightly changed by diluting it with distilled water. In this case, special tables will help, indicating changes in parameters depending on the degree of concentration of the substance.
To improve the performance characteristics of the coolant, special additives are introduced into its composition. The fact is that when the temperature rises, ethylene glycol becomes covered with foam, which provokes the appearance of gas plugs. Thanks to additives, it is possible to reduce the level of foaming and provide the substance with additional inhibitory qualities that protect metal pipes from corrosion. However, this does not help in all cases. For example, galvanized pipes retain their sensitivity, so it is prohibited to use ethylene glycol in systems equipped with them.
Another serious disadvantage of ethylene glycol coolant is its breakdown into individual components when approaching the boiling point. Therefore, systems where it is used must be carefully regulated, since solid deposits resulting from decomposition can clog narrow passages of pipes and heat exchangers. Liquid residues of the substance become very aggressive, provoking active corrosion. As a result, there is a change in the characteristics of all modifying additives and the active appearance of foam. In boiler equipment where a mechanism for precise temperature settings is not provided, ethylene glycol-based antifreeze should not be used.
This liquid is characterized by a high level of toxicity, which requires increased requirements for sealing the system. If ethylene glycol gets into your home in liquid or gaseous form, it can cause severe poisoning with a very sad outcome. Even simple contact of the substance with unprotected skin is dangerous, therefore, when flooding the heating system, the strictest safety measures must be observed. The only attractive thing here is the cost - it is the lowest of all antifreezes.
What volume should be filled?
The amount of liquid poured into the heating system depends on various factors. The main ones are:
- heating boiler volume;
- type of heating system;
- quality of materials for manufacturing pipes and radiators;
- area of the heated room.
Calculation of the volume of liquid for filling the system is carried out based on the recommendations of the manufacturers. The boiler technical data sheet contains information about what coolant can be used and in what volume.
Propylene glycol
The packaging of liquids of this type often uses the “Eco” logo, which indicates complete safety for use at normal temperatures. They can be used in double-circuit boilers, since getting a small amount of propylene glycol into the water usually does not cause negative consequences. The level of heat capacity here is higher than that of ethylene glycol. The propylene glycol solution seems to lubricate the walls of the pipeline, reducing the overall level of hydraulic resistance. This leads to a reduction in heat loss and increases the efficiency of the heating system.

As for the inadmissibility of contact with galvanized products, propylene glycol antifreeze also has this drawback. The price for coolants of this type is an order of magnitude higher than for ethylene glycol. Antifreeze goes on sale in a form ready for use: special additives increase the durability of the liquid to almost 10 years. In general, this substance is an excellent solution to the question of what is the best antifreeze for heating a home.
How much coolant to buy for heating a house?
To calculate the required amount of antifreeze for heating, there are special standards. In this case, you should take into account:
type and length of the heating system
presence or absence of a “warm floor” system
height and number of radiator sections
The amount of antifreeze can be calculated using the following general parameters
:

Glycerin
Reviews about coolants of this group are the most contradictory, from the most enthusiastic to the sharply negative.
Positive characteristics of glycerin antifreeze:
- Complete safety for the human body and the natural environment. This is the safest coolant for the heating system of all antifreezes.
- Significant range of operating temperatures. The lower limit of crystallization is 30 degrees, the boiling point is the same as that of water (sometimes higher). Freezing of glycerol is not accompanied by its expansion. An increase in temperature not only liquefies, but also completely restores all the characteristics of the substance.
- Resistant to zinc. In this regard, it is one of a kind among other antifreezes.
- No aggressive effects on the sealing gaskets of the system are observed.
- Absolute fire safety.
- Before pouring glycerin antifreeze, the heating system does not need to be thoroughly rinsed, even if another substance was poured into it before.
- Durability. If you follow the operating rules, coolants of this type can last up to 10 years.
- The level of thermal characteristics here is comparable to propylene glycol. At the same time, glycerin coolants are 20-25% cheaper.

