A glycerin-based coolant is a solution of glycerin in water with the addition of various additives and dye.
The presence of glycerin in the coolant reduces its freezing point, which makes the heating system (CO) more resistant to malfunctions that lead to temporary cessation of operation of the heating boiler.
The probability that the glycerin-based coolant will freeze in the lines, which will lead to their rupture and failure of the CO, is significantly less than that which exists for systems using only water as a coolant.
Glycerin in the heating system is the main factor influencing the further choice of the CO project for a private house, the type of heating boiler, the power of installed heating devices (convectors or radiators), the power of the main pump and the list of materials used.
Rules for commercial metering of thermal energy of a coolant: what is it?
Today, almost everything related to individual construction and arrangement of residential buildings is regulated by law.
This case is no exception, since there are special rules for accounting for thermal energy and coolant, which are formulated in the Decree of the Government of the Russian Federation of November 18, 2013. In general, the methodology for commercial metering of the thermal energy of a coolant is an interesting question, although quite complex for the average user. But if you want to understand how certain calculations are made and what the standards used in the future are made of, you can read the documentation on this topic.
According to the rules for commercial metering of thermal energy of the coolant, admission to operation of metering units is carried out by a representative of the energy supply organization
To summarize, it is worth noting that you can buy coolant for the heating system of a country house based on various criteria and factors. For many, the deciding factor is the price of the heating fluid, while others pay more attention to the issue of safety and efficiency. In any case, before purchasing, you should weigh all the arguments in favor of a particular decision.
Coolant temperature graph: requirements and standards
For the coolant, the temperature standard in the heating system is indicated based on the indicators obtained when the liquid has already completed a full circle and returns to the boiler. According to standards, the average daily room temperature should not be less than +8°C for three days.

The water temperature in the heating system should not fall below the dew point
In addition, in addition to the standards that have been provided, the minimum heating in the boiler must also be taken into account
It is very important that the water temperature does not fall below the dew point. Usually this indicator fluctuates between 60-70°C, although some deviations are possible due to the characteristics of the fuel used, as well as the unit itself
If for any reason this rule is violated, condensation will result, which will negatively affect the service life of the device.
Usually this indicator fluctuates between 60-70°C, although some deviations are possible due to the characteristics of the fuel used, as well as the unit itself. If for any reason this rule is violated, condensation will result, which will negatively affect the service life of the device.
In addition, in the process of heating the coolant, such a factor as the air temperature outside the window must be taken into account. That is, if it is very cold outside and the temperature has dropped below -20°C, then the coolant should be heated more strongly

In order for the heating system to work properly and maintain a comfortable temperature in the house, it is necessary to choose the right coolant according to the operational characteristics of the equipment
At the same time, the temperature schedule of the coolant, the limits of which are defined as 30-90 ° C, should not be violated, as this can lead to the paint coatings of the equipment decomposing. And sanitary standards prohibit exceeding these indicators.
Thus, when choosing a coolant for electrode heating boilers and other systems, it is necessary to take into account many factors. Of course, price is an important criterion, and for many it is the determining factor, but do not forget about safety
If possible, it is better not to save money and give preference to the best coolants, which are also characterized by high efficiency.
Heating with antifreeze or water
After reading this section, you will most likely refuse antifreeze in your heating system. The main advantage of antifreeze - the safety of the system at subzero temperatures - is completely negated by its disadvantages.
- Low heat capacity of antifreeze. Increasing the size of radiators
by 20-23% The heat capacity of antifreeze is significantly lower than the heat capacity of water. By diluting water with 35% antifreeze, we lose approximately 200 W per 1 kW of thermal energy. This means that the size of pipes, radiators and boiler must be increased by 20%. In terms of a country house of 300 m2, we lose approximately 60 thousand rubles by increasing the size of the system. Antifreeze is not applicable at all for underfloor heating systems, again due to low heat capacity.
