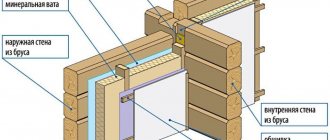
One of the most important concepts in construction is dew point. At the stage of wall insulation, this allows you to correctly select the type and thickness of the heat-insulating material and create an optimal microclimate inside the building. There are several ways to determine the dew point. However, you also need to know what to do with the results obtained.
A short excursion into the physics of the phenomenon
The dew point is the temperature of the air at which excess moisture contained in it falls out in the form of condensation. Why is there too much of it? The fact is that warm air holds a large amount of water vapor, cold air holds much less. It is this temperature difference that forms condensation . An example of the phenomenon are drops of water on cold water pipes or windows, or fog.
What else you need to know about dew point:
- The higher the humidity, the closer it is to the air temperature, and vice versa.
- Its value cannot be higher than the air temperature.
- Condensation always appears on cold surfaces . This is explained by the fact that the warm air next to them cools and its humidity decreases.
The unit of measurement for the condensation point is degrees Celsius.
When is internal insulation possible?
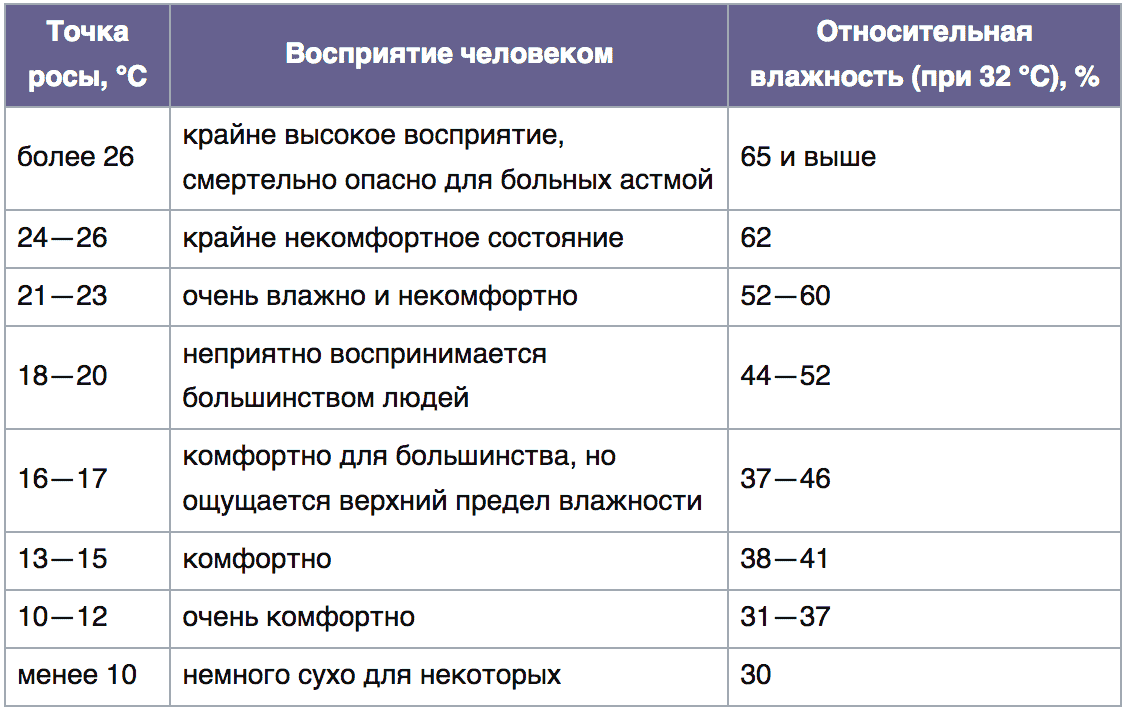
Table for determining dew point depending on air temperature and humidity.
It is not always possible to carry out insulation from the inside, since if done incorrectly, dew will constantly fall out from the inside, rendering all building materials completely unusable, creating an uncomfortable microclimate inside. Let's consider when it is not recommended to insulate from the inside, and what it depends on.
Is it possible or not to insulate from the inside? The solution to this issue largely depends on what will happen to the structure after the work is completed. If the wall remains dry all year round, then work on its thermal insulation from the inside of the room can be carried out, and in many cases it is even necessary. But if it constantly gets wet every winter, then it is absolutely impossible to carry out thermal insulation. Insulation is allowed only if the structure is dry and it gets wet extremely rarely, for example, once every ten years
But even in this case, work must be carried out very carefully, since otherwise such a phenomenon as the dew point will be observed constantly
Let's consider what determines the occurrence of the dew point, how to find out whether or not it is possible to insulate the walls of a house from the inside.