Disadvantages of glycerin:
- Outdated version. Glycerin antifreezes are the most “ancient”: it was in order to improve their performance characteristics that all of the above substances were developed.
- High density and viscosity. Pumps experience significant difficulties pumping glycerin coolant through the heating circuit. As a result, equipment wears out much faster.
- Low heat capacity. In this regard, glycerin is inferior not only to water, but also to propylene glycol.
The heat resistance and environmental safety of the substance deserve special consideration:
- Upon reaching a temperature of +90 degrees, significant foaming of glycerin is observed. To reduce this effect, special additives are usually used.
- The same temperature level triggers the process of chemical decomposition of the liquid. As a result of precipitation, the solid substance gradually layers inside the pipes, and the gas released, acrolein, has a very unpleasant odor, being a weak carcinogen.
- When overheated, water evaporates from glycerin, which makes the liquid very viscous. As a result of this, it loses its characteristics, turning into a jelly-like substance already at a temperature of +15 degrees. It is clear that normal operation of the heating system in such conditions is impossible.
The production of glycerin-based coolants is not standardized at all by any GOST standards. Everything is in the hands of manufacturers, who set their own technical conditions. It is inappropriate to talk about any quality guarantees in this state of affairs.
As studies have shown, the main component of counterfeit antifreeze coolants for heating systems is most often glycerin. This is explained by its low cost, which gave unscrupulous manufacturers the idea to use the material instead of propylene glycol, passing off their products as environmentally friendly high-quality propylene glycol antifreezes. Therefore, when purchasing non-freezing coolants, it is necessary to exercise some caution, requiring quality certificates. It should be noted that in Europe, coolants based on ethylene glycol have long been discontinued, but local companies are in no hurry to return to glycerin.
Rating of the best coolants for heating systems for 2021
Warm House Eco-30

Buyers believe that the domestic coolant Warm House Eco -30 has proven itself well. It is a propylene glycol antifreeze. The product is available in two weight categories: 10 kg and 20 kg. The packaging is equipped with comfortable handles, allowing for hassle-free transportation. To create a mixture at the desired temperature, the required amount of product is diluted with water. Dilution with water makes it possible to reduce the viscosity of the product and increase the heat capacity. Circulation is also improved. The service life of the product is 5 years, but we must remember that a lot depends on the operating conditions. If you bring the substance to a boil, thermal decomposition of propylene glycol and additives will begin. Buyers believe that if the pipes are made of plastic and the heat exchanger in the boiler is copper, then the service life is doubled.
You can buy from 1000 rubles.
Warm House Eco-30
Advantages:
- Gentle on pipe material;
- Expansion upon freezing is not observed;
- Jelly-like texture during strong cooling;
- Safe impact on pipes;
- With additives;
- Functionality is normal with sealants;
- There are no harmful components in the additives;
- There is no aggressive effect on metal.
Flaws:
- Use for electrolysis boilers is prohibited;
- Increased fluidity was observed when hot, so careful sealing is required.
DIXIS-65

The domestic coolant Dixis-65 is a concentrate that is diluted with water, thereby creating antifreeze with the required freezing point. The manufacturer does not recommend adding more than half of the water, otherwise the anti-corrosion additives will lose effectiveness, and in the future there will be a high risk of precipitation, scale and corrosion. Minimum operating temperature: -65 degrees, maximum: +110 degrees. The base is ethylene glycol. Customers like Dixis-65 because it is universal, which means it can be used with all types of radiators in a wide variety of pipe systems. The coolant composition includes devices specially created for this purpose that help eliminate the formation of foam and other problems. Duration of operation: 5 years. The yellow-green dye included in the product has fluorescent properties and easily makes it clear where the leak has formed.
You can buy from 790 rubles.
DIXIS-65
Advantages:
- Fireproof;
- High frost resistance;
- Low crystallization temperature;
- Compatible with gas and electric wall-mounted boilers;
- Economical, can be diluted with ordinary tap water;
- With additives;
- Prevents scale from forming.
Flaws:
- There are complaints about strong viscosity.
TermoTactic EcoGreen – 30

