Insulation is one of the types of building materials designed to protect a building from the negative effects of natural factors and maintain warmth and comfort inside. The main property of such thermal insulation is the minimum thermal conductivity.
- Ceiling insulation from above
Types of insulation
Currently, any construction supermarket will offer a large selection of insulation materials, differing in material of manufacture, characteristics, quality, cost and manufacturer. But in all this variety, it is necessary to choose the one that is most suitable for insulating a specific surface. Let's look at the main ones.
| Name | Characteristics | Photo |
| Insulation with an organic base | It is in great demand, made from woodworking and agricultural waste (natural raw materials) with the addition of cement and some types of plastic. It has high fire safety, is not afraid of moisture, and can withstand temperatures up to 150 degrees. | |
| Arbolite | In its production, small sawdust, shavings, chopped straw or reeds are used. Chemical additives or cement are used. The manufacturing process ends with treatment with a mineralizer. | |
| PPVC (polyvinyl chloride foam) | It contains polyvinyl chloride resins, which acquire a foamy structure during the production process. It can be either hard or soft. Used for insulation of facades, walls, roofs and other surfaces. | |
| Chipboard | It is based on small shavings (90% of the total volume) and 10% - synthetic resins and antiseptic substances. | |
| DVIP | Identical to chipboard, but straw trimmings, wood waste, and corn stalks are used in production. Synthetic resins with additives of fire retardants, antiseptics, and water-repellent substances are used as a binder. | |
| PPU (polyurethane foam) | The composition includes polyester, water, diisocyanate, emulsifier. It has excellent heat-insulating, sound-proofing and moisture-repellent properties. | |
| EPP/foam | The composition includes air (98%) and polystyrene (2%). Small amounts of flame retardants are expected. | |
| Foamed polyethylene | The porous structure, with good vapor barrier properties, does not conduct noise well. | |
| Fibryolite | The composition includes wood shavings, cement or magnesium components. It looks like slabs. Resistant to chemical and biological aggressive influences, moisture resistant, does not allow noise to pass through. | |
| Mineral wool | There are two types: stone and slag. Main composition: diabase, dolomite, basalt, limestone, bound by components containing phenol or urea. | |
| Glass wool | Glass industry waste is used in production. It has sufficient elasticity and strength, sound insulation, is not afraid of open flames, and does not emit harmful substances at high temperatures. | |
| Ceramic wool | The basis is zirconium, aluminum, silicon. Not afraid of high temperatures. |
How to insulate a ceiling in a private house with mineral wool
Before installing the insulation, they first decide how to fix the mineral wool to the ceiling - outside (from the attic), inside (in the room) or both (combined method). External thermal insulation of the ceiling of a cottage or private house with such building material is considered a more convenient, simpler and economical installation method, but the second method is not always used.
Since when the ceiling is insulated internally with fire-resistant mineral wool, a suspended ceiling is installed in the room, the second method is not suitable for low private houses. Only if the height of the room is more than 2.5 m, then ceiling insulation with this building material is considered justified.
When using combined installation, mineral wool is laid on both the attic and room sides. More often, such installation work is carried out in a sauna, bathhouse and other places where it is necessary to ensure a high, constant temperature for a long time.
Preparation for installation of mineral wool on the ceiling
In order to properly insulate the ceiling with mineral wool, when preparing for installation, perform the following steps:
- calculate the amount of insulation (how many building materials are needed to install ceiling vapor and waterproofing);
- prepare tools - a stapler, tape measure, knife, adhesive tape, several wooden slats, metal guide profiles and fasteners;
- prepare personal protective equipment - glasses, clothing, respirator and gloves.
The insulation is unpacked only before installation. After completion of the work, the room is cleaned with a vacuum cleaner, and then a warm shower is taken.
Thickness of mineral wool for ceiling insulation
When choosing the thickness of fire-resistant mineral wool, the climate in which the private house is located is taken into account. The quality of installation work is directly related to the thickness of such insulation and the value of the thermal conductivity coefficient. Mineral wool mats, which have a low density, have less thermal insulation thickness than tiles.
The thickness of mineral wool mats for thermal insulation of private households in northern latitudes is 206 mm, and in the middle zone - 163 mm. As a result, dense mineral wool has good thermal conductivity and is a fire-resistant building material.
The external walls of private households or cottages in the middle zone are covered with a layer of mineral thermal insulating wool, the thickness of which is 120-140 mm. Moreover, the standard insulation thickness is a multiple of 50 mm. Mineral wool 80 mm thick is used to cover ceilings in individual housing construction buildings.
How to attach insulation to the ceiling
When insulating a ceiling covering with mineral wool in a cottage or private house, follow the following tips from professionals:
- a sheathing of several metal guide profiles is secured with steel screws, they firmly fix the mineral wool to the ceiling;
- during installation, mineral heat-insulating wool is not specifically compacted or compressed with a press; such actions significantly reduce the thermal insulation of the building material;
- if the ceiling lathing is thinner than mineral wool, then in this case several wooden beams are stuffed onto the main boards.
Density of insulation