As already said, the dew point arises due to factors such as:
- humidity;
- indoor temperature.
Related article: How to replace cistern fittings
The humidity in the room depends on the presence of ventilation (hood, supply ventilation, air conditioners, etc.) and on the mode of residence, temporary or permanent. The temperature inside is affected by how well the insulation was installed and the level of thermal insulation of all other structures of the house, including windows, doors, and roof.
From this we can conclude that the consequences for internal insulation depend on:
- temperature of condensation moisture, that is, from the dew point;
- from the position of this point to the thermal insulation and after it.
How to determine where the dew point is? This value depends on many parameters, among which it is necessary to highlight:
- thickness, wall material;
- average indoor temperature;
- average outside temperature (influenced by climate zone, average weather conditions throughout the year);
- indoor humidity;
- the level of humidity outside, which depends not only on the climate, but also on the operating conditions of the house.
Let's put all the factors together
Graph of thermal resistance and dew point shift when using insulation.
Now we can collect all the factors that influence where the dew point will be located:
- mode of residence and operation of the house;
- availability of ventilation and its type;
- quality of the heating system;
- quality of work when insulating with foam plastic or other material all structures of the house, including the roof, doors, windows;
- thickness of individual layers of the wall;
- temperature indoors, outdoors;
- humidity indoors, outdoors;
- climate zone;
- operating mode, i.e. what is outside: street, garden, other room, attached garage, greenhouse.
Insulation from the inside is possible, based on all the above factors, in the following cases:
- when permanently residing in the house;
- when installing ventilation in accordance with all standards for a particular room;
- during normal operation of the heating system;
- with insulation, which is laid for all structures of the house that require thermal insulation;
- if the wall is dry, it has the required thickness. According to the standards, when insulating with polystyrene foam, mineral wool and other materials, the thickness of such a layer should not be more than 50 mm.
Related article: Polycarbonate canopy attached to the house: installation, photo
In other cases, insulation cannot be performed from the inside. As practice shows, in 90% of cases the walls of a house can only be thermally insulated from the outside, since it is quite difficult to provide all the conditions, and often not entirely feasible.
Dew point in the wall of a house - why it is important to know it
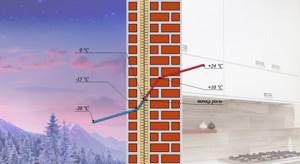
Most of the year there is a significant difference between the temperature and humidity conditions outside and indoors. That is why areas of condensation often appear in the thickness of walls with insulation. When weather conditions change, they move closer to the outer or inner surface of the wall . That is, to a colder or warmer area.
Example: air temperature is stable at 25°C and humidity at 45%. In this case, condensation forms in an area with a temperature of 12.2°C. When humidity increases to 65%, the dew point shifts to a warmer area, where 18°C.
Why is it so important to know the location of the condensation point? Because it determines which layer of the wall “pie” is exposed to the destructive effects of moisture. The worst option is when the insulation gets wet. Under such conditions, most thermal insulation materials lose their properties. They become deformed, allow cold air to pass through , rot, and lose their elasticity. Mineral wool is especially susceptible to these processes.
Useful: Frame garage: step-by-step construction instructions
Some information on how to calculate the thickness of insulation
In order to begin calculating thermal insulation, we need, first of all, to calculate Ro, then find out the required thermal resistance Rreq from the following table (abbreviated version).