Owners of private houses praise TermoTactic EcoGreen - 30. The product is made on the basis of glycerin and has a complex of functional devices called additives. Antifreeze functions well at temperatures down to -30C; thanks to high-quality European raw materials, it can be used for all kinds of premises. When buying glycerin-based water, you can be sure of its environmental friendliness, safety, inertness and stability. In addition, glycerin has the ability to mix with distilled water. The presence of a “corrosion inhibitor” helps to negate the reaction of the composition with metal and other materials.
Prices vary and depend on volume. For example, 10 liters can be purchased for 700 rubles.
TermoTactic EcoGreen – 30
Advantages:
- Has excellent hygroscopicity;
- Explosion-proof and non-toxic;
- Can be mixed with distilled water in any proportions;
- High-quality European raw materials;
- There is no freezing.
Flaws:
- It is difficult to find large canisters on sale;
- There are complaints about increased electricity consumption.
Warme AVT-ECO-30

According to the builders, Warme AVT-ECO-30 performed well. The product is based on glycerin, therefore it is considered safe for the environment and people. The manufacturer has supplied the product with the necessary anti-foam and anti-corrosion additives, which can extend the service life of the heating system. Can be used for galvanized pipes. Warme AVT-EKO-30 is an absolutely ready-made product, crystallization begins at -28C, and fluidity is lost at 38C. Dilution with water is allowed. The presence of a phosphor dye in the composition makes it possible to quickly detect a leak that has occurred in the heating system. When using the product, the manufacturer does not recommend mixing Warme AVT-ECO-30 with other antifreezes, as performance characteristics may decrease.
You can purchase it for 725 rubles and more.
Warme AVT-ECO-30
Advantages:
- Glycerin based;
- Neutral impact on people and the environment;
- Explosion-proof;
- With additives;
- Provides protection against corrosion, scale and foaming;
- The use of galvanized pipes is allowed;
- Detects leaks thanks to phosphor dye.
Flaws:
- Cannot be used for electrolysis boilers.
Aquatrust – 30

Among the more expensive antifreezes, Aquatrust-30 is popular. Its main component is propylene glycol. The manufacturer claims that its product is environmentally friendly, which means it is perfect for use in dual-circuit home heating systems. The composition is equipped with antibacterial components, due to which the heat transfer properties increase significantly, and the service life of corrosion inhibitors and antibacterial additives becomes longer. Compared to competitors, this coolant has a service life 3 times longer. The product is not suitable for galvanized surfaces. Before using Aquatrust - 30, you will need to thoroughly flush the heating system. Plastic and metal pipes remain safe and sound, as the impact is very gentle. According to builders, the product is very gentle on gaskets and plumbing rubber. It can be used not only for private and residential buildings, but also for public catering establishments.
You can buy it for 1900 rubles and more.
Aquatrust – 30
Advantages:
- High security;
- Excellent characteristics;
- Carefully goes through the pipes;
- Excellent heat transfer;
- Increased service life of corrosion inhibitors and antibacterial additives;
- Effective anti-corrosion formula.
Flaws:
- High price.
PRIMOCLIMA ANTIFROST ECO -30

PRIMOCLIMA ANTIFROST ECO-30 is considered an elite coolant, and all because it is ideally suited for autonomous closed heating systems of private houses. The product is based on glycerin and is environmentally friendly. The content of anti-corrosion additives ensures more efficient operation of the heating system. Buyers noted that the product is non-flammable and therefore does not ignite. To recognize the slightest leaks, the product is painted in a fluorescent emerald hue. The dye is not poisonous and is easily used in the confectionery industry. If the heat suddenly turns off in winter, the radiator and pipes will be safe and sound. When the heat is turned off, the product becomes a jelly-like consistency, and the volume does not increase. It is very convenient that PRIMOCLIMA ANTIFROST ECO -30 allows use for 8 years. The circulation pumps operate without interference.
You can buy it for 800 rubles.
PRIMOCLIMA ANTIFROST ECO -30
Advantages:
- Suitable for stand-alone system;
- Excellent compatibility with most glycerin-based antifreezes;
- High environmental friendliness;
- Cost-effective;
- Excellent condition of heating systems;
- With additives;
- Inertness to sealing and gasket materials.
Flaws:
- Not detected.
TermoTactic EcoBlue - 30

