Heat block - characteristics, features, scope of application
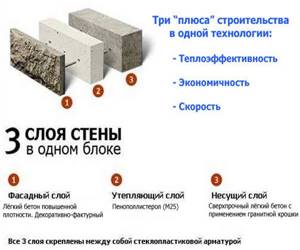
The thermally efficient block, abbreviated heatblock, consists of three layers:
- Structural (load-bearing) - porous block of expanded clay concrete, density 1300-1500 kg/mᶟ.
- Thermal insulation - expanded polystyrene (EPS) or extruded polystyrene foam (EPS), 150-200 mm thick.
- Facing (decorative) - a thin block of expanded clay concrete or concrete (on average 50 mm), characterized by increased density, strength and frost resistance; the surface imitates figured or smooth brick, natural stone.
Heat blocks are produced using two methods – vibrocasting or vibrocompression:
- Vibration casting - an insulation insert is installed in the matrix, the liquid solution is poured into the mold and processed on a vibrating table until the block is completely compacted.
- Vibrocompression - the solution is poured semi-dry into the form of a vibropress with an installed liner, the block is simultaneously exposed to vibration and pressure.
After molding, blocks produced by vibrocompression are placed in a heat chamber for finishing, and the vibrocasts dry naturally.
It is believed that stronger and more durable blocks come out of the press.
The layers are connected to each other not only due to adhesion - manufacturers use special bonds, this can be metal-plastic, fiberglass or basalt rods. Heat blocks are also produced with additional voids in the structural layer; during the laying process, reinforcement is installed in them and mortar is poured.
The facing layer can be either the original gray color or multi-colored; almost any shade can be ordered at the factory.
The main advantages of the blocks include minimal thermal conductivity, due to which a wall 30-40 cm thick does not need additional insulation, and the presence of a finishing layer. The facade is immediately decorative and does not require cladding, plaster or various hanging screens. In addition, the load-bearing part of the block made of lightweight concrete significantly reduces the weight of the structure, making it possible to get by with a strip foundation. As for the speed of construction, which is also an advantage of the material, it is also inherent in other block categories and largely depends on the skill of the performers. The same can be said about the minimum consumption of the solution - a thin seam is typical for wood concrete, gas silicate or warm ceramics, but whether it can be done this way depends on the craftsman and the geometry of the blocks.
There are also some shortcomings, the main one of which is the harmfulness of polystyrene foam, the battles on the topic of which do not subside. Perhaps PPS is not the most environmentally friendly of insulation, but still it is covered with a load-bearing layer and interior decoration, and the thermos effect inherent in such houses is neutralized by a good ventilation system. Users have much more complaints about unscrupulous manufacturers, whose products boast “walking” geometry, reduced strength and other “amenities” associated with violation of technology.
To avoid purchasing such a heat block, you need to be more careful in your choice and trust only your own eyes, hands and product certificates.
The main area of application for heat blocks is low-rise private construction, which includes not only houses, but also various outbuildings. Blocks intended for additional reinforcement can be used for laying higher buildings, but, of course, we are not talking about “candles”.
Types of external insulation of buildings
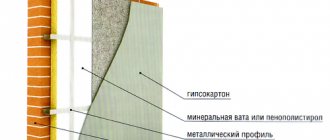
Since multilayer blocks have not yet taken root in the construction market, most specialists and home craftsmen use traditional materials when insulating a house from aerated block or brick. And in most cases, the building is insulated from the outside, even if you insulate the loggia. One way or another, any type of such thermal insulation implies the same three layers that are present in the facade multilayer block.
Let's look at the most popular types of facade insulation.
- Creation of a plaster facade or wet type of insulation. It involves the creation of a multilayer structure on the outside of the building.
- Using dowels, we attach thermal insulation to the load-bearing partition, for example Technoblock Standard insulation or Euroblock insulation.
We apply finishing material to the reinforced insulation layer
- Next, we reinforce the surface with fiberglass mesh.
- Apply the finishing material in one or two layers.
Advice! Most often, plaster is used as a finish, which should be applied in two layers: first we lay the starting layer, and after it dries, the finishing layer should be laid.