All thermal insulation materials differ from each other not only in composition and production method, but also in the main indicator - density.
| Name | Density indicator (kg/m3) |
| Cellulose wool | 30 — 70 |
| Wood-fibre board | 150 230 |
| Foam glass | 100 — 150 |
| Linen mats | 30 |
| Cotton wool | 25 — 30 |
| Mineral wool | 50 — 200 |
| Styrofoam | 25 — 35 |
| Extruded polystyrene foam | 35 — 40 |
| Expanded clay | 450 — 1200 |
| Polyurethane foam | 30 — 80 |
The type of insulation depends on the density. He can be:
- especially light;
- light;
- average;
- hard (dense).
The density of the material has a direct impact on indicators such as:
- load-bearing capacity;
- noise absorption;
- thermal conductivity;
- method of fastening.
What it is?
The density of mineral wool is the number of fibers of the material per 1 m³. The indicator, depending on the material and brand used for the manufacture of mineral wool, will be in the range of 30-220 kg per m³. A number of properties that characterize it:
- The ability to preserve its original form.
- Ability to withstand static and dynamic loads.
- Compression resistance, that is, the ability to withstand mechanical influence.
- Method, place of application. How exactly the mineral wool will be installed greatly influences the choice.
Naturally, the denser the material, the more raw materials are used in production, and this affects the price.
Stamps
At the moment there is the following classification:
- P-75 is an insulation material that is used for horizontal surfaces that are unloaded, that is, 1- or 2-story buildings. This material has the lowest density.
- P-125 - this can be used for floors and ceilings; it is successfully used in insulating frame structures. At the same time, the weight of the structure should be lightweight. The density is low, so this brand is not able to withstand loads.
- P-175 are rigid slabs, they can be successfully used for screeds.
- PPZh-200 – slabs of increased rigidity. Their weight and density are maximum. In addition to insulation, it increases the fire-resistant properties of the structure.
Density does not depend on shape and thickness
Note! It is the density of glass, slag, and stone wool that is the indicator that influences resistance to deformation under its own weight. It prevents the material from bending under pressure and additional loads.
Compacting the slab has no effect on:
- Vapor permeability.
- Noise absorption.
- Thermal insulation properties.
- The thickness of the material, regardless of the form of its release (rolls, slabs).
To determine density, the material weight of 1 m³ is used. When choosing, you don’t always need to buy the densest cotton wool. To make the right choice, you need to take into account the characteristics of the room in which it will be installed.
Comparative characteristics of insulation materials
In order to make the right choice, you need to understand the difference between one insulation and another.
| Name | Moisture absorption(%) | Flammability | Vapor permeability Mg/m*h*Pa | Thermal conductivity W/m*K |
| Mineral wool | 1,5 | does not burn | 0,49 – 0,6 | 0,037 – 0,048 |
| PPU | 2,0 | burns moderately | 0,02 | 0,023 – 0,035 |
| Styrofoam | 3,0 | burns intensely | 0,03 | 0,036 – 0,041 |
| Ecowool | 1,0 | burns moderately | 0,3 | 0,032 – 0,041 |
| Penoizol | 18,0 | burns low | 0,21 – 0,24 | 0,028 – 0,034 |
To purchase the thermal insulation material you need, you need to pay attention to the following factors:
- where it will be used (for external or internal work);
- it will be laid vertically or horizontally;
- preload on the material;
- the need for sound insulation;
- weather conditions in a particular region.
The functionality of the insulated structure is also of great importance. For example, for commercial buildings, preference should be given to material with significant density and the impossibility of damage by small rodents or other pests.
Types of mineral wool and their distinctive characteristics
Mineral wool is a fibrous material produced in the form of mats or rolls and obtained from melts:
- glass (glass);
- blast furnace slag metals (slag);
- rock eruptions (rock or basalt wool).
Each option has different thermal conductivity and operating temperature limits. Plus, many manufacturers add their own components to the composition to achieve the unique characteristics of the produced insulation.
The most common and long known is glass wool. It retains its characteristics at temperatures ranging from -60 C to +450 C and has good thermal conductivity of 0.38-0.45 W/m*K.
Slag wool is slightly worse in thermal conductivity, but only by 5-10%. But at temperatures above 300 C it begins to sinter and lose its thermal insulation properties. It also has the worst hygroscopic properties among analogues; it absorbs moisture with ease. And for all mineral wool, water is the main enemy. After absorbing moisture, their thermal insulation characteristics sharply decrease.
Basalt wool is able to properly perform its functions at temperatures up to +600 C, and some options up to +1000 C. Its thermal conductivity from various manufacturers varies around 0.035-0.05 W/m*K. Plus it has better vapor permeability, the walls will be more “breathable”
All mineral wools are non-flammable.
All of them are afraid of moisture and during installation it is imperative to install a high-quality vapor barrier. Otherwise, they will absorb moisture, which, when the air temperature drops, can simply turn into ice and destroy the material.
And they all have a common drawback - the fragility of the fibers during installation and, as a result, a lot of small pieces that penetrate everywhere and cause severe itching. Which can cause serious breathing problems. Therefore, when working with all mineral wool, be sure to wear gloves and a respirator with goggles.
Which insulation is better for walls?
The most suitable material for this type of work is considered to be mineral wool. It has good properties and a long service life. But in order for it to meet your expectations, it is necessary not only to purchase a high-quality product, but also to follow the installation technology, prepare the walls properly, and determine the dimensions and physical characteristics (density and thickness).