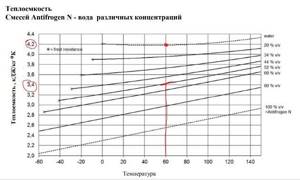
- The service life of antifreeze is from 5 to 10 years. Over the years, antifreeze oxidizes and successfully destroys brass connections. After 5 - 10 years, ethylene glycol and propylene glycol must be drained, disposed of and replaced with a new one. You will not only have to buy new antifreeze, but also pay to dispose of the old one. Unfortunately, in our country there is no service for recycling ethylene glycol in small volumes, so finding someone to hand over this chemical to will be difficult. I won’t consider the idea of dumping antifreeze on my neighbor’s property.
- The use of sectional radiators in systems with antifreeze is unacceptable. Rubber sectional gaskets quickly oxidize, and the radiators leak. We use only steel panels. The use of galvanized pipes is also unacceptable. Antifreeze safely washes away the zinc, and the pipe remains bare.
- Why is antifreeze useless for a country house? Antifreeze will successfully cope with the task - the heating system will not freeze in winter in your absence, but what to do with the water supply system? At subzero temperatures, water supply pipes will freeze faster and with worse consequences, because... laid not only in the floor, but also in the walls. You will have to remove the tiles, beat the screed and change the pipes in the bathrooms, showers, kitchen, and also replace the entire water supply system of the boiler room. Of course, pumping antifreeze into the water supply system will not work, nor will laying all the pipes with a heating cable.
Antifreeze for the heating system of a country house is needed if: ✔ you do not plan to live in the house in winter; ✔ the house has 1-2 bathrooms with a tee water supply system (without a collector), which can be drained before the onset of cold weather; ✔ there are no water-heated floors in the house. If they are water-based, then there is no point in using antifreeze in heating.
It is impossible to leave a full-fledged country house in winter without heating on duty. In winter, it is necessary to maintain constant standby heating +10-12°C. Heating a full-fledged country house for permanent residence with antifreeze is the same losing option as heating a house with heated floors, which is applicable only in the southern regions of our country.
The boiler can be controlled remotely via a phone or tablet via an Internet connection or GPS. You can set the air temperature for a specific date and time of arrival, and the boiler will accurately signal possible errors in operation. To maintain the heating system in the event of a failure of the main boiler, a backup electric boiler is often installed, which also turns on automatically. You can order a project for such a boiler room and heating system from us on the Services page.
This way your engineering systems will be truly protected without antifreeze.
Preliminary project cost calculator
If you liked my article and are looking for reliable design specialists, call or email me.
201301230950_15
Why is methanol added to the coolant?
Mainly - to reduce the overall viscosity/density of the “mixture” into which the manufacturer swelled diethylene glycol, glycerin, and propylene glycol. But methanol is a low-boiling liquid (boiling point = 64.7°C at atmospheric pressure!), and therefore its presence immediately lowers the overall boiling point of the “mixture,” which is a scourge in the summer. In addition, methanol is toxic, volatile, and a carcinogen. It also increases cavitation wear. Finally, methanol is a strong solvent and, when hot, damages rubber and polymer parts that it comes into contact with.
What do designations like G11, G12 mean?
These designations are not official. The fashion for them was generated by Volkswagen, for whose cars the VW coolant G11 and VW coolant G12 were produced. Thus, the G11 and G12 symbols are associated with this brand - and only with it. As a rule, antifreeze manufacturers do not indicate the components included in the antifreeze. But in any case, it makes no sense to look for G11 or G12 in the store.
The difficulty of choosing a coolant for a country house
The choice of the type of coolant for a country house begins even before the system design stage, or at least in parallel.
Unfortunately, water as a traditional liquid cannot always be used for such cases. This is due to several factors, one of the main ones being its high freezing point.
If a country house is not used as a place for permanent residence, this characteristic of water can damage the system during even mild cold weather. But even if the system is in constant use, emergency situations are also possible.
For example, power outages can also be fatal. Most gas boilers, not to mention electrical equipment and pumps, require a stable supply of electricity to operate, otherwise the water will freeze and break the system. The option with a backup source can only be considered as an emergency one and you shouldn’t rely on it too much.

Therefore, a non-freezing liquid for heating a country cottage or house is the best option, but before choosing a composition, you should carefully read the instructions for the boiler you plan to install.