Builders approve of TermoTactic EcoBlue - 30 coolant. Its main active ingredient is propylene glycol. The peculiarity of this liquid is that its density is lower than that of monoethylene glycol or glycerin, but its viscosity is higher. Propylene glycol is allowed to be used in all types of residential and non-residential premises. It is used as a coolant and coolant. TermoTactic EcoBlue - 30. The product is non-toxic and fully meets safety requirements. There is equipment in the form of a functional additive that combats physiological and physico-chemical processes, that is, there is no need to worry about corrosion and negative interaction with metal and plastic pipes. Distilled water is allowed to be mixed with liquid. Since the main active ingredient is not produced in our country, the raw materials are purchased in Europe, because of this, the cost becomes higher. Available in plastic containers of various capacities.
Sold from 900 rubles and above, depending on the capacity.
TermoTactic EcoBlue - 30
Advantages:
- Low crystallization temperature;
- Excellent heat transfer;
- Has the ability to mix with distilled water;
- Retains original functionality during heating and cooling;
- The composition contains multifunctional additives;
- Stabilization of the state of the liquid during cooling.
Flaws:
- Not detected.
Thermagent -65

Of the high-quality concentrates, buyers highly rated Thermagent-65. In temperate climates it can be diluted with water, and in very cold weather in its original form. In general, the product is intended as a non-freezing heating liquid in closed heating systems. Raw materials and all components of the product were purchased in Germany and are of high quality. Organic-based anti-corrosion additives do not contain silicates, amines, phosphates and nitrites. Suitable for use in gas, diesel and electric boilers. The basis of Thermagent-65 is purified ethylene glycol. The manufacturer recommends that before you start pouring Thermagent-65, you pressure test the system and carefully look for any leaks. This is quite an important point, since we should not forget that ethylene glycol is poisonous. The company conducted its tests with the liquid and found that it is well compatible with rubber, Teflon and paronite gaskets. To eliminate the possibility of the slightest leaks, it is necessary that the assembly of the system is of high quality, and the most reliable gaskets are installed.
You can buy it for 1000 rubles.
Thermagent -65
Advantages:
- Quality components;
- Does not harm the heating system;
- Long service life;
- Suitable for all European boilers;
- Lowest freezing point;
- Can be diluted with water;
- Antifreeze is based on purified ethylene glycol of the highest quality.
Flaws:
- Toxic substance, must be handled with caution.
Hot Point 65

In autonomous closed systems, builders recommend using Hot Point 65. The product belongs to the Italian brand Pipal, but is produced in Russia. It is based on ethylene glycol. Hot Point 65 is a thick concentrate that can be diluted with softened or distilled water. It is allowed to be used for heating residential buildings, industrial buildings and passenger cars. Thanks to a balanced complex of multifunctional additives, the heating system is protected from insidious corrosion, and the properties of the coolant itself are maximally preserved.
You can buy it for about 1000 rubles.
Hot Point 65
Advantages:
- High quality material;
- Compliance with all international safety and quality standards;
- Excellent heat transfer;
- Dilution with distilled water is allowed;
- There is no risk of premature wear of the heating system;
- The silicate additive extends the service life to 5 years.
Flaws:
- Toxic substance, must be handled with caution.
Coolant for electrode boiler
Antifreeze for electrode boilers is usually considered separately. We are talking about liquids intended for heating systems with installed electrode (ion) boilers. For such circuits, the chemical content of the coolant is of particular importance, since it is heated by passing alternating current through the liquid. This implies that the substance has not only the properties of antifreeze and high thermal performance, but also the concentration of certain salts. This ensures the required ionization and electrical conductivity, with a specific resistance indicator.

Typically, manufacturers of such boiler equipment also produce carefully selected coolants for electrode heating boilers, taking into account the operational features of the system as much as possible. Therefore, it is recommended to refrain from any experiments and purchase branded antifreezes with perfectly adapted compositions. Usually, independent selection of coolant for an electrode boiler is fraught not only with equipment failure, but also with the manufacturer’s refusal to fulfill its warranty obligations.
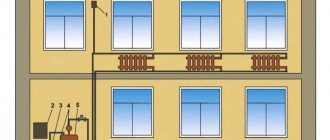
Device
Structurally, the electrode boiler is an all-metal pipe with polyamide insulating coating. On the case there are power terminals and coolant input/output (water or other liquid). At one end of the cylinder, electrodes are inserted into the boiler, and the other has an outlet into the heating system.
On the picture:
- 1 - pipe for supplying hot coolant to the external system;
- 2 — steel body;
- 3 - layer of electrically insulating material;
- 4 - coolant heated by current;
- 5 — electrode block;
- 6 - pipe for introducing cold liquid for subsequent heating;
- 7 - insulation and seal;
- 8 - power input.
The composition also usually includes an electronic control unit. There are samples of ready-made automation units for factory boilers on the market; they can also be adapted to a homemade “water heater”.

