Which is better to install a gas boiler
Editorial
Promdevelop editorial team
Many people see only the difference in price between these two systems.
However, there is a fundamental difference in fuel combustion technology.
Advantages
Convection boilers are less efficient than condensing models. Such units heat the coolant only due to the heat obtained from gas combustion. At the same time, approximately 20 percent of the energy is lost along with combustion products into the atmosphere.
But despite this, such boilers have a number of the following important advantages, which determine their popularity among consumers:
- One of the most significant advantages is the significantly low price compared to condensation, one and a half to two times.
- The installation method can be either wall or floor. It has a cast iron heat exchanger, which is one of the most reliable and will last a long time.
- a small amount of acid condensate, which is formed during the operation of the boiler, the bulk of which goes into the pipe along with the combustion products.
- Having an open combustion chamber, it uses ambient air for the combustion process, due to which the air in the room where the gas boiler is installed is cooled.
- easy installation, repair and dismantling.
- simple design.

- low noise level during operation.
- a wide selection of models, both single-circuit and double-circuit.
Advantages and disadvantages
The main advantages of condensing gas heating boilers include:
- minimal amount of waste due to complete combustion of fuel, which increases efficiency and has a positive effect on the environment, reducing emissions of harmful substances by 7 times;
- efficiency on average 35% + energy efficiency;
- low smoke temperature below 40°C, which allows the installation of an inexpensive plastic chimney with pipes of the smallest cross-section;
- compact size, light weight;
- low noise and vibration levels;
- ease of installation with the ability to use several boilers in one system;
- modulating burner;
- high power;
- automation.
The main advantages include the fact that the equipment quickly pays for itself. A double-circuit condensing boiler also has some disadvantages:
- the need to provide a drainage system for condensate;
- obtaining permission for installation from the relevant services;
- strict compliance with installation technology requirements.
The bureaucratic side of the procedure is as simple as possible. However, before installation, it will be necessary to perfectly level the walls and floor, assemble the chimney, and maintain the distance. All this is normal troubles when organizing gas heating and ensuring your own safety.
Features of work
What is a convection boiler? It is a traditional device with an open, or less often closed, combustion chamber, consisting of one heat exchanger, a gas burner and automation that regulates the gas supply. When the gas has entered the system, using piezo ignition or electric ignition (depending on the model), the pilot burner is ignited, burning constantly.
It ignites the main burner, heating the coolant to the temperature set by the thermostat. After this, the automation turns off the main burner. When the temperature drops, the thermocouple is triggered and the valve opens, allowing gas to flow. Such processes occur cyclically in the boiler.
Convection units are divided into single-circuit, which are intended only for heating; heating water requires the installation of additional equipment, and double-circuit. The latter are intended for both heating and hot water. In the summer, the heating mode is turned off, the boiler is used only as a water heater.
When fuel burns, steam is generated, which is discharged through the chimney. The chimney must be made of materials that are resistant to corrosion, and that is why it should not be made of brick, which is not resistant to aggressive environments. Such a chimney must be lined with either stainless steel or acid-resistant tiles.