Manufacturers often recommend a certain type of coolant, which is required to fill the system. Otherwise, all warranty obligations on his part are canceled. But this requirement does not apply to all models, and even with restrictions, you can take a risk and fill in a different type of liquid. But the consumer will bear all the risks, including the repair of boiler equipment.
When designing heating in a country house, it is important to immediately resolve the issue of the type of coolant, since this factor imposes certain conditions on the technical parameters of the system and the features of its installation.
What types of antifreeze are there, which one is better to choose, features of their use
When talking about the use of antifreeze for heating systems, you need to understand what it is and which antifreeze to choose. These are aqueous solutions of polyhydric alcohols, although not so long ago a new type of antifreeze appeared, for which glycerin was used as a base. In order to figure out which option is best to choose, let’s take a closer look at the characteristics and properties of each of them.
Types of antifreeze for the heating system of a country house
Today, the production of antifreeze is based on the use of two substances: propylene glycol and ethylene glycol. The first option is more expensive, but it is completely safe, even if taken internally. But it has another serious drawback - it can lose fluidity at low temperatures, to which ethylene glycol would not react.

The best option for filling the heating system is to use a safe coolant based on propylene glycol
It is interesting that, despite all the dangers of using ethylene glycol, it is preferred much more often, which is most likely due to its lower cost.
Antifreezes made on the basis of ethylene glycol are also distinguished by the fact that they are chemically active, have increased fluidity and are capable of foaming. And if foaming can still be combated with the help of special additives, the increased level of fluidity cannot be adjusted. And given that the substance is also toxic, this significantly increases the risks of using such antifreeze.
To summarize, we can say that if it is possible to use propylene glycol for the heating system, then it should be used. Therefore, ethylene glycol will definitely leak wherever possible. And its toxic fumes can cause serious poisoning and further health problems.

The use of toxic ethylene glycol-based coolant requires high-quality connectors and pipes
Thermal conductivity of a mixture of glycerin and water
The thermal conductivity values of an aqueous glycerol solution are shown in the table for a temperature range from 20 to 80 degrees Celsius and glycerol concentration from 10% to 70%. With increasing glycerol concentration, the thermal conductivity of the aqueous solution decreases. With a glycerol content of 50%, the thermal conductivity of the mixture is ~29% less than that of pure water.
| Thermal conductivity of a mixture of glycerin (content in percent by weight) with water | |||||||
| Temperature | 10% | 20% | 30% | 40% | 50% | 60% | 70% |
| OS | W/(m•oC) | W/(m•oC) | W/(m•oC) | W/(m•oC) | W/(m•oC) | W/(m•oC) | W/(m•oC) |
| 20 | 0,557 | 0,519 | 0,481 | 0,448 | 0,414 | 0,381 | 0,352 |
| 40 | 0,586 | 0,540 | 0,502 | 0,460 | 0,423 | 0,385 | 0,356 |
| 60 | 0,611 | 0,565 | 0,519 | 0,477 | 0,435 | 0,393 | 0,360 |
| 80 | 0,636 | 0,590 | 0,540 | 0,494 | 0,448 | 0,402 | 0,364 |
Water is an accessible coolant
Most consumers use plain water as a coolant. This is due to its low price, absolute availability, and good heat transfer performance. The great advantage of water is its safety for people and the environment. If for any reason a water leak occurs, its level can be easily replenished, and the leaked liquid can be eliminated in the usual way.
The peculiarity of water is that it expands when it freezes and can damage radiators and pipes. If you don’t know which coolant to choose for the heating system in your home, take into account situations related to the lack of heating. Water can be chosen as a coolant only if the heating system operates smoothly and continuously.
You should not fill the heating system with coolant from the tap. Tap water contains too many impurities, which will eventually settle in the pipes and cause them to break. Salt impurities and hydrogen are especially dangerous for heating systems. Salts react with metal surfaces and provoke corrosion. In order to improve the quality of water, it is necessary to make it “softer” by eliminating impurities. This can be achieved in two ways: by temperature exposure, or by using a chemical reaction.