The size of mineral wool is determined taking into account the following data:
- humidity indicator;
- climatic features of the area;
- insulated surface;
- minimum and maximum temperatures throughout the calendar year.
If you purchase mineral wool with low thermal conductivity, it will not be able to perform its main functions. There is also no need to opt for cheap options packaged in rolls. In their production, as a rule, low-quality components are used. Moreover, the material in rolls is 50mm thick, which is unacceptable for work outside the building. It is advisable to purchase mineral wool slabs of significant size.

The higher the density of the insulation, the heavier it is, and, therefore, more expensive. The density of mineral wool varies from 20 kg/m3 to 250 kg/m3, and therefore there will be a significant difference between the materials. To understand which insulation is best for you, you need to understand what depends on the density:
- can the building withstand such a load;
- how much deformation is possible;
- how much the material can be compressed.
But the density indicator has no effect on:
- thickness of the slabs;
- insulating qualities;
- vapor permeability;
- soundproofing protection.
Which mineral wool is best for walls
In order not to make a mistake with insulation, it is necessary, first of all, to take into account the climate characteristics in the place of residence. In temperate climates, the recommended insulation thickness should be 80 – 100mm. For continental, sharply continental, sea, monsoon, arctic, subarctic climates, the range of mineral wool can be from 110mm to 150mm.

Insulation with a low density of 40 kg/m3. can only be used on horizontal surfaces that may not withstand significant loads. The minimum density for walls is 50-75 kg/m3. If the facade is supposed to be ventilated, then the density of the insulation should be 110 kg/m3, subject to subsequent finishing with siding. With further plastering of the walls, the density indicator can reach 140 kg/m3.
Brief description of the material
Cotton wool for wall insulation is the optimal price-quality ratio when creating comfortable living conditions. It consists of a large number of fibers that are obtained by specific processing. They can be made of glass, slag, stone. The density of any mineral wool, measured in kg per m3, also depends on the material of manufacture. Insulation has a number of advantages, including:
- Easy to install. Mineral wool can be presented in the form of a roll or slabs that hold their shape.
- The light weight of the material allows it to be used for floors without weighing them down.
- Convenience of subsequent finishing. This indicator depends, among other things, on the density of the insulation.
- Environmentally friendly - mineral wool is created from natural materials, which allows it to be completely safe.
- The material is a good sound insulator.
- Non-flammable - it melts but does not burn.
There are also disadvantages and they should be taken into account when insulating with mineral wool:
- Glass and slag wool are very prickly, this must be taken into account during the installation process. Stone wool is practically free from this drawback.
- The material, together with air, allows moisture to pass through, which leads to its loss of its technical characteristics. To avoid this, it is necessary to isolate the insulation from moisture.
- To purchase high-density mineral wool, you will have to spend a lot of money, but the result will exceed expectations.

Insulation structure with different densities
Which roof insulation is best?
Manufacturers produce a wide variety of this material. They all differ in their characteristics, quality and cost. Let's focus on the main ones:
- Styrene materials, which include polyurethane foam, polystyrene foam, polystyrene foam. They are lightweight, easy to install, convenient in size, moisture-resistant, and durable.

- Glass wool or mineral wool. The main advantages are low cost and fire safety. But the disadvantages include excessive absorbency of cotton wool, which negatively affects its density and service life. Its negative effect on the human body has been established.

- Expanded clay, slag, sand, sawdust. They belong to the category of environmentally friendly materials. But they are used only for flat roofs and are mounted exclusively on top. The insulation capabilities of such material are insufficient. Negative aspects include their friability and moisture absorption.