- After finishing, the surface is covered with special facade paint.
- Well masonry (another name is “three-layer system”). The wall is erected in two layers: load-bearing, after which a small gap is left and a half-brick layer is laid out. In the gap, ecowool insulation (spray foam, etc.) should be placed.

Insulation of well brickwork - photo
- Ventilated facade. The design assumes the presence of a sheathing, which is made of metal or wood. Insulation is placed in the sheathing, and facing material (most often siding) is mounted on top.
Advice! Wooden sheathing beams must be treated with protective compounds.
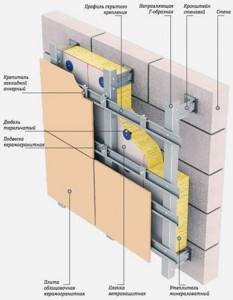
Schematic representation of a ventilated facade using metal profiles.
How I built a house from thermal blocks
One of the craftsmen of our portal with the nickname Skazochnik14 posted a detailed description of the construction of a house from a heating block and his feelings from its operation in the topic of the same name.
Storyteller14FORUMHOUSE Member
At first I didn’t know what to build a house from, but by chance I saw a house made of thermal blocks and I liked the material. I went to that construction site, asked around, and decided to build a house from a heating block. Firstly, the house should turn out to be very warm, secondly, there should be savings on finishing work on the outside, the heating block is already lined beautifully, and thirdly, there should be savings on the work of insulating the facade and painting.
At the production site, calculations were made based on the project, the craftsman ordered wall, corner blocks and quarters, chose colors, and for the base - concrete tiles with a texture like the blocks, fastened with dowels. The promised deadline was a month, but in reality they didn’t even meet it in two; instead of October, the blocks were ready only in May. On the plus side - no problems with storage, one hundred thousand penalties and free delivery. The downside is that different batches differed in the shade of the cladding, the gamma is the same, but the saturation is different, we had to solve this problem during the laying process. To save additional money, we purchased all the lumber (150×150 boards and inch boards) in winter.
The foundation is an insulated tape 1 meter deep with compacted sand bedding and crushed stone cushion, insulation with PSB slabs. In the outgoing construction season, the base was laid out from expanded clay concrete and left to winter.
The box -walls began to be erected in May, since the foundation was not initially tied to the wall material; the thickness of the seam on different walls ranged from 5 to 10 mm. This led to difficulties with the masonry mixture - the purchased adhesive for foam concrete was not designed for such fluctuations, so they began to mix it with cement, and the seams were also foamed with polyurethane foam. The addition of cement showed itself as efflorescence on the masonry.
The roof - the grooves for the joists in the blocks were sawed out with a grinder, all the seams were carefully foamed, the floor beams were glued together by a craftsman from boards. The project provides for a low roof, and although, according to the discussion participants, it looks organic on a one-story house with an area of 130 m², Storyteller14 believes that the roof should have been raised. As a roofing covering, the craftsman chose metal tiles with a sheet thickness of 0.5 mm.
Energy efficiency parameters - not only are the walls made of heat-efficient material, the heat loss of the house also depends on the insulation parameters of the floors, and on the tightness of windows and doors. The house has a large proportion of glazing, in order to reduce heat loss through the windows, energy-saving double-glazed windows were chosen.
Storyteller14
There are a lot of windows in the house, but since we wanted to retain the heat as much as possible, they were given special attention. We installed windows 74 mm thick, with two energy-saving glasses, a warm frame and argon filling, plus medium armor glass - A3.
Initially, the floor and attic were insulated with 200 mm thick mineral wool slab insulation; this turned out to be enough for the floor, but not enough for the attic, as a thermal imaging test showed. The attic floor was insulated with another 200 mm thick layer of mineral wool.
To further increase the energy efficiency of the house, Skazochnik14 organized fresh air ventilation through a ground heat exchanger. I buried a HDPE pipe with a cross-section of 160 mm on the site at a depth of two meters, the length of the main line is 50 meters. According to calculations, 60 were needed, but the area is compact, the pipe comes out in the base. As winter tests showed, everything worked out.
