Features of the material
There are several types of bulk material for insulation. Each of them has its own properties. List of bulk insulation materials:
- expanded clay;
- polystyrene foam in granules;
- foam concrete crumbs;
- ecowool;
- sawdust and sand;
- boiler slag;
- vermiculite
Expanded clay
The usual form of this material is round or oval granules. Granules or other shaped material are porous and very light (some types can float on the surface of the water). Expanded clay is formed by firing light alloy clay. It is absolutely non-flammable, safe, and environmentally friendly in its composition.

The material can be in three forms:
- sand with grain size from 0.14 to 5 mm. It is used as a filler for lightweight concrete and for floor insulation;
- Expanded expanded clay crushed stone is granules with a fraction of 5–40 mm. The best option for thermal insulation of foundations and floors of residential premises;
- expanded clay gravel. Round granules 5–40 mm with a fused surface, absolutely resistant to fire. They have closed pores inside, which gives them excellent frost resistance. This gravel is recommended for insulating attic floors: the material is lightweight and has low thermal conductivity.

The labeling of a material must include the size of its fraction:
- 5–10 mm – floors and roofs;
- 10–20 mm – baths and saunas, able to maintain temperature and humidity in the room for some time;
- more than 20 mm - for foundations and basements.
Expanded polystyrene granules
This is the most controversial bulk material. It is a very light, airy white granule. It is used as backfill for insulating roofs and walls; it is also used as an additive in mixtures for insulating concrete.

The disadvantages are toxicity and flammability, but its properties have not yet been fully studied. Instead, it is recommended to use granulated foam glass. Expanded polystyrene is cheap and convenient for insulation using the well-laying method.
Vermiculite
This is a mica-based layered material. No chemical additives or impurities are used in the manufacturing process. It is an excellent option for insulating loggias and rooms. Used as an energy-saving cladding for housing inside and outside. For floors and walls, a layer of at least 10 cm is recommended, for the roof - at least 5 cm. Backfilling with this material 5 cm thick reduces heat loss by 75%, 10 cm - 92%.

- high breathability of insulation - the material is porous - which allows the walls to “breathe”, ideal for natural circulation, air renewal and ensuring a microclimate in the room;
- environmentally friendly, without toxic substances;
- non-flammable, fire-resistant, belongs to the G1 flammability group;
- fungi, mold, rodents, insects are not afraid of such isolation;
- special skills or experience, special tools are not needed to fill it. The layer of material is simply poured back and compacted. No additional fasteners are needed;
- service life - more than 50 years.

For walls, a vermiculite backfill thickness of 10 cm is sufficient, for attics, roofs, and interfloor ceilings – 5 cm. When laying, it is advisable to use a vapor barrier film - this will additionally protect the insulation from moisture.
Sawdust and sand
These are traditional heat preservation materials that are used in attics and basements and have been used for centuries. Disadvantages: they are poorly insulated from moisture, pests can grow in them. Sawdust is flammable and susceptible to mold and mildew. It is still recommended to use more modern materials.

For insulation, they use not ordinary sand, but perlite. It is light weight, less hygroscopic, and its characteristics resemble mineral wool. Due to its low bulk density, it does not create a load on the walls and does not burst them.
Ecowool or cellulose
The components of this insulation are ecowool (7%), shredded paper (81%), antiseptics (12%) and fire retardants (7%). The material is non-flammable and does not rot thanks to special impregnations. It has been used in the world for more than 80 years; it has been known in the CIS for the last decade.