The temperature effect assumes normal boiling. You need to boil water in a metal container without a lid, preferably with a large bottom surface. During the heating process, carbon dioxide will be released into the air, and salts will settle to the bottom. Chemical removal of impurities occurs through a reaction with soda ash and slaked lime. These substances make the salts insoluble in water, and they precipitate. Before pouring coolant into the heating system, it must be filtered so that sediment does not interfere with its normal operation.
Distilled water is ideal for heating systems. The distillate is free of any impurities and does not require additional processing. Such water must be purchased in a store, since it is produced only industrially.
Properties
Glycerin is a hygroscopic liquid with a sweet taste. It absorbs water vapor from the air well. Alcohol mixes with water regardless of proportions. When combined with propylene glycol, the liquid becomes fluid.
The melting point of this alcohol is 180C. The substance boils at 2900C. Due to its hygroscopicity, glycerin will always draw water.
Glycerin solution also has the following properties:
- antiseptic effect;
- moisturizing effect;
- preservative component;
- imparting softness and sweetness to products.
The substance actively participates in vaporization. In this regard, it acts as the main component of e-cigarette liquid. Alcohol increases the nutritional value of foods. Due to its preservative properties, they can remain fresh for a long time. Alcohol also cleans surfaces well from grease and dirt, which allows it to be successfully used as a cleaning agent.

The substance is used in the manufacture of dynamite. When it reacts, it burns. As a result, water and carbon dioxide are formed.
Advantages and disadvantages of propylene glycol as a coolant
The advantages and disadvantages of propylene glycol can be clearly identified by comparing it with water (which is also a coolant fluid in some heating systems):
- the density of diatomic alcohol is 1037 kg/m³, which is more than that of water (1000 kg/m³): a difference of 3.7%;
- the substance begins to boil at +187 °C, and water at +100 °C, the difference is 87%;
- alcohol freezes at -60 °C, water already at 0 °C;
- the specific heat capacity is 2483 J/(kg K), almost 2 times lower than that of water (4.187 J/(kg K));
- thermal conductivity – 0.218 W/(m K), which is three times lower than that of water 0.6 W/(m K);
- the dynamic viscosity of alcohol is 56 mPa s, eight hundred times greater than that of water (0.894 mPa s).
Several conclusions can be drawn from this list.
- The density of propylene glycol is higher than that of water, so the static load and pressure in the heating system will also increase.
- A high boiling point of +187 °C is not such an advantage. The specific heat of propylene glycol is two times lower than that of water. This means that these two liquids can be brought to a boil with the same amount of heat. Their temperature will reach its extreme point almost simultaneously, only the water will bubble at +100 °C, and the alcohol at +187 °C.
- The freezing point of propylene glycol is noticeably lower. In addition, it practically does not expand when cooled, and this does not damage the heating system.
- The low specific heat capacity is a clear advantage, hence the rapid heating of the heating system, however, propylene glycol can accumulate little heat - and this is already a disadvantage.
- High dynamic viscosity will add load to the circulation pump, which moves the coolant through pipes and radiators.
However, in some situations, propylene glycol will cope with its tasks better than water:
- if you do not use a water heating system in winter and do not drain the water, the system may fail (even after complete draining, water will still remain in the pipes, causing corrosion) - and propylene glycol can be used all year round and not drained in winter;
- Antifreeze, which is made from propylene glycol, is non-corrosive and does not form scale.
Such antifreezes also have disadvantages:
- the cost is higher than that of water;
- a complete fluid change is required every five years;
- the heating system should not contain parts that contain zinc - propylene glycol quickly dissolves them;
- Propylene glycol is extremely fluid and can penetrate small connections in the heating system.
Many manufacturers dilute antifreeze with water to offset some of the disadvantages of propylene glycol. What will it give:
- the cost of antifreeze will become noticeably lower;
- viscosity will decrease;
- heat capacity will increase;
- the heat transfer rate will increase;
- the boiling point will decrease, but most boilers are still not designed to operate at 160 °C;
- freezing temperature ranges from -30 to -40 °C degrees;
- Antifreeze based on propylene glycol expands slightly with water, so destruction of the heating system will not occur.