The boiler chimney is made of steel
When installing the unit, it is necessary to design the heating system taking into account that the outlet temperature of the combustion products is from 58 degrees. This requirement is necessary to ensure that aggressive condensate does not form on the surfaces of the combustion chamber, heat exchanger and chimney, which destroys the surfaces of these devices and leads to failure of the unit itself.
But it is precisely because of this condition that a significant part of the power is lost, about 20 percent of it flies into the chimney. If you decide to install a convection gas boiler, then you must understand that some of your money will evaporate into the air.
Operating principle and design of the heating device
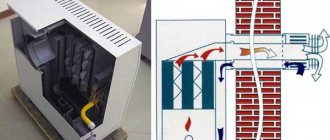
The following main components are located inside the unit:
- gas-burner;
- igniter (not on all models);
- ignition device;
- heat exchanger;
- automation system.
Most boilers are additionally equipped with:
- circulation pump;
- expansion tank;
- safety group: consists of a pressure gauge, safety valve and air vent.
The internal space where the burner and heat exchanger are located is called the firebox. The pipe for connecting to the chimney is located in its upper part.
The boiler works as follows:
- By pressing a special button, the gas supply valve to the igniter opens. The fuel ignites upon contact with a spark produced by the piezoelectric element of the ignition mechanism. After 2-3 seconds the button is released. Models with electronic activation do not have a pilot light.
- The temperature of the working medium entering the boiler heat exchanger is analyzed by a temperature sensor. When it reaches the set minimum value, the device sends a signal to the controller, which opens the gas supply valve to the main burner. The fuel is ignited by a pilot light or electronic ignition.
- Convection causes hot gas decay products to rise upward. They wash the heat exchanger, heating it, and rush into the chimney.
- The temperature of the working medium at the outlet of the device is analyzed by a second temperature sensor. As soon as it reaches the set maximum, the sensor will signal the controller and it will shut off the gas supply to the main burner.
- When the coolant cools down again, repeat steps 2-4.
Most models provide the following functions:
- Frost protection. When the coolant cools down to +5°C, the device starts automatically with a minimum output sufficient to maintain the temperature of the working environment above the specified mark.
- Indoor microclimate control. Using a remote thermostat, the device maintains the air temperature in the room at the desired level.
The automation system also includes sensors:
- draft: blocks the flow of gas if the smoke removal process is disrupted;
- flame: acts similarly when the main burner goes out.
Boilers in the upper price segment are equipped with weather-dependent automation. When connecting temperature sensors located outside, the heater promptly changes its thermal output in accordance with weather fluctuations.
Structural differences between gas convectors and boilers
A convector is a device for heating one separate room; it does not require the installation of radiator heating pipes throughout the room. Outwardly it resembles an electric fireplace or radiator, only larger. Inside it there is a burner in a closed combustion chamber, into which air enters, thanks to which the gas is burned and exhaust gas products are removed.
When fuel burns, the combustion chamber is heated, which warms the surrounding air using a fan installed inside the convector. When installing such a device, a gas supply and a coaxial chimney are required to each unit. It can operate on both main and liquefied gas, i.e. from the cylinder.
The use of a convector heater is limited, taking into account the disadvantages of such a device:
- a large number of pipes and holes punched for them, necessary for the installation of each convector,

Gas convector - the decrease in room temperature is directly proportional to the distance from the device, low inertia. As a result, rapid heating and equally rapid cooling occurs, and this has a detrimental effect on both the interior decoration of the premises and the furniture in them.
Based on the foregoing, we can conclude that it is better to install such devices in garages, warehouses, and industrial premises, where it is not necessary to maintain a constant temperature.
The main structural difference between a boiler and a convector is the presence of a heat exchanger and the need to distribute radiator pipes throughout the room, with the help of which the room is heated evenly and for a long time. The waste products are removed through the chimney if the boiler has an open combustion chamber. A double-circuit boiler provides both room heating and the need for hot water.
Comparison of convection and condenser boilers
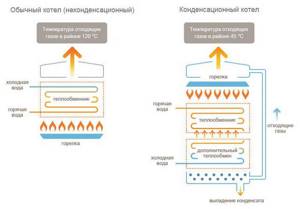
The condensing unit uses not only the energy released when gas is burned, but also the heat that is generated when steam is formed in the gas combustion products. Structurally, it differs from convection in the presence of another additional heat exchanger - an economizer, installed at the outlet of waste gas products. In fact, it is primary, since after heating it, the coolant enters the main heat exchanger.

Condensing boiler design
To form condensate, it is necessary to achieve cooling of the steam that is formed as a result of gas combustion products below the dew point - 56 degrees when using main gas. The need to supply cooled return water allows you to expand the heating system, for example, you can make heated floors, which cannot be done with a convection boiler.
The need to obtain a lower temperature at the outlet requires the installation of radiators with increased heat transfer, for example, aluminum and bimetallic, which are quite expensive. It will be impossible to achieve efficient operation with cast iron batteries.
In conventional boilers, the temperature of the combustion products is quite high and therefore condensation practically does not form. Energy is partially wasted, but the parts of the unit and the chimney itself are not exposed to aggressive influence.
A condensing boiler is available only with a closed combustion chamber, in contrast to a convection boiler, which can be either closed or open, depending on the model. A closed chamber is the safest. It is equipped with a fan, with the help of which air enters the firebox; excess pressure itself pushes the exhaust gases through the coaxial channel.
Thus, combustion products do not enter the room where the boiler operates. If the boiler has a power of less than 30 kW, the duct can be installed in the wall; with a higher power it must be mounted above the roof level.