This material uses boric acid as an antiseptic and borax as a fire retardant. These substances are environmentally friendly.
The material is quite practical: the fibers fill small voids well, so it is recommended for complex structures.
Expanded polystyrene
A product of the chemical industry, polystyrene foam, consists of a gas-filled mixture of components, polystyrene and additives that improve ductility, fire resistance and others. Polystyrene foam, both pressed and loose, consists of many small grains (granules or balls). If polystyrene foam in granules is not compressed, the material will be free-flowing. We will not describe in detail the production of expanded polystyrene, we will only focus on the properties.
The nuances of using polystyrene in granules:
Use this material only on horizontal surfaces or in a closed, inclined space where the polystyrene foam insulation cannot spill out.
- This material is also used to fill the cavities and crevices of structures by blowing them in with a compressor so that the crumbs are packed as tightly as possible.
- Polystyrene granules are used to create a “warm floor screed” by adding it to the solution. Waterproofing must be installed before installation.
What is good about granulated polystyrene:
1. The low thermal conductivity of polystyrene due to its flowability makes the material 30 times “warmer” than concrete and holds the body well indoors.
3. Low cost.
4. Resistance to the development of fungus and insects.
Loose penoizol
Penoizol flakes have a random shape.
In appearance, penoizol looks like foam chips, but if you look more closely, the difference is obvious. Despite the visual similarity, these are two completely different materials. Penoizol is more reminiscent of snow flakes, it does not have an ideal ball shape, this material is softer. Penoizol is used as fill-in insulation for walls and horizontal ceilings. In addition, it is also available in sheets, but is mainly used in liquid form. Unlike polystyrene foam, penoizol:
- does not burn;
- does not smoke;
- allows moisture to pass through, but does not absorb it.
The thermal conductivity characteristics of both materials are almost equal.
Penoizol backfill insulation for walls is made from resin. The quality of the material primarily depends on the quality of the resin used for production.
First, the liquid substance is poured into blocks, about a meter by meter. Then the blocks are cut into sheets, and only then the sheets are crumbled. Installation is carried out using a blowing machine or manually. When working, you need to control the degree of density of the material.
Content
The ceiling is insulated if there is a non-residential attic above it, which is not equipped with thermal insulation. It is not used as a living space in winter, therefore, it does not need to lay a layer of insulation on the slopes. Often this is just a warehouse for equipment or a room for drying mushrooms/berries.

The non-residential attic itself plays the role of an air chamber, preventing the movement of heat waves both inside and outside the building. However, to dry the wooden elements of the frame structure, roofing, and metal fastening parts, a cold attic is usually equipped with effective ventilation. It is ventilated naturally, i.e. regular ventilation without the use of any mechanisms. The system operates without coercion. The air moves due to the difference in temperature and pressure outside the attic and inside it. The air flow enters the attic space through the dormer windows in the summer and the gaps framing them in the winter, when a vacuum of air is formed inside. It is removed spontaneously, replaced by a new portion coming from the street.
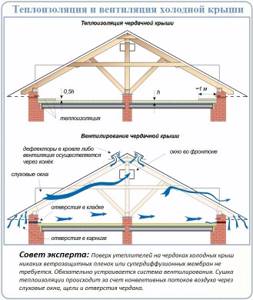
For building structures, constant air circulation is really necessary. But along with continuously moving air masses, heat is blown out of the attic. As a result, instead of saving it to save energy resources, you end up with additional costs. How to deal with them? Be sure to insulate! Insulation is carried out in two standard ways:
- Installation of thermal insulation along the ceiling from above. Those. From the attic side, slabs of foamed polymers, mineral wool are placed on the reinforced concrete floor or between wooden joists, expanded clay or folk remedies (sawdust, dry leaves, etc.) are poured in.
- Installation of slab insulation from inside the premises. Simply put, fastening insulating boards from the premises to the lower plane of the ceiling.
In both cases, the insulation layer increases around the perimeter, i.e. along the line of connection between the ceiling and the adjacent wall. Reinforcement is required here due to increased heat loss. A vapor barrier membrane is placed between the wall, ceiling and insulating layer.

Why is it not waterproofing that is used in the formation of a heat-insulating pie over the ceiling? Yes, because it is necessary to protect it, first of all, from steam penetrating from living quarters, and not from atmospheric water flowing from above. It is the fumes emitted during breathing by us, our pets and house plants, as well as those formed during the cooking process, during consumption hygiene procedures can harm the thermal insulation system. But the roof must protect the top from water. By the way, when laying all types of insulation on the cold attic side, they are not covered with either vapor or waterproofing on top. This allows the materials to dry out spontaneously when the attic space is ventilated.

Under no circumstances should insulation materials get wet or wet under a practically sealed insulating film. Together with moisture, they lose their insulating properties. Wet thermal insulation preserves almost nothing, but it can rot, and mold will spread to wooden elements. The vapor barrier under the insulation, laid from the attic side, is arranged in the form of a trough: with the edges of the panel extending to the walls. So it will prevent the insulation from getting wet not only from steam moving upward from the side of the premises, but also from the side of the walls that absorb atmospheric moisture. It is permissible not to use a vapor barrier layer only when extruded polystyrene boards are used as thermal insulation. They have practically no pores capable of absorbing and retaining moisture. Moreover, this is only allowed over rooms with a stable “dry” operating mode. Above bathrooms, showers, and swimming pools, a vapor barrier layer is installed in combination with extruded polystyrene as usual. Since there is a possibility of moisture penetration between the joints of the slabs.