Required values of heat transfer resistance of enclosing structures
| Buildingroom | Degree-day of the heating period D d , °C day | Reduced heat transfer resistance of fences R req, m2 °C/W | |||
| walls | coatings | attic floors and ceilings over cold basements | windows and balcony doors, shop windows and stained glass | ||
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 |
| 1. Residential, medical and children's institutions, schools, boarding schools | 2 000 | 2,1 | 3,2 | 2,8 | 0,30 |
| 4 000 | 2,8 | 4,2 | 3,7 | 0,45 | |
| 6 000 | 3,5 | 5,2 | 4,6 | 0,60 | |
| 8 000 | 4,2 | 6,2 | 5,5 | 0,70 | |
| 10 000 | 4,9 | 7,2 | 6,4 | 0,75 | |
| 12 000 | 5,6 | 8,2 | 7,3 | 0,80 | |
| A | — | 0,00035 | 0,005 | 0,00045 | — |
| b | — | 1,4 | 2,2 | 1,9 | — |
| 2. Public, administrative, domestic and other premises with wet or wet conditions | 2 000 | 1,8 | 2,4 | 2,0 | 0,3 |
| 4 000 | 2,4 | 3,2 | 2,7 | 0,4 | |
| 6 000 | 3,0 | 4,0 | 3,4 | 0,5 | |
| 8 000 | 3,6 | 4,8 | 4,1 | 0,6 | |
| 10 000 | 4,2 | 5,6 | 4,8 | 0,7 | |
| 12 000 | 4,8 | 6,4 | 5,5 | 0,8 | |
| A | — | 0,0003 | 0,0004 | 0,00035 | 0,00005 |
| b | — | 1,2 | 1,6 | 1,3 | 0,2 |
Coefficients a and b are necessary for those cases when the value of D d, °C day differs from that given in the table, then R req, m2 °C/W is calculated by the formula R req = a D d + b. For column 6 of the first group of buildings, there are corrections: if the degree-day value is less than 6000 °C day, a = 0.000075, and b = 0.15, if the same indicator is in the range of 6000-8000 °C day, then a = 0.00005, b = 0.3, but if more than 8000 °C day, then a = 0.000025, and b = 0.5. When all the data has been collected, we proceed to calculating thermal insulation.
Now let's find out how to calculate the thickness of the insulation. This is where you'll have to resort to some math, so be prepared to work with formulas. Here is the first of them, using it we determine the required conditional heat transfer resistance Rousl. tr = R req/r. We need this parameter to determine the required heat transfer resistance of the insulation Rttr = Rousl. tr – (Rв + ΣRт. izv. + Rн), here ΣRт. izv is the sum of the thermal resistance of the fencing layers without taking into account thermal insulation. We find the thickness of the insulation δth = Rthtr λut (m), and λth is taken from table D.1 SP 23-101-2004, and round the result up to the design value, taking into account the manufacturer’s nomenclature.
The photo shows heat gain and heat loss in a public building, xiron.ru
Photo of the table for determining the correction factor for calculating heat loss, radiatorprado.ru
The photo shows a table of heat loss during frost in insulated and non-insulated housing, idea5.narod.ru
Photo of the main cause of high heat loss, intekosib.ru
In the photo - correction factor to the calculated temperature difference, 56kss.ru
Options for location of problem areas
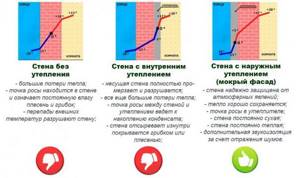
The dew point tends to shift, but most often there are three zones of its location:
- Closer to the outer surface of the wall. This option occurs if the wall is not insulated . The appearance of a problem area is also possible if the external insulation is of insufficient thickness.
- Closer to the inner surface of the wall. In the absence of insulation, condensation easily forms in this place during cold weather. Internal insulation shifts the area of condensation formation to the area between the wall surface and the insulation . With external insulation, this phenomenon rarely occurs if all calculations were performed correctly.
- In the thickness of the insulation. For external thermal insulation this is the best option. With internal insulation, there is a high risk of mold appearing in the room and, as a result, microclimate disturbance .
Note! The formation of condensation in the wall is affected not only by the temperature and humidity conditions from the street and the room. Determining factors are also the thickness of the structure and the thermal conductivity of the materials used.
What can influence this value?
There are several things that can affect this:
- wall thickness, as well as building materials used for insulation;
- humidity (when there is a high concentration of moisture, the dew point rises);
- temperature - it varies greatly and depends on the specific area.
To get a more detailed look at the process, let's look at several common situations.
- If the wall is not insulated, the dew point will begin to fluctuate under the influence of climatic conditions. If the weather is stable, the point will move closer to the outer wall. In this case, the house itself will not be damaged. And if it gets colder sharply, then this point will shift to the inner wall. The room will become saturated with condensation, and the walls will slowly become wet.
- If the wall is insulated from the inside, then the dew point will be located somewhere in the center between it and the insulation. With high humidity, this is hardly the best option, since after a sudden cold snap the point will move closer to the junction with the insulation, which can have a destructive effect on the structure. Note that in a humid climate, insulation from the inside is possible only with an efficient heating system capable of providing the same temperature conditions in all rooms.
- In the case of external wall insulation, the dew point will move inside the insulating layer. When purchasing material for thermal insulation, you need to take this point into account and correctly determine the required thickness.
Note! If climatic conditions were not taken into account during repair work, then if troubles arise, it will be very difficult, almost impossible, to eliminate them. All that remains is to undo everything that has been done and start again (read: additional costs)
Dew point calculation
The parameter value is calculated in several ways. This could be an online calculator, a pivot table, a special device, or a mathematical formula.