Roof insulation with expanded clay - Polyurethane liquid insulation. Currently very popular. They have many advantages, including significant density.

Polyurethane - Cellulose. A new trend in construction. Its density is good. Thanks to fire retardant additives, it is considered fire resistant. But such insulation can negatively affect the health of residents, so it is not recommended to insulate the roof of residential premises with it.

To select the right material, you need to consider the following points:
- its weight should be insignificant so as not to additionally load the roof;
- mandatory environmental cleanliness, since under constant exposure to the sun, volatile chemicals enter the premises, causing harm to people;
- the optimal service life of the insulation is about 50 years, with maximum preservation of all its qualities;
- the presence of such qualities as heat resistance, moisture resistance, noise absorption.
The design of roofs is of great importance. For flat ones, styrene and environmentally friendly materials are suitable, for pitched ones - cotton wool. For such work, combined options can be used. Such insulation is fastened using a stapler or construction tape.
Attention! Roofs on residential buildings are insulated in one or two layers, and baths and saunas in three or four. Metal roofs require higher density insulation than tile roofs.
Features and benefits
Mineral wool is a fibrous slab with dimensions of 60x120 and 50x100 cm. The thickness of the products is 5, 10 and 15 cm. Ten-centimeter slabs are the most in demand. This thickness is sufficient for using the material in harsh climatic conditions, under the influence of negative temperatures and large amounts of precipitation.
The fiber density of facade slabs is slightly higher than that of the material intended for interior decoration and corresponds to 130 kg/m3. The high density and elasticity of mineral wool are necessary conditions for its installation under plaster. The slabs must withstand the weight of the applied solution and retain their original qualities when it dries.

Due to the fact that most of the country is located in a cold climate zone, mineral wool is in high demand in the domestic building materials market.
The popularity of the material is due to a number of undeniable advantages:
- The excellent heat and sound insulation properties of wool guarantee heat retention at temperatures below 30 degrees, and reliably protect the home from street noise;
- High fire resistance and non-flammability of the material guarantee complete fire safety of the slabs, which begin to melt only at a temperature of 1000 degrees;

- Rodents, insects and other pests do not show interest in mineral wool, so their appearance in it is excluded;
- Excellent vapor permeability promotes moisture removal and rapid elimination of condensation;
- Resistance to moderate mechanical stress significantly increases the service life of the facade, and makes the use of cotton wool preferable to the use of polystyrene foam;

- The absence of the need for additional thermal insulation of interpanel seams solves the problem of heat loss in large-panel buildings;
- The low cost and availability of the material make it possible to finish large areas at minimal cost.

The disadvantages of mineral wool include the presence of formaldehydes in its composition, which have a negative impact on the health and well-being of others. When purchasing, you need to make sure that you have a certificate of conformity and markings from the regulatory authority. This will help avoid purchasing low-quality products and will guarantee the safety of raw materials.
Mineral wool installation work must be carried out using personal protective equipment. The disadvantages include the need to treat the slabs with a hydrophobic compound. If this is not done, the cotton wool will absorb moisture and lose its thermal insulation qualities.

Mineral wool is produced in three modifications, which differ in composition, purpose and performance characteristics.
- Glass wool. Made from sand, soda, borax, dolomite and limestone. The fiber density corresponds to 130 kg per cubic meter. The material is able to withstand heavy loads, has a thermal resistance limit of 450 degrees and thermal conductivity of up to 0.05 W/m3.
Which insulation is better for the ceiling
There are several ways of ceiling insulation: from above (from the attic) or from below (from the room). There are five main types of insulation for such work:
| Mineral wool | It has a thickness of 20mm to 200mm, is sold in bales or rolls, and may have one foil side to improve thermal insulation properties. |
| Foiled polyethylene foam | Thickness from 1mm to 20mm, rolls 1m wide. Effective, can be used as a second layer to mineral wool to increase the power of the thermal barrier. |
| Styrofoam | Sold in squares with sides of 1m and thickness from 20mm to 100mm. Density ranges from 15kg/sq.m. up to 25kg/sq.m. They are used as intermediate insulation before installing suspended and suspended frames or as a rough base before filling the ceiling. |
| Polyplex | Presented in the form of sheets 120cm x 60cm, thickness from 10mm to 200mm, in a variety of colors and with special bevels for installation. Products with a density of 35 kg/m2 are in great demand. or 45kg/sq.m. Used as a rough coat before puttying. |
| Expanded clay | It has a porous structure, light weight, and oval shape. The attic floor is covered with it to create a thermal cushion under the screed. |
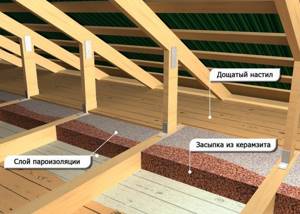
Ceiling insulation from above
Any insulation is suitable for the attic, especially since there is no need to attach them. They are laid tightly on the surface so that there are no gaps or cracks through which heat will escape. Products that are not too expensive are suitable for these purposes, as long as the thermal insulation properties are at their best. The main insulation materials are mineral wool and expanded clay.
Insulation of the ceiling from below
You definitely need to take care of the hanging frame or special fastenings, since fastening work is carried out on weight. The easiest way is to fill the voids between the base and the suspended ceiling with thermal insulation material. You can also use U-shaped hangers. In this case, the insulation is threaded inside the devices, and then profiles made of wood or metal are installed. But this method is only suitable if the height of the ceiling allows them to be reduced by lowering the frame.