It is made from broken glass, which is crushed into smallest fractions, melted and mixed with coal. As a result, carbon dioxide begins to escape from the material, which forms air spheres in the structure of the foam glass. This is a very expensive material; it is used in industrial facilities or in the construction of high-rise buildings. It is used extremely rarely in private construction, since not everyone can afford such a cost. They are used as bulk insulation for ceilings, floors and walls, and in the form of slabs or blocks. Bulk comes in different fractions, based on this, it looks like:

Types of backfill thermal insulation
Hundreds of years ago, in the construction of wooden houses from timber or logs, the very first fill-in insulation was used - sawdust. Like modern analogues, they were quite good in terms of thermal conductivity, but they shrink or lose their properties when wet. Today's materials are more advanced in many ways. The most popular of them are discussed in detail below.
Insulation based on clay. It is used as an independent heat insulator for residential or industrial buildings, or in combination with concrete (expanded clay concrete is obtained). Today it is obtained by burning clay shale.
Production technology varies depending on the required size of the final granules.
By studying the labeling of the fill-in insulation, you can understand what size granules of the material are and for what areas of the house it is suitable. For example, expanded clay sand is used as a heat insulator for floors or acts as a component of concrete cladding. Granules with a diameter of 5-10 mm are suitable for pitched and flat roofs, floors, and attics; larger than 15 mm - for insulating a basement or foundation.

Expanded clay inevitably settles as it is used, so during initial installation it must be compacted strongly to minimize shrinkage. It is recommended to insulate walls with this material only in regions where the temperature in winter does not drop below −20 degrees.
The insulation is made from silicate volcanic rocks using the same technology as expanded clay. When heated to 1000-1200 degrees, moisture evaporates from the surface of the stones, leaving air inside them. The result is white or gray granules with a diameter of 1 to 10 mm. The density of perlite ranges from 75 to 150 kg/m3, and because of its color it is also called “glass insulation.”
Minimum size granules (1-2 mm) form perlite sand, used in the following areas:
- insulation of premises of residential buildings;
- production of acoustic materials;
- production of insulating plaster;
- creation of fire-resistant concrete.
Granules filled with air weigh less than expanded clay, so they are suitable for thermal insulation of walls. In addition, the material will resemble mineral wool, since in addition to preserving heat, it will prevent the penetration of extraneous noise into the room.

Expanded material made of hydrated mica, increased in volume by 15-20 times through heat treatment. It has increased fire-resistant properties, due to which it is used when installing chimneys. Ideal for floors and walls.
A thin layer of vermiculite 5 cm thick will retain up to 70% of the heat of the room. This is enough to insulate the roof. For walls, floors and foundations, it is recommended to make twice as much material.
The density of vermiculite is lower than that of expanded clay or perlite - the highest volumetric mass is 100 kg/m3. This fill-in insulation is supplied in bags of a certain volume, and is used in almost all rooms of a residential building.

The advantages of vermiculite include:
- low thermal conductivity coefficient (0.04-0.06), comparable to foam plastic and mineral wool;
- no possibility of voids and seams;
- high melting point (1400 degrees);
- absence of toxic materials;
- biological resistance (prevents mold, mildew, is not of interest to rodents);
- good sound insulation;
- the lightness of the material, allowing it to be used in frame houses, on supporting systems or foundations;
- ease of insulation work and time saving.
- Ecowool.
A relatively new material that appeared on the market only 10 years ago. Made from recycled paper, fire retardants (substances that prevent fire), and antiseptics. Safe for humans, resistant to rotting, and does not spread fire. It is most often used for thermal insulation of walls, attics or roofs of complex construction.