Using table data
A special table for calculating the dew point contains its approximate values. This is due to the fact that when breeding them, only air temperature and relative humidity were taken into account. The left column of the table shows the air temperature, the top line shows the relative air humidity as a percentage. At the intersection of columns and rows, the desired value is obtained.
There are several table options. However, most often the temperature range is -5°C..+30°C, and humidity – 30-95%. Using a table is convenient if you need to make calculations quickly. If possible, it is better to double-check the result in another way, for example, using a special online calculator.
Calculation using a mathematical formula
The mathematical formula for calculating the condensation temperature is complex and cumbersome. To perform calculations, two constant values are used, the actual value of air temperature and relative humidity . The latter must be taken in volume fractions.
Unlike working with a table, the range of the last two parameters is larger. The formula allows you to take into account temperatures from 0 to +60°C, humidity - from 1 to 100%. The error of the result does not exceed half a degree Celsius. However, it is convenient to use the formula only when you have free time for it.
Useful: Ursa: a wide range of insulation materials
Calculation in a calculator program
Special calculators allow you to calculate the dew point in the wall of a house online. You can find them on specialized websites. For the calculation you will need to enter a number of initial data. They vary from resource to resource, but the standard set includes information about the following parameters:
- wall material;
- the number of its layers and their thickness;
- temperature outside and inside the house;
- humidity indoors and outdoors.
Most calculators don't just calculate the required value. They also provide graphs of its possible movement and zones of moisture condensation.
Using instruments to perform calculations
Regardless of the method in which the calculations will be performed, source data .
To obtain them you need to stock up on some devices. So, a regular thermometer is suitable for determining temperature, and a hygrometer is suitable for determining humidity. For convenience, they are combined in a device such as a digital thermohygrometer. All obtained values are displayed on a small screen. Some models of devices also determine the temperature of condensation. Some models of construction thermal imagers can also identify the problem area.
Thermal insulation material
To protect buildings from heat loss, high humidity and point shifts, it is insulated with thermal insulation materials. In winter, insulation helps reduce heating costs, and in summer it keeps the room cool. Each product has its own areas of application and properties. Eco-friendly and easy-to-install materials are used in construction. The required type of insulation is selected for certain conditions.

With proper insulation from the outside, the dew point will be located inside the insulation.
According to their form, materials are divided into:
- roll;
- leafy;
- bulk;
- single.
By structure:
- fiber;
- cells;
- grainy.
Raw materials can be organic, inorganic and mixed.
Main characteristics of insulating materials:
- thermal conductivity;
- moisture absorption;
- porosity;
- humidity;
- density;
- vapor permeability;
- specific heat;
- strength, etc.
Penoplex
Penoplex is also called expanded polystyrene. Unlike foam polystyrene, the material has a higher density and is less subject to mechanical damage. It almost does not conduct steam due to its low vapor permeability coefficient. However, it belongs to group IV of flammability (it ignites quickly).

Penoplex is recommended for external wall insulation.
Penoplex of the “comfort” category is produced for insulating walls, terraces, loggias, and balconies. Its thermal conductivity coefficient is 9 times less than that of mineral wool. The material requires little time to heat the room after cooling due to its low heat capacity. The operating temperature range is -70…+70°C. Penoplex of this type does not have the best sound insulation, has the lowest density and lower tensile strength compared to other materials.
Penoplex for walls is suitable only if an effective ventilation system is installed in the room to maintain comfortable humidity.
A 2 cm wide layer of polystyrene foam retains heat almost as well as 40 cm of mineral wool or 37 cm of brickwork.
Styrofoam
Polystyrene foam is a material characterized by lightness and buoyancy. It is resistant to fire, but when exposed to fire it begins to melt. The material is easy to process and is not subject to infection by fungi and mold.
Polystyrene foam is obtained from foamed polymer raw materials: polystyrene, polyethylene, polyvinyl chloride or polyurethane. It consists of small identical balls that are fastened together. High-density rigid foam is used for insulation. The panels are easy to connect using rubber or epoxy adhesive.
The temperature range is not important for polystyrene foam, but the material is subject to mechanical damage.
Slabs 5 and 10 cm thick are used as thermal insulation. But, despite the structure, the material is sound-permeable.

Polystyrene foam is one of the most common materials for home insulation.
Mineral wool
Thermal insulation material consists of compressed fibers. Glass, basalt and slag are used as raw materials. The starting material is melted and spun into fibers. Their length is 2-60 mm. The air pores of the mats fill approximately 95% of the total volume. The product is easy to produce and has a low cost.