Technical characteristics of glycerin-based coolants

Glycerin based coolant
When deciding to purchase a coolant produced using glycerin, you should definitely analyze the main parameters of the latter so as not to experience unnecessary difficulties in the future with the operation and maintenance of CO:
- The temperature range in which the specified coolant will operate normally, without significant losses in its consumer parameters.
- The heat capacity of glycerin, i.e. the required amount of coolant that needs to be pumped per unit of time in order to transfer the required amount of heat.
- Viscosity coefficient, which affects the circulation rate of the coolant, the value of the heat transfer coefficient, etc. and its change depending on the temperature of the coolant.
- Corrosive activity, which imposes a number of restrictions on the use of coolant with glycerin additives without adding the required corrosion inhibitors, as well as on the choice of coolant circuit material.
- Issues of safety of using such coolants for the environment and humans.
- Lubricity, which determines the restrictions imposed by the use of the specified coolant on the design of CO elements.
- An indicator of inertness to foaming, which directly affects the efficiency of the transfer pump.
The ideal choice is a glycerin-based coolant, the chemical composition of which takes into account the possible results of its interaction with all substances currently used in the designs of heating boilers and CO heating lines of private houses (steel, cast iron, copper, aluminum). Because otherwise reactions may occur leading to electrochemical corrosion.
Glycerin in the heating system must have additives that prevent oxidation and foaming.
Inhibitors that increase the fragility of polymers (seals, pipes) must be strictly excluded.
Benefits of using glycerin for heating
- A coolant containing glycerin has a significantly lower crystallization temperature (the freezing point of glycerin is minus 30 degrees).
- Glycerin is explosion- and fire-safe because it doesn't ignite at all.
- Such coolants are harmless to health.
- The level of heat transfer significantly exceeds similar indicators of other coolants.
- CO with the specified coolant is capable of operating at temperatures from -30 degrees to +105 degrees.
Glycerin for heating does not have a hazard class assigned to it and, according to international standards, is considered a food additive with code E 422.
Which coolant is better to use in the heating system: features of using water
If we talk about water as a liquid used to transfer heat from a source to radiators, then this option can confidently be called ideal. Its heat capacity and fluidity are extremely high, so that heat can be delivered to the radiator in the required quantity without any problems.
Many people are interested in the question of what kind of water is best to pour into the heating system. In this case, the answer is simple - ordinary tap water is suitable for closed heating systems. Of course, its composition can hardly be called ideal, and one way or another, it contains salts, as well as a certain amount of mechanical impurities that can settle on the equipment. However, this process will happen only once, and given that ordinary water can circulate properly through the heating system for years and does not require replacement, the damage will be insignificant. Simply put, the amount of precipitation that appears in the system simply will not be able to somehow affect its operation.

When using a closed heating system, it is necessary to control the coolant level
You need to pay more attention to the choice of water for closed-type systems, since during the operation of the system, partial evaporation of the liquid occurs, and water must be periodically added. As a result of this, the concentration of salts and impurities will constantly increase, which, accordingly, will lead to the accumulation of more sediment on the internal surface of the equipment. Therefore, for systems that have an expansion tank, you need to use distilled or purified water.
Of course, constantly adding distilled water to the system is quite expensive, and it is not always available in the required volume. Therefore, filtered water can be used as an alternative.

For an autonomous heating system, it is recommended to use only clean water without impurities
What to do before adding water to the heating system
You can prepare water for use yourself. This will take some time, but it will save you from having to spend money on buying distilled water. Here are some simple recommendations:
- First of all, the required amount of water needs to be collected in a container of suitable volume and allowed to stand. This will allow most of the iron to settle to the bottom;
- After the water has settled, it must be carefully poured into another container and boiled without covering it with a lid. Thus, magnesium and potassium salts are eliminated.
Water prepared using these simple tips can already be considered sufficiently prepared for use. Of course, carrying out such procedures every time is quite tedious, so you can add already distilled or filtered water, but as an initial fill, this option is excellent.