Vermiculite
Another popular fill-in insulator is vermiculite. It is made on the basis of mica, just like perlite. The raw material is heated to 700-1000 ° C and as a result of evaporation of water, the granules increase in size and acquire a layered porous structure. The material is completely natural and has no chemical impurities.
Where and how to use vermiculite:
Insulation of roofs, thermal insulation of walls, floors, ceilings. Installation is similar to perlite and requires compaction. Due to its good flowability, vermiculite is distributed throughout all cavities and does not shrink. To insulate the roof, a layer of vermiculite of only 50 mm is sufficient. This will save up to 70% of the heat in the room. To insulate walls and ceilings, you need to double the layer.
- Fine-structured vermiculite is added to plaster compositions to increase the plasticity of the mixture. The solution is suitable for thermal insulation and finishing of walls, building facades, and due to its attractive appearance, it can serve as a decorative finish.
- Vermiculite is used in concrete mixtures to reduce their weight and increase thermal insulation properties, as well as for the manufacture of building slabs. Vermiculite boards can also be used to insulate fireplaces, stoves and pipes.
Vermiculite: pros:
1. Fire resistance - vermiculite tolerates operating temperature differences from -260 to +1200 C ° and does not emit harmful vapors when heated.
2. The material has low thermal conductivity and serves as a good insulator for the home.
3. Due to its layered structure, vermiculite is a good sound absorber and this effect depends on the size of the granules.
4. Environmentally friendly and non-toxic insulation. Does not cause allergies.
5. Vermiculite is not susceptible to the formation of fungus and mold, as well as insects and rodents.
6. Very durable and not susceptible to adverse effects.
Arguments against":
Firstly, the material is hygroscopic and can absorb 3-4 times its weight in water. Therefore, vermiculite cannot be used to insulate basements and basements without a diffuse membrane for additional waterproofing.
Secondly, the cost of vermiculite is higher than other backfill materials.
Advantages of bulk insulation
Everyone is interested in insulating their home.
All that remains is to choose the right insulation material. Bulk insulation materials are best suited for this. Their advantages are obvious:
- environmentally friendly material;
- have low weight;
- excellent heat retention;
- fireproof;
- easy to handle when working with them;
- durable.
Loose-fill insulation easily penetrates into any space and leaves no gaps . The main thing is to choose the right faction, and success will be guaranteed.
Watch the video in which a specialist explains how to insulate a ceiling with a mixture of vermiculite and sawdust:
Installation
There are several basic rules for installing bulk materials. But each type has its own nuances, so experts recommend following the instructions with a complete technological description for filling this or that insulation.
Let's get acquainted with the general recommendations for the correct implementation of energy-saving cladding with bulk materials.
- Insulation of pitched roofs occurs from the outside after laying the vapor barrier. For good and uniform distribution of thermal insulation along the slope, it is necessary to install transverse stops.
- When insulating the floor and basement, after filling the raw material, it is important to compact it thoroughly. This is done to avoid shrinkage of the insulation and subsequent deformation of the finish.
- When finishing rooms with high humidity, such as baths, saunas, a layer of fill insulation will require additional, high-quality hydro- and vapor barrier.
- Loose-fill heat insulators are laid in such a way as to prevent them from spilling through cracks and cracks in the finishing.

Bulk insulation can be used to fill any space in building structures. This type of insulation does not lead to disruption of the main finish and its structure. Therefore, if it is impossible to insulate with traditional slabs or rolls, bulk materials will come in handy.

Thanks to the huge assortment of backfill thermal insulation materials, the consumer is given the opportunity to make an independent decision in favor of choosing one or another raw material.
For an overview of perlite bulk insulation, see the following video.
Features and cost of stone wool aspiration
To understand the pros and cons of basalt wool chips, you need to understand what kind of material it is. Aspiration of mineral wool is a waste product. For example, from a factory where stone wool slabs or sandwich panels are produced. The trimmings are crushed and poured into bags with a volume of 0.2 - 0.3 m³ or big bags with a capacity of 500 - 1000 liters.