Technology of wall insulation with basalt
Inside with sheathing
Refers to the simplest option for insulating a private home and industrial structures. The essence of the method is to create a sheathing frame. Assembly is made from wooden beams or metal profiles. The width of the mats is first measured and, subtracting 5-7 cm from the obtained values, the sheathing is assembled.
Next, mineral wool is tightly inserted into the cells of the frame, filling the entire space. A vapor barrier membrane must be attached on top of the insulation.

Lathing
Insulation of walls using the “well” method
If the house design involves laying facing bricks, then the best insulation option would be “well”.
Consider the composition of the “well” pie:
- Bearing wall. As a rule, it is brickwork laid out in one row. Although other materials are also used for load-bearing structures. Depending on the required load-bearing capacity, the walls are laid out in half a brick, a brick and a half or two.
- Insulation. In this case, basalt wool is used. Fastening to the surface is done using umbrella dowels.
- Facing wall. Masonry begins after complete installation of the insulation or as the inner layer builds up. Ceramic or silicate brick is used as the outer layer. The usual installation method is half a brick. A prerequisite for laying facing bricks is the presence of a concrete base.
- Ventilation gap. Since the appearance of condensation on the inside of the insulation is undesirable, a ventilation gap is created for this purpose to ensure sufficient ventilation.

Well method
Attention! If for some reason it is not possible to create a ventilation gap, then it is better to abandon the well method of insulation altogether. This applies to mineral wool.
Wet insulation of walls
The method is used for plastering, because with the “wet” method of insulation, lathing is not provided. Since a high load will be applied to the mineral wool, it is recommended to use high-density mineral wool.

Wet method
Basalt wool fastening technology:
- Following the instructions supplied by the manufacturer on bags of glue, we prepare a liquid solution.
- Apply the prepared mixture onto the mineral coating with a notched trowel. The glue is applied in a continuous layer without coating the end part, which can lead to a decrease in the level of thermal insulation.
- We install mineral mats on the basement of the building and press them against the wall. To increase adhesion, it is necessary to smooth the surface using pressing movements, applying little force. Installation of basalt wool is done from bottom to top. The next row is laid with an offset of half the mat. The same applies to places near window and door openings.
- External and internal corners are reinforced with plaster corner plates.
- We fix the mineral wool with umbrella dowels - 5 fasteners per sheet.
- Using an adhesive solution, we attach the reinforced fiberglass mesh. Make sure that the material overlaps each other by 15-20 cm.
- At the final stage, plastering is carried out.
Frameless method of insulation from the inside
The frameless installation method refers to the wet fastening method. To complete this task you will need an adhesive solution and a cleaned wall surface. The mortar is applied directly to the wall using a notched trowel. Next, a mat of stone wool is applied. To improve the quality of adhesion, umbrella fasteners or self-tapping screws are used, depending on the type of coating.
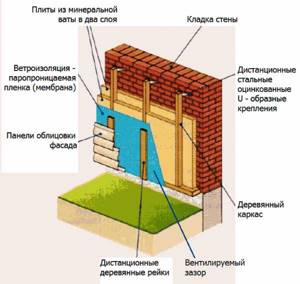
Installation of mineral wool on a ventilated facade
This method requires the assembly of the sheathing, as it involves the installation of facing material.
Ventilated facade
Warming process:
- The sheathing structure is assembled taking into account the width of the mats.
- Mineral mats are laid at random.
- Next we move on to attaching the windproof membrane.
- For further fastening of the cladding, a counter-lattice is assembled from 50x50 mm slats.
At the final stage, façade finishing work is carried out.
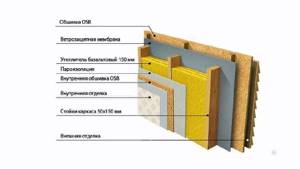
Insulation of the wall of a frame house
Thermal insulation of a frame house differs in that it involves the installation of slabs inside the walls, and on the inside and outside of the building. As a rule, manufacturers of frame buildings create walls with a thickness of about 15 cm, which allows you to place 3 mats of 5 cm each. It is also possible to combine wool of different thicknesses - 10 cm and 5 cm. If it is necessary to carry out finishing work on the facade of the building, lathing is assembled on top of the insulation.
Thermal insulation of a frame building
Density of floor insulation
If you choose the right floor insulation, you can save a third of your heat payment. You can use heated floors, or you can use insulation. The main thing is to make the right choice. It is not recommended to use materials that are too thin, as their benefits are minimal. Too much thickness will also not be acceptable. We need to settle on the “golden mean”.