Mineral wool has many qualities suitable for home insulation.
Due to its porosity, cotton wool allows air and steam to pass through, maintaining air exchange. At the same time, it does not burn and is resistant to moisture, has good sound insulation. But the material has 2 drawbacks:
- contains phenol;
- Flying pieces of cotton wool, falling on human skin, cause itching.
How to move the dew point in a wall
If after all the calculations you are not satisfied with the location of the dew point, you should think about shifting it. To do this you can:
- increase the layer of insulation on the outside;
- use material with high vapor permeability;
- dismantle the layer of internal insulation, moving it outside;
- adjust the microclimate in the room - install forced ventilation, additionally heat the air.
The appropriate option is chosen based on the climatic conditions of the region of residence, the design features of the house, financial capabilities and the building materials used.
Ignoring such a phenomenon as moisture condensation in the wall “pie” can be very expensive. At a minimum, this is an unpleasant smell in the room, constant dampness . At the most, there are large colonies of mold fungi that spoil the interior decoration of the walls, destroy the insulation and harm the health of household members. Therefore, calculating the dew point is essential if you want to build safe and dry walls for your home.
Possible consequences
Improper installation of thermal insulation can lead to unpleasant consequences. The material is applied only to the facade, since additional insulation from the inside is considered impractical for the following reasons:
- Living space is decreasing.
- The wall freezes because the heat from the room does not reach the ceiling. As a result, condensation penetrates inside the thermal insulation. The wall is wet and subject to corrosion.
Poor installation results in wall destruction. If the surface under the insulation is uneven and old, it will have to be reapplied, after making repairs. If the insulation on the outside is not additionally covered, then in one season it will become wet, become unusable and begin to move away from the walls. The thermal layer must be protected from the external environment.
Causes of window fogging and how to fix them
The first reason for the formation of condensation on the front door is based on increased air humidity, when the indicator exceeds 55%.
Then the condensate is collected on the surface, where the temperature is slightly below the “dew point”. In winter, such a surface is the front door. It is important to maintain indoor air humidity of about 45% for the health of residents. The humidity of the internal climate is affected by both ventilation devices and the temperature of the heated air in the room. The second reason for condensation is hidden in low thermal insulation - a metal door is more prone to a large amount of condensation due to poor sealing between the metal sheet and the frame. In a typical embodiment, there is not enough air outflow for those purposes so that vapors escape, but it is quite enough to deposit them on the surface
In a typical version, there is not enough air outflow for those purposes to allow vapors to escape, but it is quite enough to deposit them on the surface.
Example of a door with a thermal break
A kind of “cold bridges” with an increased thermal conductivity on the front door are concentrated mainly on the door handle, peephole, and door part. Vulnerable freezing points especially concern metal doors, which have increased heat transfer.
Condensing moisture settles due to the large temperature difference between the outside and the room. In this case, it is recommended to install an unheated vestibule at the entrance. It would not be superfluous to install a canopy above the entrance that protects the door from direct exposure to the sun’s rays and precipitation. It is recommended to open the metal sheet of the front door with special powder polymers. It is better to fill all hollow elements in a metal door with foam in order to eliminate the appearance of cold bridges.
Very often, manufacturers of modern windows have to accept complaints that their customers' windows are fogging up. The formation of condensation on windows is not only aesthetically unsightly, but also threatens the wooden structures with waterlogging and, as a result, the formation of mold. Let's look at the possible causes of condensation on windows.
Well, if this happened on windows, then only the windows and their manufacturers are to blame. Logically this is correct, but if there is no water in the window itself and it cannot release it, where does the condensation come from?
Single-chamber double-glazed windows - you should not save on double-glazed windows, as they say, the miser pays twice. An ordinary double-glazed window with one chamber (not energy-saving) will certainly allow you to get acquainted with condensation on the windows. To eliminate the cause of fogging, it is necessary to replace the double-glazed window, not the entire window, but only the double-glazed window.
Wrong
Right
Heating radiators blow warm air onto the window, and if they are blocked by the window sill, then there will be no circulation of warm air - the window will always be cold, and as a result, condensation will appear on it.
You can get rid of condensation by reducing the size of the window sill or moving the battery outside the window sill board. If such options are not possible, you will have to look for an additional source for heating the glass.
Poor ventilation
Ventilation grilles often tend to become clogged with all sorts of rubbish - dust, cobwebs, after which they stop drawing in moist air, moisture settles on the glass and the windows begin to cry. And in old houses, the ventilation ducts are almost always clogged and have never been cleaned.
An example of organizing air flow: ventilation and air ionization