The physical properties of thermal insulation directly affect the scope of its application and the specifics of the work. Manufacturers and sellers of aspiration recommend placing crumbs only on horizontal surfaces so that they do not slide down over time, for example, in a wall. By compacting, you can increase the density of the laid insulation. The main thing here is not to overdo it. If you fanatically compact the poured basalt chips, you can achieve a packing density of 100 or more kg/m³. But, the worse the thermal insulation properties of this material will be.
So, bulk insulation has properties similar to ordinary stone wool. This is a non-flammable, vapor-permeable friable material that must be protected from water vapor, condensation and atmospheric moisture.
The main advantage of aspiration is its low price. Compare: on average, 1 cube of stone wool crumbs costs 600 - 800 rubles , and the price of one cube of stone wool slabs varies, depending on the brand, from 1500 to 2000 rubles.
Backfilling methods
The process of filling any insulation is the same: the material is poured into the cavity and compacted. It is recommended that the issue of insulation be addressed immediately when designing a house. If there are no internal cavities for filling in insulation, layers are made using PVC panels or plasterboard.
A good option is when the insulation is poured between facing and ordinary bricks, between internal and external masonry. There may be ribs inside so that it is well distributed. Thanks to loose thermal insulation, the walls do not need to be made thick, which saves costs. There are ready-made concrete products on sale - slabs, inside of which there are already cavities filled with expanded clay; they retain heat 50% better than ordinary ones.
Options
For floors, these methods of insulation with bulk components are used. The first option is fill-in (or loose) insulation on the joists. Joists are made on the floor on posts, skull blocks are nailed, then flooring is made of boards. A vapor barrier is placed on the flooring and expanded clay is poured. Further, if necessary, the next layer of thermal insulation, on it - screed, rough wood flooring.

The second option is an embankment on top of a concrete slab. An option for low-quality housing - Khrushchev, for example - when it is possible to raise the floor level. The floor covering is removed, waterproofing is laid, expanded clay is poured onto it in a layer of 5 - 10 cm. Then you can put a mesh for reinforcement, and a rough screed is made on it - the basis of the finishing floor covering. A vapor barrier is laid on top of the expanded clay cushion, and another layer of insulation is placed on top of it.

Finally, the third option is a dry expanded clay screed. A layer of expanded clay is poured, a layer of gravel is placed on it, then another layer of expanded clay. The surface is leveled, gypsum fiber boards are laid on it, and any finishing coating is placed on them.
Floor insulation
Loose floor insulation materials are used very often.
The most popular material is expanded clay.
Its production is quite simple, the advantages of expanded clay include low price and high quality, moreover, this material is environmentally friendly, is not afraid of moisture and is quite frost-resistant. Depending on the required insulation area, you can purchase expanded clay both in bags and in bulk, which is much more economical.
To insulate floors in rooms with high humidity, perlite backfill insulation, made from volcanic rocks, is recommended. A natural material with a high degree of environmental purity, it is chemically inert and fire-resistant, and can withstand very high temperatures. Due to its porosity, perlite is an excellent thermal insulation material.
Vermiculite, a fill-in thermal insulation made from natural raw materials, with high fire resistance and hardness, is characterized by a significant coefficient of moisture absorption, chemical and bacteriological resistance. Mold and pathogens will not develop in it, and the load on the foundation from structures with this type of insulation will be minimal.
The flowability of such cheap and widespread lumber as ordinary sawdust allows it to be used after special antiseptic treatment for floor insulation.
Each person, when building his house or after, in one way or another thinks about its insulation. We all know that today the market for thermal insulation materials offers us a huge selection and assortment.
By type of material, polystyrene foam and mineral wool are widely used. Polystyrene foam and its derivatives are well known to everyone, and we will not consider it in this article. As for mineral wool, this is a collective name that includes the most common materials: glass wool or quartz wool (base sand or glass) and stone wool or basalt wool (base natural stone basalt). We will not compare the characteristics; there are plenty of them on the Internet. Basically, these insulation materials are presented on the market in slabs and in rolls (mats), but there is another type of mineral wool insulation, about which little is known, but which can save the budget on insulation by up to 300 - 400%! Do you agree that this figure is significant? And now we are talking about bulk mineral wool insulation. What is bulk insulation? Let's figure it out.
Characteristic
Bulk heat insulation is used not only for internal surfaces - it can also be used to insulate a room outside. Walls, floor, roof - you can insulate all elements that structurally allow the filling of material.

Loose fill insulation is cheap. Some of its types are simply industrial waste (sawdust) or ready-made natural materials (sand).
The only drawback is hygroscopicity. When wet, it loses its properties.
It is necessary to pay special attention to the hydro- and vapor barrier of its layers. However, the fear of moisture is characteristic to the same extent for all types of thermal insulation.
Bulk insulation for floors, walls, ceilings. Good and inexpensive thermal insulation

Bulk (bulk) insulation for floors, walls, ceilings, or as it is also called, blown-in thermal insulation (mineral wool), is a product of crushing a basalt mineral thermal insulation board with a density of 70-90 kg/m3. You can buy it in bags, in bulk form. This mineral wool insulation is installed manually or using special compressor equipment. Bulk basalt insulation (mineral) is packaged in 0.5 m3 bags and is used for thermal insulation and sound insulation:
- attic ceiling of a house, bathhouse or garage;
- horizontal partitions between floors;
- attic and floor of the house.