The climatic conditions of a particular area play a big role. But in any case, the main insulation materials are:
| Styrofoam | If the floor is above the ground, then the thickness of the insulation should be 300mm, if there is a wooden floor - 200mm, for interfloor floors 150mm is enough |
| Ecowool | The thickness of the layers is the same as glass wool |
| Glass wool | For the first floor, the insulation layer should not be less than 400mm, if there is a basement, the thickness can be reduced to 300mm, wooden floors - 200mm, floors in an apartment building - 100mm |
| Penoizol | It is identical in thickness to foam plastic for different floors |
| Expanded clay | If the floor borders the ground, then the thickness of the insulation should not be less than 400mm, if there are wooden floors - 300mm, between floors the insulation layer should be 200mm. In apartment buildings, the layer thickness is from 50mm to 80mm. |
| Cork material | The thickness of the insulation in a private house is 100mm, between floors - 50mm, if there are wooden floors, the thickness can be increased by 20mm. Floors in a multi-storey residential building require insulation thickness from 10mm to 30mm. |
| Polystyrene concrete | The floor in individual residential buildings requires a thickness of insulation of 200 mm; between floors, 100 mm is sufficient. In residential high-rise buildings, the layer should be 50mm. |
Mineral wool for external insulation. Advantages of external insulation
Insulate housing from the inside only in the most extreme cases. The justification may be the impossibility of insulating the walls due to the height, or the authorities’ ban on changing the appearance of the structure. Insulating walls outside with mineral wool often spoils the appearance of an apartment building. A separately insulated apartment stands out noticeably and disrupts the architecture of the city. But the main reason why the process is carried out outside is thermal engineering and physics. There is a term - “dew point”. If the insulation is located from the street, the dew point moves away from the internal walls. The house is warm and cozy, the walls remain dry.
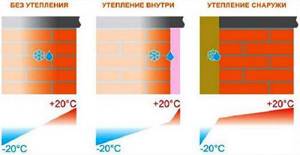
Placement of the dew point, depending on the method of wall insulation.
Placing insulation inside will cause the walls to become damp. You will need to invest a lot of effort and money into a vapor barrier. No less important reasons:
- The usable area inside the apartment does not decrease. There is not a single case when a person wants less free space.
- The outer wall of the house is perfectly protected from all negative factors of nature.
- Good indoor ventilation.
- The appearance of the building is improved. You can hide gloomy gray walls, create a unique design and update the facade. This is very beneficial if you decide to sell your home.
Material

Modern technologies have filled this market segment. The most commonly used insulation is mineral wool. It is also called basalt, because it is made from natural raw materials - basalt. An additional component is silica. During the production process, the product is treated with water-repellent compounds. Everything is thought out in such a way that vapor permeability does not become worse. The building material is supplied to the client in the form of mats and slabs. A less convenient form of delivery is in rolls. The parameters of the final product may vary. The material itself has a fibrous structure. The fibers can be oriented in all sorts of ways. When positioned “parallel” we have conventional slabs. If the fibers are oriented perpendicularly, these are lamella slabs. Most often, the walls of buildings are insulated with cotton wool with a density of 75 to 145 kg/m3. A low-density slab can be attached directly to the wall. Low density allows you to fill all the unevenness in the wall (brick, concrete). It is customary to mount slabs with a density of 100 kg/m3 above the first layer. They allow you to get a smoother surface and make finishing work easier. To calculate the required quantity, you must proceed from the total area of the walls. From the resulting amount you need to subtract the sizes of windows and doors. A reserve of 5 to 10% is quite justified: you will spoil something, and the remainder will be useful on the farm.
Advantages of mineral wool