Water for filling a closed-type heating system must first be purified
Date: September 25, 2021
Why not GLYCERIN.
Why should you NOT use a GLYCERINE mixture - antifreeze - in the heating system??
Let's look at specific examples of what is best to fill into the installed heating system in your home or into the air conditioning and ventilation system, for example, of a shopping complex.
In order for these systems to operate flawlessly at any time of the year, it is necessary to use coolants that would not only provide heating of the room, but also have properties such as a low freezing point, because frosts in Russia have not yet been canceled. When choosing a coolant, you must also not forget about such indicators as high thermal conductivity and heat capacity, protection against corrosion of all construction materials, the ability to work without scale formation, inertness in relation to sealing materials, and finally, stability and long service life during the operation of your heating system. What is best to pour into the heating system depends on the specific operating conditions, your boiler equipment, heat exchangers, pumping equipment, etc.
For any heating system, water or a special low-freezing liquid - coolant (household antifreeze) can be used as a coolant.
Water is the cheapest, most accessible and environmentally safe coolant, but it also has a number of disadvantages, since a heating system that operates on water must constantly be in a state of heating in the positive temperature zone so as not to defrost the system. The chemical composition of water contains many different impurities of iron, chlorine, salts, and therefore, when heated, these impurities are deposited on the walls of pipes, on the surfaces of heat exchangers, heating elements, which causes a deterioration in heat transfer, and the heating elements may fail due to overheating .
And one more important argument: in the event of an emergency shutdown of electricity or gas in the autumn-winter period, the system must be drained to prevent it from defrosting.
What is ANTIFREEZE.
To protect heating and cooling systems from defrosting in the 20s of the twentieth century, the first low-freezing coolant appeared, called Antifreeze (from the Greek anti - against and the English freeze - freeze).
The first coolant - antifreeze was made on the basis of glycerin - a three-atomic alcohol. Such coolants in a 35:65 mixture of water and glycerin had a freezing point of 40°C and a boiling point of +280°C. The problem and disadvantage of such antifreezes are high viscosity and insufficient fluidity. They tried to solve this problem with the help of ethanol, methanol, salts, etc. until in the 30s they found a full-fledged replacement for glycerin and the basis of coolants became two-atomic alcohol - ethylene glycol. In the USSR, as well as throughout the world, by 1937, coolants based on ethylene glycol had practically replaced glycerin and methanol antifreezes.
What kind of liquid is “GLYCERIN”?
Glycerin is 1,2,3-trihydroxypropane, 1,2,3-propanetriol, Latin versions of the names: Propantriol, Glycerol, Glycerin, an organic compound, a representative of saturated trihydric alcohols. The chemical formula of glycerol is C3H5(OH)3. The molar mass of glycerol is 92.10. A colorless, very viscous liquid with a sweet taste, the melting point of glycerol is 7.9°C, the boiling point is 245°C. The density of glycerin is 1.26 g/cm3. Self-ignition temperature 362°C. Dissolves in water and organic solvents.
Only in our country can home-grown inventors invent and impose on us what the rest of the world has long abandoned and proved that it is bad. But in our pursuit of cheap antifreeze, we don’t notice that we are throwing money away by buying this Russian miracle “New Invention” based on GLYCERIN for expensive heating and air conditioning systems . Our Russian “woeful inventors” opened our eyes to the fact that it turns out that glycerin-based antifreeze coolants are the best that exists in nature, the most environmentally friendly and reliable liquid, but let’s turn to the facts and common sense .
Why is Glycerin mixture - antifreeze so bad?
Indeed, 90 years ago the first antifreezes were glycerin-based. But, since they had an extremely high viscosity, which the pumps could not cope with, the circulation in the cooling and heating systems was insufficient, they had to be diluted with various alcohols, including methyl alcohol. Glycerin is NOT thermally stable ; with prolonged heating (even up to 80-130°C), it decomposes to form acrolein and acetone, which lower the flash point to 112°C, and acetone vapors are explosive. As a result, there were constant problems with equipment, pumping equipment, vapor poisoning of people and a high fire danger.