Advantages of bulk (blown) mineral wool:
Bulk insulation is more environmentally friendly than mineral wool in slabs, because formaldehyde resins are not used in its production. Bulk wool contains only hydrophobic additives. You can also compare bulk mineral wool insulation with cellulose ecowool, which costs even less and is just as effective in terms of heat conservation. However, ecowool has good flammability, and mineral wool, on the contrary, serves as a barrier to the spread of fire.
- low thermal conductivity of thermal insulation (only 0.036 W/m*K);
- the absence of installation seams and joints on the floor, ceiling and walls, respectively, the absence of cold bridges between mineral wool slabs;
- flammability group for bulk (blown) insulation is NG (non-flammable);
- ease of insulation of the ceiling, floor and walls of your home;
- ease of working with bulk thermal insulation.
Another important advantage of bulk mineral wool insulation over other insulation materials when insulating the floors of a private house is its high vapor permeability. When moist air from a living space, rising through the ceiling, passes through the mineral wool, after some time it will dry out and not lose its thermal insulation properties. With such bulk insulation, the occurrence of fungi and the spread of mold on house structures insulated with it is practically eliminated
For ceilings
Just like floors and walls, ceilings require insulation.
The insulation materials discussed above may well be used in this case. A more specific insulation material is penoizol. In appearance it somewhat resembles foam chips. This is where the similarity ends, if you do not take into account the thermal conductivity characteristics.
Penoizol is absolutely not flammable. Has high chemical and biological resistance. Rodents avoid it. It is good for insulating ceilings because it is very light in weight. Its density is from 5 to 75 kg/m³. Due to low thermal conductivity, an insulation layer thickness of 5 cm or more is sufficient. When working, bulk material is used, in sheets and in liquid form.
When considering bulk insulation for ceilings, one cannot ignore such a widely used material as sawdust. Sawdust is used for insulation as the cheapest material. Their use as an independent insulation material is highly undesirable. The fact is that they are susceptible to rotting due to moisture absorption.
They are also excellent breeding grounds for mice. Even if you do not take into account the fact that they are a fire hazardous material, it is easy to conclude that they are unsuitable. “Craftsmen” go to all sorts of tricks in order to somehow reduce these negative factors. To do this, sawdust is mixed with expanded clay, lime, even broken glass and other building materials. Such measures somewhat improve the properties of the insulation, but not much.
conclusions
In the article we talked about the key points for using stone wool aspiration. Let's summarize what has been said. So, the advantages of mineral wool crumbs:
- low price;
- light weight;
- ease of installation;
- obtaining a continuous layer of insulation without the formation of “cold bridges”;
- high thermal insulation properties;
- the possibility of insulating hard-to-reach places - “pockets” in walls, ceilings, etc.
Disadvantages of insulation obtained from stone wool production waste:
- thermal insulation is very dusty;
- increased requirements for the tightness of seams and junctions of steam-hydro- and windproof films;
- there is a risk of running into outright substandard behavior;
- installation should be carried out using personal protective equipment - goggles, respirator, mask, thick clothing;
- if you overdo it with tamping, you can compact the crumbs beyond the norm, which will lead to a decrease in its thermal insulation properties;
- great influence of the so-called “human factor”, workers can be lazy and leave uncompacted voids in the walls;
- It is difficult to predict how the insulation will behave in the long term, for example, whether it will become damp or whether it will settle in 10-15-20 years .
We recommend a topic that describes in detail the use of mineral wool aspiration - Decagon, or the path from the sphere to the coaxial yurt.
- Insulation of a private house: basic knowledge. We are looking for universal insulation for all occasions based on the experience of FORUMHOUSE users.
- How private houses are built in Europe: the article answers the question why in countries with a milder climate than in Russia, cottages are insulated with a layer of thermal insulation 30-40 cm thick.
- Step-by-step insulation of a timber house with stone wool: how to perform a thermal engineering calculation of the walls of a timber house, and why it is impossible to insulate a wooden house with a vapor-opaque material.