The material has significant advantages:
- Complete, high-quality filling of all voids. This cannot be achieved using polystyrene foam.
- There is no need to use a vapor barrier.
- The insulation technology is not particularly difficult.
- Fire resistance. The material does not burn and does not support combustion. It can withstand almost 6 thousand degrees of heat.
- Long service life if all installation requirements are met.
- Light weight. Mineral wool is easy to work with and does not place much load on the walls and foundation.
- Excellent thermal insulation.
The minimum total thickness of the insulation should be ten centimeters! The best option is to attach the insulation to a load-bearing wall, and then lay the brickwork using facing bricks. The insulation layer is located in the middle, is perfectly protected and “works” more efficiently. Mineral wool can be used to insulate a wooden house or a brick house. Sometimes buildings made of gas silicate blocks are finished with mineral wool. This action is justified if you live in the northern regions. But significant thickness is not required.
Insulation density for facade
The main insulation used for building facades is mineral wool. Its main advantages include the ability to restore its original shape and a long service life. If the facade assumes the presence of ventilated suspension systems, then the density of the insulation should range from 45 kg/cub.m. up to 100kg/cub.m. Such insulation can be attached using elements of the entire system, but for greater strength special dowels can be used.
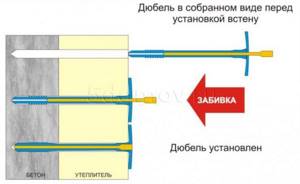
If finishing with decorative plaster is planned, then the thickness of the insulation increases to 145-165 kg/cub.m. To attach such heat-insulating material, you need to use dowels or a special mixture for gluing mineral wool. As a rule, both types of fasteners are used, which increases the level of reliability significantly.
Installation
The technology for laying mineral wool as thermal insulation for floors, walls and roofs is extremely simple. It is necessary to equip the frame and lay insulation inside it, not forgetting about the water vapor barrier. In more detail it looks like this:
- On the insulated surface, a frame is made of wooden blocks. The distance between them is made a couple of centimeters less than the width of the roll or slab of mineral wool. So that she lies between them as tightly as possible. On inclined surfaces, for reliability, it can be additionally reinforced with “fungi dowels” or glue. The bars can be replaced with drywall profiles.
- A vapor barrier is laid as the first layer. Then the mineral wool itself, and on top there is another waterproofing layer. When installing outside, an option is allowed when the first hydraulic barrier is skipped. And mineral wool is glued to the walls with a polymer-cement composition. The option depends on the selected material and type of finishing.
- The outer vapor barrier layer is strengthened on the frame. And on top of it is another lathing for pressing down the mineral wool and subsequent decorative finishing. Or plastering is done.
Results
Mineral wool allows you to quickly and independently make your home warm and cozy.
Moreover, such thermal insulation will last for many years. The main thing is to thoughtfully approach the choice of mineral wool for wall insulation and correctly perform a vapor barrier in order to minimize the effect of moisture on the material.
Source: otopleniedomov.com
Which insulation is best for the attic?
For the most part, mineral wool, glass wool, sandwich panels, organic materials and foam glass are used to insulate the attic. All of them must have fire-fighting properties, high acoustic protection, and significant vapor permeability. As a rule, two layers of material are used for insulation, but experts recommend making the thickness of the insulating layer 250 - 300 mm. These criteria apply to both roll and slab materials.
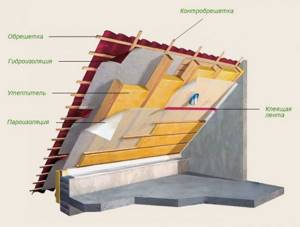
Areas of application of insulation based on basalt fiber
Basalt slabs are used for insulation of building facades, partition structures, floors, roofs and other building structures. In addition to residential buildings, basalt insulation is used on industrial sites. Most often used for insulating frame houses.
Having studied the technical characteristics, it is easy to come to the conclusion that mineral insulation can be used in almost all areas of construction. Due to its fire resistance, it is recommended to be used when insulating a building that requires a high degree of fire safety.
Low water absorption makes it possible to use insulation when insulating a bathhouse or sauna. When choosing, remember that the weight of basalt insulation exceeds the weight of polystyrene foam or mineral wool.
Mineral wool in rolls types and sizes
The modern market offers a wide variety of all kinds of innovative thermal insulation materials. This includes liquid-ceramic heat insulator, polyurethane foam, and silica mats. However, mineral wool is still the most popular of them.