Storyteller14
I watched the ground heat exchanger for a week. When the air temperature outside is down to -15⁰С, air enters the house at a stable +7⁰С. Last night it was -20⁰С, I took a measurement, the temperature of the incoming air dropped by two degrees. I am very pleased with the result! Next I plan to connect the outlet from the ground heat exchanger to the recuperator.
Types of thermally efficient building blocks
For a certain branch of construction, appropriate types of heating blocks are distinguished. Each type of heat-efficient block, as a rule, has its own equipment, which comes complete with the heat block.
The following types and types are distinguished:
- Ordinary (wall) thermally efficient blocks - standard blocks for laying walls, as well as blocks with holes for further ventilation of air in the room;
- Additional - to improve the final design;
- Belt - for laying interfloor fastenings;
- Corner - for laying the corners of a building;
In addition, it is possible to design and manufacture heat blocks to order, for example, to create rounded walls. Many companies that manufacture thermally efficient blocks offer the ability to change the thickness of the block, which will make it as efficient as possible for different climate conditions.
Presentation of the thermally efficient building block Teplosten:
Energy efficiency of heating blocks
In addition to the fact that the absence of heat loss through the walls was confirmed by a thermal imager, the effectiveness of the blocks was also proven by wintering with a partial heating system. With fifteen squares of infrared film heated floors installed, with a power of about one and a half kilowatts, the temperature in the house did not drop below ten degrees. And this is with a total area of one hundred and thirty square meters and unfinished interior decoration.
However, the past two cycles of freezing and thawing revealed some features of the heat block.
- Even seams carefully coated on the outside are not a guarantee of tightness; after the onset of frost, some blocks became colder from the inside and were even visually different. The problem was solved by drilling the seam in problem areas and adding additional foam.
- To avoid precipitation from flowing in and subsequent wetting of the walls, the seams must be rubbed down, or alternatively, use jointing during the laying process. This is easier than going over the entire façade with a spatula, and choosing the grout to match the color of the blocks.
Production of thermally efficient blocks
The manufacture and production of heat blocks is carried out on the basis of high-quality equipment and modern technologies, as well as using harmless raw materials:
- Expanded clay is used as a filler in the production of lightweight concrete;
- Expanded polystyrene is a thermal insulation material that serves as the basis for the inner layer of the block. Depending on the thickness of the polystyrene foam pad, the thermal insulation properties of the entire block completely change;
Fiberglass reinforcement rods are used to connect the layers of the heat block to each other.
Advantages of choosing thermally efficient blocks
Conclusion
At the moment, the finishing is almost complete, a film heated floor has been installed in addition to a solid fuel wood boiler. The craftsman is pleased with the chosen material, but emphasizes that an energy-efficient house means not only warm walls, but also high-quality insulation of the entire structure, plus a ventilation system with a recuperator.
All the details and experience of other portal participants who have chosen a heating block are in the author’s topic on how to profit from finishing – in the article on economical finishing of aerated concrete. Material about concrete facade tiles for those who are looking for an interesting solution for their home - in the video on how to work with facade tiles.
Subscribe to our Telegram channel Exclusive posts every week
Verified manufacturing plants

Who can you trust when planning to buy a heating block? The products are quite popular, therefore they are produced in Russia by several well-known companies. Let's look at the three most trusted suppliers.
- "Klimovsky heating block" . Strict adherence to the conditions of the technological process during production in accordance with GOST and TU. Using original high-quality raw materials. Checking materials for radiation hazards. Laboratory testing of produced concrete for compression and other characteristics. Time-tested quality.
- “Thermal block. RF" . Representative offices of this production company are located in the cities of Domodedovo and Smolensk. The company has its own production, complies with GOST , and offers a wide range of finished products.
- "Warm house" . The company operates in the Moscow region and produces high-quality products at affordable prices. The main raw material is Egyptian white cement, which is resistant to any external influences, has increased strength and a long service life.
- "Balashikha plant" . Our own production is located in the village of Sobolikha, Moscow region. This company has been producing heating blocks for more than 5 years, and all customers note the high quality of the products.