These boilers received the name “electrode” precisely because of the two electrodes located inside - the anode and the cathode. “Minus” goes to the cathode, and “plus” goes to the anode. When current is applied to the electrodes, the heat-carrying medium heats up and enters external systems. The electrical charge passes directly through the liquid, causing it to quickly become hot.
In industrial boilers, the following device diagram is usually used:
- cylindrical body with a round electrode inside;
- “zero” is connected to this electrode;
- the second contact is the housing itself - the phase is connected to it.
With such a scheme, the case is certainly grounded, for which a ground contact is placed on it. Homemade samples also adhere to this method of manufacturing electrode boilers.

Average parameters of factory products:
- pipe length - up to 60 centimeters, diameter - up to 32 centimeters;
- power - from 2 to 50 kW. The most powerful ones heat rooms up to 1500 square meters. m.;
- the current used is three- or single-phase. The latter operates relatively low-power household appliances, and three-phase current powers productive high-power boilers in commercial buildings, workshops and industrial facilities;
- The ideal temperature of the working fluid is 75 degrees. At this level, optimal energy consumption is established. At a higher temperature, the boiler consumes too much current, and at a low temperature it drops, since as it cools, the thermal conductivity of the medium decreases.

Boilers are divided according to the method of supplying water or other liquid:
- open - the movement of the working fluid is carried out naturally: it leaves the heat generator, transfers heat to the environment and returns back;
- closed - equipped with an expansion pump and tank. The pump provides circulation, and the tank serves for initial heating of the coolant.
Interesting: modern industrial boilers not only have advanced control automation, but are also often equipped with remote control systems and GSM communication modules. Such a device can be controlled via an application from anywhere in the world with Internet access.
Recommendations for the selection and operation of coolants - which one is better to choose
None of the coolant manufacturers will deny the fact that in case of stable operation of the heating system in winter, water is the best option as to which coolant to choose for heating. It is better if it is a special distilled liquid with modifying additives, as mentioned earlier. Those homeowners who consider purchasing store-bought water a waste of money usually prepare it themselves, softening it and equipping the system with the necessary filters.