Rock wool rolls are usually used to insulate horizontal surfaces. This installation requires careful handling and avoidance of too much stress on the surface. Rolls are used to insulate floors between floors, floors, attics, and roofs with a slight slope. They are also used to insulate pipes, fireplace covers and home stoves.
Roll dimensions (width, thickness, length in mm):
- Ursa M-11 – 1150 by 53 by 9000;
- Isover Classic – 1220 by 50 by 8200;
- Isover Sauna – 1200 to 50 to 8200;
- Heat Knauf Dacha - 1220 by 50 by 7380.
Bulk mineral wool is inconvenient to roll, so its thickness usually does not exceed 50 mm. Mineral wool in rolls can be used to insulate large areas where the surface is subject to significant load. For laying rolls, logs, rafters and other building elements are usually used.
Description of slabs with different density levels
There are basalt slabs of various density levels. This is reflected in the following properties of insulation: vapor permeability, moisture resistance, resistance to high loads and response to compression of the material.
Table of parameters of basalt insulation
Based on density, slabs are divided into the following categories:
- Up to 35 kg/m3 – used for vertical and inclined insulation without load.
- Up to 50 kg/m3 - with the help of such insulation they increase the level of thermal insulation of interior partitions, attics or attics. Where there is no load on the surface.
- Up to 75 kg/m3 – lightly loaded surfaces, under floors when placed between joists.
- Up to 100 kg/m3 – external insulation of industrial and residential buildings.
- Up to 125 kg/m3 – arrangement of ventilated facades.
- Up to 150 kg/m3 – single-layer insulation of reinforced concrete or metal building frames.
- Up to 175 kg/m3 – insulation of heavy buildings with further plastering of the facade. Or it is located inside a three-layer cake.
- Up to 200 kg/m3 - insulation with such a density can withstand the highest loads. The soundproofing qualities of the material are significantly higher than analogues with a lower density level.
Why do you need to know the dimensions of mineral wool in slabs?
Calculation of the amount of insulation
Positive aspects and properties are ensured by the use of insulation in all areas of construction. To accurately calculate the amount of material for external or internal installation, you will need to know the main standard sizes of slabs in m2 (squares).
When are dimensions taken into account?
Insulating the floor covering inside and creating external thermal insulation begins with drawing up a diagram and purchasing materials. You will need to know the parameters of mineral wool sheets in order to:
- creating thermal protection in accordance with the climate of the region;
- reducing time for budget preparation;
- selection of parameters when laying between floor or attic joists;
- arranging a frame for sheets in the case of external work.
The standard size of the slab is 100x50 cm, but the number of pieces depends on the square footage of the building. The thickness of the material is achieved from 150 to 600 mm. When selecting dimensions, it is necessary to take into account the density indicator - the higher it is, the higher the likelihood of withstanding mechanical loads and the absence of deformation.
Materials for insulation and methods for their selection
Materials for thermal insulation of joints between panels belong to one of three groups:
- mastics for waterproofing;
- actually, insulation;
- sealants to protect the joint from weather influences.
The best effect is achieved with the combined use of three types of materials, creating the effect of a “warm seam”.
How does insulation of interpanel seams occur?
Historically, during mass panel housing construction, seams were sealed using plaster, into which strands of flax fibers were placed. During seasonal movements of the soil, the house settled; when deformed, the plaster crumbled, opening the way into the home for cold and moisture. Today such technology is not used.
Sealants themselves have low thermal insulation; they only prevent the free movement of air and the penetration of moisture into the insulation, greatly increasing its effectiveness. The sealant also increases the durability of the insulation by protecting it from exposure to sunlight. The material fills unevenness and microcracks in the surface of the concrete panel, protecting it from seasonal exposure to moisture and chipping.
The condition of the external interpanel seam in panel houses is easy to assess visually. The internal seam is covered by a ceiling panel; to access it, you need to disassemble the entire joint.
Mastics for sealing joints are made on the basis of polyurethane and other plastics. They are produced as two-components; when mixed, they form a thick elastic mass resembling rubber and polymerize. The material retains its working properties in a wide temperature range from -40 +40°C, providing complete protection from moisture.
Two-component mastics have the following advantages:
- high adhesion to concrete, ceramics, stone, metal, plastic;
- long service life;
- resistance to sunlight and weather conditions;
- compatibility with tinting pigments, allowing you to obtain any coating color.
Mastics are widely used both in the construction of panel buildings in Moscow and other cities, and in the repair of insulation that has become unusable.
Insulation materials made from foamed plastics are characterized by high strength, low thermal conductivity and high elasticity, which allows them to fill the joint cavity and reliably insulate it. Polyethylene foam heat insulators are supplied in the form of tubes or continuous bundles. For corner joints special cross-shaped elements are made.
In addition to the insulation effect, such materials also provide excellent sound insulation, reliably cutting off the living space from street noise. The insulation does not absorb moisture, but is sensitive to ultraviolet rays.
Polyurethane foam is often used to seal joints during repairs. It is indispensable when it is not possible to dismantle the entire seam for repairs. The foam is blown into the cavity through several drilled small holes. It fills voids evenly and polymerizes within a few minutes. The hardened foam retains some elasticity, which allows it not to come off the surface with small settlements of the plates relative to each other. The main advantages of polyurethane foam are:
- high adhesion to all construction and finishing materials;
- excellent thermal insulation and sound insulation;
- ease of use;
- resistance to moisture.
Construction foam is extremely sensitive to sunlight; it must be protected from it with a layer of mastic or plaster.