The chimney is on the roof
Additional heat is the key to high efficiency (more than 100 percent) of condensing boilers. Despite the high cost compared to convection devices, approximately twice as high, such devices are more efficient, have an efficiency one and a half times higher than convection devices due to reduced gas consumption and pay for themselves within 3 years. The high cost of such boilers is due to the use of stainless steel materials, resistant to aggressive environments, and technologies that allow it to be welded.
Which is ultimately better: a convection or condensing boiler?
The choice, unfortunately, is not clear; on the one hand, the savings of condensation models seem significant. On the other hand, there is a high price, the need for condensate disposal and special requirements for the heating system and operating conditions. The fact is that in Europe the payback period for condensing models is around 4-6 years, but in domestic conditions this is not entirely true for several reasons:
- The highest efficiency of such boilers is achieved with a low-temperature heating mode, when heated floors, radiators with an increased number of sections are used, and the coolant temperature does not exceed 50°C.
- The cost of gas in Russia is quite low compared to European countries, which only delays the payback of the high initial price.
- There are additional operating costs associated with condensate disposal (organization of drainage, purchase of neutralizing filler or dilution with water).
How to choose a room thermostat and save up to 30% per month on heating
If you allow the boiler to be used in a low-temperature heating system and ignore the costs of condensate removal, you can calculate the potential savings.
Let's say there is an average house in the Moscow region with an area of 120 m2, with 2 bricks and a ceiling height of 2.7 m, the heat loss of which is 12 kW (from the rule of 1 kW for every 10 m2). This is 288 kW per day, which needs to be replenished by the boiler. The specific heat of combustion of natural gas is 9.3-10 kW per m3. It follows that for 1 kW of thermal power of a gas boiler, about 0.1-0.108 m3 of natural gas is required. We count:
- When heating with a convection boiler with an efficiency of 92% - 288 (kW) * 0.1 (m3) * 1.08 (92% efficiency) = 31.1 m3 / day of natural gas. In value terms – 31.1 (m3) * 5.7 (rub/m3, tariff in Moscow Region from July 1, 2021, valid in 2020) = 177.27 rub/day.
- When heating with a condensing boiler with an efficiency of 109% - 288 (kW) * 0.1 (m3) * 0.91 (109% efficiency) = 26.2 m3 / day of natural gas. In value terms – 26.2 (m3) * 5.7 (rub/m3) = 149.3 rub/day.
Payback periods depend on the cost of the model, its installation and operating conditions. But in practice, in domestic conditions, this is at least 6 years, and in some cases more than 10.
In our opinion, now the purchase of condensing models is justified only when used in a system with a low-temperature heating mode. However, in the future, when gas prices rise and the cost of condensing heating equipment decreases, the purchase of a condenser will be increasingly justified in domestic conditions.
Comparison table of characteristics and prices
| Manufacturer and model | power, kWt | Efficiency, % | Max gas consumption, m3/hour | price, rub. |
| Convection | ||||
| Siberia 17 | 17,4 | 90 | 1,76 | 23 500 |
| BAXI ECO Four 1.14 F | 14 | 92,5 | 1,6 | 34 500 |
| Viessmann Vitopend 100-W A1HB001 | 24 | 91 | 2,77 | 39 000 |
| Buderus Logamax U072-18 | 18 | 92 | 2,1 | 28 000 |
| Condensation | ||||
| Rinnai RB-277CMF | 29,7 | 104,6 | 1,84 | 76 000 |
| BAXI Duo-tec Compact 1.24 | 24 | 105,7 | 2,61 | 53 000 |
| iessmann Vitodens 100-W B1KC033 | 35 | 109 | 3,86 | 119 000 |
Gas boilersCondensing BoilersBoiler comparison