If a decision has been made to use non-freezing coolants, it is important to have information about the conditions that exclude the likelihood of their use:
- If the house has an open type system.
- When using natural circulation in the circuits: the system simply “will not cope” with such a concentrated coolant for heating.
- The presence of pipes or other elements in contact with the coolant that have a galvanized surface is unacceptable.
- All connecting units equipped with seals made of tow or oil paint must be repacked, since glycol substances will destroy them very quickly. As a result, antifreeze will begin to leak out, creating a real threat to people in the room. You can use the old tow as a new sealing material by treating it with a special sealing paste “Unipak”
- It is prohibited to use non-freezing liquids in systems that are not equipped with devices for accurately maintaining the temperature of the coolant. The heating level, which is dangerous for glycol antifreezes, begins already at +70-75 degrees: these processes are irreversible and fraught with the most unpleasant consequences.
- Usually, after pouring antifreeze into the system, it is necessary to increase the power of the pumping equipment, install a larger expansion tank, and increase the number of battery sections. Sometimes it is necessary to change the pipes to wider ones.
- Incorrect operation of automatic air vents after adding antifreeze has been noticed: it is recommended to replace them with Mayevsky taps.
- Before adding antifreeze, the system must be thoroughly cleaned and flushed. This is done using special compounds.
- To change the level of antifreeze concentration, it is allowed to use only distilled water. In this case, it is better to refrain from even using purified and softened water.
- The correct concentration of antifreeze coolant for heating systems is of exceptional importance. It is better not to count on the winter not being very harsh by diluting antifreeze excessively. It is recommended to adhere to the threshold of -30 degrees even in traditionally warm regions. In addition to protection from abnormal frosts, this will create optimal conditions for inhibitors and surfactants, the effectiveness of which is noticeably reduced with excessive water content.
- After filling with new coolant, it is prohibited to immediately turn on the maximum system mode. It is best to increase power gradually so that the antifreeze has time to adapt to new conditions and elements of the circuit.
- Research shows that propylene glycol is currently considered the most reliable non-freezing coolant. Ethylene glycol is too dangerous, and glycerin is so controversial that it is used very rarely. So it’s better to overpay, but sleep peacefully at night.
Where to buy antifreeze for the heating system of a private home
Ours offers a wide and complete range of equipment and components for heating systems. In our online store you can also purchase antifreeze, the use of which guarantees the safety of the heating system in the house and will protect it from freezing. But since this choice has many nuances, our specialists, taking into account all the operational and technical features, will offer the most correct and optimal choice.
When placing an order on the website of our online store “Alfatep”, we definitely recommend using the services of a transport service to deliver the goods to the site. If necessary, to fill the system and start it, you can use the services of an experienced technician who will perform all the necessary operations efficiently and completely safely for your home.
Calculation of the required amount of coolant for a country house
An accurate calculation of the required volume of coolant is especially important in cases where expensive antifreeze rather than water is used. If the heating system is at the development stage, then its filling volume is closely related to other characteristics that take into account the characteristics of the building and the boiler equipment planned for installation. This involves carrying out calculations by design engineers.
However, there are often situations when it is necessary to determine the scope of already built systems. The reasons for this need may vary. For example, if it was decided to switch from ordinary water to a non-freezing coolant, or when the previously filled antifreeze has lost its characteristics and needs to be replaced with a new one. Another common situation is the repair of a heating system, when in the process of replacing pipes, radiators, boilers and other equipment, it is necessary to drain the old coolant.

Methods for determining system volume:
- Before starting to fill the previously emptied system, note the water meter readings. After completing the procedure, look at the difference: it will indicate the volume of water that fits into the circuit. If you intend to fill in antifreeze, then in this way you can determine its exact volume, at the same time flushing the system. At the end of the procedure, the water is drained in this case.
- A similar method is to measure the volume of drained coolant or water for the heating system, using measuring containers (bucket, barrel). In this case, the measurement speed will not be as high, but there will be no need to refill the water if antifreeze is supposed to be used. The disadvantages of this approach are the conditions for completely filling the system before draining. In addition, it is problematic to calculate very large networks in this way.
- Theoretical calculation when it is necessary to sum up the volumes of the heat exchanger, boiler, all radiators or convectors, underfloor heating circuits (if any), the entire supply and return pipeline, expansion tank, and all other elements (water gun, buffer tank, boiler). Although this procedure is quite complicated, in the case of very large heating systems other options are not suitable.
The situation is simplified by the fact that most of the heating devices used are marked with appropriate parameter designations, where, among other things, their volume is also indicated. Convenient calculators have been developed especially for such calculations, the algorithm of which includes most of the options and combinations most often encountered when equipping heating systems. The final result is given in liters, and even a beginner can understand the program interface.
How to add liquid to the heating system?
There are two ways to fill a sealed closed system:
- using a pump from a tank or barrel with ready-made coolant. The hose from the pump is connected to the make-up or drain pipe through a check valve, all air valves are opened. A pressure gauge must be connected to the network. The injection must be calculated so that after air is released from the system, the pressure in it is established at a level of about 1.5 Bar (for buildings no higher than 2 floors). If necessary, the operation of pumping and releasing air will have to be repeated several times;
- Without a pump, it is much more difficult to fill the pipelines. The entire volume of liquid will have to be filled through the highest point of the system, as a rule, this is an air vent on the riser. It is necessary to open the drain valve, air valves and install a pressure gauge. Then you will have to create pressure; this can be done by connecting a manual car pump to the drain through a check valve. The pump is connected to the fitting using a regular hose 1.5-2 m long and filled with antifreeze. Manual pumping and deflation of air is carried out until the pressure gauge shows the required pressure.